慕课前端售1299元的面试题【第一阶段】JS-day03
JS面试题-后面有高阶
-
- 1. typeof运算符可以判断哪些类型?
-
- 1. 识别所有值类型
- 2. 识别函数
- 3. 判断是否是引用类型(不可再细分)**
- 2. 手写浅拷贝 和 深拷贝
-
- 1.手写浅拷贝
- 2.手写深拷贝
- 3. == 运算符何时使用
- 4.truly 变量 和 falsely 变量
- 3. class类 extends 继承
-
- 4. 类型instanceof 判断 与JS原型
- 1. JS 原型
- 2. 原型链
- 4. JS 闭包
- 5. 简述 this
-
- 1. 手写bind
- 2. 实际开发中闭包的作用
- 6. js异步和单线程
-
- promise 解决了什么问题
- 7.手写 promise 加载一张图片
- 8. DOM节点操作 面试题
-
- property 和 attribute 两种形式区别
- 获取 DOM 节点
- DOM 性能
- 9. BOM操作面试题
-
- 1.事件绑定 和事件冒泡
- 2.如何识别浏览器的类型
- 3.分拆 url 各个部分
- 4. JSONP跨域
- 5.手写Ajax核心API-XMLHttpRequset 发起请求
-
- false为同步请求,true为异步请求
- 为什么xhr.readyState === 4
- 为什么xhr.status === 200
- 10. 描述 Cookie LocalStorage SessionStorage区别
- 11. JS扩展(高阶)
-
- 1.Arrag Flatten 实现数组一级扁平化
- 2. Array Flatten 实现数组彻底拍平
- 3. 手写一个getType函数,获取详细的数据类型
- 4. new 一个对象发生了什么?请手写代码表示
- 5. 连环问:Object.create和{}有什么区别?
- 6. 遍历DOM树
- 7. 手写 LazyMan
- 7. 手写一个 curry 函数,把其他函数柯里化
- 8. instanceof 原理是什么,请用代码表示(非常重要!!!)
- 9. 手写 函数 bind
- 10. 手写函数 call 和 apply
-
- 手写 call
- 手写 apply
- 11. 手写 EventBus 自定义事件
-
- 使用 filter 过滤来写
- 拆分保存 on 和 once 事件,实现EventBus
- 12. 用js 实现 LRU 缓存(以后再加)
- 13. 手写 js 深拷贝 ,考虑Map、Set、循环引用
-
- 深拷贝 - 只考虑了简单的数组、对象
- 深拷贝,考虑 Object Array Map Set
- 补充 new set 和 new map
上一篇慕课JS面试题,链接地址
1. typeof运算符可以判断哪些类型?
1. 识别所有值类型
a 定义 undefined 不可以 使用 const ;
let a; typeof a // undefined; 未定义类型
const str = '字符串类型'; typeof str // string; 字符串类型
const n = 100; typeof n // number; 数字类型
const b = true; typeof b // boolean; 布尔类型
const s = Symbol( 's' ); typeof s // symbol; 独一无二的值
2. 识别函数
typeof console.log // function 函数
typeof function () { } // function 函数
3. 判断是否是引用类型(不可再细分)**
typeof null // object 对象
typeof [ 'a' , 'b' ] // object 对象
typeof { x: 100 } // object 对象
比如它是null 还是数组 或者对象,识别不出,不可再细分
2. 手写浅拷贝 和 深拷贝
1.手写浅拷贝
// 浅拷贝 Shallow copy
const obj1 = {
age: 20,
name: ' xxx ',
address: {
city: '北京'
},
arr: [' a ', ' b ', ' c ']
}
const obj2 = obj1
obj1.address.city = ' 上海 ';
console.log(obj.address.city) // 打印结果: 上海
2.手写深拷贝
接 浅拷贝 改 const obj2 = deepClone( obj1 ) 即可
// 深拷贝 deep copy
function deepClone ( obj = { } ) {
// 如果 obj 类型不是对象也不是数组 或者 obj 为空
if ( typeof obj !== ' object ' || obj == null ) {
return obj // 终止返回,不进行拷贝
}
// 初始化返回结果
let result ;
if ( obj instanceof Array ) { // 判断 拷贝的内容 是否是数组
result = [ ] ;
} else {
result = { } ;
}
for ( let key in obj ) {
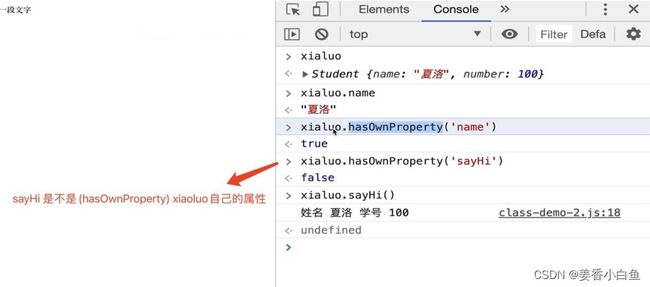
if ( obj.hasOwnProperty ( key ) ) {
// 递归调用 !!!
result [key] = deepClone( obj[ key ] )
}
}
// 返回结果
return result
}
3. == 运算符何时使用
// 除了 == null 之外, 其他都一律使用 ===,例如:
const obj = { x: 100 }
if ( obj.a == null ) { }
// 相当于 :
if ( obj.a === null || obj.a === undefined ) { }
如果不使用 === 会呈现如下效果
100 == ' 100 ' // true
0 == ' ' // true
0 == false // true
false == ' ' // true
null == undefined // true
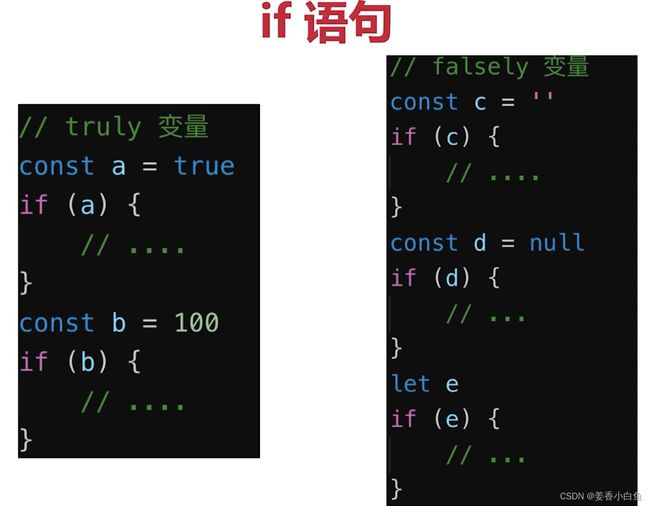
4.truly 变量 和 falsely 变量
truly 变量 : !!a === true 的变量
例如 : const n = 100
打印 !n 为 false
打印 !!n 为 true
如果是 对象 那就是 truly 变量
!!{ } 打印为 true
falsely 变量 : !!a === false 的变量
例如 : const n1 = 0
打印 !!0 为 false
打印 !0 为 true
以下是falsely 变量。除此之外都是 truely 变量
!!0 === false
!!null === false
!!' ' === false
!!NaN === false (NaN = not a number 把一个个字符串,转换为数字 转换不出来,使用)
!!false === false
!!undefined === false
1. console.log ( 10 && 0) // 结果: 0
10 为 truely变量,接着往后判断 0 为falsely变量,返回0
2. console.log ( ’ ’ || ’ abc ’ ) // ‘ abc ’
’ ‘为falsely 变量,往后判断 ‘abc’ 为truely 变量,返回 ‘abc’
3. console.log ( !window.abc ) // true
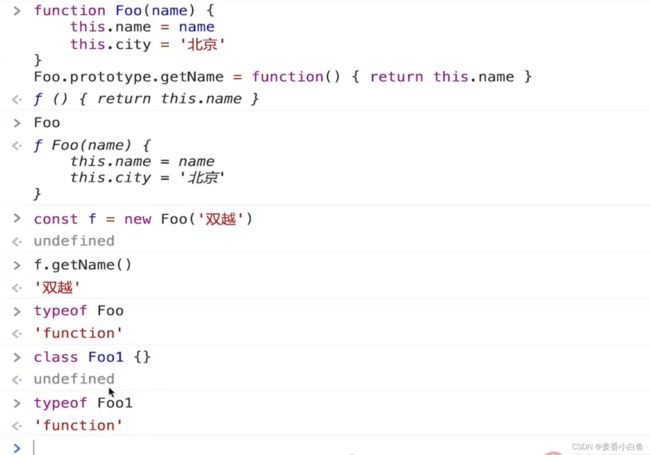
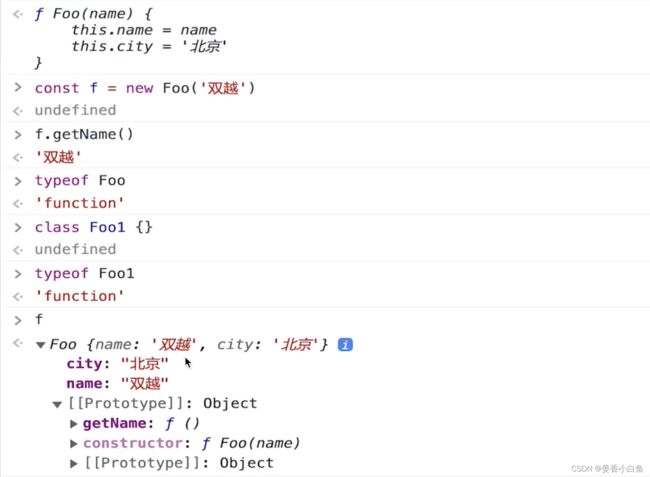
3. class类 extends 继承
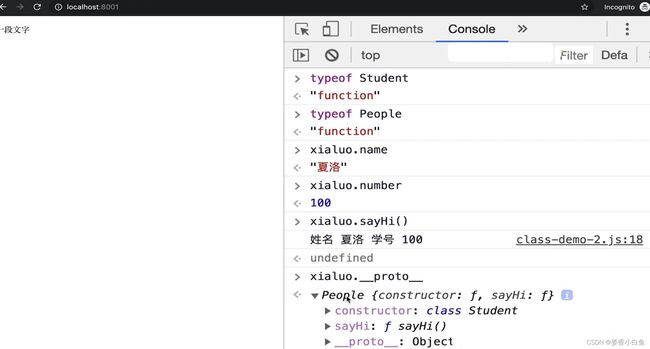
4. 类型instanceof 判断 与JS原型
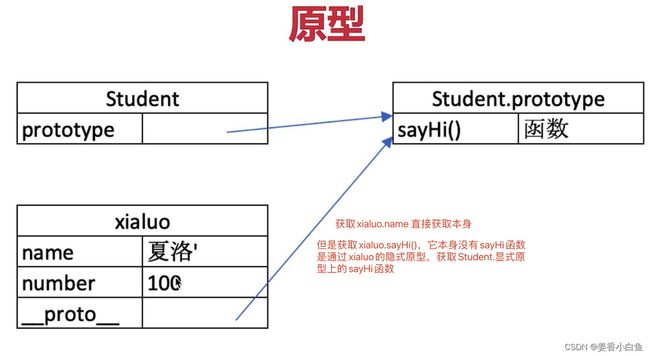
1. JS 原型
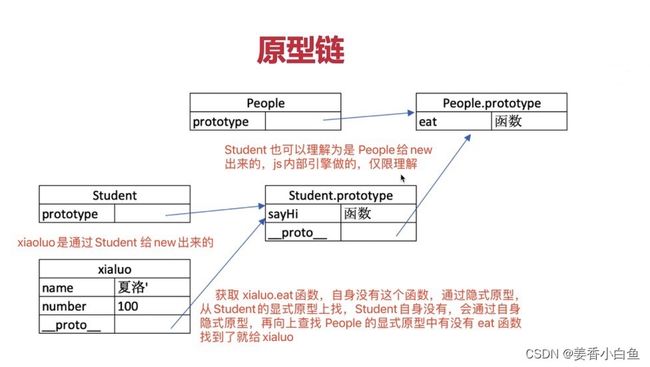
2. 原型链
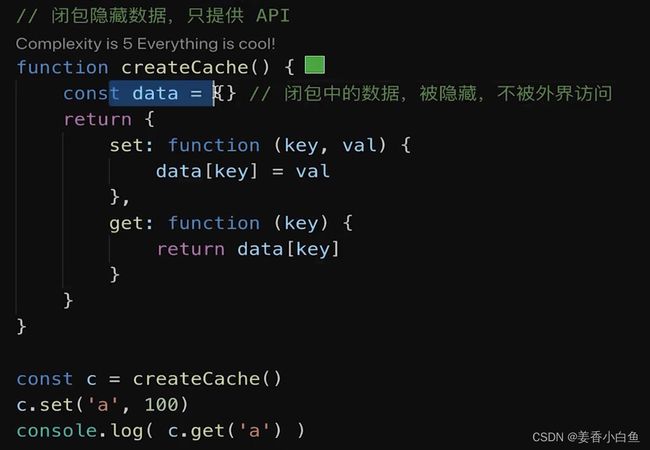
4. JS 闭包
- 闭包:自由变量的查找,是在函数定义的地方,
向上级作用域查找,不是在函数执行的地方查找!!!
5. 简述 this
1. 手写bind
2. 实际开发中闭包的作用
6. js异步和单线程
promise 解决了什么问题
7.手写 promise 加载一张图片
8. DOM节点操作 面试题
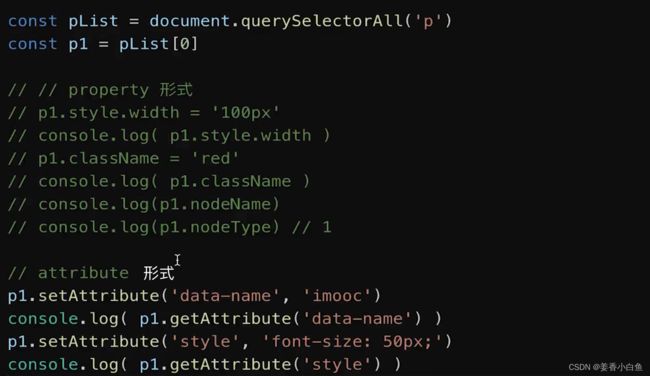
property不是API名字的一部分,它是一种形式,一种使用js属性操作dom元素的形式

property 和 attribute 两种形式区别
property 形式
对dom元素js变量做的修改
property: 修改对象属性,不会体现到 html 中attribute 形式
对dom元素 结构的属性,也是节点属性做的修改,它可以真正作用到节点属性上去
attribute:修改html属性,会改变 html结构两者都有可能引起 DOM 重新渲染,如必要情况:推荐使用 property 形式
获取 DOM 节点
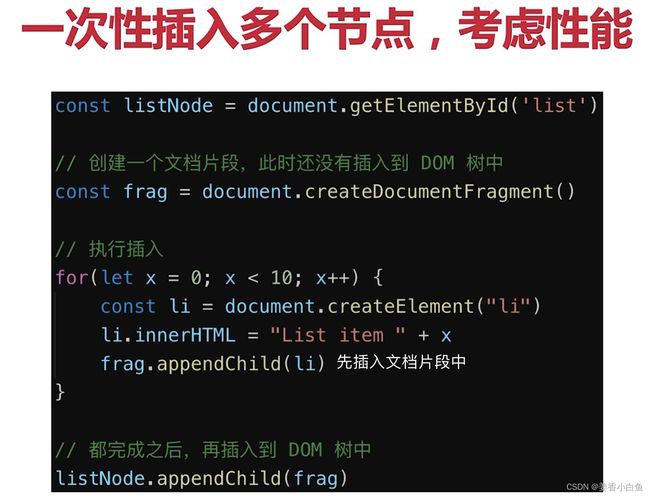
DOM 性能
9. BOM操作面试题
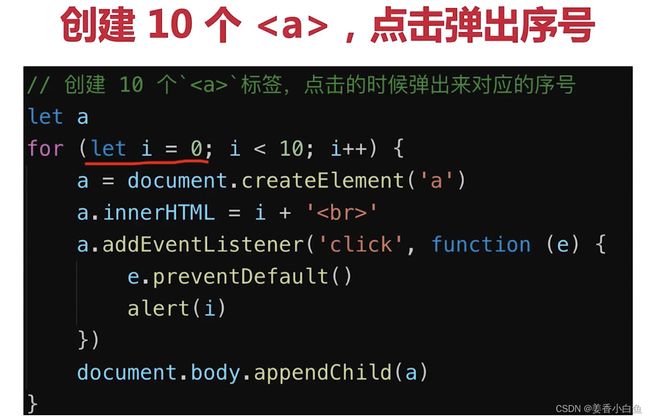
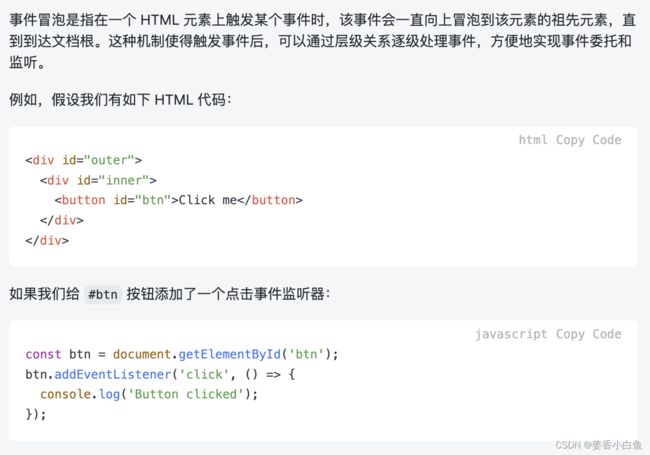
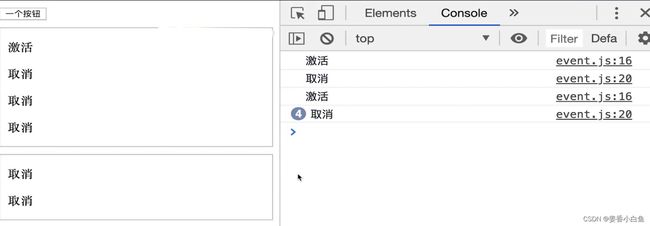
1.事件绑定 和事件冒泡
2.如何识别浏览器的类型
3.分拆 url 各个部分
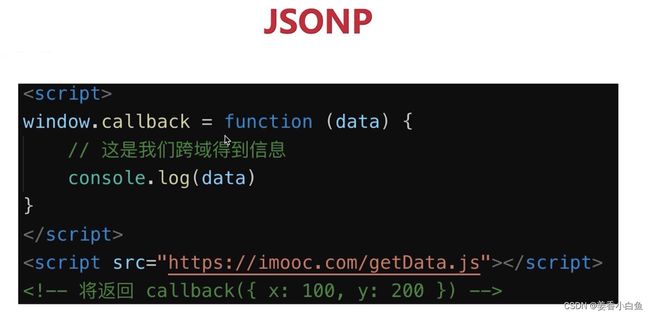
4. JSONP跨域
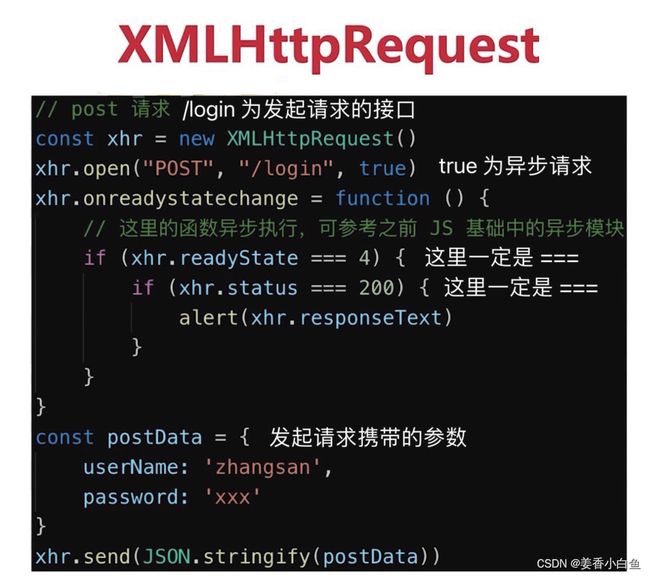
5.手写Ajax核心API-XMLHttpRequset 发起请求
false为同步请求,true为异步请求
为什么xhr.readyState === 4
为什么xhr.status === 200
10. 描述 Cookie LocalStorage SessionStorage区别
11. JS扩展(高阶)
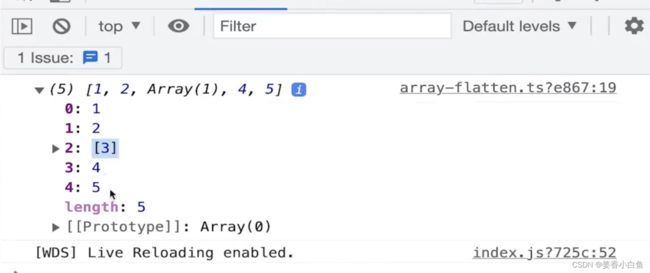
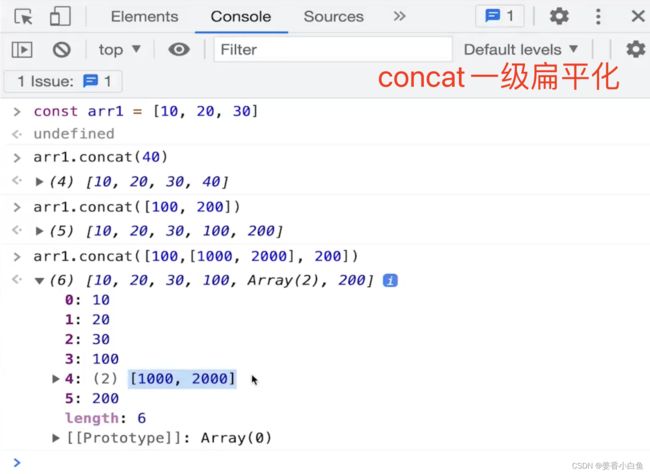
1.Arrag Flatten 实现数组一级扁平化
function flatten1(arr) {
// 定义了一个空数组变量 res,用于储存展开后的结果。
const res = [];
// 使用 forEach 方法遍历输入数组 arr 中的每一个元素,并对每个元素执行一个回调函数。
arr.forEach(item => {
// Array.isArray 方法检查当前处理的元素是否为数组类型。如果是数组类型
if (Array.isArray(item)) {
// 使用 forEach 方法遍历当前元素(即数组)中的每一个元素,并将其加入结果数组 res 中。
item.forEach(n => res.push(n));
} else {
// 将当前元素直接加入结果数组 res 中。
res.push(item);
}
});
return res;
}
// 功能测试
const arr = [1, [2, [3], 4], 5, 6];
console.info(flatten1(arr));
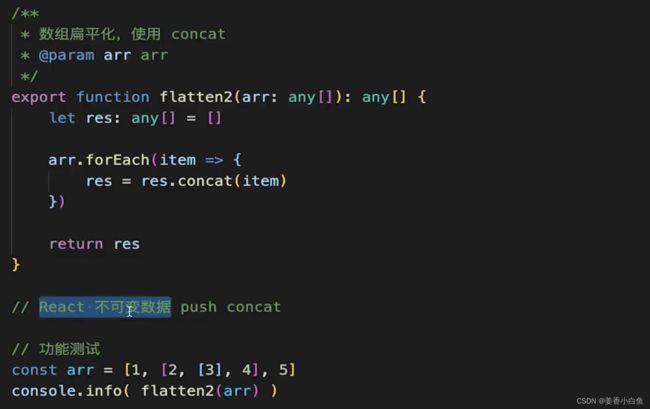
function flatten2(arr) { // 声明一个函数,接收一个数组作为参数
let res = []; // 声明一个空数组用于存放扁平化后的结果
arr.forEach(item => { // 使用 forEach() 方法遍历传入的数组 arr
res = res.concat(item); // 将当前元素 item 连接到结果数组 res 中
});
return res; // 返回结果数组 res
}
const arr = [1, [2, [3], 4], 5, 6]; // 声明一个多维数组 arr,用于测试 flatten2 函数
console.info(flatten2(arr)); // 执行函数并打印结果
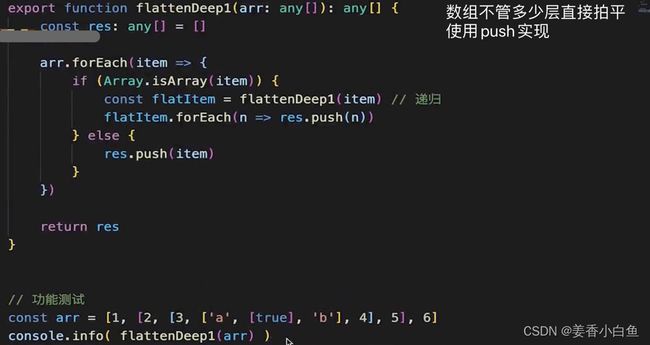
2. Array Flatten 实现数组彻底拍平
- 先实现一级扁平化,然后递归调用,直到全部扁平
function flattenDeep1(arr) {
const res = [];
arr.forEach(item => {
if (Array.isArray(item)) {
const flatItem = flattenDeep1(item); // 递归
flatItem.forEach(n => res.push(n));
} else {
res.push(item);
}
});
return res;
}
// 功能测试
const arr = [1, [2, [3, ['a', [true], 'b'], 4], 5], 6];
console.info(flattenDeep1(arr));
function flattenDeep2(arr) {
let res = []
arr.forEach(item => {
if (Array.isArray(item)) {
const flatItem = flattenDeep2(item) // 递归
res = res.concat(flatItem)
} else {
res = res.concat(item)
}
})
return res
}
// 功能测试
const arr = [1, [2, [3, ['a', [true], 'b'], 4], 5], 6];
console.info(flattenDeep2(arr));
3. 手写一个getType函数,获取详细的数据类型
4. new 一个对象发生了什么?请手写代码表示
5. 连环问:Object.create和{}有什么区别?
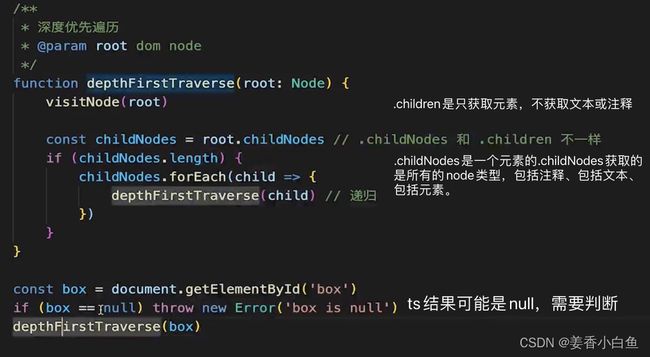
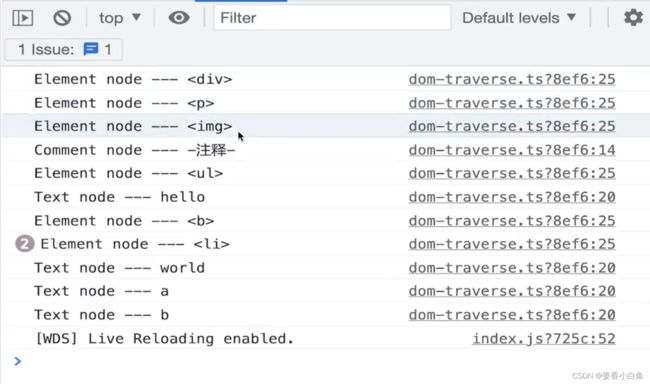
6. 遍历DOM树
- 深度优先是: 、随后
,再是"hello",再往下就没了,回溯到,在往下走,走到world,回溯到,再回溯到,走到- 下
- 标签下的"b"走完结束。
- 广度优先是:
完后,往下、
、、
function breadthFirstTraverse(root: Node) { const queue: Node[] = [] // 数组 vs 链表 // 根节点入队列 queue.unshift(root) while (queue.length > 0) { const curNode = queue.pop() if (curNode == null) break visitNode(curNode) // 子节点入队 const childNodes = curNode.childNodes if (childNodes.length) { childNodes.forEach(child => queue.unshift(child)) } } } const box = document.getElementById('box') if (box == null) throw new Error('box is null') breadthFirstTraverse(box)7. 手写 LazyMan
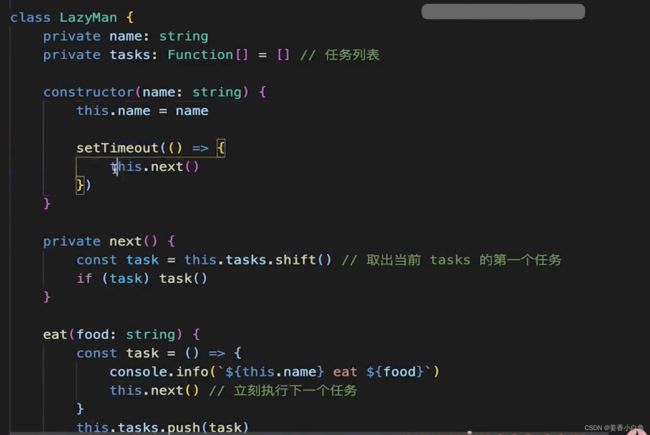
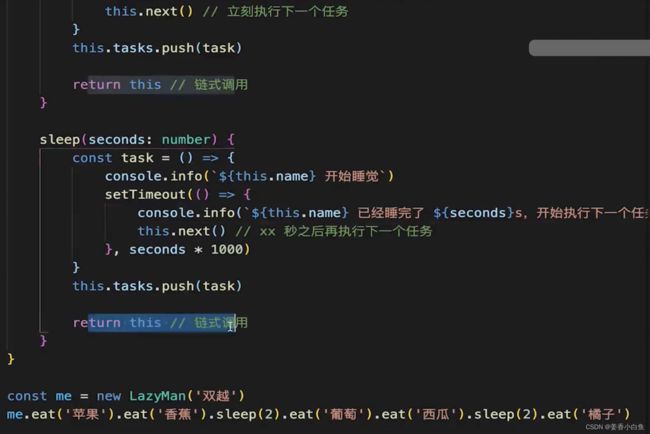
7. 手写一个 curry 函数,把其他函数柯里化
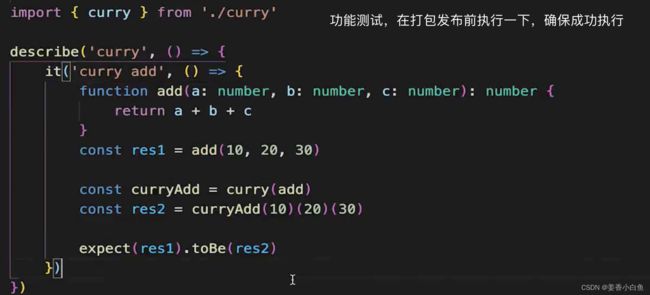
export function curry(fn:Function){ curry是:输入函数,返回函数 const fnArgsLength = fn.length // 传入函数的参数长度 let args: any[] = [] // ts中,独立的函数,this 仅仅需要声明类型,并不是参数,而且要放到第一位 function calc(this: any,...newArys:any[]){ // 积累参数 arg = [ ...args, ...newArgs ] 中间状态,当前积累的参数,如果小于传入函数参数长度的话,就返回一个函数 if(args.length < fnArgsLength){ // 参数不够,返回函数 return calc }else{ 如果参数够了,=甚至是>了当前函数参数的长度,那就执行返回结果 // 参数够了,返回执行结果 执行参数结果,使用apply来执行,将this传入,将参数做一个截断,传入参数长度多少就截取多少 return fn.apply(this,arg.slice(0, fnArgsLength)) } } return calc } function add(a:number,b:number,c:number):number{ return a+b+c } const curryAdd = curry(add) const res = curryAdd(10)(20)(30) console.log(res) // 结果 608. instanceof 原理是什么,请用代码表示(非常重要!!!)
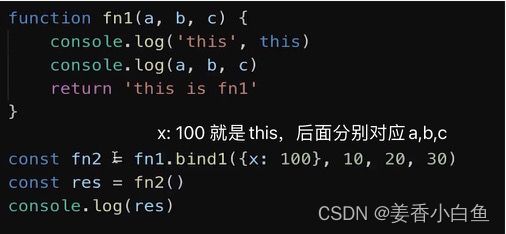
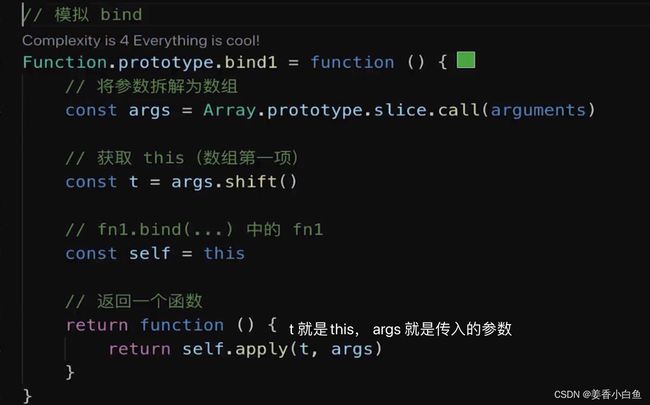
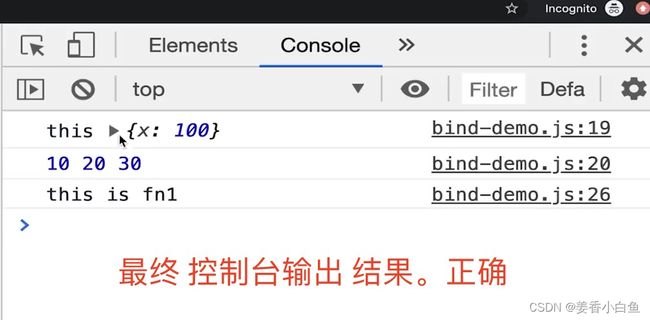
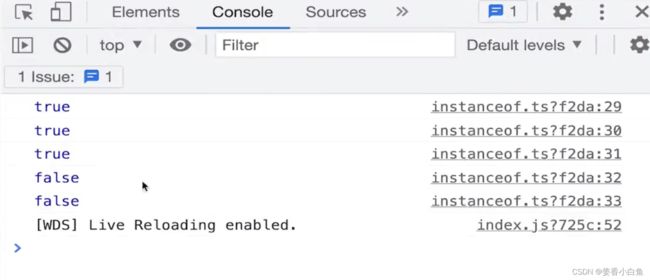
/** * 自定义 instanceof 方法 * @param instance instance 就是实例 * @param origin 就是class or function */ // 传入两个参数一个是 instance实例,any类型。 第二个是origin。返回boolean类型 export function myInstanceof(instance: any, origin: any): boolean { if (instance == null) return false // 如果instance 是null undefined 就返回 false const type = typeof instance // 判断instance 的类型 // 如果不是 object对象 并且 不是 function函数 if (type !== 'object' && type !== 'function') { // 值类型; (所有的值类型,进行 instanceof 都是 false return false } let temInstance = instance // 使用临时变量赋值 instance,为了防止修改 instance while (temInstance) { // 只要有 temInstance // 判断 当前实例的隐式原型 是否全等于 class或function 的显示原型 if (temInstance.__proto__ === origin.prototype) { 比如 instance是个数组,origin是个 Array的构造函数,那就匹配上了 return true // 匹配上了 } // 未匹配上 temInstance = temInstance.__proto__ // 顺着原型链,往上找 比如图上 new Foo() 未匹配上,会往上走到 Foo 圆圈哪里再进行匹配,此时就匹配上了 } // 原型链结束了,还没匹配上,返回 false return false } // 功能测试 console.log(myInstanceof({},Object)) console.log(myInstanceof([],Object)) console.log(myInstanceof([],Array)) console.log(myInstanceof({}, Array)) console.log(myInstanceof('abc',String))9. 手写 函数 bind
10. 手写函数 call 和 apply



如果 content == null,打印的是window。

- new Object(‘abc’) 会判断生成 String(‘abc’) 对象;
- new Object(true) 会判断生成 Boolean(true)对象
手写 call
// 自定义 call // @ts-ignore 取消文件下一行的错误提示。 ...args传入的是零散的参数 Function.prototype.customCall = function (context: any, ...args: any[]) { if (context == null) context = globalThis // 如果 call == null,打印的是window。 // 值类型,变对象类型 if (typeof context !== 'object') context = new Object(context) const fnKey = Symbol() // 不会出现属性名称的覆盖,是唯一的 context[fnKey] = this // this就是当前的函数 const res = context[fnKey](...args) // 绑定了 this delete context[fnKey] // 清理掉 fn ,防止污染 return res } // 测试 function fn(this: any, a: any, b: any, c: any) { console.log(this, a, b, c) } // @ts-ignore fn.customCall({ x: 100 }, 10, 20, 30)手写 apply
// 自定义 apply // @ts-ignore 取消文件下一行的错误提示。 args传入的是数组 Function.prototype.customApply = function (context: any, args: any[] =[]) { if (context == null) context = globalThis // 如果 apply == null,打印的是window。 // 值类型,变对象类型 if (typeof context !== 'object') context = new Object(context) const fnKey = Symbol() // 不会出现属性名称的覆盖,是唯一的 context[fnKey] = this // this就是当前的函数 const res = context[fnKey](...args) // 绑定了 this delete context[fnKey] // 清理掉 fn ,防止污染 return res } // 测试 function fn(this: any, a: any, b: any, c: any) { console.log(this, a, b, c) } // @ts-ignore fn.customApply({ x: 200 }, [100, 200, 300])11. 手写 EventBus 自定义事件
使用 filter 过滤来写
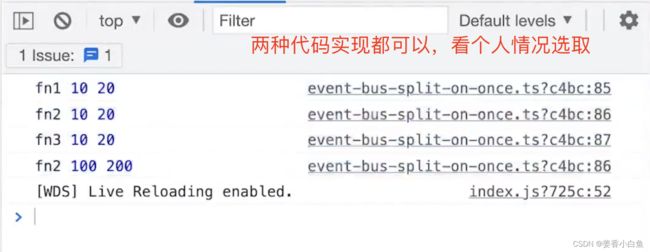
// 手写 EventBus class EventBus { /** * { * "key1":[ * { fn: fn1, isOnce: false}, * { fn: fn2, isOnce: false}, * { fn: fn3, isOnce: true}, * ] * "key2":[] // Object是无序的,需要使用 数组是有序的 * "key3":[] * } */ private events: { // Array<里面是对象{}> 数组 [key: string]: Array<{ fn: Function, isOnce: boolean }> } // 构造函数 constructor() { this.events = {} } // 绑定。 第一个参数 是type ,第二个参数是 函数 , 第三个参数 默认值为false on(type: string, fn: Function, isOnce: boolean = false) { const events = this.events // 获取 this.events if (events[type] == null) { // 如果 events[type] = [] // 初始化 key 的 fn 数组 } events[type].push({ fn, isOnce: false }) } // 只执行一次,就解绑 once(type: string, fn: Function) { this.on(type, fn, true) } // 解绑 off(type: string, fn?: Function) { // 如果 fn 没有值, 可以根据 type 解绑所有函数 if (!fn) { // 解绑所有 type 的函数 this.events[type] = [] } else { // 解绑 单个 fn const fnList = this.events[type] // 如果 type的函数有值是个数组,重新赋值 if (fnList) { // 如果 单个 type 的 fn 不等于 当前的fn, 那就过滤出来。 // 如果 等于 那就不要了 this.events[type] = fnList.filter(item => item.fn !== fn) } } } // 触发 emit(type: string, ...args: any[]) { // ...args 多个参数 const fnList = this.events[type] // 触发这个事件,将这个类型的事件 全部获取出来 if (fnList == null) return // 注意, 过滤的前提是遍历 this.events[type] = fnList.filter(item => { const { fn, isOnce } = item // 在这个item里面找到 fn isOnce fn(...args) // 触发 fn // once 执行一次就要呗过滤掉 if (!isOnce) return true return false; }) } }拆分保存 on 和 once 事件,实现EventBus
class EventBus { // { key1: [fn1,fn2], key2:[fn1,fn2]} private events: { [key: string]: Array<Function> } private onceEvents: { [key: string]: Array<Function> } // 构造函数 constructor() { this.events = {} // 赋值为空对象 this.onceEvents = {} // 赋值为空对象 } // on 绑定 on(type: string, fn: Function) { const events = this.events if (events[type] == null) events[type] = [] events[type].push(fn) } // 只执行一次就解绑 once(type: string, fn: Function) { const onceEvents = this.onceEvents if (onceEvents[type] == null) onceEvents[type] = [] onceEvents[type].push(fn) } // off 解绑 off(type: string, fn?: Function) { if (!fn) { // 解绑所有事件 this.events[type] = [] this.onceEvents[type] = [] } else { // 解绑单个事件 const fnList = this.events[type] const onceFnList = this.onceEvents[type] if (fnList) { this.events[type] = fnList.filter(curFn => curFn !== fn) } if (onceFnList) { this.onceEvents[type] = onceFnList.filter(curFn => curFn !== fn) } } } // 触发 emit emit(type: string, ...args: any[]) { const fnList = this.events[type] const onceFnList = this.events[type] if (fnList) { fnList.forEach(f => f(...args)) } if (onceFnList) { onceFnList.forEach(f => f(...args)) // once 执行一次就删除 this.onceEvents[type] = [] } } }总体来说这两个 代码 都可以实现,具体使用哪个 看个人理解代码的能力12. 用js 实现 LRU 缓存(以后再加)
13. 手写 js 深拷贝 ,考虑Map、Set、循环引用
深拷贝 - 只考虑了简单的数组、对象
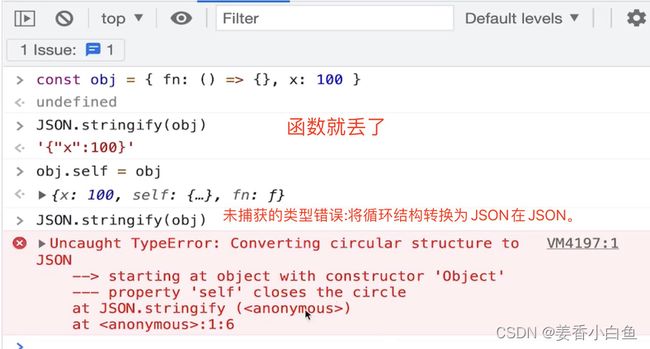
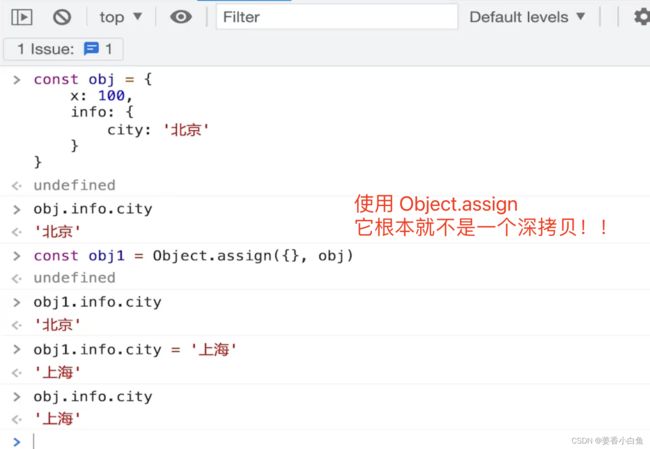
function cloneDeep(obj: any) { if (typeof obj !== 'object' || obj == null) return obj let result: any if (obj instanceof Array) { result = [] } else { result = {} } for (let key in obj) { if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) { result[key] = cloneDeep(obj[key]) // 递归调用 } } return result } // 功能测试 // const a: any = { // set: new Set([10, 20, 30]), // map: new Map([['x', 10], ['y', 20]]) // } // // a.self = a // console.log(cloneDeep(a)) // 无法处理 Map set 和循环引用 interface Person { name: string, age: number, hobbies: string[] } const person1: Person = { name: 'Alice', age: 30, hobbies: ['reading', 'cooking'] } const person2 = cloneDeep(person1) person2.hobbies.push('swimming') console.log(person1.hobbies) // ['reading', 'cooking'] console.log(person2.hobbies) // ['reading', 'cooking', 'swimming']深拷贝,考虑 Object Array Map Set
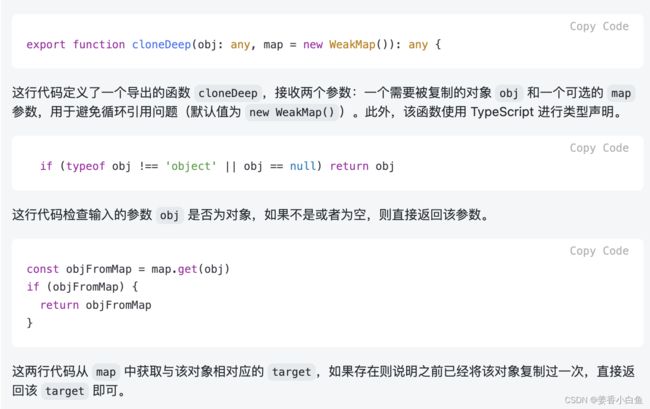
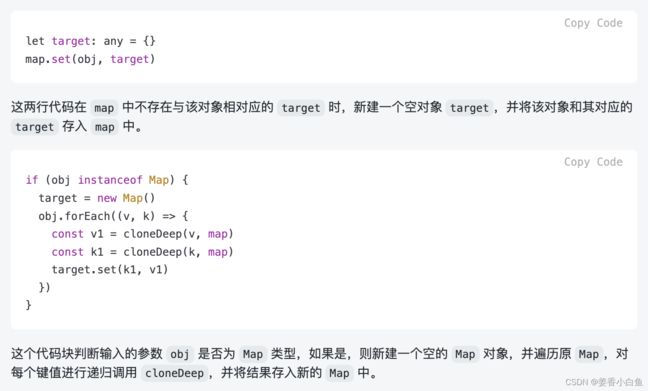
/** * 深拷贝 * @param map weakmap 为了避免循环引用, 弱引用。 * 不影响存在里面对象,垃圾销毁垃圾回收,不会导致内存泄漏 */ export function cloneDeep(obj: any, map = new WeakMap()): any { if (typeof obj !== 'object' || obj == null) return obj //避免循环引用 const objFromMap = map.get(obj) if (objFromMap) return objFromMap // 如果有值直接返回 // target 经过很多深拷贝处理,返的结果。 let target: any = {} // target是存储结果。 map.set(obj, target) // Map 处理 if (obj instanceof Map) { target = new Map() // 重新赋值 obj.forEach((v, k) => { // val , key const v1 = cloneDeep(v, map) const k1 = cloneDeep(k, map) target.set(k1, v1) }) } // Set 处理 if (obj instanceof Set) { target = new Set() obj.forEach(v => { // 只有 val const v1 = cloneDeep(v, map) target.add(v1) // 使用 add() 方法向 Set 对象添加元素。 }) } // Array 处理 if (obj instanceof Array) { // map 可以返回一个新的数组 target = obj.map(item => cloneDeep(item, map)) } // Object 处理 for (const key in obj) { // 对象的key,一版是字符串,是值类型,不需要深拷贝 const val = obj[key] const val1 = cloneDeep(val, map) // 只拷贝val就可以 target[key] = val1 } return target } // 功能测试 const a: any = { set: new Set([10, 20, 30]), map: new Map([['x', 10], ['y', 20]]), info: { city: '北京' }, fn: () => { console.info(100) } } a.self = a console.log(cloneDeep(a))补充 new set 和 new map