springboot中Thymeleaf模板引擎
模板引擎
前端交给我们的页面,是html页面。如果是我们以前开发,我们需要把他们转成jsp页面,jsp好处就是当我们查出一些数据转发到JSP页面以后,我们可以用jsp轻松实现数据的显示,及交互等。
jsp支持非常强大的功能,包括能写Java代码,但是呢,我们现在的这种情况,SpringBoot这个项目首先是以jar的方式,不是war,像第二,我们用的还是嵌入式的Tomcat,所以呢,他现在默认是不支持jsp的。
那不支持jsp,如果我们直接用纯静态页面的方式,那给我们开发会带来非常大的麻烦,那怎么办呢?
SpringBoot推荐的模板引擎
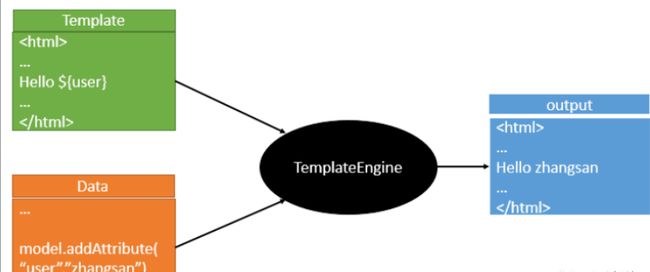
模板引擎,我们其实大家听到很多,其实jsp就是一个模板引擎,还有用的比较多的freemarker,包括SpringBoot给我们推荐的Thymeleaf,模板引擎有非常多,但再多的模板引擎,他们的思想都是一样的,什么样一个思想呢我们来看一下这张图:
模板引擎的作用就是我们来写一个页面模板,比如有些值呢,是动态的,我们写一些表达式。而这些值,从哪来呢,就是我们在后台封装一些数据。然后把这个模板和这个数据交给我们模板引擎,模板引擎按照我们这个数据帮你把这表达式解析、填充到我们指定的位置,然后把这个数据最终生成一个我们想要的内容给我们写出去,这就是我们这个模板引擎,不管是jsp还是其他模板引擎,都是这个思想。只不过呢,就是说不同模板引擎之间,他们可能这个语法有点不一样。我们主要学习SpringBoot推荐的Thymeleaf模板引擎。
引入Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf官网:https://www.thymeleaf.org/
Thymeleaf在Github的主页:https://github.com/thymeleaf/thymeleaf
-
导入Thymeleaf的启动器依赖
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf -
maven会自动下载jar包,我们可以去我们的资源下看看
Thymeleaf分析
我们已经引入了Thymeleaf,那这个要怎么使用呢?
我们按照SpringBoot的自动配置原理来看一下Thymeleaf的自动装配原理,根据原理来进行使用。
我们可以去找Thymeleaf的自动配置类:ThymeleafProperties
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.thymeleaf"
)
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING;
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
private boolean checkTemplate = true;
我们可以扛到其中的前缀和后缀
我们只需要把我们的html页面放到类路劲下的templates下,thymeleaf就可以帮我们自动渲染了。
使用thymeleaf什么都不需要去配置,只需要将html页面放在指定文件夹里面即可
测试
-
编写一个TestController
@Controller public class TestController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ return "test"; } } -
编写一个测试页面 test.html放在我们的resources目录下的templates目录下
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" > <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <div> hello thymeleafdiv> body> html> -
启动测试
Thymeleaf 快速入门
我们可以到官网去看一下官方文档
Thymeleaf 官网:https://www.thymeleaf.org/ , 简单看一下官网!我们去下载Thymeleaf的官方文档!
简单的练习:查询数据到页面展示
-
修改测试请求,增加数据传输;
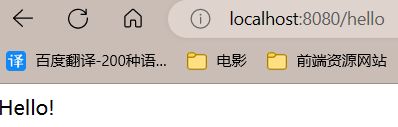
@Controller public class TestController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(Model model) { model.addAttribute("msg", "Hello!"); return "test"; } } -
我们需要使用thymeleaf,需要在html文件中导入我们的命名空间约束,方便提示。
官方文档的#3中看一下把命名空间拿过来
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" -
编写前端页面
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" > <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <div th:text="${msg}"> hello thymeleafdiv> body> html> -
测试:
ok,我们的Thymeleaf 快速入门就解决了
Thymeleaf的一些基本语法
-
我们可以使用任意的th:attr来替换html中原生属性的值
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-2uYEjsem-1685445037680)(C:\Users\A’n’le\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230529115631957.png)]
我们可以写的表达式
Simple expressions:(表达式语法)
Variable Expressions: ${...}:获取变量值;OGNL;
1)、获取对象的属性、调用方法
2)、使用内置的基本对象:#18
#ctx : the context object.
#vars: the context variables.
#locale : the context locale.
#request : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletRequest object.
#response : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletResponse object.
#session : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpSession object.
#servletContext : (only in Web Contexts) the ServletContext object.
3)、内置的一些工具对象:
#execInfo : information about the template being processed.
#uris : methods for escaping parts of URLs/URIs
#conversions : methods for executing the configured conversion service (if any).
#dates : methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc.
#calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects.
#numbers : methods for formatting numeric objects.
#strings : methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc.
#objects : methods for objects in general.
#bools : methods for boolean evaluation.
#arrays : methods for arrays.
#lists : methods for lists.
#sets : methods for sets.
#maps : methods for maps.
#aggregates : methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections.
==================================================================================
Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}:选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样;
Message Expressions: #{...}:获取国际化内容
Link URL Expressions: @{...}:定义URL;
Fragment Expressions: ~{...}:片段引用表达式
Literals(字面量)
Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,…
Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,…
Boolean literals: true , false
Null literal: null
Literal tokens: one , sometext , main ,…
Text operations:(文本操作)
String concatenation: +
Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}|
Arithmetic operations:(数学运算)
Binary operators: + , - , * , / , %
Minus sign (unary operator): -
Boolean operations:(布尔运算)
Binary operators: and , or
Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not
Comparisons and equality:(比较运算)
Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne )
Conditional operators:条件运算(三元运算符)
If-then: (if) ? (then)
If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
Special tokens:
No-Operation: _
测试练习
-
我们写一个Controller,存放一些数据
@Controller public class TestController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(Model model) { model.addAttribute("msg", "Hello!
"); model.addAttribute("user", Arrays.asList("zhangsan", "lisi")); return "test"; } } -
测试页面取出数据
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" > <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <div th:text="${msg}"> hello thymeleafdiv> <div th:utext="${msg}"> hello thymeleafdiv> <hr> <h2 th:each="users:${user}" th:text="${users}">h2> body> html> -
启动项目
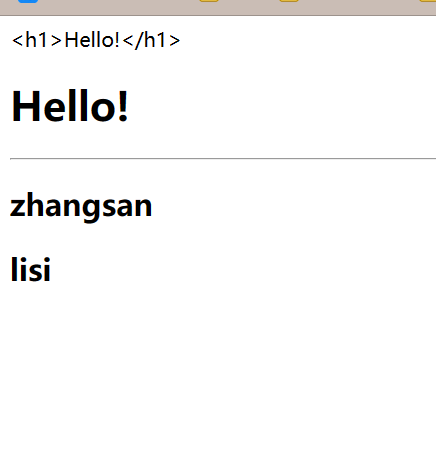
这样就成功了
}">
```这样就成功了
我们看完语法,很多样式,我们即使现在学习了,也会忘记,所以我们在学习过程中,需要使用什么,根据官方文档来查询,才是最重要的,要熟练使用官方文档!