Android OpenSL ES 音频采集与播放
本篇详细介绍一下基于 Android OpenSL ES 实现音频的采集与播放。
1、OpenSL ES 是什么?
OpenSL ES 是一个针对嵌入式系统的开放硬件音频加速库,也可以将其视为一套针对嵌入式平台的音频标准,全称为: Open Sound Library for Embedded Systems ,它提供了一套高性能、 低延迟的音频功能实现方法,并且实现了软硬件音频性能的跨平台部署,大大降低了上层处理音频应用的开发难度。
在 Android 开发中,Google 官方从 Android 2.3 (API 9)开始,便支持了 OpenSL ES 标准 ,并且对其进行了扩展。本文介绍的 OpenSL ES 是针对 Android NDK 开发来说。
2、OpenSL ES 的一些基本概念
2.1 基于 c 语言的面向对象接口
OpenSL ES 是基于 c 语言实现的,但其提供的接口是采用面向对象的方式实现,OpenSL ES 的大多数 API 是通过对象来调用的。例如,以下代码片段,主要的逻辑是实例化引擎对象和获取引擎对象接口。
SLresult result;
// realize the engine
result = (*engineObject)->Realize(engineObject, SL_BOOLEAN_FALSE);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void)result;
result = (*engineObject)->GetInterface(engineObject, SL_IID_ENGINE, &engineEngine);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void)result;2.2 对象和接口概念
Object 和 Interface OpenSL ES 中的两大基本概念,可以类比为 Java 中的对象和接口。
在 OpenSL ES 中, 每个 Object 可以存在一系列的 Interface ,并且为每个对象都提供了一系列的基本操作,如 Realize,GetState,Destroy 等。重要的一点,只有通过 GetInterface 方法拿到 Object 的 Interface ,才能使用 Object 提供的功能。
2.3 对象的生命周期
OpenSL ES 的 Object 一般有三种状态,分别是:UNREALIZED (不可用),REALIZED(可用),SUSPENDED(挂起)。
Object 处于 UNREALIZED (不可用)状态时,系统不会为其分配资源;调用 Realize 方法后便进入 REALIZED(可用)状态,此时对象的各个功能和资源可以正常访问;当系统音频相关的硬件设备被其他进程占用时,OpenSL ES Object 便会进入 SUSPENDED (挂起)状态,随后调用 Resume 方法可使对象重回 REALIZED(可用)状态;当 Object 使用结束后,调用 Destroy 方法释放资源,是对象重回 UNREALIZED (不可用)状态。
【学习地址】:FFmpeg/WebRTC/RTMP/NDK/Android音视频流媒体高级开发
【文章福利】:免费领取更多音视频学习资料包、大厂面试题、技术视频和学习路线图,资料包括(C/C++,Linux,FFmpeg webRTC rtmp hls rtsp ffplay srs 等等)有需要的可以点击1079654574加群领取哦~
3、 OpenSL ES 常用的 Object 和 Interface
3.1 Audio 引擎对象和接口
Audio 引擎对象和接口,即 Engine Object 和 SLEngineItf Interface 。Engine Object 的主要功能是管理 Audio Engine 的生命周期,提供引擎对象的管理接口。引擎对象的使用方法如下:
SLresult result;
// 创建引擎对象
result = slCreateEngine(&engineObject, 0, NULL, 0, NULL, NULL);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void)result;
// 实例化
result = (*engineObject)->Realize(engineObject, SL_BOOLEAN_FALSE);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void)result;
// 获取引擎对象接口
result = (*engineObject)->GetInterface(engineObject, SL_IID_ENGINE, &engineEngine);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void)result;
// 释放引擎对象的资源
result = (*engineObject)->Destroy(engineObject, SL_BOOLEAN_FALSE);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void)result;3.2 SLRecordItf 和 SLPlayItf
SLRecordItf 和 SLPlayItf 分别抽象多媒体功能 recorder 和 player ,通过 SLEngineItf 的 CreateAudioPlayer 和 CreateAudioRecorder 方法分别创建 player 和 recorder 对象实例。
// 创建 audio recorder 对象
result = (*engineEngine)->CreateAudioRecorder(engineEngine, &recorderObject , &recSource, &dataSink,
NUM_RECORDER_EXPLICIT_INTERFACES, iids, required);
// 创建 audio player 对象
SLresult result = (*engineEngine)->CreateAudioPlayer(
engineEngine,
&audioPlayerObject,
&dataSource,
&dataSink,
1,
interfaceIDs,
requiredInterfaces
);3.3 SLDataSource 和 SLDataSink
OpenSL ES 中的 SLDataSource 和 SLDataSink 结构体,主要用于构建 audio player 和 recorder 对象,其中 SLDataSource 表示音频数据来源的信息,SLDataSink 表示音频数据输出信息。
// 数据源简单缓冲队列定位器
SLDataLocator_AndroidSimpleBufferQueue dataSou
SL_DATALOCATOR_ANDROIDSIMPLEBUFFERQUEU
1
};
// PCM 数据源格式
SLDataFormat_PCM dataSourceFormat = {
SL_DATAFORMAT_PCM, // 格式类型
wav_get_channels(wav), // 通道数
wav_get_rate(wav) * 1000, //采样率
wav_get_bits(wav), // 位宽
wav_get_bits(wav),
SL_SPEAKER_FRONT_CENTER, // 通道屏蔽
SL_BYTEORDER_LITTLEENDIAN // 字节顺序
};
// 数据源
SLDataSource dataSource = {
&dataSourceLocator,
&dataSourceFormat
};
// 针对数据接收器的输出混合定位器(混音器)
SLDataLocator_OutputMix dataSinkLocator = {
SL_DATALOCATOR_OUTPUTMIX, // 定位器类型
outputMixObject // 输出混合
};
// 输出
SLDataSink dataSink = {
&dataSinkLocator, // 定位器
0,
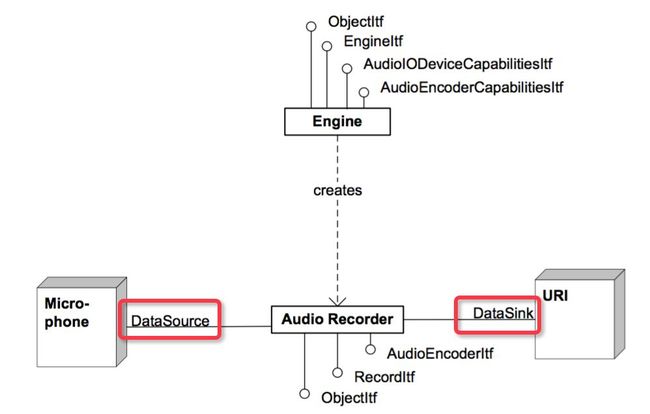
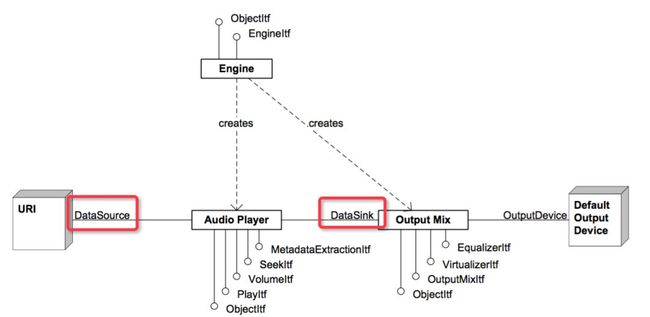
};4、OpenSL ES Recorder 和 Player 功能构建
Audio Recorder
Audio Player
PS:Audio Player 的 Data Source 也可以是本地存储或缓存的音频数据,以上图片来自于 Jhuster 的博客。
5、代码实现
以下代码主要实现音频数据的采集、保存和播放。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define AUDIO_SRC_PATH "/sdcard/audio.pcm"
#define LOGI(FORMAT, ...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO,"byteflow",FORMAT,##__VA_ARGS__);
#define LOGE(FORMAT, ...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_ERROR,"byteflow",FORMAT,##__VA_ARGS__);
#define NUM_RECORDER_EXPLICIT_INTERFACES 2
#define NUM_BUFFER_QUEUE 1
#define SAMPLE_RATE 44100
#define PERIOD_TIME 20 // 20ms
#define FRAME_SIZE SAMPLE_RATE * PERIOD_TIME / 1000
#define CHANNELS 2
#define BUFFER_SIZE (FRAME_SIZE * CHANNELS)
// engine interfaces
static SLObjectItf engineObject = NULL;
static SLEngineItf engineEngine = NULL;
// audio recorder interfaces
static SLObjectItf recorderObject = NULL;
static SLRecordItf recorderRecord = NULL;
static SLAndroidSimpleBufferQueueItf recorderBuffQueueItf = NULL;
static SLAndroidConfigurationItf configItf = NULL;
// pcm audio player interfaces
static SLObjectItf playerObject = NULL;
static SLPlayItf playerPlay = NULL;
static SLObjectItf outputMixObjext = NULL; // 混音器
static SLAndroidSimpleBufferQueueItf playerBufferQueueItf = NULL;
void createEngine(){
SLEngineOption EngineOption[] = {
{(SLuint32) SL_ENGINEOPTION_THREADSAFE, (SLuint32) SL_BOOLEAN_TRUE}
};
SLresult result;
result = slCreateEngine(&engineObject, 1, EngineOption, 0, NULL, NULL);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
/* Realizing the SL Engine in synchronous mode. */
result = (*engineObject)->Realize(engineObject, SL_BOOLEAN_FALSE);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
// get the engine interface, which is needed in order to create other objects
result = (*engineObject)->GetInterface(engineObject, SL_IID_ENGINE, &engineEngine);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
}
class AudioContext {
public:
FILE *pfile;
uint8_t *buffer;
size_t bufferSize;
AudioContext(FILE *pfile, uint8_t *buffer, size_t bufferSize){
this->pfile = pfile;
this->buffer = buffer;
this->bufferSize = bufferSize;
}
};
static AudioContext *recorderContext = NULL;
// 录制音频时的回调
void AudioRecorderCallback(SLAndroidSimpleBufferQueueItf bufferQueueItf, void *context){
AudioContext *recorderContext = (AudioContext*)context;
assert(recorderContext != NULL);
if (recorderContext->buffer != NULL) {
fwrite(recorderContext->buffer, recorderContext->bufferSize, 1, recorderContext->pfile);
LOGI("save a frame audio data.");
SLresult result;
SLuint32 state;
result = (*recorderRecord)->GetRecordState(recorderRecord, &state);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void) result;
if (state == SL_RECORDSTATE_RECORDING) {
result = (*bufferQueueItf)->Enqueue(bufferQueueItf, recorderContext->buffer, recorderContext->bufferSize);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void) result;
}
}
}
// 播放音频时的回调
void AudioPlayerCallback(SLAndroidSimpleBufferQueueItf bufferQueueItf, void *context){
AudioContext *playerContext = (AudioContext*)context;
if (!feof(playerContext->pfile)) {
fread(playerContext->buffer, playerContext->bufferSize, 1, playerContext->pfile);
LOGI("read a frame audio data.");
(*bufferQueueItf)->Enqueue(bufferQueueItf, playerContext->buffer, playerContext->bufferSize);
} else {
fclose(playerContext->pfile);
delete playerContext->buffer;
}
}
// 创建音频播放器
void createAudioPlayer(SLEngineItf engineEngine, SLObjectItf outputMixObject, SLObjectItf &audioPlayerObject){
SLDataLocator_AndroidSimpleBufferQueue dataSourceLocator = {
SL_DATALOCATOR_ANDROIDSIMPLEBUFFERQUEUE,
1
};
// PCM 数据源格式
SLDataFormat_PCM dataSourceFormat = {
SL_DATAFORMAT_PCM,
2,
SL_SAMPLINGRATE_44_1,
SL_PCMSAMPLEFORMAT_FIXED_16,
16,
SL_SPEAKER_FRONT_LEFT| SL_SPEAKER_FRONT_RIGHT,
SL_BYTEORDER_LITTLEENDIAN
};
SLDataSource dataSource = {
&dataSourceLocator,
&dataSourceFormat
};
SLDataLocator_OutputMix dataSinkLocator = {
SL_DATALOCATOR_OUTPUTMIX, // 定位器类型
outputMixObject // 输出混合
};
SLDataSink dataSink = {
&dataSinkLocator, // 定位器
0,
};
// 需要的接口
SLInterfaceID interfaceIDs[] = {
SL_IID_BUFFERQUEUE
};
SLboolean requiredInterfaces[] = {
SL_BOOLEAN_TRUE
};
// 创建音频播放对象
SLresult result = (*engineEngine)->CreateAudioPlayer(
engineEngine,
&audioPlayerObject,
&dataSource,
&dataSink,
1,
interfaceIDs,
requiredInterfaces
);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void) result;
}
extern "C" {
// 开始播放音频
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_com_byteflow_opensl_1es_AudioRecorder_startPlay(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance) {
// 创建引擎
if (engineEngine == NULL) {
createEngine();
}
// 创建混音器
SLresult result;
result = (*engineEngine)->CreateOutputMix(engineEngine, &outputMixObjext, 0, 0, 0);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void) result;
result = (*outputMixObjext)->Realize(outputMixObjext, SL_BOOLEAN_FALSE);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void) result;
FILE *p_file = fopen(AUDIO_SRC_PATH, "r");
// 创建播放器
createAudioPlayer(engineEngine, outputMixObjext, playerObject);
result = (*playerObject)->Realize(playerObject, SL_BOOLEAN_FALSE);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void) result;
result = (*playerObject)->GetInterface(playerObject, SL_IID_BUFFERQUEUE,
&playerBufferQueueItf);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void) result;
uint8_t *buffer = new uint8_t[BUFFER_SIZE];
AudioContext *playerContext = new AudioContext(p_file, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
result = (*playerBufferQueueItf)->RegisterCallback(playerBufferQueueItf, AudioPlayerCallback,
playerContext);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void) result;
result = (*playerObject)->GetInterface(playerObject, SL_IID_PLAY, &playerPlay);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
(void) result;
result = (*playerPlay)->SetPlayState(playerPlay, SL_PLAYSTATE_PLAYING);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
AudioPlayerCallback(playerBufferQueueItf, playerContext);
}
// 停止播放音频
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_com_byteflow_opensl_1es_AudioRecorder_stopPlay(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance) {
if (playerPlay != NULL) {
SLresult result;
result = (*playerPlay)->SetPlayState(playerPlay, SL_PLAYSTATE_STOPPED);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
}
}
// 开始采集音频数据,并保存到本地
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_com_byteflow_opensl_1es_AudioRecorder_startRecord(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance) {
if (engineEngine == NULL) {
createEngine();
}
if (recorderObject != NULL) {
LOGI("Audio recorder already has been created.");
return ;
}
FILE *p_file = fopen(AUDIO_SRC_PATH, "w");
if (p_file == NULL) {
LOGI("Fail to open file.");
return ;
}
SLresult result;
/* setup the data source*/
SLDataLocator_IODevice ioDevice = {
SL_DATALOCATOR_IODEVICE,
SL_IODEVICE_AUDIOINPUT,
SL_DEFAULTDEVICEID_AUDIOINPUT,
NULL
};
SLDataSource recSource = {&ioDevice, NULL};
SLDataLocator_AndroidSimpleBufferQueue recBufferQueue = {
SL_DATALOCATOR_ANDROIDSIMPLEBUFFERQUEUE,
NUM_BUFFER_QUEUE
};
SLDataFormat_PCM pcm = {
SL_DATAFORMAT_PCM, // pcm 格式的数据
2, // 2 个声道(立体声)
SL_SAMPLINGRATE_44_1, // 44100hz 的采样频率
SL_PCMSAMPLEFORMAT_FIXED_16,
SL_PCMSAMPLEFORMAT_FIXED_16,
SL_SPEAKER_FRONT_LEFT| SL_SPEAKER_FRONT_RIGHT,
SL_BYTEORDER_LITTLEENDIAN
};
SLDataSink dataSink = { &recBufferQueue, &pcm };
SLInterfaceID iids[NUM_RECORDER_EXPLICIT_INTERFACES] = {SL_IID_ANDROIDSIMPLEBUFFERQUEUE, SL_IID_ANDROIDCONFIGURATION};
SLboolean required[NUM_RECORDER_EXPLICIT_INTERFACES] = {SL_BOOLEAN_TRUE, SL_BOOLEAN_TRUE};
/* Create the audio recorder */
result = (*engineEngine)->CreateAudioRecorder(engineEngine, &recorderObject , &recSource, &dataSink,
NUM_RECORDER_EXPLICIT_INTERFACES, iids, required);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
/* get the android configuration interface*/
result = (*recorderObject)->GetInterface(recorderObject, SL_IID_ANDROIDCONFIGURATION, &configItf);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
/* Realize the recorder in synchronous mode. */
result = (*recorderObject)->Realize(recorderObject, SL_BOOLEAN_FALSE);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
/* Get the buffer queue interface which was explicitly requested */
result = (*recorderObject)->GetInterface(recorderObject, SL_IID_ANDROIDSIMPLEBUFFERQUEUE, (void*) &recorderBuffQueueItf);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
/* get the record interface */
result = (*recorderObject)->GetInterface(recorderObject, SL_IID_RECORD, &recorderRecord);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
uint8_t *buffer = new uint8_t[BUFFER_SIZE];
recorderContext = new AudioContext(p_file, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
result = (*recorderBuffQueueItf)->RegisterCallback(recorderBuffQueueItf, AudioRecorderCallback, recorderContext);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
/* Enqueue buffers to map the region of memory allocated to store the recorded data */
result = (*recorderBuffQueueItf)->Enqueue(recorderBuffQueueItf, recorderContext->buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
/* Start recording */
// 开始录制音频
result = (*recorderRecord)->SetRecordState(recorderRecord, SL_RECORDSTATE_RECORDING);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
LOGI("Starting recording");
}
// 停止音频采集
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_com_byteflow_opensl_1es_AudioRecorder_stopRecord(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance) {
if (recorderRecord != NULL) {
SLresult result = (*recorderRecord)->SetRecordState(recorderRecord, SL_RECORDSTATE_STOPPED);
assert(SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result);
if (recorderContext != NULL) {
fclose(recorderContext->pfile);
delete recorderContext->buffer;
}
}
}
// 释放资源
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_com_byteflow_opensl_1es_AudioRecorder_release(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance) {
if (recorderObject != NULL) {
(*recorderObject)->Destroy(recorderObject);
recorderObject = NULL;
recorderRecord = NULL;
recorderBuffQueueItf = NULL;
configItf = NULL;
recorderContext = NULL;
}
if (playerObject != NULL) {
(*playerObject)->Destroy(playerObject);
playerObject = NULL;
playerPlay = NULL;
playerBufferQueueItf = NULL;
outputMixObjext = NULL;
}
// destroy engine object, and invalidate all associated interfaces
if (engineObject != NULL) {
(*engineObject)->Destroy(engineObject);
engineObject = NULL;
engineEngine = NULL;
}
}
}; CMake 脚本 CMakeLists.txt 。
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
audio-recorder
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).
src/main/cpp/audio-recorder.cpp)
target_link_libraries(audio-recorder
android
log
OpenSLES)原文链接:Android OpenSL ES 音频采集与播放