浅析HDFS FairCallQueue
背景
Hadoop服务组件,尤其是NameNode,处理来自Client的RPC请求时,往往承受较重的负载。默认情况下,各种请求在FIFO的队列中进行处理(具体实现为java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue)。此时如果某个用户执行的 I/O 操作较多,那么相比其他 I/O 操作较少的用户,他将获得更多服务。在这种情况下,FIFO 有失公平性,并且会导致其它用户的延迟大大增加。
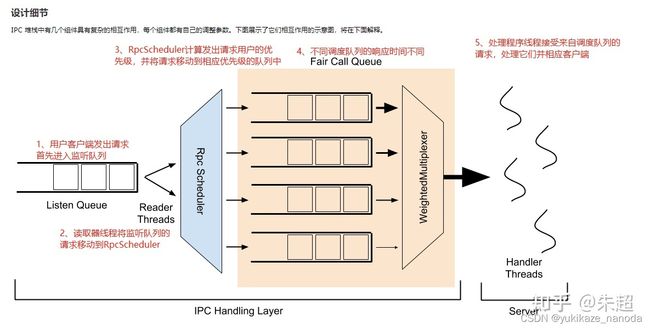
因此针对这个问题提出FairCallQueue(FCQ),其设计细节如图:
其中,3和4是可拔插的,替换了原有的FIFO队列分配逻辑,也是FCQ的核心逻辑。我们一个一个来看。
一、RpcScheduler
RpcScheduler计算用户优先级是通过请求数量(默认)或者请求花费而进行的, 请求数量越大,优先级越低。比如,在相同时限内,A用户请求50次,B用户请求5次,则B用户将放入优先级较高的队列。这就涉及到在一定时间内统计用户请求频率。FairCallQueue设计了一种频率衰减算法,前面时段内的计数结果通过衰减因子会用在在下一轮的计算中,占比逐步衰减,这种做法比完全清零统计要平滑得多。
默认情况下,与 FairCallQueue 一起使用的 RpcScheduler 的实现是DecayRpcScheduler,它记录了每个用户发送的请求的数量,暂且叫请求值。每经过一个扫描周期(默认为 5 秒),每个用户的请求值都会更新为周期内的请求数量加上上次请求值乘上衰减系数(默认为0.5)。例如本次A用户请求数量为10,5s过去后,产生了20个请求,则本次计算请求值为20 + 10 * 0.5 = 25。根据请求值的占比,DecayRpcScheduler分配用户请求到不同优先级的队列。
每次执行扫描时,所有已知用户的请求值都会从高到低排列。根据来自该用户请求值的比例,为每个用户分配一个优先级(默认为 0-3,0 为最高优先级)。默认优先级阈值为 (0.125, 0.25, 0.5),表示请求值占总数 50% 以上的用户(最多可以有一个这样的用户)被置于最低优先级;请求值占总数 25% 到 50 %之间的用户位于第二低优先级;请求值占 12.5% 到 25% 的用户位于第二高优先级;其他所有用户位于最高优先级。在扫描结束时,每个已知用户都有一个缓存的优先级,将使用到下一次扫描;在扫描之间出现的新用户将即时计算其优先级。
总之,RpcScheduler解决了RPC请求怎么放进相应的优先级队列的问题。
二、WeightedMultiplexer
RpcScheduler决定了请求放入哪些优先级队列,WeightedMultiplexer则决定如何为这些请求分配计算。目前,WeightedMultiplexer的实现为WeightedRoundRobinMultiplexer(WRRM),采用加权轮训算法进行分配。对于FairCallQueue 中的多个优先级队列(可配置,默认为4),为每个队列都设置一个权重。默认 4 个优先级队列的权重为 (8, 4, 2, 1),即WRRM会依次从四个队列中拿取8,4,2,1个请求交给线程处理,然后循环下去。
三、回退机制
回退机制(Backoff):指服务器在某种情况下,向客户端的请求抛出异常而非对其进行处理。此时,客户端在重试之前需要等待一段时间。
通常,两种情况会触发back:
1.当队列已满,尝试将请求放入优先级队列中时,会触发退避。
2.按响应时间退避——高优先级的请求服务太慢,将导致较低优先级的请求回退。
例如,如果优先级 1 的响应时间阈值设置为 10 秒,但该队列中的平均响应时间为 12 秒,则优先级为 2 或更低的传入请求将收到退避异常,而优先级为0 和 1 将正常进行。其目的是当整个系统负载足够重,以致于高优先级用户受到影响时,强制负载较重的客户端退出。
四、Cost-based Fair Call Queue
尽管公平调用队列本身可以有效减轻提交大量请求的用户的影响,但它并没有考虑到每个请求的处理成本。比如,在考虑 HDFS NameNode 时,提交 1000 个“getFileInfo”请求的用户的优先级将与提交 1000 个“mkdir”请求的用户相同。但是,后者需要对namesystem加写锁,调用成本更大。因此,FCQ有一个基于cost的扩展,它基于用户操作的总处理时间来确定用户的优先级。
默认情况下,成本中不考虑队列等待处理所花费的时间和等待获取锁所花费的时间,无锁处理所花费的时间是base加权,处理读锁的权重是base的 10 倍,使用排他锁的处理时间权重高 100 倍。这会尝试根据用户在服务器上的实际负载对用户进行优先级排序。要启用此功能,请将costprovder.impl配置设置为org.apache.hadoop.ipc.WeightedTimeCostProvider。
我的理解是,给与重锁的调用更大的时间权重。这样做更偏向于先处理无锁或者加读锁的RPC请求。
五、配置
所有与调用队列相关的配置仅与单个 IPC 服务器相关,即允许使用单个配置文件来配置不同的组件,甚至是一个组件内的不同 IPC 服务器,以具有唯一配置的调用队列。格式为ipc.端口.xxxx.xxx.xxxx。例如,ipc.8020.callqueue.impl将为在端口 8020 上运行的 IPC 服务器调整调用队列实现。对于本节的其余部分,将省略此前缀。
| Configuration Key | Applicable Component | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| backoff.enable | General | Whether or not to enable client backoff when a queue is full. | false |
| callqueue.impl | General | The fully qualified name of a class to use as the implementation of a call queue. Use org.apache.hadoop.ipc.FairCallQueue for the Fair Call Queue. | java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue (FIFO queue) |
| scheduler.impl | General | The fully qualified name of a class to use as the implementation of the scheduler. Use org.apache.hadoop.ipc.DecayRpcScheduler in conjunction with the Fair Call Queue. | org.apache.hadoop.ipc.DefaultRpcScheduler (no-op scheduler) If using FairCallQueue, defaults to org.apache.hadoop.ipc.DecayRpcScheduler |
| scheduler.priority.levels | RpcScheduler, CallQueue | How many priority levels to use within the scheduler and call queue. | 4 |
| faircallqueue.multiplexer.weights | WeightedRoundRobinMultiplexer | How much weight to give to each priority queue. This should be a comma-separated list of length equal to the number of priority levels. | Weights descend by a factor of 2 (e.g., for 4 levels: 8,4,2,1) |
| identity-provider.impl | DecayRpcScheduler | The identity provider mapping user requests to their identity. | org.apache.hadoop.ipc.UserIdentityProvider |
| cost-provider.impl | DecayRpcScheduler | The cost provider mapping user requests to their cost. To enable determination of cost based on processing time, use org.apache.hadoop.ipc.WeightedTimeCostProvider. | org.apache.hadoop.ipc.DefaultCostProvider |
| decay-scheduler.period-ms | DecayRpcScheduler | How frequently the decay factor should be applied to the operation counts of users. Higher values have less overhead, but respond less quickly to changes in client behavior. | 5000 |
| decay-scheduler.decay-factor | DecayRpcScheduler | When decaying the operation counts of users, the multiplicative decay factor to apply. Higher values will weight older operations more strongly, essentially giving the scheduler a longer memory, and penalizing heavy clients for a longer period of time. | 0.5 |
| decay-scheduler.thresholds | DecayRpcScheduler | The client load threshold, as an integer percentage, for each priority queue. Clients producing less load, as a percent of total operations, than specified at position i will be given priority i. This should be a comma-separated list of length equal to the number of priority levels minus 1 (the last is implicitly 100). | Thresholds ascend by a factor of 2 (e.g., for 4 levels: 13,25,50) |
| decay-scheduler.backoff.responsetime.enable | DecayRpcScheduler | Whether or not to enable the backoff by response time feature. | false |
| decay-scheduler.backoff.responsetime.thresholds | DecayRpcScheduler | The response time thresholds, as time durations, for each priority queue. If the average response time for a queue is above this threshold, backoff will occur in lower priority queues. This should be a comma-separated list of length equal to the number of priority levels. | Threshold increases by 10s per level (e.g., for 4 levels: 10s,20s,30s,40s) |
| decay-scheduler.metrics.top.user.count | DecayRpcScheduler | The number of top (i.e., heaviest) users to emit metric information about. | 10 |
| weighted-cost.lockshared | WeightedTimeCostProvider | The weight multiplier to apply to the time spent in the processing phase which holds a shared (read) lock. | 10 |
| weighted-cost.lockexclusive | WeightedTimeCostProvider | The weight multiplier to apply to the time spent in the processing phase which holds an exclusive (write) lock. | 100 |
| weighted-cost.{handler,lockfree,response} | WeightedTimeCostProvider | The weight multiplier to apply to the time spent in the processing phases which do not involve holding a lock. See org.apache.hadoop.ipc.ProcessingDetails.Timing for more details on each phase. | 1 |
参考文档:Apache Hadoop 3.3.4 – Fair Call Queue Guide