Java关于二叉树的16个经典例题
目录
- 一、二叉树的前序遍历
- 二、二叉树的中序遍历
- 三、二叉树的后序遍历
- 四、判断两棵树是否相同
- 五、判断一棵树是否是另一棵树的子树
- 六、判断一棵树是否为平衡二叉树(AVL树)
- 七、判断一棵树是否为对称二叉树
- 七、二叉树遍历
- 八、二叉树层序遍历
- 九、二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 十、二叉搜索树与双向链表
- 十一、从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 十二、根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树
- 十三、二叉树创建字符串
- 十四、二叉树的镜像
- 十五、二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
- 十六、二叉树中和为某一值的路径
一、二叉树的前序遍历
144.二叉树的前序遍历
方法一:
class Solution {
List <Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return tmp;
}
tmp.add(root.val);
preorderTraversal(root.left);
preorderTraversal(root.right);
return tmp;
}
}
方法二:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List <Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return tmp;
}
tmp.add(root.val);
List<Integer> leftTree = preorderTraversal(root.left);
tmp.addAll(leftTree);
List<Integer> rightTree = preorderTraversal(root.right);
tmp.addAll(rightTree);
return tmp;
方法三:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null ||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
// System.out.print(cur.val);
list.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
cur = top.right;
}
return list;
}
}
二、二叉树的中序遍历
94.二叉树的中序遍历
方法一:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List <Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return tmp;
}
List <Integer> leftTree = inorderTraversal(root.left);
tmp.addAll(leftTree);
tmp.add(root.val);
List <Integer> rightTree = inorderTraversal(root.right);
tmp.addAll(rightTree);
return tmp;
}
方法二:
class Solution {
List <Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return tmp;
inorderTraversal(root.left);
tmp.add(root.val);
inorderTraversal(root.right);
return tmp;
}
}
方法三:非递归的方法
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
tmp.add(top.val);
cur = top.right;
}
return tmp;
}
}
三、二叉树的后序遍历
145.二叉树的后序遍历
方法一:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List <Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return tmp;
}
List <Integer> leftTree = postorderTraversal(root.left);
tmp.addAll(leftTree);
List <Integer> rightTree = postorderTraversal(root.right);
tmp.addAll(rightTree);
tmp.add(root.val);
return tmp;
}
}
方法二:
class Solution {
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return tmp;
postorderTraversal(root.left);
postorderTraversal(root.right);
tmp.add(root.val);
return tmp;
}
}
方法三:非递归方法实现后序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode pre = null;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.peek();
if(top.right == null || top.right == pre){
stack.pop();
tmp.add(top.val);
pre = top; //将pre指向top
}else{
cur = top.right;
}
}
return tmp;
}
}
四、判断两棵树是否相同
100.相同的树
给你两棵二叉树的根节点 p 和 q ,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同。
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == null && q == null) return true;
if((p == null && q != null) ||(p != null && q == null)){
return false;
}
if(p.val != q.val){
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
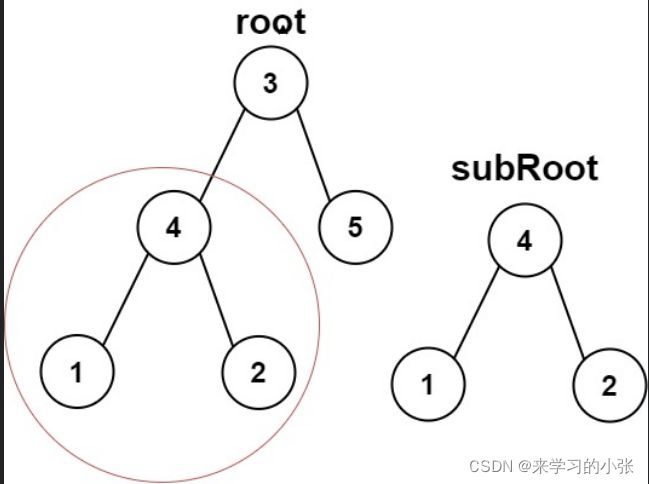
五、判断一棵树是否是另一棵树的子树
572.另一棵树的子树
给你两棵二叉树 root 和 subRoot 。检验 root 中是否包含和 subRoot 具有相同结构和节点值的子树。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
二叉树 tree 的一棵子树包括 tree 的某个节点和这个节点的所有后代节点。tree 也可以看做它自身的一棵子树。
/**
1. Definition for a binary tree node.
2. public class TreeNode {
3. int val;
4. TreeNode left;
5. TreeNode right;
6. TreeNode() {}
7. TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
8. TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
9. this.val = val;
10. this.left = left;
11. this.right = right;
12. }
13. }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//如果两个都为空
if(p == null && q == null){
return true;
}
//一个为空
if((p == null && q != null) ||(q == null && p != null)){
return false;
}
//p q都不为空,但是p,q的值不相等
if(p.val != q.val){
return false;
}
//p q都不为空,且对应的值是相同的
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if(root == null || subRoot == null){
return false;
}
if( isSameTree(root,subRoot)){
return true;
}
if(isSubtree(root.left,subRoot)){
return true;
}
if(isSubtree(root.right,subRoot)){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
六、判断一棵树是否为平衡二叉树(AVL树)
110.平衡二叉树
平衡二叉树的定义:一个二叉树每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。
解题思路:
- 一棵树如果要是AVL树,那么这颗树的每颗子树都必须是AVL(平衡二叉树)树。
- 求当前根的左树和右树高度,计算绝对值
- 如果没有超过1,只能证明当前根是平衡的,继续判断根的左树和右树,直到找到高度差超过1,则证明其不是平衡的。
方法一:
class Solution {
//求二叉树的高度
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftTree = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightTree = maxDepth(root.right);
return ((leftTree > rightTree) ? leftTree + 1 : rightTree + 1);
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
//从上往下
int leftTree = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightTree = maxDepth(root.right);
return (Math.abs(leftTree - rightTree)<=1 && isBalanced(root.left) &&isBalanced(root.right));
}
}
方法二:
class Solution {
//求二叉树的高度
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftTree = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightTree = maxDepth(root.right);
//在求高度的时候,只要某一个子树不满足就直接结束 从下往上
if(leftTree >=0 && lrightTree >= 0 && Math.abs(leftTree - rightTree) <= 1){
return Math.max(leftTree,rightTree) + 1;
//return ((leftTree > rightTree) ? leftTree + 1 : rightTree + 1);
}else{
return -1;
}
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return maxDepth(root) >= 0;
}
}
七、判断一棵树是否为对称二叉树
101.对称二叉树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。

class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode leftTree,TreeNode rightTree) {
if(leftTree == null && rightTree == null){
return true;
}
if((leftTree == null && rightTree !=null) || (leftTree != null && rightTree == null)){
return false;
}
if(leftTree.val != rightTree.val){
return false;
}
return isSymmetricChild(leftTree.left,rightTree.right) && isSymmetricChild(leftTree.right,rightTree.left);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return isSymmetricChild(root.left,root.right);
}
}
七、二叉树遍历
KY11二叉树遍历
编一个程序,读入用户输入的一串先序遍历字符串,根据此字符串建立一个二叉树(以指针方式存储)。 例如如下的先序遍历字符串: ABC##DE#G##F### 其中“#”表示的是空格,空格字符代表空树。建立起此二叉树以后,再对二叉树进行中序遍历,输出遍历结果。
import java.util.*;
class TreeNode{
public char val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
public TreeNode (char val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public class Main{
public static int i = 0;
public static TreeNode createTree(String str){
if(str == null){
return null;
}
TreeNode root = null;
if(str.charAt(i) != '#'){
root = new TreeNode(str.charAt(i));
i++;
root.left = createTree(str);
root.right = createTree(str);
}else{
i++;
}
return root;
}
//中序遍历
public static void inorder(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scanner.nextLine();
TreeNode root = createTree(str);
inorder(root);
}
}
八、二叉树层序遍历
102.二叉树的层序遍历
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
//满足结果的要求
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return ret;
}
//队列的作用是为了实现层序遍历
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while(size!= 0){
TreeNode top = queue.poll();
list.add(top.val);
if(top.left != null){
queue.offer(top.left);
}
if(top.right != null){
queue.offer(top.right);
}
size--;
}
ret.add(list);
}
return ret;
}
}
九、二叉树的最近公共祖先
236.二叉树的最近公共祖先
最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
//前序遍历 根-》左-》右
//1.p和q在根节点的两侧,此时root就是最近的公共祖先
//当前根的左树不为空,右树为空,左树找到的节点就是公共祖先
//左树为空,右树不为空,右树找到的节点就是公共祖先
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
if(root == p || root == q){
return root;
}
TreeNode leftTree = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode rightTree = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(leftTree != null && rightTree != null){
return root;
}
//说明有一个肯定为空
if(leftTree != null ){
return leftTree;
}
if(rightTree != null){
return rightTree;
}
//左右都为空,没有公共祖先
return null;
}
}
方法二:
//1.用两个栈存贮路径
//2.求栈的大小
//3.让栈中多的元素出差值个元素
//4.开始出栈,直到栈顶元素相同,此时就是公共祖先
//node 指定的节点 root:根节点
public boolean getPath(TreeNode root,TreeNode node,Stack<TreeNode> stack){
if(root == null || node == null){
return false;
}
stack.push(root);
if(root == node){
return true;
}
boolean flg = getPath(root.left,node,stack);
if(flg == true) return true;
flg = getPath(root.right,node,stack);
if(flg == true) return true;
stack.pop();
return false;
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<>();
getPath(root,p,stack1);
getPath(root,q,stack2);
int size1 = stack1.size();
int size2 = stack2.size();
if(size1> size2){
int size = size1 - size2;
while(size != 0){
stack1.pop();
size--;
}
while(!stack1.isEmpty() && !stack2.isEmpty()){
if(stack1.peek() == stack2.peek()){
return stack1.pop();
}else{
stack1.pop();
stack2.pop();
}
}
}else{
int size = size2 - size1;
while(size != 0){
stack2.pop();
size--;
}
while(!stack1.isEmpty() && !stack2.isEmpty()){
if(stack1.peek() == stack2.peek()){
return stack1.pop();
}else{
stack1.pop();
stack2.pop();
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
十、二叉搜索树与双向链表
//此题的解决方法其实就是中序遍历,因为要排好序
public class Solution {
public TreeNode prev = null;
public void ConvertChild(TreeNode pCur) {
if(pCur == null){
return;
}
ConvertChild(pCur.left);
//第一次递归,将节点的左边置为空
pCur.left = prev;
if(prev != null){
prev.right = pCur;
}
//将prev移向pCur位置
prev = pCur;
ConvertChild(pCur.right);
}
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
//找链表的头节点,直接从根节点出发,往左边找,直到某个节点的left = null
if(pRootOfTree == null){
return null;
}
ConvertChild(pRootOfTree);
TreeNode head = pRootOfTree;
while(head.left != null){
head = head.left;
}
return head;
}
}
十一、从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树
class Solution {
public int prindex = 0;
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend){
if(inbegin > inend){
return null;//左树或者右树为空
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[prindex]);
//找根节点在中序遍历的数组中的结果
int rootindex = findRootIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[prindex]);
prindex++;
root.left = buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,inbegin,rootindex - 1);
root.right = buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,rootindex + 1,inend);
return root;
}
//找根节点
public int findRootIndex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key){
for(int i = inbegin;i<= inend;i++){
if(inorder[i] == key){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(preorder == null || inorder == null) return null;
return buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length - 1);
}
}
十二、根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
class Solution {
public int postindex = 0;
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] postorder, int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend){
if(inbegin > inend){
return null;//左树或者右树为空
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[postindex]);
//找根节点在后序遍历的数组中的结果
int rootindex = findRootIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,postorder[postindex]);
postindex--;
root.right = buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,rootindex + 1,inend);
root.left = buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,inbegin,rootindex - 1);
return root;
}
//在中序遍历中找根节点
public int findRootIndex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key){
for(int i = inbegin;i<= inend;i++){
if(inorder[i] == key){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if(postorder == null || inorder == null) return null;
postindex = postorder.length - 1
return buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,0,inorder.length - 1);
}
}
十三、二叉树创建字符串
606.根据二叉树创建字符串
class Solution {
public void tree2strChild(TreeNode t,StringBuilder sb) {
if(t == null) return;
sb.append(t.val);
if(t.left == null){
if(t.right == null){
return;
}else{
sb.append("()");
}
}else{
sb.append("(");
tree2strChild(t.left,sb);
sb.append(")");
}
if(t.right == null){
return;
}else{
sb.append("(");
tree2strChild(t.right,sb);
sb.append(")");
}
}
public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
tree2strChild(root,sb);
return sb.toString();
}
}
十四、二叉树的镜像
NC72二叉树的镜像
public TreeNode Mirror (TreeNode pRoot) {
if(pRoot == null){
return pRoot;
}
if(pRoot.left == null && pRoot.right == null){
return pRoot;
}
TreeNode tmp = pRoot.left;
pRoot.left = pRoot.right;
pRoot.right = tmp;
if(pRoot.left != null){
Mirror(pRoot.left);
}
if(pRoot.right != null){
Mirror(pRoot.right);
}
return pRoot;
}
}
十五、二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
牛客链接
描述:
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。如果是则返回 true ,否则返回 false 。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
提示:
1.二叉搜索树是指父亲节点大于左子树中的全部节点,但是小于右子树中的全部节点的树。
2.该题我们约定空树不是二叉搜索树。
3.后序遍历是指按照 “左子树-右子树-根节点” 的顺序遍历。
public class Solution {
public boolean VerifySquenceOfBSTCore(int[] sequence,int start,int end){
if(start >= end){
return true;
}
int i = start;
//后续遍历为左右根
//该二叉树的左子树的值都小于二叉树的值,右子树的值都大于二叉树的值
//先遍历左半部分,拿到左子树序列
while(i < end && sequence[i] < sequence[end]){
i++;
}
//判断右子树部分是否有小于根节点值的情况,如果有,则就不是二叉搜索树
for(int j = i; j < end;j++){
if(sequence[j] < sequence[end]){
return false;
}
}
return VerifySquenceOfBSTCore(sequence,start,i - 1) && VerifySquenceOfBSTCore(sequence,i,end - 1);
}
public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int [] sequence) {
if(sequence == null || sequence.length == 0){
return false;
}
return VerifySquenceOfBSTCore(sequence,0,sequence.length - 1);
}
}
十六、二叉树中和为某一值的路径
牛客链接
描述:
输入一颗二叉树的根节点root和一个整数expectNumber,找出二叉树中结点值的和为expectNumber的所有路径。
1.该题路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶子结点所经过的结点;
2.叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点;
3.路径只能从父节点到子节点,不能从子节点到父节点;
4.总节点数目为n;
这是一个典型的回溯法(DFS)的使用:
回溯法本质是一个基于DFS的穷举的过程。
- 先添加值
- 在判定现有结果是否满足条件
- DFS
- 回退
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public void FindPathDFS(TreeNode root, int expectNumber,ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res, ArrayList<Integer> list){
if(root == null){
return;
}
//将当前值放入list待选集当中
list.add(root.val);
//更新目标值
expectNumber -= root.val;
回溯剪枝,去掉不满足条件的
if(root.left == null && root.right == null && expectNumber == 0){
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer> (list));
}
FindPathDFS(root.left,expectNumber,res,list); // DFS递归统计
FindPathDFS(root.right,expectNumber,res,list);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);//回退
}
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindPath(TreeNode root,int expectNumber) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return res;
}
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
FindPathDFS(root,expectNumber,res,list);
return res;
}
}
以上。