swift算法:买卖股票的最佳时机II
1、描述
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润,你可以尽可能的完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票)。
注意:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
例1:输入:[7, 1, 5, 3, 6, 4]
输出:7
解释:在第2天(股票价格=1)的时候买入,在第3天(股票价格=5)的时候卖出,这笔交易所能获得利润=5-1=4
随后,在第4天(股票价格=3)的时候买入,在第5天(股票价格=6)的时候卖出,这笔交易所能获得利润=6-3=3
例1:输入:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
输出:4
解释: 在第1天(股票价格=1)的时候买入,在第5天(股票价格=5)的时候卖出,这笔交易所能获得利润=5-1=4
注意你不能在第1天和地2天接连购买股票,之后再将它们卖出。
因为这样属于同时参与了多笔交易,你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票。
2、算法
1)暴力法
思想:利用递归,遍历计算所有可能的交易组合相对应的利润且相加
时间复杂度:O(n^n)
func maxProfitII(_ prices: [Int]) -> Int {
/*
暴力法
*/
return calculate(prices, 0)
}
private func calculate(_ prices : [Int], _ s : Int)->Int{
if s >= prices.count {
return 0
}
var max = 0
for start in s.. maxpfrofit{
maxpfrofit = profit
}
}
}
if maxpfrofit > max {
max = maxpfrofit
}
}
return max
} 2)一次遍历
思想:在斜坡上爬升并持续增加从连续交易中获得的利润
图示[1, 7, 2, 3, 6, 7, 6, 7],所求即为 A+B+C = D
时间复杂度::O(n)
func maxProfitII(_ prices: [Int]) -> Int {
/*
一次遍历
*/
if prices.count==0 || prices.count==1{
return 0
}
var maxprofit : Int = 0
for i in 1.. prices[i-1] {
maxprofit += prices[i] - prices[i-1]
}
}
return maxprofit
} 3)峰谷法
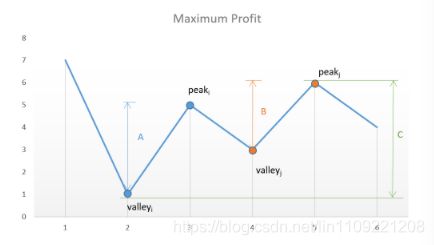
思想:计算峰谷与山顶的最大距离即为最大利润
图示 [7, 1, 5, 3, 6, 4],c即为所求的最大利润
时间复杂度:O(n)
func maxProfitII(_ prices: [Int]) -> Int {
/*
峰谷法:
TotalProfit=∑下i(height(peak下i)−height(valley下i))
*/
if prices.count==0 || prices.count==1{
return 0
}
var maxprofit : Int = 0
var valley = prices[0]
var peak = prices[0]
var i = 0
while i < prices.count-1 {
while i < prices.count-1 && prices[i]>=prices[i+1]{
i += 1
}
valley = prices[i]
while i < prices.count-1 && prices[i] <= prices[i+1]{
i += 1
}
peak = prices[i]
maxprofit += peak - valley
}
return maxprofit
}