Lua脚本如何调用C/C++模块,Windows以及Linux版本演示
Windows下
我用的是vs2019,由于Windows下不像Linux可以直接直接安装lua程序直接运行lua代码,所以这里我们演示的是,通过c/c++调用lua脚本,lua脚本再调用其他的C/C++文件。
先用vs2019创建一个windows桌面向导–控制台程序的工程
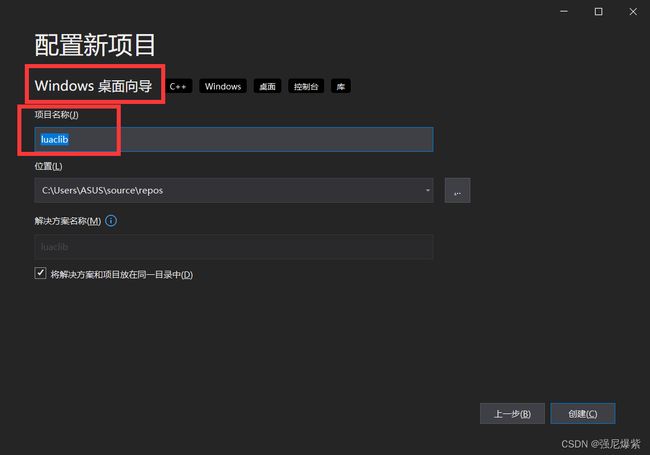
注意是选择windows桌面向导,项目名称必须是luaclib,到时候生成的dll文件为luaclib.dll,后边lua层用require调用c模块的时候dll文件的名称很重要。
一班的动态库都需要.cpp和.h文件,但对于lua调用C/C++,不用.h文件也行, 这里我们为了正规一点,.cpp和.h一起用
在开始之前,我们需要了解,lua5.1之后,lual_register()就被舍弃了,使用
lua_newtable(L);
luaL_setfuncs(L, myLib, 0);
一起使用来进行替代。
为了大家能够更深的理解,对于Windows下的lua调用C/C++模块,我们采用了lua5.1版本的方式,也就是使用lual_register()来进行测试;
在Linux环境下,我们采用lua5.2版本(即使用lua_newtable(L);
luaL_setfuncs(L, myLib, 0);来测试)
首先是windows下
luaclib.h
#pragma once
#include luaclib.cpp
#include 将这个工程编译成.dll文件,可在创建工程的时候选择生成.dll文件,若忘记选择了,也可使用下图的方式设置后,将工程重新编译生成.dll文件。
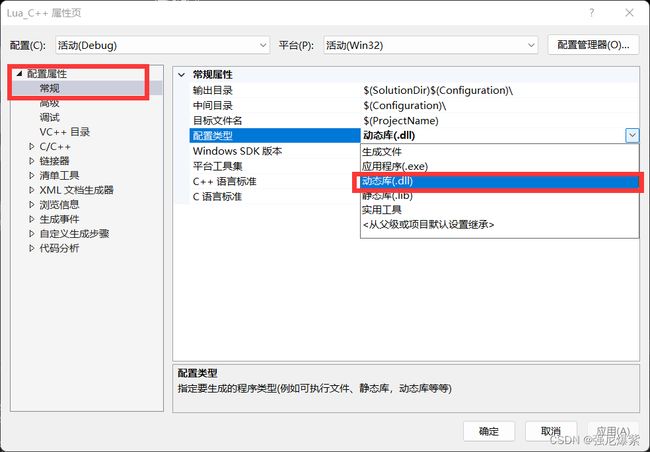 不出意外得到的dll文件为luaclib.dll。
不出意外得到的dll文件为luaclib.dll。
至此动态库就准备好了,这个动态库就是我们后边要用lua来调用的C++模块。
接下来重新创建一个工程,并且需要把上边得到的.dll 文件放到这个工程下。
新建两个文件,一个test.cpp. 一个hello.lua
test.cpp
#include
#include
#include
#include
*/ using namespace std;
int main() {
lua_State* L = luaL_newstate(); //lua_open();
luaL_openlibs(L); //必不可少
//加载lua文件
int bRet = luaL_loadfile(L, "hello.lua");
if (bRet) {
cout << "load file error" << endl;
return 0;
}
//运行lua文件
bRet = lua_pcall(L, 0, 0, 0);
if (bRet) {
cout << "pcall error" << endl;
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
hello.lua
require "luaclib"
local avg,sum =ss.average(1,2,3,4,5)
print(avg,sum) -- 3 15
ss.sayHello() -- hello world!
到此为止,项目已经可以运行测试, 前提是配置好了lua环境,也就是一些头文件的引用,以及库文件的引用,如果你是新手,lua运行环境配置,去这篇文章配置好环境。
Linux下
Linux下就很简单了,因为可以在控制台上直接运行lua程序
需要一个.c文件作为被调用的模块, 以及一个.lua文件
test.c 其实和上边windows的test.c几乎一样,代码末端有区别。
#includetest.lua
#!/usr/local/bin/lua //有了这行命令,可以直接 ./test.lua 运行lua程序
local mylib = require("luaclib") --对应于teste.c中的包名
local avg,sum =mylib.average(1,2,3,4,5)
print(avg,sum) -- 3 15
mylib.sayHello() -- hello world!
需要把test.c文件编译成一个动态库
gcc -o luaclib.so -fPIC -shared test.c
-
-shared,众所周知啊,.so时share object的缩写。为了让gcc知道是在编译 .so而不是可执行文件,所以需要-shared
-
-fPIC,这是编译动态库必须的。可见黄色圈起来的地方,分开编译,没加-fPIC,就会报错,提醒重新编译。其实-fPIC是编译选项,PIC是 Position Independent Code 的缩写,表示要生成位置无关的代码,这是动态库需要的特性。
这里必须是gcc, 不能用g++, g++是用在cpp文件中的。
建议你先不要用cpp文件,和我一样,先用c文件测试成功后再尝试cpp,因为cpp涉及了extern ”c”的使用,不然函数名字导出成动态库的时候会出错。
使用命令, lua test.lua 即可看到效果。
如果lua文件中添加了#!/usr/local/bin/lua, 可直接 ./test.lua
上边这种是调用的c模块,如果是c++模块有一点小区别, 必须要使用extern"C", 它的作用是告诉系统以c语言的方式来导出动态库文件,我们都知道c++有函数重载这个说法,所以,在c++中的动态库的函数名字与c语言中是不一样的,因为c++中可能出现同名函数,所以c++在导出的动态库中对函数名进行了一些额外的标志,所以我们需要用到extern“C”来以C语言的方式导出
只需把上边的test.c 改为 test.cpp
test.cpp
#include区别就是加了extern“C“ ,然后将命令改成
g++ -o luaclib.so -fPIC -shared test.c (上边用的是gcc)
编译好的动态库静态库资源
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1hbLQm508bV-8PNgO6qiG1A?pwd=200v
提取码:200v
这里只是lua调用C/C++,去这一篇学习 C/C++ 如何调用lua(点我)
如遇任何问题,欢迎评论区留言~