Spring源码篇(十)@Bean怎么注册一个bean
文章目录
- 前言
- 配置类里的@Bean解析
- sourceClass是什么
- 解析@Bean方法
- 添加@Bean注解的方法信息
- 注册
- 总结
-
- @Bean注册的过程
- 注意点
前言
配置类的解析之前有聊过,这篇也会涉及到一部分,因为@Bean本身也是配置类里的一个东西,本篇会着重解析@Bean注册bean的过程。
配置类里的@Bean解析
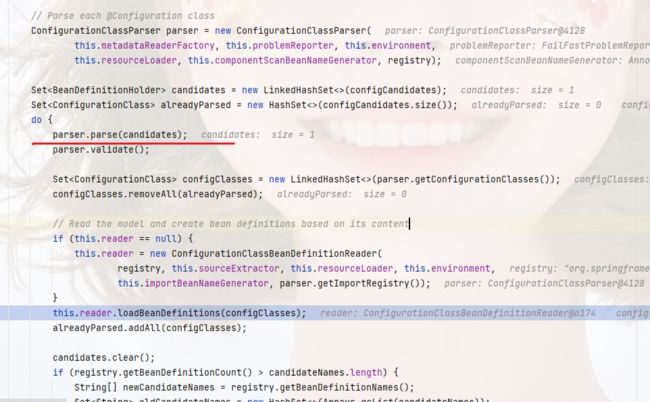
位置:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#processConfigBeanDefinitions
这一部分就是解析配置类的流程
底层的解析逻辑在:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser#doProcessConfigurationClass
这里它解析了Component、componentScan、import、importSource、PropertySource、bean,那我们只看解析bean的部分.
sourceClass是什么
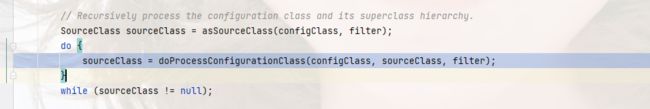
这里我们会看到有一个sourceClass的对象,这个对象保存了配置类的资源,以及注解信息;
它怎么来的?
在外面那一层方法创建的
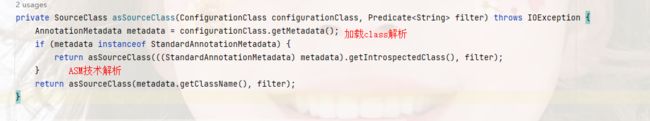
上面这段,它做了一个判断,如果是java后缀结尾的化,就以Class.forName的方式加载class,然后解析得到StandardAnnotationMetadata对象,否则就是ASM根据类名解析class;
可是,在第二张图种,先判断了是否是StandardAnnotationMetadata类型,这个是因为,springBoot启动时我们的主函数类会进行注册,并且会通过JVM加载,而且只要是通过@Import引入的都会被JVM加载,也会变成StandardAnnotationMetadata,所以只要是直接引用了类,都会变成StandardAnnotationMetadata。
sourceClass有两个类型:
-
StandardAnnotationMetadata:标准的注解元数据信息,这个是由反射操作的,所以,它会被加载到JVM中; -
SimpleMetadataReader:这个是由ASM技术解析字节码得到的,不会加载到JVM中;
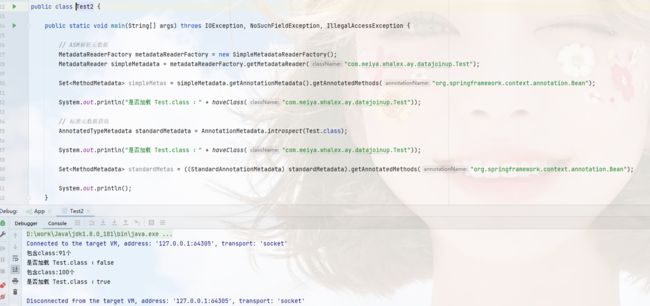
测试示例:
@Component
public class Test {
@Bean
public Amend amend() {
return new Amend();
}
}
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
// ASM解析元数据
MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory = new SimpleMetadataReaderFactory();
MetadataReader simpleMetadata = metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader("com.meiya.whalex.ay.datajoinup.Test");
Set<MethodMetadata> simpleMetas = simpleMetadata.getAnnotationMetadata().getAnnotatedMethods("org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean");
System.out.println("是否加载 Test.class :" + haveClass("com.meiya.whalex.ay.datajoinup.Test"));
// 标准元数据获取
AnnotatedTypeMetadata standardMetadata = AnnotationMetadata.introspect(Test.class);
System.out.println("是否加载 Test.class :" + haveClass("com.meiya.whalex.ay.datajoinup.Test"));
Set<MethodMetadata> standardMetas = ((StandardAnnotationMetadata) standardMetadata).getAnnotatedMethods("org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean");
System.out.println();
}
private static boolean haveClass(String className) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Field classes = ClassLoader.class.getDeclaredField("classes");
classes.setAccessible(true);
Vector<Class> o = (Vector)classes.get(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
System.out.println("包含class:" + o.size() +"个");
for (int i = 0; i < o.size(); i++) {
Class<?> o1 = o.get(i);
if (o1.getName().equals(className)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
这两种方式获取得到的注解信息差不多,都能获取到注解,方法,返回类型等信息,不同的点在于是否加载到JVM,通过上面的示例,可以看到,使用ASM技术解析的并不会加载class;
解析@Bean方法
进入retrieveBeanMethodMetadata方法,这里是对这个元数据进行解析,刚刚说过,这个sourceClass是包含注解元数据信息的,那么这里的这个方法就是解析含有@Bean注解的方法,位置:
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser#retrieveBeanMethodMetadata
private Set<MethodMetadata> retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(SourceClass sourceClass) {
// 获取配置类里的注解元数据信息
AnnotationMetadata original = sourceClass.getMetadata();
// 获取标注有@Bean注解的方法元数据信息列表
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = original.getAnnotatedMethods(Bean.class.getName());
// 存在@Bean标注的方法,并且,是属于是通过JVM加载的类才会进去
if (beanMethods.size() > 1 && original instanceof StandardAnnotationMetadata) {
// 这里就是ASM解析class(spring中解析class都是ASM,没有加载到JVM)
// 因为判断中包含 StandardAnnotationMetadata 类型判断,这个类型是JVM加载后的类型
// 虽然StandardAnnotationMetadata也能获取到注解元数据信息,但是因为JVM反射回来的元数据信息是无顺序的,在spring中@Bean注解是有顺序的,所以这里它做了ASM解析
try {
AnnotationMetadata asm =
this.metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(original.getClassName()).getAnnotationMetadata();
Set<MethodMetadata> asmMethods = asm.getAnnotatedMethods(Bean.class.getName());
if (asmMethods.size() >= beanMethods.size()) {
Set<MethodMetadata> selectedMethods = new LinkedHashSet<>(asmMethods.size());
for (MethodMetadata asmMethod : asmMethods) {
for (MethodMetadata beanMethod : beanMethods) {
if (beanMethod.getMethodName().equals(asmMethod.getMethodName())) {
selectedMethods.add(beanMethod);
break;
}
}
}
if (selectedMethods.size() == beanMethods.size()) {
// All reflection-detected methods found in ASM method set -> proceed
beanMethods = selectedMethods;
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
logger.debug("Failed to read class file via ASM for determining @Bean method order", ex);
// No worries, let's continue with the reflection metadata we started with...
}
}
return beanMethods;
}
添加@Bean注解的方法信息
然后再回到一开始的那个地方:
位置:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser#doProcessConfigurationClass
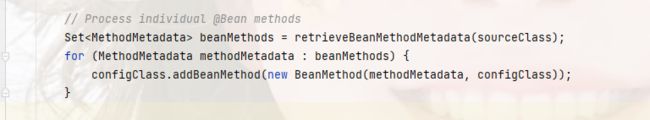
这里可以看到,它再拿到@Bean注解标注的方法元数据后就直接添加到配置类的beanMethod集合中,并没有再进一步的操作;
上面这是一种情况,另外还有一种情况,就是接口上的@Bean
比如说像这样:
public interface Test6 {
@Bean
default Log og(){
return new Log();
}
}
其实这Log也能被注册上去的,如下:
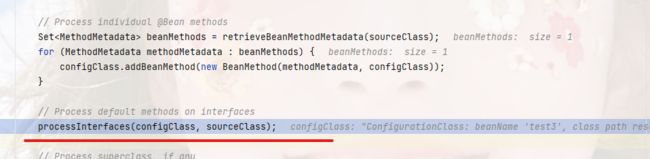
private void processInterfaces(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass) throws IOException {
// 获取到配置类的接口列表,然后遍历
for (SourceClass ifc : sourceClass.getInterfaces()) {
// retrieveBeanMethodMetadata 和上面一样,就是解析@Bean的方法,然后生成beanMethod
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(ifc);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
if (!methodMetadata.isAbstract()) {
// 添加非抽象的方法
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
}
processInterfaces(configClass, ifc);
}
}
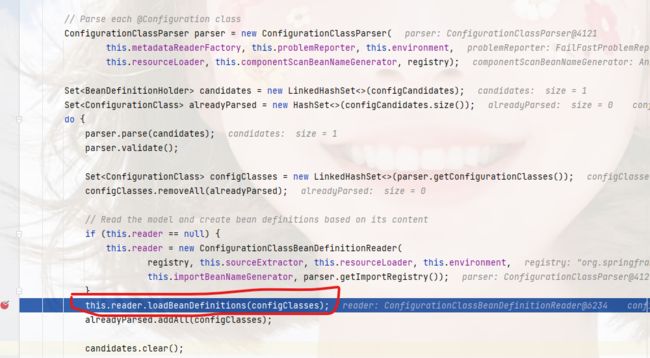
注册
再所有的配置类都解析完后,后面还有一个loadBeanDefinitions的操作,这个操作会加载由@Import,@ImportRsource,@Import(ImportBeanRegister)导入的类;
位置:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#processConfigBeanDefinitions
底层位置:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass
private void loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, TrackedConditionEvaluator trackedConditionEvaluator) {
// 判断是否需要跳过,判断是否有@Import导入的类和@Conditional一类的条件注解,还有是否有@Bean的方法信息
if (trackedConditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass)) {
String beanName = configClass.getBeanName();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.registry.containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
this.registry.removeBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
this.importRegistry.removeImportingClass(configClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
return;
}
// 这里是判断@Import导入的类是否存在
if (configClass.isImported()) {
// 存在就注册
registerBeanDefinitionForImportedConfigurationClass(configClass);
}
// 这里是按顺序对@Bean注册类
for (BeanMethod beanMethod : configClass.getBeanMethods()) {
loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(beanMethod);
}
// @ImportResource注册
loadBeanDefinitionsFromImportedResources(configClass.getImportedResources());
// @Import注册ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar时
loadBeanDefinitionsFromRegistrars(configClass.getImportBeanDefinitionRegistrars());
}
着重看下loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod
它有几个步骤:
-
获取基础信息:配置类、@Bean方法元数据、方法名
-
是否跳过:Conditional判断
-
获取beanName:取@Bean属性name,如果没有,就取方法名作为beanName
-
注册别名:同样是@Bean属性name,如果存在就注册
-
是否覆盖的校验,它覆盖的规则是:
- 同样由@Bean方式注册的(ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition),同一个配置类中,beanName相同,最先注册的,也就是写在最前面的为准,写在后面的都不会注册
- 如果存在相同的bean,如果先注册的是通过class扫描注册的,继续注册
- 如果存在相同的bean,其权限不是应用级别(
role != 0),继续注册 - 如果存在相同的bean,beanFactory的allowBeanDefinitionOverriding=false,默认false,那么报错
-
创建beanDefinition(
ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition)- 设置方法元数据
- beanClassName(实例方法时设置)或者是beanClass(静态方法时设置)
- 工厂方法名
- 自动注入模式为构造器注入
- @Required校验开关,打开(true)
- 公共注解@Lazy,@Primary,@DependsOn,@Role,@Description这些注解的设置,设置到beanDefinition
- 设置是否自动注入
autowire,默认不自动注入 - 设置
initMethod``destroyMethod方法 - 设置代理模式,然后如果要进行代理,怎会创建一个proxy的beanDefinition
-
注册beanDefinition
private void loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(BeanMethod beanMethod) {
// 1. 获取基础信息
// 获取@Bean的配置类
ConfigurationClass configClass = beanMethod.getConfigurationClass();
// 获取方法元数据信息
MethodMetadata metadata = beanMethod.getMetadata();
// 获取方法名
String methodName = metadata.getMethodName();
// 2. 是否需要跳过,也是Conditional判断
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
configClass.skippedBeanMethods.add(methodName);
return;
}
if (configClass.skippedBeanMethods.contains(methodName)) {
return;
}
// 3. 获取beanName
// 获取注解@Bean的属性信息
AnnotationAttributes bean = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(metadata, Bean.class);
Assert.state(bean != null, "No @Bean annotation attributes");
// 找出name属性的值
// 注意,@Bean的name属性是一个数组,也就是对于这个bean可以有多个别名
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(bean.getStringArray("name")));
// 取name数组中的第一个为beanName,或者取方法名
String beanName = (!names.isEmpty() ? names.remove(0) : methodName);
// 4. 注册别名:为这个bean注册别名
for (String alias : names) {
this.registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
// 5. 是否覆盖的校验,它覆盖的规则是:
// 判断已存在的bean否是配置类ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition(由@Bean注册的),且对应的配置类的全类名相同 return true(不继续注册)
// 判断已存在的bean是否是扫描得到的beanDefinition(ScannedGenericBeanDefinition),return false(继续注册)
// 判断已存在的bean是否是应用级别的bean(role == 0),role != 0 return false(继续注册)
// 判断已存在的bean是否是bean工厂(DefaultListableBeanFactory),当allowBeanDefinitionOverriding=true时,return true, 默认false,(继续注册)
if (isOverriddenByExistingDefinition(beanMethod, beanName)) {
// @Bean方法的beanName == 这个配置类的beanName
// beanName不唯一,因为是同一个类里出现beanName不唯一的请情况,所以直接抛出异常
if (beanName.equals(beanMethod.getConfigurationClass().getBeanName())) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanMethod.getConfigurationClass().getResource().getDescription(),
beanName, "Bean name derived from @Bean method '" + beanMethod.getMetadata().getMethodName() +
"' clashes with bean name for containing configuration class; please make those names unique!");
}
return;
}
// 6. 创建beanMethod的beanDefinition
// 6.1 设置方法元数据
// 创建一个配置类的bean定义(ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition)
ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition beanDef = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition(configClass, metadata);
// 这里其实就是用metadata进行赋值
beanDef.setSource(this.sourceExtractor.extractSource(metadata, configClass.getResource()));
// 6.2 beanClassName(实例方法时设置)或者是beanClass(静态方法时设置)
// 6.3 设置工厂方法名
// 从这里可以看出@Bean支持静态方法
if (metadata.isStatic()) {
// 设置配置类的class,或者是className,就看是否用ASM解析
if (configClass.getMetadata() instanceof StandardAnnotationMetadata) {
beanDef.setBeanClass(((StandardAnnotationMetadata) configClass.getMetadata()).getIntrospectedClass());
}
else {
beanDef.setBeanClassName(configClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
// 设置唯一的工厂方法名,也就是@Bean的方法名称
beanDef.setUniqueFactoryMethodName(methodName);
}
else {
// 非静态方法的@Bean方法
// 设置工厂bean名称为配置类的名称
beanDef.setFactoryBeanName(configClass.getBeanName());
// 设置唯一的工厂方法名,也就是@Bean的方法名称
beanDef.setUniqueFactoryMethodName(methodName);
}
// 这里是JVM加载后才会走的
if (metadata instanceof StandardMethodMetadata) {
beanDef.setResolvedFactoryMethod(((StandardMethodMetadata) metadata).getIntrospectedMethod());
}
// 6.4 自动注入模式为构造器注入
// 设置注入模式为构造器注入
beanDef.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR);
// 6.5 @Required校验开关,打开(true)
// 指定RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor后置处理器的校验跳过,
// 也就是@Required的检查,不过这个注解后面是要被废弃的,我看的版本是5.2.6
beanDef.setAttribute(org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
SKIP_REQUIRED_CHECK_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
// 6.6 设置公用注解的配置
// @Lazy,@Primary,@DependsOn,@Role,@Description这些注解的设置,设置到beanDefinition
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(beanDef, metadata);
// 6.7 @Bean里的autowire属性,默认不自动注入
// 一般我们写@Bean的时候也是直接设置好了属性,但是这里可以通过设置@Bean的autowire属性,完成自动注入,但这样对于自定义的bean可能还是有限制
Autowire autowire = bean.getEnum("autowire");
if (autowire.isAutowire()) {
beanDef.setAutowireMode(autowire.value());
}
// 可作为其他bean的注入的候选bean对象,@Bean中,这个属性默认为true
// 所以,在某些场景中,我们可以设置这个属性为false,使之不能被其他bean注入
boolean autowireCandidate = bean.getBoolean("autowireCandidate");
if (!autowireCandidate) {
beanDef.setAutowireCandidate(false);
}
// 6.8 设置`initMethod``destroyMethod`方法
// 设置initMethod方法,这个是在bean生命周期中,在bean初始化后会调用的一个方法
// 可以理解为一个bean创建的回调方法
String initMethodName = bean.getString("initMethod");
if (StringUtils.hasText(initMethodName)) {
beanDef.setInitMethodName(initMethodName);
}
// 设置destroyMethod方法,同样是在bean生命周期中会被调用的一个方法
String destroyMethodName = bean.getString("destroyMethod");
beanDef.setDestroyMethodName(destroyMethodName);
// 6.9 设置代理模式
// ScopedProxyMode代理模式,可以设置jdk动态代理,cglib动态代理
// 默认是不进行代理
ScopedProxyMode proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.NO;
// 如果这个@Bean的方法有配置@Scope注解,那么会获取到,然后赋值
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(metadata, Scope.class);
if (attributes != null) {
// 存在@Scope,获取值并设置到beanDefinition
beanDef.setScope(attributes.getString("value"));
// 赋值
proxyMode = attributes.getEnum("proxyMode");
if (proxyMode == ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT) {
proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.NO;
}
}
// 如果需要代理,那么就会创建一个proxy的BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition beanDefToRegister = beanDef;
if (proxyMode != ScopedProxyMode.NO) {
BeanDefinitionHolder proxyDef = ScopedProxyCreator.createScopedProxy(
new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName), this.registry,
proxyMode == ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS);
beanDefToRegister = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition(
(RootBeanDefinition) proxyDef.getBeanDefinition(), configClass, metadata);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(String.format("Registering bean definition for @Bean method %s.%s()",
configClass.getMetadata().getClassName(), beanName));
}
// 7 进行注册
this.registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefToRegister);
}
总结
@Bean注册的过程
@Bean注入类的过程:
-
配置类解析,解析
@ComponentScan,@ImportSource,@Import,@PropertySource,@Bean -
添加:添加解析
@Bean得到的BeanMethod到配置类中,包含接口里的默认方法 -
注册:在所有的配置类都解析完后,执行
loadBeanDefinitions,遍历beanMethod-
获取基础信息:配置类、@Bean方法元数据、方法名
-
是否跳过:Conditional判断
-
获取beanName:取@Bean属性name,如果没有,就取方法名作为beanName
-
注册别名:同样是@Bean属性name,如果存在就注册
-
是否覆盖的校验,它覆盖的规则是:
- 同样由@Bean方式注册的(ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition),同一个配置类中,
beanName相同,最先注册的,也就是写在最前面的为准,写在后面的都不会注册 - 如果存在相同的bean,如果先注册的是通过class扫描注册的,继续注册
- 如果存在相同的bean,其权限不是应用级别(
role != 0),继续注册 - 如果存在相同的bean,beanFactory的allowBeanDefinitionOverriding=false,默认false,那么报错
- 同样由@Bean方式注册的(ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition),同一个配置类中,
-
创建
beanMethod的beanDefinition(ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition)- 设置方法元数据
- beanClassName(实例方法时设置)或者是beanClass(静态方法时设置)
- 工厂方法名
- 自动注入模式为构造器注入
- @Required校验开关,打开(true)
- 公共注解@Lazy,@Primary,@DependsOn,@Role,@Description这些注解的设置,设置到beanDefinition
- 设置是否自动注入
autowire,默认不自动注入 - 设置
initMethod``destroyMethod方法 - 设置代理模式,然后如果要进行代理,怎会创建一个proxy的beanDefinition
-
注册beanDefinition
-
-
bean生命周期 -> 实例化、初始化、代理、添加单例池
注意点
-
@Bean标注的方法都在同一个配置类中,出现相同
beanName,那么优先级以最先写的方法为准,后面的方法不会进行注册 -
@Bean标注的方法不再同一个配置中,相同的
beanName,属于重写注册的bean,需要设置spring.main.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding=true -
@Bean标注的方法可以时
static修饰的(静态方法) -
@Bean默认是不自动注入的,但是它可以通过设置属性
autowire完成自动注入 -
如果配置类实现里某个接口,而这个接口存在默认方法,且有
@Bean注解,也会被注册