- 2020-01-25
晴岚85
郑海燕坚持分享590天2020.1.24在生活中只存在两个问题。一个问题是:你知道想要达成的目标是什么,但却不知道如何才能达成;另一个问题是:你不知道你的目标是什么。前一个是行动的问题,后一个是结果的问题。通过制定具体的下一步行动,可以解决不知道如何开始行动的问题。而通过去想象结果,对结果做预估,可以解决找不着目标的问题。对于所有吸引我们注意力,想要完成的任务,你可以先想象一下,预期的结果究竟是什
- 谢谢你们,爱你们!
鹿游儿
昨天家人去泡温泉,二个孩子也带着去,出发前一晚,匆匆下班,赶回家和孩子一起收拾。饭后,我拿出笔和本子(上次去澳门时做手帐的本子)写下了1\2\3\4\5\6\7\8\9,让后让小壹去思考,带什么出发去旅游呢?她在对应的数字旁边画上了,泳衣、泳圈、肖恩、内衣内裤、tapuy、拖鞋……画完后,就让她自己对着这个本子,将要带的,一一带上,没想到这次带的书还是这本《便便工厂》(晚上姑婆发照片过来,妹妹累得
- 《策划经理回忆录之二》
路基雅虎
话说三年变六年,飘了,飘了……眨眼,2013年5月,老吴回到了他的家乡——油城从新开启他的工作幻想症生涯。很庆幸,这是一家很有追求,同时敢于尝试的,且实力不容低调的新星房企——金源置业(前身泰源置业)更值得庆幸的是第一个盘就是油城十路的标杆之一:金源盛世。2013年5月,到2015年11月,两年的陪伴,迎来了一场大爆发。2000个筹,5万/筹,直接回笼1个亿!!!这……让我开始认真审视这座看似五线
- Long类型前后端数据不一致
igotyback
前端
响应给前端的数据浏览器控制台中response中看到的Long类型的数据是正常的到前端数据不一致前后端数据类型不匹配是一个常见问题,尤其是当后端使用Java的Long类型(64位)与前端JavaScript的Number类型(最大安全整数为2^53-1,即16位)进行数据交互时,很容易出现精度丢失的问题。这是因为JavaScript中的Number类型无法安全地表示超过16位的整数。为了解决这个问
- LocalDateTime 转 String
igotyback
java开发语言
importjava.time.LocalDateTime;importjava.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;publicclassMain{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){//获取当前时间LocalDateTimenow=LocalDateTime.now();//定义日期格式化器DateTimeFormatterformat
- Linux下QT开发的动态库界面弹出操作(SDL2)
13jjyao
QT类qt开发语言sdl2linux
需求:操作系统为linux,开发框架为qt,做成需带界面的qt动态库,调用方为java等非qt程序难点:调用方为java等非qt程序,也就是说调用方肯定不带QApplication::exec(),缺少了这个,QTimer等事件和QT创建的窗口将不能弹出(包括opencv也是不能弹出);这与qt调用本身qt库是有本质的区别的思路:1.调用方缺QApplication::exec(),那么我们在接口
- 高级编程--XML+socket练习题
masa010
java开发语言
1.北京华北2114.8万人上海华东2,500万人广州华南1292.68万人成都华西1417万人(1)使用dom4j将信息存入xml中(2)读取信息,并打印控制台(3)添加一个city节点与子节点(4)使用socketTCP协议编写服务端与客户端,客户端输入城市ID,服务器响应相应城市信息(5)使用socketTCP协议编写服务端与客户端,客户端要求用户输入city对象,服务端接收并使用dom4j
- 今日联对0306
诗图佳得
自对联:烟销皓月临江浒,水漫金山荡塔裙。一一肖士平2020.3.6.1、试对肖老师联:烟销皓月临江浒,夜笼寒沙梦晚舟。耀哥求正2、试对萧老师联:烟销浩月临江浒,雾散乾坤解汉城。秀霞习作请各位老师校正3、自对联:烟销皓月临江浒,水漫金山荡塔裙。一一肖士平2020.3.6.4、试对肖老师垫场联:烟销皓月临江浒,雾锁寒林缈葉丛。小智求正[抱拳]5、试对肖老师联:烟销皓月临江浒;风卷乱云入峰巅。一一五品6
- 每日一题——第八十一题
互联网打工人no1
C语言程序设计每日一练c语言
打印如下图案:#includeintmain(){inti,j;charch='A';for(i=1;i<5;i++,ch++){for(j=0;j<5-i;j++){printf("");//控制空格输出}for(j=1;j<2*i;j++)//条件j<2*i{printf("%c",ch);//控制字符输出}printf("\n");}return0;}
- 每日一题——第八十四题
互联网打工人no1
C语言程序设计每日一练c语言
题目:编写函数1、输入10个职工的姓名和职工号2、按照职工由大到小顺序排列,姓名顺序也随之调整3、要求输入一个职工号,用折半查找法找出该职工的姓名#define_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS#include#include#defineMAX_EMPLOYEES10typedefstruct{intid;charname[50];}Empolyee;voidinputEmploye
- 《小满细雨轻湿尘》
快乐的人ZZM
图片发自App《小满细雨轻湿尘》文/快乐的人zzm小满细雨轻湿尘石榴花开落纷纷落红不是无情物坠入泥土育养根2018-5-23
- Python中os.environ基本介绍及使用方法
鹤冲天Pro
#Pythonpython服务器开发语言
文章目录python中os.environos.environ简介os.environ进行环境变量的增删改查python中os.environ的使用详解1.简介2.key字段详解2.1常见key字段3.os.environ.get()用法4.环境变量的增删改查和判断是否存在4.1新增环境变量4.2更新环境变量4.3获取环境变量4.4删除环境变量4.5判断环境变量是否存在python中os.envi
- 情殇——(5)压抑的小木匠放纵了自己。
石疯聊情感故事
木讷的小木匠,其实只是不苟言笑。其实内心深处也是挣扎着,由于性格内敛,不喜形于色,给人的感觉非常的木讷。其实小木匠情商智商都不低。他为人扎实,非常的务实。他的爱是既深沉又宽容。可是是一个男人,都会对妻子出轨的事儿,不会忘怀!只是压抑在心底,为了某种考量或许是真爱。小木匠对于丽影和别人私奔又重回家庭,表面上并没有,天翻地覆,暴风骤雨,其内心深处也是经历了,痛苦的挣扎。。。再一次酒后,他和一个离家多年
- 怎么起诉借钱不还的人?怎样起诉欠款不还的人?
影子爱学习
怎么起诉借钱不还的人?怎样起诉欠款不还的人?如果遇到难以解决的法律问题,我们可以匹配专业律师。例如:婚姻家庭(离婚纠纷)、刑事辩护、合同纠纷、债权债务、房产(继承)纠纷、交通事故、劳动争议、人身损害、公司相关法律事务(法律顾问)等咨询推荐手机/微信:15633770876【全国案件皆可】借钱不还起诉对方需要哪些资料起诉欠钱不还的,一般需要的材料包括以下这些:借据、收据、欠条、付款凭证等证据,以及向
- 第四天旅游线路预览——从换乘中心到喀纳斯湖
陟彼高冈yu
基于Googleearthstudio的旅游规划和预览旅游
第四天:从贾登峪到喀纳斯风景区入口,晚上住宿贾登峪;换乘中心有4路车,喀纳斯①号车,去喀纳斯湖,路程时长约5分钟;将上面的的行程安排进行动态展示,具体步骤见”Googleearthstudio进行动态轨迹显示制作过程“、“Googleearthstudio入门教程”和“Googleearthstudio进阶教程“相关内容,得到行程如下所示:Day4-2-480p
- linux sdl windows.h,Windows下的SDL安装
奔跑吧linux内核
linuxsdlwindows.h
首先你要下载并安装SDL开发包。如果装在C盘下,路径为C:\SDL1.2.5如果在WINDOWS下。你可以按以下步骤:1.打开VC++,点击"Tools",Options2,点击directories选项3.选择"Includefiles"增加一个新的路径。"C:\SDL1.2.5\include"4,现在选择"Libaryfiles“增加"C:\SDL1.2.5\lib"现在你可以开始编写你的第
- Python教程:一文了解使用Python处理XPath
旦莫
Python进阶python开发语言
目录1.环境准备1.1安装lxml1.2验证安装2.XPath基础2.1什么是XPath?2.2XPath语法2.3示例XML文档3.使用lxml解析XML3.1解析XML文档3.2查看解析结果4.XPath查询4.1基本路径查询4.2使用属性查询4.3查询多个节点5.XPath的高级用法5.1使用逻辑运算符5.2使用函数6.实战案例6.1从网页抓取数据6.1.1安装Requests库6.1.2代
- 相信相信的力量
孙丽_cdb3
孙丽中级十期坚持分享第345天有一个特别有哲理的故事:有一只老鹰下了蛋,这个蛋,不知怎的就滚到了鸡窝里去了,鸡也下了一窝蛋,然后鸡妈妈把这些蛋全都浮出来了,孵出来之后等小鸡长大一点了,就觉得鹰蛋孵出来的那只小鹰怪模怪样,这些小鸡都嘲笑它,真难看,真笨,丑死了,那只小鹰觉得自己真是谁也不像,真是不好看,后来鸡妈妈也不喜欢他,我怎么生出你这样的孩子来了?真烦人,后来这群小鸡和小鹰一起生活,有一天,老鹰
- 基于社交网络算法优化的二维最大熵图像分割
智能算法研学社(Jack旭)
智能优化算法应用图像分割算法php开发语言
智能优化算法应用:基于社交网络优化的二维最大熵图像阈值分割-附代码文章目录智能优化算法应用:基于社交网络优化的二维最大熵图像阈值分割-附代码1.前言2.二维最大熵阈值分割原理3.基于社交网络优化的多阈值分割4.算法结果:5.参考文献:6.Matlab代码摘要:本文介绍基于最大熵的图像分割,并且应用社交网络算法进行阈值寻优。1.前言阅读此文章前,请阅读《图像分割:直方图区域划分及信息统计介绍》htt
- 509. 斐波那契数(每日一题)
lzyprime
lzyprime博客(github)创建时间:2021.01.04qq及邮箱:2383518170leetcode笔记题目描述斐波那契数,通常用F(n)表示,形成的序列称为斐波那契数列。该数列由0和1开始,后面的每一项数字都是前面两项数字的和。也就是:F(0)=0,F(1)=1F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2),其中n>1给你n,请计算F(n)。示例1:输入:2输出:1解释:F(2)=F(1)+
- 使用 FinalShell 进行远程连接(ssh 远程连接 Linux 服务器)
编程经验分享
开发工具服务器sshlinux
目录前言基本使用教程新建远程连接连接主机自定义命令路由追踪前言后端开发,必然需要和服务器打交道,部署应用,排查问题,查看运行日志等等。一般服务器都是集中部署在机房中,也有一些直接是云服务器,总而言之,程序员不可能直接和服务器直接操作,一般都是通过ssh连接来登录服务器。刚接触远程连接时,使用的是XSHELL来远程连接服务器,连接上就能够操作远程服务器了,但是仅用XSHELL并没有上传下载文件的功能
- 18-115 一切思考不能有效转化为行动,都TM是扯淡!
成长时间线
7月25号写了一篇关于为什么会断更如此严重的反思,然而,之后日更仅仅维持了一周,又出现了这次更严重的现象。从8月2号到昨天8月6号,5天!又是5天没有更文!虽然这次断更时间和上次一样,那为什么说这次更严重?因为上次之后就分析了问题的原因,以及应该如何解决,按理说应该会好转,然而,没过几天严重断更的现象再次出现,想想,经过反思,问题依然没有解决与改变,这让我有些担忧。到底是哪里出了问题,难道我就真的
- 郎朗大婚娶公主:所有光环的背后,都是十年如一日的自律
简小尘
近日,关于郎朗大婚的新闻上了热搜,看了新娘的照片,既有天使般的面容,更有魔鬼般的身材,关键是人家还身世好,又有才华,这真的是让所有男人羡慕嫉妒恨哪。有些人不禁会想,“凭什么郎朗的人生就象开挂了一样,可我却每天都活得这么狼狈!”其实,每个开挂的人生背后,都是苦行僧般的自律。01欲戴王冠,必承其重。练琴不能只靠兴趣,更需要自律!我们先来看一下朗朗在小时候的作息时间表:早晨5:45起床,练琴1小时。中午
- 《中华小厨师》单行VS爱藏:姜是老的辣,书是新的好
cicoky
《汉书·郦食其传》有曰:“王者以民为天,而民以食为天。”自古以来,吃饱饭是每一个人的基本要求,而吃好饭却是每一个人的最终追求。于是,厨师这一职业孕育而生,其渊源之久,甚至可追溯到4000年前的奴隶时代。职业本身无贵贱,但职业能力却有高低之分。所以一家餐馆生意好不好,厨师的水平决定一切,而站在所有厨师顶端的就被称之为“特级厨师”。今天要说的就是一个关于“特级厨师刘昴星”的故事。连载历程1995年第4
- 读《人世间》有感
一0一
这个寒假,就如同朋友圈中的一段话:一闭眼,一睁眼假期还有5天,在一闭眼一睁眼假期还有12天;再一闭眼一睁眼假期还有20天;不敢睡,不敢睡啊……受疫情影响,这个假期变得漫长又煎熬,我也无时无刻不关注着疫情的变化。当然这样的一个假期,我还真得要感谢周翔,因为他有个爱看书的习惯,所以家里有不少他看过的书,可以让我随意挑选,因此也让我的假期不至于那么无所事事。这次我选了一本梁晓声的《人世间》,作为一名语文
- 四章-32-点要素的聚合
彩云飘过
本文基于腾讯课堂老胡的课《跟我学Openlayers--基础实例详解》做的学习笔记,使用的openlayers5.3.xapi。源码见1032.html,对应的官网示例https://openlayers.org/en/latest/examples/cluster.htmlhttps://openlayers.org/en/latest/examples/earthquake-clusters.
- DIV+CSS+JavaScript技术制作网页(旅游主题网页设计与制作)云南大理
STU学生网页设计
网页设计期末网页作业html静态网页html5期末大作业网页设计web大作业
️精彩专栏推荐作者主页:【进入主页—获取更多源码】web前端期末大作业:【HTML5网页期末作业(1000套)】程序员有趣的告白方式:【HTML七夕情人节表白网页制作(110套)】文章目录二、网站介绍三、网站效果▶️1.视频演示2.图片演示四、网站代码HTML结构代码CSS样式代码五、更多源码二、网站介绍网站布局方面:计划采用目前主流的、能兼容各大主流浏览器、显示效果稳定的浮动网页布局结构。网站程
- 运城寻访重逢石头纪实【严建设老照片395 集】 我简直能把你想透, 当我走进运城的时候。 我已急得热汗直流, 访问了十九个老头, 把晋南的小城转了三周。 虽然是悠久的思旧, 我仍然是牛样的执...
严建设
运城寻访重逢石头纪实【严建设老照片395集】我简直能把你想透,当我走进运城的时候。我已急得热汗直流,访问了十九个老头,把晋南的小城转了三周。虽然是悠久的思旧,我仍然是牛样的执拗。说什么变换的世情,泛起了过去的逝流,你就是真正的故友。踏破铁鞋的淡愁,已化为不废功夫的范畴,是就像远在天涯近在咫尺,就像是梦乡的邂逅,我紧紧地攥着你的手。你已长成了高高的个头,俊逸的容颜却很清瘦,你那样顽皮的童音,已变到老
- 【华为OD机试真题2023B卷 JAVA&JS】We Are A Team
若博豆
java算法华为javascript
华为OD2023(B卷)机试题库全覆盖,刷题指南点这里WeAreATeam时间限制:1秒|内存限制:32768K|语言限制:不限题目描述:总共有n个人在机房,每个人有一个标号(1<=标号<=n),他们分成了多个团队,需要你根据收到的m条消息判定指定的两个人是否在一个团队中,具体的:1、消息构成为:abc,整数a、b分别代
- 高端密码学院笔记285
柚子_b4b4
高端幸福密码学院(高级班)幸福使者:李华第(598)期《幸福》之回归内在深层生命原动力基础篇——揭秘“激励”成长的喜悦心理案例分析主讲:刘莉一,知识扩充:成功=艰苦劳动+正确方法+少说空话。贪图省力的船夫,目标永远下游。智者的梦再美,也不如愚人实干的脚印。幸福早课堂2020.10.16星期五一笔记:1,重视和珍惜的前提是知道它的价值非常重要,当你珍惜了,你就真正定下来,真正的学到身上。2,大家需要
- 分享100个最新免费的高匿HTTP代理IP
mcj8089
代理IP代理服务器匿名代理免费代理IP最新代理IP
推荐两个代理IP网站:
1. 全网代理IP:http://proxy.goubanjia.com/
2. 敲代码免费IP:http://ip.qiaodm.com/
120.198.243.130:80,中国/广东省
58.251.78.71:8088,中国/广东省
183.207.228.22:83,中国/
- mysql高级特性之数据分区
annan211
java数据结构mongodb分区mysql
mysql高级特性
1 以存储引擎的角度分析,分区表和物理表没有区别。是按照一定的规则将数据分别存储的逻辑设计。器底层是由多个物理字表组成。
2 分区的原理
分区表由多个相关的底层表实现,这些底层表也是由句柄对象表示,所以我们可以直接访问各个分区。存储引擎管理分区的各个底层
表和管理普通表一样(所有底层表都必须使用相同的存储引擎),分区表的索引只是
- JS采用正则表达式简单获取URL地址栏参数
chiangfai
js地址栏参数获取
GetUrlParam:function GetUrlParam(param){
var reg = new RegExp("(^|&)"+ param +"=([^&]*)(&|$)");
var r = window.location.search.substr(1).match(reg);
if(r!=null
- 怎样将数据表拷贝到powerdesigner (本地数据库表)
Array_06
powerDesigner
==================================================
1、打开PowerDesigner12,在菜单中按照如下方式进行操作
file->Reverse Engineer->DataBase
点击后,弹出 New Physical Data Model 的对话框
2、在General选项卡中
Model name:模板名字,自
- logbackのhelloworld
飞翔的马甲
日志logback
一、概述
1.日志是啥?
当我是个逗比的时候我是这么理解的:log.debug()代替了system.out.print();
当我项目工作时,以为是一堆得.log文件。
这两天项目发布新版本,比较轻松,决定好好地研究下日志以及logback。
传送门1:日志的作用与方法:
http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/why-and-how-log
上面的作
- 新浪微博爬虫模拟登陆
随意而生
新浪微博
转载自:http://hi.baidu.com/erliang20088/item/251db4b040b8ce58ba0e1235
近来由于毕设需要,重新修改了新浪微博爬虫废了不少劲,希望下边的总结能够帮助后来的同学们。
现行版的模拟登陆与以前相比,最大的改动在于cookie获取时候的模拟url的请求
- synchronized
香水浓
javathread
Java语言的关键字,可用来给对象和方法或者代码块加锁,当它锁定一个方法或者一个代码块的时候,同一时刻最多只有一个线程执行这段代码。当两个并发线程访问同一个对象object中的这个加锁同步代码块时,一个时间内只能有一个线程得到执行。另一个线程必须等待当前线程执行完这个代码块以后才能执行该代码块。然而,当一个线程访问object的一个加锁代码块时,另一个线程仍然
- maven 简单实用教程
AdyZhang
maven
1. Maven介绍 1.1. 简介 java编写的用于构建系统的自动化工具。目前版本是2.0.9,注意maven2和maven1有很大区别,阅读第三方文档时需要区分版本。 1.2. Maven资源 见官方网站;The 5 minute test,官方简易入门文档;Getting Started Tutorial,官方入门文档;Build Coo
- Android 通过 intent传值获得null
aijuans
android
我在通过intent 获得传递兑现过的时候报错,空指针,我是getMap方法进行传值,代码如下 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
public
void
getMap(View view){
Intent i =
- apache 做代理 报如下错误:The proxy server received an invalid response from an upstream
baalwolf
response
网站配置是apache+tomcat,tomcat没有报错,apache报错是:
The proxy server received an invalid response from an upstream server. The proxy server could not handle the request GET /. Reason: Error reading fr
- Tomcat6 内存和线程配置
BigBird2012
tomcat6
1、修改启动时内存参数、并指定JVM时区 (在windows server 2008 下时间少了8个小时)
在Tomcat上运行j2ee项目代码时,经常会出现内存溢出的情况,解决办法是在系统参数中增加系统参数:
window下, 在catalina.bat最前面
set JAVA_OPTS=-XX:PermSize=64M -XX:MaxPermSize=128m -Xms5
- Karam与TDD
bijian1013
KaramTDD
一.TDD
测试驱动开发(Test-Driven Development,TDD)是一种敏捷(AGILE)开发方法论,它把开发流程倒转了过来,在进行代码实现之前,首先保证编写测试用例,从而用测试来驱动开发(而不是把测试作为一项验证工具来使用)。
TDD的原则很简单:
a.只有当某个
- [Zookeeper学习笔记之七]Zookeeper源代码分析之Zookeeper.States
bit1129
zookeeper
public enum States {
CONNECTING, //Zookeeper服务器不可用,客户端处于尝试链接状态
ASSOCIATING, //???
CONNECTED, //链接建立,可以与Zookeeper服务器正常通信
CONNECTEDREADONLY, //处于只读状态的链接状态,只读模式可以在
- 【Scala十四】Scala核心八:闭包
bit1129
scala
Free variable A free variable of an expression is a variable that’s used inside the expression but not defined inside the expression. For instance, in the function literal expression (x: Int) => (x
- android发送json并解析返回json
ronin47
android
package com.http.test;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.HttpStatus;
import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import
- 一份IT实习生的总结
brotherlamp
PHPphp资料php教程php培训php视频
今天突然发现在不知不觉中自己已经实习了 3 个月了,现在可能不算是真正意义上的实习吧,因为现在自己才大三,在这边撸代码的同时还要考虑到学校的功课跟期末考试。让我震惊的是,我完全想不到在这 3 个月里我到底学到了什么,这是一件多么悲催的事情啊。同时我对我应该 get 到什么新技能也很迷茫。所以今晚还是总结下把,让自己在接下来的实习生活有更加明确的方向。最后感谢工作室给我们几个人这个机会让我们提前出来
- 据说是2012年10月人人网校招的一道笔试题-给出一个重物重量为X,另外提供的小砝码重量分别为1,3,9。。。3^N。 将重物放到天平左侧,问在两边如何添加砝码
bylijinnan
java
public class ScalesBalance {
/**
* 题目:
* 给出一个重物重量为X,另外提供的小砝码重量分别为1,3,9。。。3^N。 (假设N无限大,但一种重量的砝码只有一个)
* 将重物放到天平左侧,问在两边如何添加砝码使两边平衡
*
* 分析:
* 三进制
* 我们约定括号表示里面的数是三进制,例如 47=(1202
- dom4j最常用最简单的方法
chiangfai
dom4j
要使用dom4j读写XML文档,需要先下载dom4j包,dom4j官方网站在 http://www.dom4j.org/目前最新dom4j包下载地址:http://nchc.dl.sourceforge.net/sourceforge/dom4j/dom4j-1.6.1.zip
解开后有两个包,仅操作XML文档的话把dom4j-1.6.1.jar加入工程就可以了,如果需要使用XPath的话还需要
- 简单HBase笔记
chenchao051
hbase
一、Client-side write buffer 客户端缓存请求 描述:可以缓存客户端的请求,以此来减少RPC的次数,但是缓存只是被存在一个ArrayList中,所以多线程访问时不安全的。 可以使用getWriteBuffer()方法来取得客户端缓存中的数据。 默认关闭。 二、Scan的Caching 描述: next( )方法请求一行就要使用一次RPC,即使
- mysqldump导出时出现when doing LOCK TABLES
daizj
mysqlmysqdump导数据
执行 mysqldump -uxxx -pxxx -hxxx -Pxxxx database tablename > tablename.sql
导出表时,会报
mysqldump: Got error: 1044: Access denied for user 'xxx'@'xxx' to database 'xxx' when doing LOCK TABLES
解决
- CSS渲染原理
dcj3sjt126com
Web
从事Web前端开发的人都与CSS打交道很多,有的人也许不知道css是怎么去工作的,写出来的css浏览器是怎么样去解析的呢?当这个成为我们提高css水平的一个瓶颈时,是否应该多了解一下呢?
一、浏览器的发展与CSS
- 《阿甘正传》台词
dcj3sjt126com
Part Ⅰ:
《阿甘正传》Forrest Gump经典中英文对白
Forrest: Hello! My names Forrest. Forrest Gump. You wanna Chocolate? I could eat about a million and a half othese. My momma always said life was like a box ochocol
- Java处理JSON
dyy_gusi
json
Json在数据传输中很好用,原因是JSON 比 XML 更小、更快,更易解析。
在Java程序中,如何使用处理JSON,现在有很多工具可以处理,比较流行常用的是google的gson和alibaba的fastjson,具体使用如下:
1、读取json然后处理
class ReadJSON
{
public static void main(String[] args)
- win7下nginx和php的配置
geeksun
nginx
1. 安装包准备
nginx : 从nginx.org下载nginx-1.8.0.zip
php: 从php.net下载php-5.6.10-Win32-VC11-x64.zip, php是免安装文件。
RunHiddenConsole: 用于隐藏命令行窗口
2. 配置
# java用8080端口做应用服务器,nginx反向代理到这个端口即可
p
- 基于2.8版本redis配置文件中文解释
hongtoushizi
redis
转载自: http://wangwei007.blog.51cto.com/68019/1548167
在Redis中直接启动redis-server服务时, 采用的是默认的配置文件。采用redis-server xxx.conf 这样的方式可以按照指定的配置文件来运行Redis服务。下面是Redis2.8.9的配置文
- 第五章 常用Lua开发库3-模板渲染
jinnianshilongnian
nginxlua
动态web网页开发是Web开发中一个常见的场景,比如像京东商品详情页,其页面逻辑是非常复杂的,需要使用模板技术来实现。而Lua中也有许多模板引擎,如目前我在使用的lua-resty-template,可以渲染很复杂的页面,借助LuaJIT其性能也是可以接受的。
如果学习过JavaEE中的servlet和JSP的话,应该知道JSP模板最终会被翻译成Servlet来执行;而lua-r
- JZSearch大数据搜索引擎
颠覆者
JavaScript
系统简介:
大数据的特点有四个层面:第一,数据体量巨大。从TB级别,跃升到PB级别;第二,数据类型繁多。网络日志、视频、图片、地理位置信息等等。第三,价值密度低。以视频为例,连续不间断监控过程中,可能有用的数据仅仅有一两秒。第四,处理速度快。最后这一点也是和传统的数据挖掘技术有着本质的不同。业界将其归纳为4个“V”——Volume,Variety,Value,Velocity。大数据搜索引
- 10招让你成为杰出的Java程序员
pda158
java编程框架
如果你是一个热衷于技术的
Java 程序员, 那么下面的 10 个要点可以让你在众多 Java 开发人员中脱颖而出。
1. 拥有扎实的基础和深刻理解 OO 原则 对于 Java 程序员,深刻理解 Object Oriented Programming(面向对象编程)这一概念是必须的。没有 OOPS 的坚实基础,就领会不了像 Java 这些面向对象编程语言
- tomcat之oracle连接池配置
小网客
oracle
tomcat版本7.0
配置oracle连接池方式:
修改tomcat的server.xml配置文件:
<GlobalNamingResources>
<Resource name="utermdatasource" auth="Container"
type="javax.sql.DataSou
- Oracle 分页算法汇总
vipbooks
oraclesql算法.net
这是我找到的一些关于Oracle分页的算法,大家那里还有没有其他好的算法没?我们大家一起分享一下!
-- Oracle 分页算法一
select * from (
select page.*,rownum rn from (select * from help) page
-- 20 = (currentPag
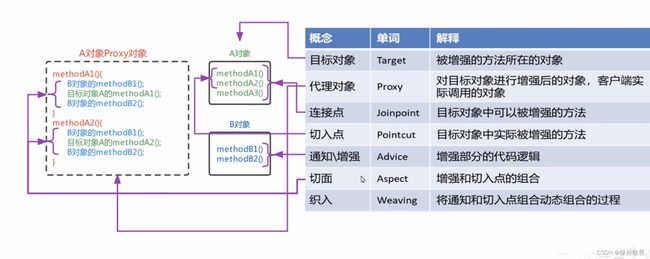
![]() 当然你也可以使用xml配置文件的方式,将对应类的bean对象交给Spring容器管理,具体如何实现可以参考我的往期Spring注解开发、基于Xml方式配置Bean的相关文章
当然你也可以使用xml配置文件的方式,将对应类的bean对象交给Spring容器管理,具体如何实现可以参考我的往期Spring注解开发、基于Xml方式配置Bean的相关文章