- linux脚本怎么访问http,如何使用现有的tcp连接从bash脚本访问http服务器?
玲珑阁玉韦
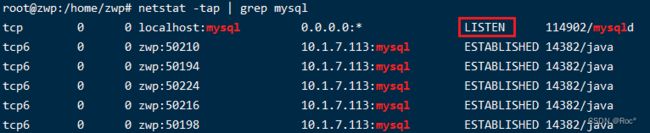
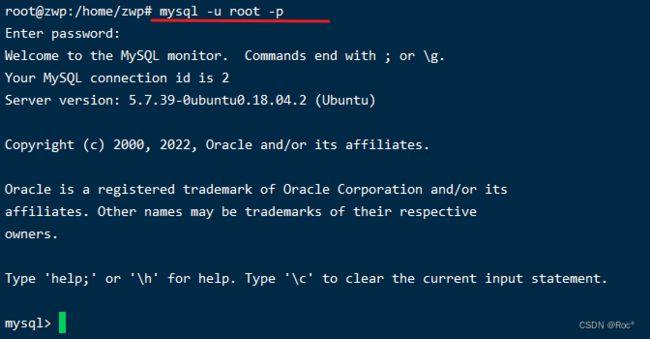
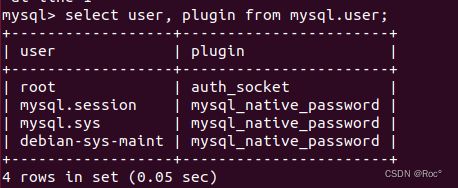
linux脚本怎么访问http
在bashshellscipt中,我使用几个命令行工具(wget,curl,httpie)来测试我的http服务器.当使用例如curl调用GET请求,我看到tcp连接打开到我的服务器并在http通信完成后立即关闭.$curlhttp://10.5.1.1/favicon.ico-o/dev/null为了更好地测试我的服务器的保持活动行为,我想在多个http请求/响应周期中保持tcp连接打开.我可以
- SQL自学:怎么创建视图
m0_74823471
面试学习路线阿里巴巴sql数据库
在SQL中,视图是一种虚拟表,它是基于一个或多个表的查询结果集。视图并不实际存储数据,而是在每次查询时动态生成结果。一、创建视图的语法(以MySQL为例)CREATEVIEWview_nameASSELECTcolumn1,column2,...FROMtable_nameWHEREcondition;view_name:是要创建的视图的名称。column1,column2,...:要在视图中显示
- 环境配置(1):笔记本window、虚拟机ubuntu、开发板三者互ping通信,并且虚拟机ubuntu和开发板能上网
lishing6
ubuntulinuxmcu嵌入式硬件arm开发物联网硬件工程
1.配置网络我们配置网络是为了方便后续调试开发板系统或者应用程序时,能够使用tftp协议nfs协议等拷贝文件,以及设置文件系统启动方式为nfs挂载启动。2.设置Ubuntu使用NAT网络NAT是什么意思?NetworkAddressTranslation,网络地址转换。举个例子,在NAT里,Windows就是一个爱护孩子的父亲,Ubuntu就是受保护的小孩。小孩要买东西,都由他父亲代劳,别人根本不
- systemd-networkd 的 /etc/systemd/network/*.network 的配置属性名称是不是严格区分大小写?是
kfepiza
#LinuxCentOSUbuntu等网络通讯传输协议物联网络运维tcp/iplinux
systemd-networkd的/etc/systemd/network/*.network的配置属性名称是不是严格区分大小写?是查看官方文档可以用mansystemd.network命令,或访问:https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/latest/systemd.network.html亲测在Debian10.12-standard中
- systemd-networkd NetworkManager 介绍
追心嵌入式
linux
systemd-networkd和NetworkManager的详细介绍systemd-networkd和NetworkManager都是Linux系统中常用的网络管理工具,但它们的设计目标和使用场景不同。以下是它们的详细介绍、功能、使用场景和差异。1.systemd-networkdsystemd-networkd是一个由systemd提供的网络管理工具,旨在为Linux系统提供网络配置和管理的
- 【Linux 下的 bash 无法正常解析, Windows 的 CRLF 换行符问题导致的】
待磨的钝刨
linuxbashwindows
文章目录报错原因:解决办法:方法一:用`dos2unix`修复方法二:手动转换换行符方法三:VSCode或其他编辑器手动改总结这个错误很常见,原因是你的wait_for_gpu.sh脚本文件格式不对,具体来说是Windows的CRLF换行符问题导致的,Linux下的bash无法正常解析。hadoop@hadoop:~/anaconda3$bashwait_for_gpu.sh:invalidopt
- Linux部署模型报错OSError: Error no file named pytorch_model.bin, tf_model.h5, model.ckpt.index or flax_mod
dkgee
linuxpytorch运维
报错内容:OSError:Errornofilenamedpytorch_model.bin,tf_model.h5,model.ckpt.indexorflax_model.msgpackfoundindirectory主要原因是transformer版本不对,需要升级pipinstall--upgradehuggingface_hubpipinstalltransformers[torch]其
- Xilinx系ZYNQ学习笔记(二)ZYNQ入门及点亮LED灯
贾saisai
FPGA学习学习笔记fpga开发
系列文章目录文章目录系列文章目录前言简单介绍简称xc7z020型号FPGAZYNQ实操通用IO点亮LED灯硬件逻辑基础前言简单入门一下ZYNQ是何种架构,如何编程,至于深入了解应该要分开深入学习Linux和FPGA简单介绍其基本架构都是在同一个硅片上集成FPGA和CPU,并通过高速、高带宽的互联架构连接起来。ARM的顺序控制、丰富外设,开源驱动、FPGA的并行运算、高速接口、灵活定制、数字之王的特
- Ubuntu 20.04 安装并使用Cursor
爱学习的小道长
AIubuntulinux运维pythonai
1.安装1.1下载cursor官网:https://www.cursor.com/cn点击下载LINUX查看下载下来的文件:$ls~/Downloads/Cursor-0.47.8-82ef0f61c01d079d1b7e5ab04d88499d5af500e3.deb.glibc2.25-x86_64.AppImage/home/xxx/Downloads/Cursor-0.47.8-82ef0
- pythontype函数使用_Python astype(np.float)函数使用方法解析
weixin_39870238
pythontype函数使用
Pythonastype(np.float)函数使用方法解析我的数据库如图结构我取了其中的nameagenr,做成array,只要所取数据存在str型,那么取出的数据,全部转化为str型,也就是array阵列的元素全是str,不管数据库定义的是不是int型。那么问题来了,取出的数据代入公式进行计算的时候,就会类型不符,这是就用到astype(np.float)代码如下importpymysqlim
- 如何安全删除MySQL字段?从原理到实战的保姆级指南!
小丁学Java
产品资质管理系统安全mysql数据库
从MyISAM到InnoDB:解锁MySQL在线删除字段的终极指南真实案例:一次失败的DDL操作引发的思考场景复现:某业务表invite_codes需要删除invitor字段,执行以下命令时触发报错:ALTERTABLEinvite_codesDROPCOLUMNinvitor,ALGORITHM=INPLACE;--报错信息:ALGORITHM=INPLACEisnotsupportedfort
- Ubuntu-Server 设置多个ip和多个ipv6 笔记250320
kfepiza
#LinuxCentOSUbuntu等#控制台命令行Shell脚本shcmd等网络通讯传输协议物联ubuntutcp/ip笔记
Ubuntu-Server设置多个ip和多个ipv6在UbuntuServer上为同一网卡配置多个IPv4和IPv6地址,Ubuntu-server-16用的是/etc/network/interfaces配置的networkingUbuntu-server-17.10及更新版本默认用的是systemd-networkd+Netplan,用Netplan来管理systemd-networkd对于U
- ubuntu环境使用海康威视SDK获取视频流
Joemt
ubuntu人工智能计算机视觉
获取监控摄像头视频流可以采用rtsp快速获取,但是该方案可能出现延时较大的情况,而采用海康威视提供的SDK可以降低延时。#include#include#include#include#include#include#include"HCNetSDK.h"#include"iniFile.h"#include"PlayM4.h"//解码回调视频为YUV数据(YV12),音频为PCM数据voidCA
- Ubuntu实时读取音乐软件的音频流
冬瓜~
Linux开发ubuntu音视频数据库portaudio
文章目录一.前言二.开发环境三.具体操作四.实际效果一.前言起因是这样的,我需要在Ubuntu中,实时读取正在播放音乐的音频流,然后对音频进行相关的处理。本来打算使用的Pipewire+Helvum的方式实现,好处是可以直接利用Helvum图形化工具对软件输出的音频进行重定向,但是由于使用的是Ubuntu20.04,默认的音频服务器使用的是PulseAudio,替换为Pipewire后,播放的音频
- 利用docker部署单节点milvus并实现图像化管理
听说唐僧不吃肉
Linuxdockermilvus
Docker部署单机版milvus使用DockerCompose安装Milvusstandalone(即单机版),进行一个快速milvus的体验。1.前提条件系统可以使用centos或者ubuntu系统已经安装docker和docker-composemilvus版本这里选择2.3.12.启动etcd、minio、milvus由于milvus依赖etcd和minio,因此需要先启动这2个组件。同样
- linux 逻辑卷LVM
IT小饕餮
linux基础linux运维服务器
LVM(LogicalVolumeManager)逻辑卷管理是一种在Linux系统中用于管理磁盘空间的技术,它提供了一种灵活、高效的方式来管理硬盘分区和卷。以下是关于LVM逻辑管理的详细介绍:LVM的基本概念物理卷(PhysicalVolume,PV)物理卷是LVM的基本组成部分,可以是一块磁盘、也可以是一个分区。物理卷是LVM存储的基础,用于提供实际的存储空间。卷组(VolumeGroup,VG
- mysql与mariadb版本对应_MySQL与MariaDB及各种版本杂谈
weixin_39616416
MySQL1.MySQLCommunityServer社区版本,开源免费,但不提供官方技术支持。(我们通常使用的MySQL版本)2.MySQLEnterpriseEdition企业版本,需付费,可以试用30天。3.MySQLCluster集群版,开源免费。可将几个MySQLServer封装成一个Server。4.MySQLClusterCGE高级集群版,需付费。5.MySQLWorkbench(G
- nginx-部署Python网站项目
skyQAQLinux
pythonlinuxnginx服务器
一、部署Python网站项目实验要求配置Nginx使其可以将动态访问转交给uWSGI安装Python工具及依赖1)拷贝软件到proxy主机[root@server1~]#scp-r/linux-soft/s2/wk/python/192.168.99.5:/root2)安装python依赖软件[root@proxy~]#yum-yinstallgccmakepython3python3-devel
- MariaDB 和 MySQL 版本关联
java我跟你拼了
数据库笔记mariadbmysql数据库数据库篇版本关联
MariaDB和MySQL是两个常用的关系型数据库管理系统(RDBMS),它们在很多方面非常相似,因为MariaDB是MySQL的一个分支。MariaDB和MySQL之间的版本关联可以通过以下几个方面来理解:1.历史背景MySQL:MySQL是一个开源的数据库管理系统,由MySQLAB开发,后来被SunMicrosystems收购,再之后被Oracle收购。MariaDB:MariaDB是MySQ
- AWS CLI with MinIO Server
库海无涯
aws云计算
1、InstallMinIOServerhttps://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.htmlCreateAKandSKandrecordinformation.AK:ZYYMPcLi6dSPsDfr5QeWSK:Am3m2qtpkUk2wAgT5dPbpE4hGD2tX7a6RpjsbeEdAndcreateabucketnamedaswtest.2、Install
- 因为mysql 8新的认证插件导致主从复制的IO线程失败
库海无涯
mysql
1、错误信息Last_IO_Error:errorconnectingtomaster'
[email protected]:3306'-retry-time:60retries:1message:Authenticationplugin'caching_sha2_password'reportederror:Authenticationrequiressecureconnection.2、
- MySQL HA的全新篇章:Semisynchronous Replication迁移至InnoDB Cluster的实用指南
库海无涯
MySQLmysql
1、概述临时接了一个搭建InnoDBCluster的活儿,客户给我说是有数据的,我当时想这不是非常简单吗?干活儿的时候,才发现并没有这么简单,接手的时候发现是SemisynchronousReplication的环境,然后把从库切换成InnoDBCluster的primary。2、环境复现2.1、从库5.140信息采集mysql>showreplicastatus\G***************
- RK3588开发笔记-buildroot添加telnet服务
flypig哗啦啦
RK3588buildrootbusybox
目录前言一、Telnet服务背景与适用场景二、telnet服务开启Busybox配置三、固件编译及烧录RK3588烧录验证客户端连接测试3.1Linux/MacOS连接3.2Windows连接总结前言本文主要介绍在RK3588SDK文件包中添加telnet服务,由于sdkbuildroot默认添加的是ssh服务,如用户需要主动开启telnet,则需要另外在busybox中开启telnetd服务,下
- 安卓 vs iOS 文件系统深度解析:开放自由与封闭安全的终极博弈
jingling1007
Androidandroidios安全安全性测试
安卓和iOS的差异远不止于界面和生态,它们的文件系统设计更是体现了两种截然不同的技术哲学。安卓的开放目录允许用户“为所欲为”,而iOS的沙盒机制则像一座密不透风的堡垒。本文将通过技术细节对比、真实场景案例、用户操作指南,深度剖析两大系统的核心设计,回答一个关键问题:谁的设计更能平衡自由与安全?一、文件系统架构:从根目录到沙盒1.安卓:Linux的开放基因目录结构全景根目录(/):包含所有系统层级(
- Linux线程控制封装及线程互斥
z一一m
Linuxlinux
1.clone函数的使用#define_GNU_SOURCE#include#includeintclone(int(*fn)(void*),void*child_stack,intflags,void*arg,...);fn:子进程或线程的入口函数child_stack:子进程的栈地址,通常需要手动分配,栈的大小需要足够容纳子进程变量的局部变量和函数调用。flags:控制子进程或线程共享哪些资源
- Docker-部署ES和Kibana
相逢太短,莫等茶凉
dockerelasticsearchmac
资料kibana和elasticserch兼容性表https://www.elastic.co/cn/support/matrix#matrix_compatibilityMac系统安装需要版本支持linux/arm64,需要两个都要支持有arm64,有些es支持,kibana不支持。ps:dockerpullelasticsearch出现elasticsearch:latestnotfound,
- Linux——Linux系统编程之基于TFTP实现服务器与开发板间的文件传输实战总结
Winter_world
Linux系统TFTP服务器搭建TFTP文件传输
目录0引言1TFTP服务器搭建1.1TFTP基础1.2Ubuntu搭建TFTP服务器1.3测试TFTP服务器2开发板实现TFTP文件传输2.1同一网段2.2配置2.3客户端与服务器的通信0引言我们前面总结的Linux字符设备、串口编程博文中,在虚拟机中编译得到可执行文件后,都是通过U盘连接开发板进行测试验证的,或者就是把可执行文件编译到最小系统中,再OTG烧写进开发板,这两种方法都比较麻烦,这里我
- NVIDIA Dynamo源码编译
Luchang-Li
大模型推理引擎大模型推理引擎dynamo
Refhttps://github.com/PyO3/maturinRust程序设计语言代码库:https://github.com/ai-dynamo/dynamohttps://github.com/ai-dynamo/nixldynamo/container/Dockerfile.vllm相关whl包官方提供了4个whl包ai_dynamo#这个包ubuntu22.04也可以用,ubuntu
- docker 内容器访问另一个容器中的服务
docker容器网络
docker中有两个容器,分别名为mq和hyperf,想在hyperf中访问mq可以使用下面的方法1.创建网络dockernetworkcreatemynetwork2.将使用到的容器(如业务容器,mysql,redis,mq等容器)都加入到网络中dockernetworkconnectmynetworkhyperfdockernetworkconnectmynetworkmqdockernetw
- 使用Docker部署MySQL8.0.29
九思x
docker
第一步:拉取镜像dockerpullmysql:8.0.29作用:从DockerHub拉取MySQL8.0.29官方镜像。第二步:启动容器dockerrun--nameshare_mysql\--restart=always\-vmysql-data:/var/lib/mysql\-p3306:3306\-eMYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root\-dmysql:8.0.29参数说明:-
- java工厂模式
3213213333332132
java抽象工厂
工厂模式有
1、工厂方法
2、抽象工厂方法。
下面我的实现是抽象工厂方法,
给所有具体的产品类定一个通用的接口。
package 工厂模式;
/**
* 航天飞行接口
*
* @Description
* @author FuJianyong
* 2015-7-14下午02:42:05
*/
public interface SpaceF
- nginx频率限制+python测试
ronin47
nginx 频率 python
部分内容参考:http://www.abc3210.com/2013/web_04/82.shtml
首先说一下遇到这个问题是因为网站被攻击,阿里云报警,想到要限制一下访问频率,而不是限制ip(限制ip的方案稍后给出)。nginx连接资源被吃空返回状态码是502,添加本方案限制后返回599,与正常状态码区别开。步骤如下:
- java线程和线程池的使用
dyy_gusi
ThreadPoolthreadRunnabletimer
java线程和线程池
一、创建多线程的方式
java多线程很常见,如何使用多线程,如何创建线程,java中有两种方式,第一种是让自己的类实现Runnable接口,第二种是让自己的类继承Thread类。其实Thread类自己也是实现了Runnable接口。具体使用实例如下:
1、通过实现Runnable接口方式 1 2
- Linux
171815164
linux
ubuntu kernel
http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.1.2-unstable/
安卓sdk代理
mirrors.neusoft.edu.cn 80
输入法和jdk
sudo apt-get install fcitx
su
- Tomcat JDBC Connection Pool
g21121
Connection
Tomcat7 抛弃了以往的DBCP 采用了新的Tomcat Jdbc Pool 作为数据库连接组件,事实上DBCP已经被Hibernate 所抛弃,因为他存在很多问题,诸如:更新缓慢,bug较多,编译问题,代码复杂等等。
Tomcat Jdbc P
- 敲代码的一点想法
永夜-极光
java随笔感想
入门学习java编程已经半年了,一路敲代码下来,现在也才1w+行代码量,也就菜鸟水准吧,但是在整个学习过程中,我一直在想,为什么很多培训老师,网上的文章都是要我们背一些代码?比如学习Arraylist的时候,教师就让我们先参考源代码写一遍,然
- jvm指令集
程序员是怎么炼成的
jvm 指令集
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/hudashi/article/details/7062675#comments
将值推送至栈顶时 const ldc push load指令
const系列
该系列命令主要负责把简单的数值类型送到栈顶。(从常量池或者局部变量push到栈顶时均使用)
0x02 &nbs
- Oracle字符集的查看查询和Oracle字符集的设置修改
aijuans
oracle
本文主要讨论以下几个部分:如何查看查询oracle字符集、 修改设置字符集以及常见的oracle utf8字符集和oracle exp 字符集问题。
一、什么是Oracle字符集
Oracle字符集是一个字节数据的解释的符号集合,有大小之分,有相互的包容关系。ORACLE 支持国家语言的体系结构允许你使用本地化语言来存储,处理,检索数据。它使数据库工具,错误消息,排序次序,日期,时间,货
- png在Ie6下透明度处理方法
antonyup_2006
css浏览器FirebugIE
由于之前到深圳现场支撑上线,当时为了解决个控件下载,我机器上的IE8老报个错,不得以把ie8卸载掉,换个Ie6,问题解决了,今天出差回来,用ie6登入另一个正在开发的系统,遇到了Png图片的问题,当然升级到ie8(ie8自带的开发人员工具调试前端页面JS之类的还是比较方便的,和FireBug一样,呵呵),这个问题就解决了,但稍微做了下这个问题的处理。
我们知道PNG是图像文件存储格式,查询资
- 表查询常用命令高级查询方法(二)
百合不是茶
oracle分页查询分组查询联合查询
----------------------------------------------------分组查询 group by having --平均工资和最高工资 select avg(sal)平均工资,max(sal) from emp ; --每个部门的平均工资和最高工资
- uploadify3.1版本参数使用详解
bijian1013
JavaScriptuploadify3.1
使用:
绑定的界面元素<input id='gallery'type='file'/>$("#gallery").uploadify({设置参数,参数如下});
设置的属性:
id: jQuery(this).attr('id'),//绑定的input的ID
langFile: 'http://ww
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(17)使用ORACLE系统包
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
/*
*使用ORACLE系统包
*/
--1.DBMS_OUTPUT
--ENABLE:用于激活过程PUT,PUT_LINE,NEW_LINE,GET_LINE和GET_LINES的调用
--语法:DBMS_OUTPUT.enable(buffer_size in integer default 20000);
--DISABLE:用于禁止对过程PUT,PUT_LINE,NEW
- 【JVM一】JVM垃圾回收日志
bit1129
垃圾回收
将JVM垃圾回收的日志记录下来,对于分析垃圾回收的运行状态,进而调整内存分配(年轻代,老年代,永久代的内存分配)等是很有意义的。JVM与垃圾回收日志相关的参数包括:
-XX:+PrintGC
-XX:+PrintGCDetails
-XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps
-XX:+PrintGCDateStamps
-Xloggc
-XX:+PrintGC
通
- Toast使用
白糖_
toast
Android中的Toast是一种简易的消息提示框,toast提示框不能被用户点击,toast会根据用户设置的显示时间后自动消失。
创建Toast
两个方法创建Toast
makeText(Context context, int resId, int duration)
参数:context是toast显示在
- angular.identity
boyitech
AngularJSAngularJS API
angular.identiy 描述: 返回它第一参数的函数. 此函数多用于函数是编程. 使用方法: angular.identity(value); 参数详解: Param Type Details value
*
to be returned. 返回值: 传入的value 实例代码:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
- java-两整数相除,求循环节
bylijinnan
java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class CircleDigitsInDivision {
/**
* 题目:求循环节,若整除则返回NULL,否则返回char*指向循环节。先写思路。函数原型:char*get_circle_digits(unsigned k,unsigned j)
- Java 日期 周 年
Chen.H
javaC++cC#
/**
* java日期操作(月末、周末等的日期操作)
*
* @author
*
*/
public class DateUtil {
/** */
/**
* 取得某天相加(减)後的那一天
*
* @param date
* @param num
*
- [高考与专业]欢迎广大高中毕业生加入自动控制与计算机应用专业
comsci
计算机
不知道现在的高校还设置这个宽口径专业没有,自动控制与计算机应用专业,我就是这个专业毕业的,这个专业的课程非常多,既要学习自动控制方面的课程,也要学习计算机专业的课程,对数学也要求比较高.....如果有这个专业,欢迎大家报考...毕业出来之后,就业的途径非常广.....
以后
- 分层查询(Hierarchical Queries)
daizj
oracle递归查询层次查询
Hierarchical Queries
If a table contains hierarchical data, then you can select rows in a hierarchical order using the hierarchical query clause:
hierarchical_query_clause::=
start with condi
- 数据迁移
daysinsun
数据迁移
最近公司在重构一个医疗系统,原来的系统是两个.Net系统,现需要重构到java中。数据库分别为SQL Server和Mysql,现需要将数据库统一为Hana数据库,发现了几个问题,但最后通过努力都解决了。
1、原本通过Hana的数据迁移工具把数据是可以迁移过去的,在MySQl里面的字段为TEXT类型的到Hana里面就存储不了了,最后不得不更改为clob。
2、在数据插入的时候有些字段特别长
- C语言学习二进制的表示示例
dcj3sjt126com
cbasic
进制的表示示例
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i = 0x32C;
printf("i = %d\n", i);
/*
printf的用法
%d表示以十进制输出
%x或%X表示以十六进制的输出
%o表示以八进制输出
*/
return 0;
}
- NsTimer 和 UITableViewCell 之间的控制
dcj3sjt126com
ios
情况是这样的:
一个UITableView, 每个Cell的内容是我自定义的 viewA viewA上面有很多的动画, 我需要添加NSTimer来做动画, 由于TableView的复用机制, 我添加的动画会不断开启, 没有停止, 动画会执行越来越多.
解决办法:
在配置cell的时候开始动画, 然后在cell结束显示的时候停止动画
查找cell结束显示的代理
- MySql中case when then 的使用
fanxiaolong
casewhenthenend
select "主键", "项目编号", "项目名称","项目创建时间", "项目状态","部门名称","创建人"
union
(select
pp.id as "主键",
pp.project_number as &
- Ehcache(01)——简介、基本操作
234390216
cacheehcache简介CacheManagercrud
Ehcache简介
目录
1 CacheManager
1.1 构造方法构建
1.2 静态方法构建
2 Cache
2.1&
- 最容易懂的javascript闭包学习入门
jackyrong
JavaScript
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2009/08/learning_javascript_closures.html
闭包(closure)是Javascript语言的一个难点,也是它的特色,很多高级应用都要依靠闭包实现。
下面就是我的学习笔记,对于Javascript初学者应该是很有用的。
一、变量的作用域
要理解闭包,首先必须理解Javascript特殊
- 提升网站转化率的四步优化方案
php教程分享
数据结构PHP数据挖掘Google活动
网站开发完成后,我们在进行网站优化最关键的问题就是如何提高整体的转化率,这也是营销策略里最最重要的方面之一,并且也是网站综合运营实例的结果。文中分享了四大优化策略:调查、研究、优化、评估,这四大策略可以很好地帮助用户设计出高效的优化方案。
PHP开发的网站优化一个网站最关键和棘手的是,如何提高整体的转化率,这是任何营销策略里最重要的方面之一,而提升网站转化率是网站综合运营实力的结果。今天,我就分
- web开发里什么是HTML5的WebSocket?
naruto1990
Webhtml5浏览器socket
当前火起来的HTML5语言里面,很多学者们都还没有完全了解这语言的效果情况,我最喜欢的Web开发技术就是正迅速变得流行的 WebSocket API。WebSocket 提供了一个受欢迎的技术,以替代我们过去几年一直在用的Ajax技术。这个新的API提供了一个方法,从客户端使用简单的语法有效地推动消息到服务器。让我们看一看6个HTML5教程介绍里 的 WebSocket API:它可用于客户端、服
- Socket初步编程——简单实现群聊
Everyday都不同
socket网络编程初步认识
初次接触到socket网络编程,也参考了网络上众前辈的文章。尝试自己也写了一下,记录下过程吧:
服务端:(接收客户端消息并把它们打印出来)
public class SocketServer {
private List<Socket> socketList = new ArrayList<Socket>();
public s
- 面试:Hashtable与HashMap的区别(结合线程)
toknowme
昨天去了某钱公司面试,面试过程中被问道
Hashtable与HashMap的区别?当时就是回答了一点,Hashtable是线程安全的,HashMap是线程不安全的,说白了,就是Hashtable是的同步的,HashMap不是同步的,需要额外的处理一下。
今天就动手写了一个例子,直接看代码吧
package com.learn.lesson001;
import java
- MVC设计模式的总结
xp9802
设计模式mvc框架IOC
随着Web应用的商业逻辑包含逐渐复杂的公式分析计算、决策支持等,使客户机越
来越不堪重负,因此将系统的商业分离出来。单独形成一部分,这样三层结构产生了。
其中‘层’是逻辑上的划分。
三层体系结构是将整个系统划分为如图2.1所示的结构[3]
(1)表现层(Presentation layer):包含表示代码、用户交互GUI、数据验证。
该层用于向客户端用户提供GUI交互,它允许用户