【go语言之panic和recover源码分析】
go语言之panic和recover源码分析
- gorecover
- _panic
- gopanic
前面说了defer的源码,defer的重要功能之一就是在发生panic的时候,去捕获到panic,不导致整个线程挂掉。
先看看一段经典的panic和defer已经recover配合的例子,
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
defer func() {
if err := recover(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
panic("panic")
}
deferreturn是我们之前说过的,主要是调用当前gouroutine上面的_defer链表,并调用闭包方法。然后可以看出来多了一个gopanic方法和gorecover方法,gorecover只是把当前链表上的panic设置为已恢复,在gopanic中会说。所以这里主要说一下gopanic这个方法。
gorecover
// The implementation of the predeclared function recover.
// Cannot split the stack because it needs to reliably
// find the stack segment of its caller.
//
// TODO(rsc): Once we commit to CopyStackAlways,
// this doesn't need to be nosplit.
//
//go:nosplit
func gorecover(argp uintptr) any {
// Must be in a function running as part of a deferred call during the panic.
// Must be called from the topmost function of the call
// (the function used in the defer statement).
// p.argp is the argument pointer of that topmost deferred function call.
// Compare against argp reported by caller.
// If they match, the caller is the one who can recover.
gp := getg() // 获取当前的goroutine
p := gp._panic // 当前panic的链表
// 判断是否有需要恢复的panic
if p != nil && !p.goexit && !p.recovered && argp == uintptr(p.argp) {
// panic的链表设置成恢复状态
p.recovered = true
return p.arg
}
return nil
}
这里看出来这个方法主要是将recovered设置成true
_panic
// A _panic holds information about an active panic.
//
// A _panic value must only ever live on the stack.
//
// The argp and link fields are stack pointers, but don't need special
// handling during stack growth: because they are pointer-typed and
// _panic values only live on the stack, regular stack pointer
// adjustment takes care of them.
type _panic struct {
argp unsafe.Pointer // pointer to arguments of deferred call run during panic; cannot move - known to liblink defer 函数的闭包函数的地址
arg any // argument to panic panic函数的参数
link *_panic // link to earlier panic // 上一个panic
pc uintptr // where to return to in runtime if this panic is bypassed
sp unsafe.Pointer // where to return to in runtime if this panic is bypassed
recovered bool // whether this panic is over 是否恢复
aborted bool // the panic was aborted 是否终止
goexit bool // 当前goroutine是否被终止
}
可能有人疑问,panic后recover不就没有panic了,这个是因为在recover后仍然有可能panic,因此panic是一个链表。
gopanic
看一下这个方法,是当发生panic的时候调用。
// The implementation of the predeclared function panic.
func gopanic(e any) {
// 当前goroutine
gp := getg()
if gp.m.curg != gp {
print("panic: ")
printany(e)
print("\n")
throw("panic on system stack")
}
if gp.m.mallocing != 0 {
print("panic: ")
printany(e)
print("\n")
throw("panic during malloc")
}
if gp.m.preemptoff != "" {
print("panic: ")
printany(e)
print("\n")
print("preempt off reason: ")
print(gp.m.preemptoff)
print("\n")
throw("panic during preemptoff")
}
if gp.m.locks != 0 {
print("panic: ")
printany(e)
print("\n")
throw("panic holding locks")
}
// 声明一个结构体
var p _panic
// 添加参数到arg
p.arg = e
// 指向上一个panic
p.link = gp._panic
// 替换成当前的panic结构体
gp._panic = (*_panic)(noescape(unsafe.Pointer(&p)))
atomic.Xadd(&runningPanicDefers, 1)
// By calculating getcallerpc/getcallersp here, we avoid scanning the
// gopanic frame (stack scanning is slow...)
addOneOpenDeferFrame(gp, getcallerpc(), unsafe.Pointer(getcallersp()))
for {
// 依次查询当前的defer链表
d := gp._defer
if d == nil {
break
}
// If defer was started by earlier panic or Goexit (and, since we're back here, that triggered a new panic),
// take defer off list. An earlier panic will not continue running, but we will make sure below that an
// earlier Goexit does continue running.
// 如果已经开始了说明这个defer已经处理过之前的panic,因此把之前的panic设置为终止
if d.started {
if d._panic != nil {
d._panic.aborted = true
}
d._panic = nil
if !d.openDefer {
// For open-coded defers, we need to process the
// defer again, in case there are any other defers
// to call in the frame (not including the defer
// call that caused the panic).
d.fn = nil
gp._defer = d.link
freedefer(d)
continue
}
}
// Mark defer as started, but keep on list, so that traceback
// can find and update the defer's argument frame if stack growth
// or a garbage collection happens before executing d.fn.
// 设置成已经开始
d.started = true
// Record the panic that is running the defer.
// If there is a new panic during the deferred call, that panic
// will find d in the list and will mark d._panic (this panic) aborted.
// 将当前的panic放到defer中
d._panic = (*_panic)(noescape(unsafe.Pointer(&p)))
done := true
// 是否是openDefer
if d.openDefer {
done = runOpenDeferFrame(gp, d)
if done && !d._panic.recovered {
addOneOpenDeferFrame(gp, 0, nil)
}
} else {
// 设置参数
p.argp = unsafe.Pointer(getargp())
// 调用defer中的闭包函数
d.fn()
}
p.argp = nil
// Deferred function did not panic. Remove d.
if gp._defer != d {
throw("bad defer entry in panic")
}
d._panic = nil
// trigger shrinkage to test stack copy. See stack_test.go:TestStackPanic
//GC()
pc := d.pc
sp := unsafe.Pointer(d.sp) // must be pointer so it gets adjusted during stack copy
// 是否已经完成
if done {
d.fn = nil
gp._defer = d.link
freedefer(d)
}
// 是否调用了recover
if p.recovered {
gp._panic = p.link
if gp._panic != nil && gp._panic.goexit && gp._panic.aborted {
// A normal recover would bypass/abort the Goexit. Instead,
// we return to the processing loop of the Goexit.
gp.sigcode0 = uintptr(gp._panic.sp)
gp.sigcode1 = uintptr(gp._panic.pc)
// 从recovery的堆栈上继续执行
mcall(recovery)
throw("bypassed recovery failed") // mcall should not return
}
atomic.Xadd(&runningPanicDefers, -1)
// After a recover, remove any remaining non-started,
// open-coded defer entries, since the corresponding defers
// will be executed normally (inline). Any such entry will
// become stale once we run the corresponding defers inline
// and exit the associated stack frame. We only remove up to
// the first started (in-progress) open defer entry, not
// including the current frame, since any higher entries will
// be from a higher panic in progress, and will still be
// needed.
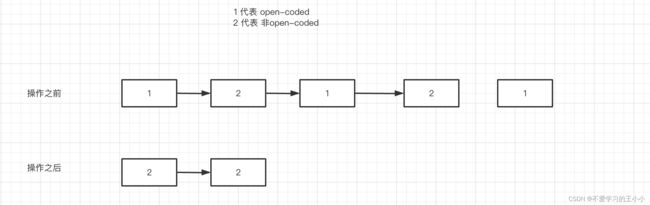
// 这里是为了把open coded的defer给释放了,正如同注释所说的open-coded 最终都会通过内敛的方法去操作
// 这里是通过链表操作进行释放。下面通过一张图显示作用
d := gp._defer
var prev *_defer
if !done {
// Skip our current frame, if not done. It is
// needed to complete any remaining defers in
// deferreturn()
prev = d
d = d.link
}
for d != nil {
if d.started {
// This defer is started but we
// are in the middle of a
// defer-panic-recover inside of
// it, so don't remove it or any
// further defer entries
break
}
if d.openDefer {
if prev == nil {
gp._defer = d.link
} else {
prev.link = d.link
}
newd := d.link
freedefer(d)
d = newd
} else {
prev = d
d = d.link
}
}
gp._panic = p.link
// Aborted panics are marked but remain on the g.panic list.
// Remove them from the list.
for gp._panic != nil && gp._panic.aborted {
gp._panic = gp._panic.link
}
if gp._panic == nil { // must be done with signal
gp.sig = 0
}
// Pass information about recovering frame to recovery.
gp.sigcode0 = uintptr(sp)
gp.sigcode1 = pc
// 从recovery中进行恢复程序
mcall(recovery)
throw("recovery failed") // mcall should not return
}
}
// ran out of deferred calls - old-school panic now
// Because it is unsafe to call arbitrary user code after freezing
// the world, we call preprintpanics to invoke all necessary Error
// and String methods to prepare the panic strings before startpanic.
// 打印panics信息
preprintpanics(gp._panic)
// 退出程序
fatalpanic(gp._panic) // should not return
*(*int)(nil) = 0 // not reached
}