【Spring】Spring MVC 程序开发
Spring MVC 程序开发
- 一. 什么是 Spring MVC
-
- 1. MVC
- 2. Spring、Spring Boot 与 Spring MVC
- 二. 创建 Spring MVC 项目
-
- 1. 创建项目
- 2. 用户和程序的映射
- 3. 获取用户请求参数
-
- ①. 获取单个参数
- ②. 获取多个参数
- ③. 传递对象
- ④. 后端参数重命名(后端参数映射)@RequestParam
- ⑤. @RequestBody 接收JSON对象
- ⑥. 获取URL中参数 @PathVariable
- ⑦. 上传文件 @RequestPart
- ⑧. 获取Cookie
- ⑨. 获取 Session
- ⑩. 获取 header
- 4. 返回数据
-
- ① 返回静态页面
- ②. 返回 text/html
- ③. 返回 JSON 对象
- ④. 请求转发或请求重定向
一. 什么是 Spring MVC
1. MVC
- Model(模型)是应⽤程序中⽤于处理应⽤程序数据逻辑的部分。通常模型对象负责在数据库中存取数据。
- View(视图)是应⽤程序中处理数据显示的部分。通常视图是依据模型数据创建的。
- Controller(控制器)是应⽤程序中处理⽤户交互的部分。通常控制器负责从视图读取数据,控制⽤户输⼊,并向模型发送数据。
MVC 是⼀种思想,⽽ Spring MVC 是对 MVC 思想的具体实现。
2. Spring、Spring Boot 与 Spring MVC
Spring MVC 与 Spring 同时产生,Spring MVC 是 Spring 的 Web 模块部分,也是 Spring 框架的核心部分,又叫 Spring Web MVC, Spring MVC 是基于 Servlet API 构建的。
而 Spring Boot 是后来产生的基于 Spring 为了更高效的使用 Spring 而开发出来的。
二. 创建 Spring MVC 项目
1. 创建项目
在创建 Spring Boot 项目时添加 Spring Web 依赖就是 Spring MVC 项目
2. 用户和程序的映射
创建⼀个 UserController 类,实现⽤户到 Spring 程序的互联互通
@Controller // 让 spring 框架启动时,把类加载进去
@ResponseBody // 返回⾮⻚⾯数据
@RequestMapping("/user") // 路由规则映射 一级路径
public class UserController {
// 路由规则映射
@RequestMapping("/hi") // 二级路径
public String sayHi(){
return "Hi,Spring MVC.
";
}
}
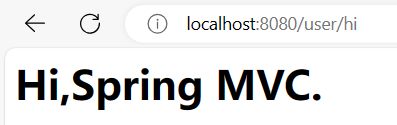
程序启动,访问地址:http://localhost:8080/user/hi 时就能打印“hello,spring mvc”的信息
@RequestMapping
⽤来注册接⼝的路由映射的。
路由映射指的是,当⽤户访问⼀个 url 时,将⽤户的请求对应到程序中某个类的某个⽅法的过程就叫路由映射。
- @RequestMapping 即可修饰类,也可以修饰⽅法,当修饰类和⽅法时,访问的地址是 类 + ⽅法 的路径 。
- @RequestMapping 也可以直接修饰⽅法,访问的地址直接就是⽅法上面的 路径。
- 注意 @RequestMapping 要搭配 @Controller 才能生效
@Controller // 让 spring 框架启动时,把类加载进去
@ResponseBody // 返回⾮⻚⾯数据
public class UserController {
// 路由规则映射
@RequestMapping("/hi")
public String sayHi(){
return "Hi,Spring MVC.
";
}
}
此时访问的路径是:http://localhost:8080/hi
默认 @RequestMapping 可以同时支持 GET 和 POST 请求,也可以进行设置。
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/hi") // 设置只支持 GET 请求
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST, value = "/hi") // 设置只支持 POST 请求
也可以直接使用 @GetMapping 或者 @PostMapping
@GetMapping("/hi")
@PostMapping("/hi")
3. 获取用户请求参数
①. 获取单个参数
直接⽤⽅法中的参数来实现传参
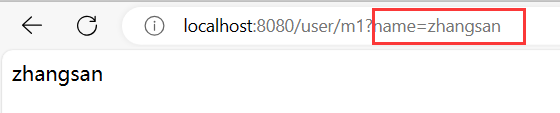
@RequestMapping("/m1")
public Object method_1(String name){
System.out.println("参数 name:"+name);
return name;
}
- 前端传递的参数名称要与后端接收时使用的参数名一致
- 参数使用包装类,防止出现异常。比如整数使用 Integer.
②. 获取多个参数
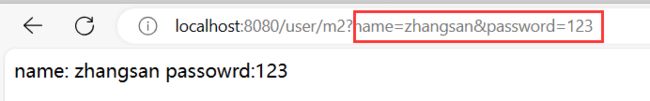
与获取单个参数一样,参数写多个就行了,注意前后端名称一致, 前后端进⾏参数匹配时,是以参数的名称进⾏匹配的,因此参数的位置
是不影响后端获取参数的结果。
@RequestMapping("/m2")
public Object method_2(String name, String password){
System.out.println("参数 name:"+name+" password: "+ password);
return "name: " + name + " passowrd:" + password;
}
③. 传递对象
直接写对象即可,用户传递的参数的名称与对应的属性名一致。
⽐如 Person 对象:
@Data
public class Person {
private int id;
private String name;
private String password;
}
@RequestMapping("/m3")
public Object method_2(Person p){
System.out.println("对象中的 name:"+p.getName());
System.out.println("对象中的 password:"+p.getPassword());
return "用户信息: " + p;
}
当传递的参数与类的属性个数不一致时, 没有匹配上的属性取默认值.
④. 后端参数重命名(后端参数映射)@RequestParam
当前端传入的参数名称与后端参数不一致时, 可以使用 @RequestParam 来重命名前后端的参数值。
比如前端参数名为 time, 但是后端用 createtime, 后端就可以使用 @RequestParam 来重命名前后端的参数值.
也就是说使用 time 和 createtime 都能访问到 这个参数
@RequestMapping("/m4")
public Object method_4(@RequestParam("time") String createtime) {
System.out.println("时间:" + createtime);
return "时间:" + createtime;
}
注意: 假如我们使用 @RequestParam 了,那么如果前端不传递这个参数的话就会报错, 但是有时候这个参数不是必传参数, 此时我们就可以进行设置.
设置 @RequestParam 的一个属性 required = false 表示不传递这个参数也可以
@RequestParam(value = "time", required = false) String createtime
⑤. @RequestBody 接收JSON对象
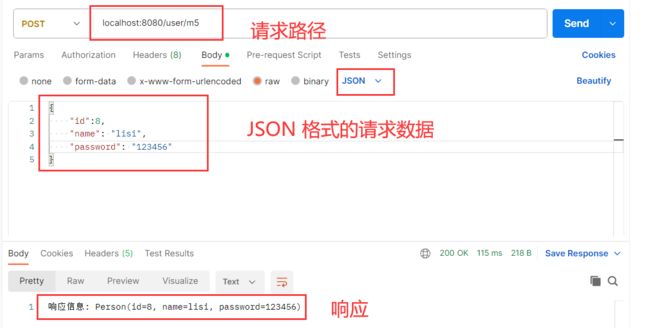
@RequestMapping("/m5")
public Object method_5(@RequestBody Person person) {
System.out.println(person);
return "响应信息: " + person;
}
使用 POSTMAN 软件发送 JSON 格式的请求
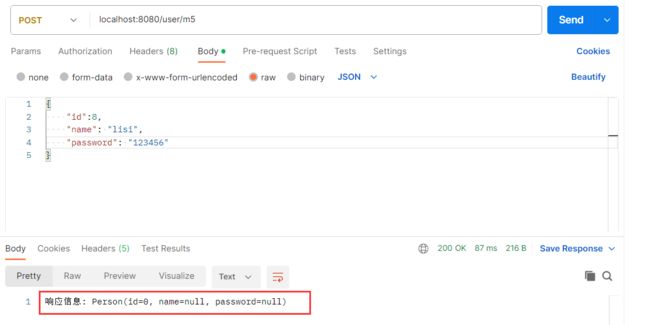
假如把 @RequestBody 去掉
@RequestMapping("/m5")
public Object method_5(Person person) {
System.out.println(person);
return "响应信息: " + person;
}
后端根本就接收不到对应的信息
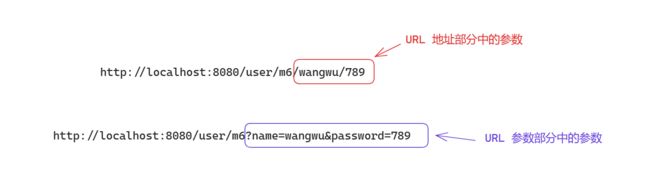
⑥. 获取URL中参数 @PathVariable
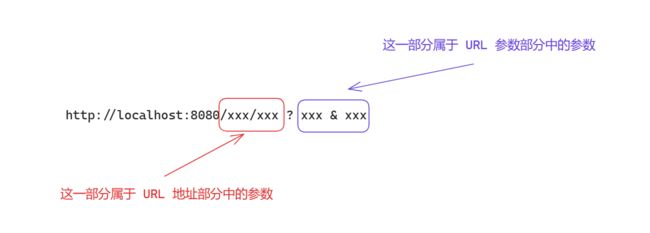
URL 中的参数, 并不是 URL 参数部分的参数
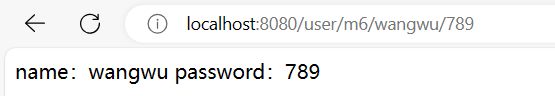
@RequestMapping("/m6/{name}/{password}")
public Object method_6(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable String password) {
System.out.println("name:" + name);
System.out.println("password:" + password);
return "name:" + name + " password:" + password;
}
注意: 这里面 @RequestMapping(“/m6/{name}/{password}”) 中的参数名称与下面方法中的参数名称也要保持一致

为什么在 URL 地址部分中要带参数, 写进参数部分中不是更好么?
- 因为在搜索结果中 参数写在地址部分中比写在参数部分中优先级更高.
1 属于 URL 地址, 一般不会改动, 2 中既有 URL 地址又有 URL 参数, 更容易发生改动, 所以 搜索结果中 1 排在更前面, 从而更容易让用户点击, 从而提高效益.
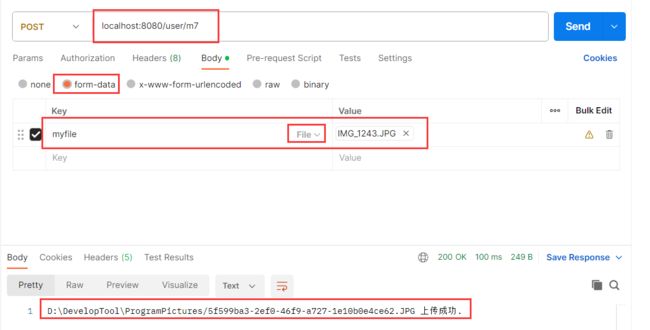
⑦. 上传文件 @RequestPart
@RequestMapping("/m7")
public String method_7(@RequestPart("myfile") MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
// 获取⽂件后缀名
String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename().substring(file.getOriginalFilename().lastIndexOf("."));
// ⽂件保存地址
String filePath = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader().getResource("static").getPath() +
"/" + UUID.randomUUID() + fileName;
// 保存⽂件
file.transferTo(new File(filePath));
return filePath + " 上传成功.";
}
到对应文件存放的目录进行查找
注意 3 个要点:
- 存放的目录是什么? Linux 和 Windows 不一样, 要根据配置文件变化.
- 文件名称不能冲突, 所以可以使用 UUID (全球唯一 ID)防止覆盖(不使用时间戳因为高并发情况下很可能冲突)
- 文件格式不能变,所以需要获取文件的后缀
⑧. 获取Cookie
传统获取 cookie
Spring MVC 基于 Servlet 所以每个函数中都默认带有 HttpServletResponse、HttpServletRequest 这两个参数
@RequestMapping("/m8")
@ResponseBody
public String method_8(HttpServletResponse response, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 获取所有 cookie 信息
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
// 遍历 cookies, 找到自己需要的 cookie
for (Cookie cookie: cookies) {
if (cookie.getName().equals("username")) {
// ...
}
}
return "成功获取 cookie";
}
简洁的获取 Cookie—@CookieValue, 直接获取自己想要的那个 cookie
@RequestMapping("/cookie")
@ResponseBody
public String cookie(@CookieValue("username") String username) {
return "cookie:" + username;
}
⑨. 获取 Session
Session 存储和 Servlet 类似,是使⽤ HttpServletRequest 中获取的
@RequestMapping("/setsess")
@ResponseBody
public String setsess(HttpServletRequest request) {
// 获取 HttpSession 对象,参数设置为 true 表示如果没有 session 对象就创建⼀个session
HttpSession session = request.getSession(true);
if(session!=null){
session.setAttribute("username","java");
}
return "session 存储成功";
}
读取 Session 可以使⽤ HttpServletRequest
@RequestMapping("/sess")
@ResponseBody
public String sess(HttpServletRequest request) {
// 参数为 false 如果 session 不存在,不会⾃动创建
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
String username = "暂⽆";
if(session!=null && session.getAttribute("username")!=null){
username = (String) session.getAttribute("username");
}
return "username:"+username;
}
获取 Session 更简洁的⽅式:
@RequestMapping("/sess2")
@ResponseBody
public String sess2(@SessionAttribute(value = "username",required = false)
String username) {
return "username:"+username;
}
⑩. 获取 header
传统获取 header
@RequestMapping("/m9")
@ResponseBody
public String method_9(HttpServletResponse response, HttpServletRequest request) {
String userAgent = request.getHeader("User-Agent");
return userAgent;
}
简洁获取 Header—@RequestHeader
@RequestMapping("/header")
@ResponseBody
public String header(@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent) {
return "userAgent:"+userAgent;
}
4. 返回数据
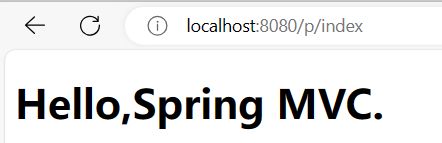
① 返回静态页面
默认情况下返回的是视图(静态页面)(xxx.html)
创建前端⻚⾯ index.html
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>hello,spring mvc</title>
<script src="index.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello,Spring MVC.</h1>
</body>
</html>
创建控制器 controller:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/p")
public class PersonController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public Object index(){
// 执⾏业务...
// 返回view -> index.html
return "/index.html";
}
}
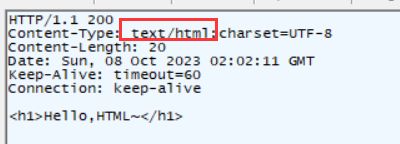
②. 返回 text/html
想要返给给前端数据,这个时候我们就需要使⽤ @ResponseBody 注解
当返回数据是字符串是格式就是 text/html
@RequestMapping("/m")
@ResponseBody
public String method_7() {
return "Hello,HTML~
";
}
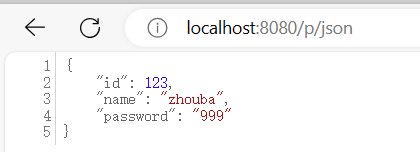
③. 返回 JSON 对象
使用 @ResponseBody 注解后, 如果返回值是对象, 那么默认返回的就是 JSON 对象
@RequestMapping("/json")
@ResponseBody
public Object method_2() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setId(123);
person.setName("zhouba");
person.setPassword("999");
return person;
}
@ResponseBody 说明:
- @ResponseBody 返回的值如果是字符会转换成 text/html,如果返回的是对象会转换成 application/json 返回给前端。
- @ResponseBody 可以⽤来修饰⽅法或者是修饰类,修饰类表示类中的所有⽅法都会返回 html 或者 json,⽽不是视图。
- 组合注解:@RestController
@RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody
④. 请求转发或请求重定向
return 不但可以返回⼀个视图,还可以实现跳转,跳转的⽅式有两种:
- forward 是请求转发;
- redirect:请求重定向。
举个栗子:
你告诉妈妈想吃辣条,如果妈妈说好,我帮你去买,这就是 forward 请求转发;如果妈妈让你⾃⼰去买,那么就是请求 redirect 重定向。
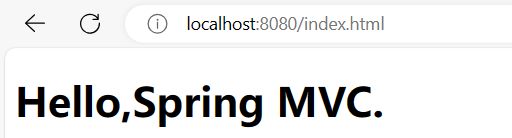
请求重定向:
// 请求重定向
@RequestMapping("/index1")
public String index1(){
return "redirect:/index.html";
}
浏览器中输入 http://localhost:8080/p/index1 会直接跳转到 http://localhost:8080/index.html
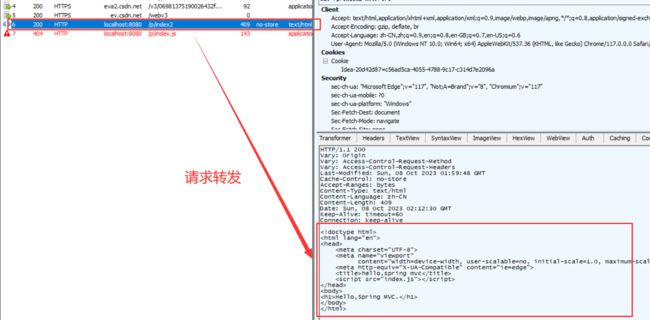
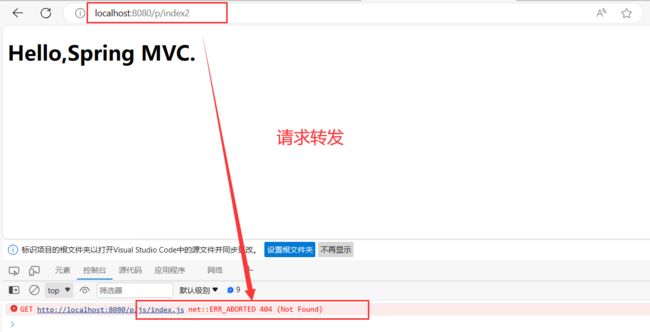
// 请求转发
@RequestMapping("/index2")
public String index2(){
return "forward:/index.html";
}
forward VS redirect :
- 请求重定向(redirect)将请求重新定位到资源,客户端重新请求;请求转发(forward)是服务器端转发。即请求重定向客户端两次请求, 而请求转发客户端只一次请求。
- 请求重定向地址发⽣变化,请求转发地址不发⽣变化。
- 请求重定向与直接访问新地址效果⼀直,不存在原来的外部资源不能访问;请求转发服务器端转发
有可能造成原外部资源不能访问。
请求转发如果资源和转发的⻚⾯不在⼀个⽬录下,会导致外部资源不可访问 (因为你只转发了一个页面,这个页面依赖的其他文件没有进行转发):
换为请求重定向:
好啦! 以上就是对 Spring MVC 程序开发 的讲解,希望能帮到你 !
评论区欢迎指正 !