信号采样基本概念 —— 7.数模转换(DAC & ADC)
文章目录
- 数字转模拟(DAC)
-
- 一个简单的数字转模拟方案
- 模拟转数字(ADC)
数字转模拟(DAC)
通常来说,我们在设备上存储的数据是以二进制进行传输的,但是当我们试图将数据传输到更远的地方时,或者通过一些其他介质,例如WI-FI、蓝牙,同轴电缆、或者其他无线电信号进行远距离传输的时候,我们就需要把数据转化为模拟信号进行传输。
常见的数模转换,例如对于一个8bit的数据来说,我们可以通过把电势划分成8个不同的等级来代表每一个位,如果一个位为1,那么对应的电势就会被调高,而如果为0,则对应的电势会被调低。
一个简单的数字转模拟方案
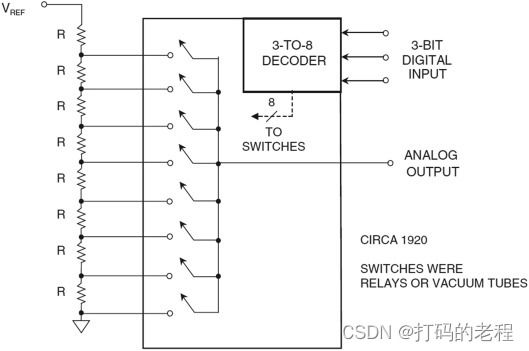
数模转换最常见的方案是通过数模转换芯片来完成信号的转换。比方说德仪的PCM1808就是这样一款数模转换芯片。

通过6,7,8,9引脚分别输入数字信号和时钟输入,就可以在13和14引脚得到其对应的模拟信号。一般来说,其实现数模转换通过类似电压串联来实现。就像下面这样的示例
所以,我们可以根据这样的原理,写出它对应的数学表达式,例如对于4位的DAC,就可以表示如下:
V o u t = b 3 × V r e f × 8 16 + b 2 × V r e f × 4 16 + b 1 × V r e f × 2 16 + b 0 × V r e f × 1 16 V_{out} = b_3 \times V_{ref} \times \frac{8}{16} + b_2 \times V_{ref} \times \frac{4}{16} + b_1 \times V_{ref} \times \frac{2}{16} + b_0 \times V_{ref} \times \frac{1}{16} Vout=b3×Vref×168+b2×Vref×164+b1×Vref×162+b0×Vref×161
所以自然的,可以得到一个简单的数模转换代码
def dac_output(binary_input, V_ref):
"""
Calculate the output of a 4-bit DAC for a given binary input.
:param binary_input: A string of 4 bits, e.g., "1010".
:param V_ref: Reference voltage of the DAC.
:return: Analog output voltage.
"""
if len(binary_input) != 4 or not set(binary_input).issubset({"0", "1"}):
raise ValueError("binary_input must be a 4-bit binary string.")
# Mapping each bit to its weighted value
weights = [8/16, 4/16, 2/16, 1/16]
V_out = sum(int(bit) * weight * V_ref for bit, weight in zip(binary_input, weights))
return V_out
# Example:
binary_input = ["1010", "0101", "1111", "0000"]
V_ref = 5.0 # Let's assume the reference voltage is 5 volts.
for b_input in binary_input:
output_voltage = dac_output(b_input, V_ref)
print(f"For binary input {b_input}, the DAC output voltage is: {output_voltage:.2f} V")
其输出结果如下:
For binary input 1010, the DAC output voltage is: 3.12 V
For binary input 0101, the DAC output voltage is: 1.56 V
For binary input 1111, the DAC output voltage is: 4.69 V
For binary input 0000, the DAC output voltage is: 0.00 V
模拟转数字(ADC)
有DAC自然就有ADC,我们自然可以得到这样的简易数学表达式
Δ V = V r e f 2 4 \Delta V = \frac{V_{ref}}{2^4} ΔV=24Vref
这样,我们就可以得到如下的代码
def adc_output(V_in, V_ref):
"""
Calculate the output of a 4-bit ADC for a given analog input voltage.
:param V_in: Input analog voltage.
:param V_ref: Reference voltage of the ADC.
:return: 4-bit binary string representation.
"""
if V_in > V_ref:
raise ValueError("Input voltage exceeds reference voltage.")
quantization_levels = 2**4
delta_V = V_ref / quantization_levels
digital_value = round(V_in / delta_V) # Use rounding here
binary_output = format(digital_value, '04b') # Convert to 4-bit binary string
return binary_output
# Example:
V_in = [3.12, 1.56, 4.69, 0.00]
V_ref = 5.0 # Reference voltage, same as before
for v in V_in:
binary_output = adc_output(v, V_ref)
print(f"For input voltage {v} V, the ADC output is: {binary_output}")
那么它的输出结果如下:
For input voltage 3.12 V, the ADC output is: 1010
For input voltage 1.56 V, the ADC output is: 0101
For input voltage 4.69 V, the ADC output is: 1111
For input voltage 0.0 V, the ADC output is: 0000