Android:ARouter原理源码解析
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、ARouter使用
- 二、ARouter初始化
-
- init()函数
-
-
- 整体
- LogisticsCenter初始化
- 拦截器初始化
-
- 三、跳转解析
-
- 跳转
- 总结
前言
一、ARouter使用
ARouter的基本使用请参考这篇博客
ARouter的基本使用
二、ARouter初始化
init()函数
public static void init(Application application) {
if (!hasInit) {
logger = _ARouter.logger;
_ARouter.logger.info(Consts.TAG, "ARouter init start.");
///调用初始化代码
hasInit = _ARouter.init(application);
///初始化完成后,加载拦截器服务,并初始化所有拦截器
if (hasInit) {
_ARouter.afterInit();
}
_ARouter.logger.info(Consts.TAG, "ARouter init over.");
}
}
//_ARouter的init方法
protected static synchronized boolean init(Application application) {
mContext = application;
LogisticsCenter.init(mContext, executor);
logger.info(Consts.TAG, "ARouter init success!");
hasInit = true;
mHandler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper());
return true;
}
//LogisticsCenter的初始化方法
/**
* LogisticsCenter init, load all metas in memory. Demand initialization
*/
public synchronized static void init(Context context, ThreadPoolExecutor tpe) throws HandlerException {
mContext = context;
executor = tpe;
try {
long startInit = System.currentTimeMillis();
//billy.qi modified at 2017-12-06
//load by plugin first
//1.加载路由映射表 (通过 ARouter 插件 注册)
loadRouterMap();
//2.是否通过插件注册初始化
if (registerByPlugin) {
logger.info(TAG, "Load router map by arouter-auto-register plugin.");
} else {
Set<String> routerMap;
// It will rebuild router map every times when debuggable.
//可调试 和新版本的时候 重建路由表
if (ARouter.debuggable() || PackageUtils.isNewVersion(context)) {
logger.info(TAG, "Run with debug mode or new install, rebuild router map.");
// These class was generated by arouter-compiler.
routerMap = ClassUtils.getFileNameByPackageName(mContext, ROUTE_ROOT_PAKCAGE);
// These class was generated by ARouter-compiler.
//3.在线程池中,扫描所有dex文件,通过包名获取路由映射表类名
//包名 ROUTE_ROOT_PAKCAGE :com.alibaba.android.ARouter.routes
if (!routerMap.isEmpty()) {
context.getSharedPreferences(AROUTER_SP_CACHE_KEY, Context.MODE_PRIVATE).edit().putStringSet(AROUTER_SP_KEY_MAP, routerMap).apply();
}
PackageUtils.updateVersion(context); // Save new version name when router map update finishes.
} else {
///从 SharedPreferences 缓存中获取所有的路由类文件
logger.info(TAG, "Load router map from cache.");
routerMap = new HashSet<>(context.getSharedPreferences(AROUTER_SP_CACHE_KEY, Context.MODE_PRIVATE).getStringSet(AROUTER_SP_KEY_MAP, new HashSet<String>()));
}
logger.info(TAG, "Find router map finished, map size = " + routerMap.size() + ", cost " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startInit) + " ms.");
startInit = System.currentTimeMillis();
///4.加载 IRouteRoot,IInterceptorGroup,IProviderGroup 类,填充Warehouse 的路由信息组索引
for (String className : routerMap) {
if (className.startsWith(ROUTE_ROOT_PAKCAGE + DOT + SDK_NAME + SEPARATOR + SUFFIX_ROOT)) {
// This one of root elements, load root.
((IRouteRoot) (Class.forName(className).getConstructor().newInstance())).loadInto(Warehouse.groupsIndex);
} else if (className.startsWith(ROUTE_ROOT_PAKCAGE + DOT + SDK_NAME + SEPARATOR + SUFFIX_INTERCEPTORS)) {
// Load interceptorMeta
((IInterceptorGroup) (Class.forName(className).getConstructor().newInstance())).loadInto(Warehouse.interceptorsIndex);
} else if (className.startsWith(ROUTE_ROOT_PAKCAGE + DOT + SDK_NAME + SEPARATOR + SUFFIX_PROVIDERS)) {
// Load providerIndex
((IProviderGroup) (Class.forName(className).getConstructor().newInstance())).loadInto(Warehouse.providersIndex);
}
}
}
//检验WareHouse是否存入
if (Warehouse.groupsIndex.size() == 0) {
logger.error(TAG, "No mapping files were found, check your configuration please!");
}
if (ARouter.debuggable()) {
logger.debug(TAG, String.format(Locale.getDefault(), "LogisticsCenter has already been loaded, GroupIndex[%d], InterceptorIndex[%d], ProviderIndex[%d]", Warehouse.groupsIndex.size(), Warehouse.interceptorsIndex.size(), Warehouse.providersIndex.size()));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new HandlerException(TAG + "ARouter init logistics center exception! [" + e.getMessage() + "]");
}
}
我们可以通过以上的初始化了解到ARouter在初始化阶段完成的大致构造
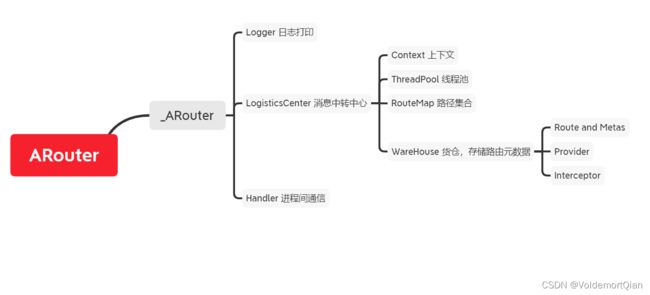
整体
- 初始化了日志打印
- 初始化了消息中转中心,包含线程池、路径集合、WareHouse货仓等多种结构;WareHouse存储路径、Provider和拦截器等多种数据
- 初始化Handler,并放入主线程的Looper
LogisticsCenter初始化
- 选择一:ARouter-auto-register 插件加载路由表(如果有该插件)
- 选择二:在需要的时候扫描所有 dex文件,找到所有包名为com.alibaba.android.ARouter.routes的类,类名放到routerMap 集里面;实例化上面找到的所有类,并通过这些集类加载对应的集映射索引到WareHouse中。
下面我们来看看com.alibaba.android.ARouter.routes的类下包含了哪些信息
IRouteRoot
/**
* DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE!!! IT WAS GENERATED BY AROUTER. */
public class ARouter$$Root$$login implements IRouteRoot {
@Override
public void loadInto(Map<String, Class<? extends IRouteGroup>> routes) {
routes.put("login", ARouter$$Group$$login.class);
}
}
/**
* DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE!!! IT WAS GENERATED BY AROUTER. */
public class ARouter$$Group$$login implements IRouteGroup {
@Override
public void loadInto(Map<String, RouteMeta> atlas) {
atlas.put("/login/LoginActivity", RouteMeta.build(RouteType.ACTIVITY, LoginActivity.class, "/login/loginactivity", "login", new java.util.HashMap<String, Integer>(){{put("key1", 4); put("key2", 8); put("data", 9); }}, -1, -2147483648));
}
}
于是我们从中看到,RouteMeta元信息包含了具体如下的信息
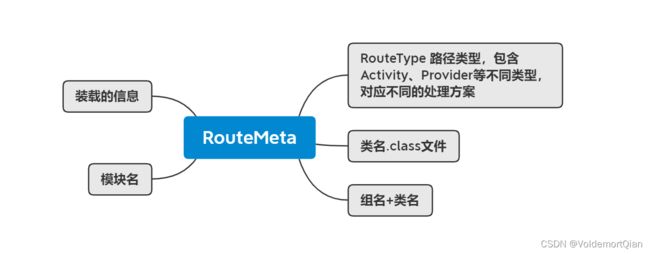
这部分信息最终被放入WareHouse中作为路由信息进行维护
拦截器初始化
static void afterInit() {
// Trigger interceptor init, use byName.
interceptorService = (InterceptorService) ARouter.getInstance().build("/ARouter/service/interceptor").navigation();
}
来看看具体的初始化工作
@Override
public void init(final Context context) {
LogisticsCenter.executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (MapUtils.isNotEmpty(Warehouse.interceptorsIndex)) {
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Class<? extends IInterceptor>> entry : Warehouse.interceptorsIndex.entrySet()) {
Class<? extends IInterceptor> interceptorClass = entry.getValue();
try {
IInterceptor iInterceptor = interceptorClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
iInterceptor.init(context);
Warehouse.interceptors.add(iInterceptor);
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new HandlerException(TAG + "ARouter init interceptor error! name = [" + interceptorClass.getName() + "], reason = [" + ex.getMessage() + "]");
}
}
interceptorHasInit = true;
logger.info(TAG, "ARouter interceptors init over.");
synchronized (interceptorInitLock) {
interceptorInitLock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
});
}
这一部分代码告诉我们,该初始化代码从拦截器路由信息索引里面加载并实例化了所有拦截器。然后通知等待的拦截器开始拦截。
所以我们不妨进行一番总结,初始化ARouter的流程如下
- 初始化上下文、日志打印、Handler、消息中转中心
- 在消息中转中心中加载路由映射表,新建时,获取指定包名下的类文件,并放置到RouteMap中,而后将其中的对应的RouteMeta数据存入到WareHouse中;新建完成后将路由表放入SharedPerfence缓存中,当有新版本发布或者debug时重新生成路由表,反之直接从缓存中读取路由表
- 对WareHouse中的加载并实例化所有的拦截器,并通知等待的拦截器开始进行拦截
三、跳转解析
跳转
完成了上述的阅读后,我们继续阅读ARouter的源码,我们从最简单的跳转函数入口开始解析
ARouter.getInstance().build("/test/activity").navigation();
当我们调用build()方法时,调用的源码如下
public Postcard build(String path) {
return _ARouter.getInstance().build(path);
}
//调用_ARouter的build方法
protected Postcard build(String path) {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(path)) {
throw new HandlerException(Consts.TAG + "Parameter is invalid!");
} else {
PathReplaceService pService = ARouter.getInstance().navigation(PathReplaceService.class);
if (null != pService) {
path = pService.forString(path);
}
return build(path, extractGroup(path), true);
}
}
//extractGroup(path)方法
/**
* Extract the default group from path.
*/
private String extractGroup(String path) {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(path) || !path.startsWith("/")) {
throw new HandlerException(Consts.TAG + "Extract the default group failed, the path must be start with '/' and contain more than 2 '/'!");
}
try {
String defaultGroup = path.substring(1, path.indexOf("/", 1));
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(defaultGroup)) {
throw new HandlerException(Consts.TAG + "Extract the default group failed! There's nothing between 2 '/'!");
} else {
return defaultGroup;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warning(Consts.TAG, "Failed to extract default group! " + e.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
//传入参数调用的build方法
/**
* Build postcard by path and group
*/
protected Postcard build(String path, String group, Boolean afterReplace) {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(path) || TextUtils.isEmpty(group)) {
throw new HandlerException(Consts.TAG + "Parameter is invalid!");
} else {
if (!afterReplace) {
PathReplaceService pService = ARouter.getInstance().navigation(PathReplaceService.class);
if (null != pService) {
path = pService.forString(path);
}
}
return new Postcard(path, group);//构造PostCard对象
}
}
//其中用到的navigation部分
public <T> T navigation(Class<? extends T> service) {
return _ARouter.getInstance().navigation(service);
}
protected <T> T navigation(Class<? extends T> service) {
try {
Postcard postcard = LogisticsCenter.buildProvider(service.getName());
// Compatible 1.0.5 compiler sdk.
// Earlier versions did not use the fully qualified name to get the service
if (null == postcard) {
// No service, or this service in old version.
postcard = LogisticsCenter.buildProvider(service.getSimpleName());
}
if (null == postcard) {
return null;
}
LogisticsCenter.completion(postcard);
return (T) postcard.getProvider();
} catch (NoRouteFoundException ex) {
logger.warning(Consts.TAG, ex.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
从上面的源码,我们可以阅读出大致的Build过程如下
- 先调用PathReplaceService和相关方法进行预处理方法生成path和Group两个参数,调用Build()含参方法,生成PostCard对象
return new Postcard(path, group);//构造PostCard对象
如此,便初步生成了Postcard对象,注意这里是初步生成Postcard对象,Postcard对象的信息在这里并不完成,需要调用LogisticsCenter中的方法完善Postcard相关信息,关于LogisticsCenter可以看上一部分的介绍
-下面是navigation()部分,
protected Object navigation(final Context context, final Postcard postcard, final int requestCode, final NavigationCallback callback) {
///1.自定义预处理代码
PretreatmentService pretreatmentService = ARouter.getInstance().navigation(PretreatmentService.class);
if (null != pretreatmentService && !pretreatmentService.onPretreatment(context, postcard)) {
// 预处理拦截了 返回
return null;
}
// 设置context
postcard.setContext(null == context ? mContext : context);
try {
///2.通过路由信息,找到对应的路由信息 RouteMeta ,根据路由类型 RouteType
///完善posrcard
LogisticsCenter.completion(postcard);
} catch (NoRouteFoundException ex) {
///... 省略异常日志和弹窗展示。以及相关回调方法
///值得一提的是走了 DegradeService 的自定义丢失回调
}
if (null != callback) {
callback.onFound(postcard);
}
///3.如果不是绿色通道,需要走拦截器:InterceptorServiceImpl
if (!postcard.isGreenChannel()) { // It must be run in async thread, maybe interceptor cost too mush time made ANR.
interceptorService.doInterceptions(postcard, new InterceptorCallback() {
@Override
public void onContinue(Postcard postcard) {
///4.继续导航方法
_navigation(postcard, requestCode, callback);
}
@Override
public void onInterrupt(Throwable exception) {
///省略拦截后的一些代码
}
});
} else {
///4.继续导航方法
return _navigation(postcard, requestCode, callback);
}
return null;
}
这部分的思路如下
- 有自定义预处理导航部分逻辑,则进行预处理和拦截
- 完善前面生成的Postcard逻辑,通过path路径找到对应的routemeta路由信息,用该信息完善postcard对象(LogisticsCenter.completion方法中完成,细节后文分析,包括postcard中的type等属性
- 如果不是绿色通道,需要走拦截器:InterceptorServiceImpl。该拦截器服务类中完成拦截器一一执行。(2的源码细节可知,PROVIDER和FRAGMENT类型是绿色通道)
- 继续导航方法,调用_navigation。
_navigation部分的源码如下:
private Object _navigation(final Postcard postcard, final int requestCode, final NavigationCallback callback) {
final Context currentContext = postcard.getContext();
switch (postcard.getType()) {
case ACTIVITY:
// Build intent
final Intent intent = new Intent(currentContext, postcard.getDestination());
//...省略完善intent代码
// Navigation in main looper.
runInMainThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
startActivity(requestCode, currentContext, intent, postcard, callback);
}
});
break;
case PROVIDER:
return postcard.getProvider();
case BOARDCAST:
case CONTENT_PROVIDER:
case FRAGMENT:
Class<?> fragmentMeta = postcard.getDestination();
try {
Object instance = fragmentMeta.getConstructor().newInstance();
if (instance instanceof Fragment) {
((Fragment) instance).setArguments(postcard.getExtras());
} else if (instance instanceof android.support.v4.app.Fragment) {
((android.support.v4.app.Fragment) instance).setArguments(postcard.getExtras());
}
return instance;
} catch (Exception ex) {
logger.error(Consts.TAG, "Fetch fragment instance error, " + TextUtils.formatStackTrace(ex.getStackTrace()));
}
case METHOD:
case SERVICE:
default:
return null;
}
return null;
}
这一部分处理的逻辑如下:
- *ACTIVITY:*新建Intent ,通过postcard信息,完善intent走context.startActivity或者 context.startActivityForResult。
- PROVIDER:==postcard.getProvider()==获取provider实例(实例化代码在 LogisticsCenter.completion)
- FRAGMENT,BOARDCAST,CONTENT_PROVIDER:routeMeta.getConstructor().newInstance() 通过路由信息实例化出实例,如果是Fragment的话,则另外再设置extras信息。
- *METHOD,SERVICE:*返回空,啥也不做。说明该类型路由调用navigation没啥意义。
看到这里,对于Activity 的路由跳转就很直观了,就是调用了startActivity 或者 startActivityForResult 方法,其他provider fragment等实例的获取也十分得清晰明了了
接下来介绍LogisticsCenter.completion()方法用于补全postCard相关信息
完善postcard信息代码是通过LogisticsCenter.completion 方法完成的
/**
* 通过RouteMate 完善 postcard
* @param postcard Incomplete postcard, should complete by this method.
*/
public synchronized static void completion(Postcard postcard) {
//省略空判断
RouteMeta routeMeta = Warehouse.routes.get(postcard.getPath());
if (null == routeMeta) {
// 如果路由的组group没有找到,直接抛异常
if (!Warehouse.groupsIndex.containsKey(postcard.getGroup())) {
throw new NoRouteFoundException(TAG + "There is no route match the path [" + postcard.getPath() + "], in group [" + postcard.getGroup() + "]");
} else {
//...省略一些日志代码
// 1.动态添加组元素(从groupsIndex 中找到对应 IRouteGroup的生成类,再对组元素进行加载)
addRouteGroupDynamic(postcard.getGroup(), null);
completion(postcard); // Reload
}
} else {
postcard.setDestination(routeMeta.getDestination());
postcard.setType(routeMeta.getType());
postcard.setPriority(routeMeta.getPriority());
postcard.setExtra(routeMeta.getExtra());
Uri rawUri = postcard.getUri();
///2.如果有uri 信息,解析uri相关参数。解析出AutoWired的参数的值
if (null != rawUri) { // Try to set params into bundle.
Map<String, String> resultMap = TextUtils.splitQueryParameters(rawUri);
Map<String, Integer> paramsType = routeMeta.getParamsType();
if (MapUtils.isNotEmpty(paramsType)) {
// Set value by its type, just for params which annotation by @Param
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> params : paramsType.entrySet()) {
setValue(postcard,
params.getValue(),
params.getKey(),
resultMap.get(params.getKey()));
}
// Save params name which need auto inject.
postcard.getExtras().putStringArray(ARouter.AUTO_INJECT, paramsType.keySet().toArray(new String[]{}));
}
// Save raw uri
postcard.withString(ARouter.RAW_URI, rawUri.toString());
}
///3.获取provider实例,如果初始获取,初始化该provider, 最后赋值给postcard
switch (routeMeta.getType()) {
case PROVIDER: // if the route is provider, should find its instance
// Its provider, so it must implement IProvider
Class<? extends IProvider> providerMeta = (Class<? extends IProvider>) routeMeta.getDestination();
IProvider instance = Warehouse.providers.get(providerMeta);
if (null == instance) { // There's no instance of this provider
IProvider provider;
try {
provider = providerMeta.getConstructor().newInstance();
provider.init(mContext);
Warehouse.providers.put(providerMeta, provider);
instance = provider;
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(TAG, "Init provider failed!", e);
throw new HandlerException("Init provider failed!");
}
}
postcard.setProvider(instance);
postcard.greenChannel(); // Provider should skip all of interceptors
break;
case FRAGMENT:
postcard.greenChannel(); // Fragment needn't interceptors
default:
break;
}
}
}
总结
以上便是关于ARouter的源码阅读,如有理解不对的地方,欢迎指正