【LeetCode高频SQL50题-基础版】打卡第四天:第21~25题
文章目录
- 【LeetCode高频SQL50题-基础版】打卡第四天:第21~25题
-
- ⛅前言
- 即时食物配送II
-
- 题目
- 题解
- 游戏玩法分析IV
-
- 题目
- 题解
- 每位教师所教授的科目种类的数量
-
- 题目
- 题解
- 查询近30天活跃用户数
-
- 题目
- 题解
- 销售分析III
-
- 题目
- 题解
【LeetCode高频SQL50题-基础版】打卡第四天:第21~25题
⛅前言
在这个博客专栏中,我将为大家提供关于 LeetCode 高频 SQL 题目的基础版解析。LeetCode 是一个非常受欢迎的编程练习平台,其中的 SQL 题目涵盖了各种常见的数据库操作和查询任务。对于计算机科班出身的同学来说,SQL 是一个基础而又重要的技能。不仅在面试过程中经常会遇到 SQL 相关的考题,而且在日常的开发工作中,掌握 SQL 的能力也是必备的。
本专栏的目的是帮助读者掌握 LeetCode 上的高频 SQL 题目,并提供对每个题目的解析和解决方案。我们将重点关注那些经常出现在面试中的题目,并提供一个基础版的解法,让读者更好地理解问题的本质和解题思路。无论你是准备找工作还是提升自己的技能,在这个专栏中,你可以学习到很多关于 SQL 的实践经验和技巧,从而更加深入地理解数据库的操作和优化。
我希望通过这个专栏的分享,能够帮助读者在 SQL 的领域里取得更好的成绩和进步。如果你对这个话题感兴趣,那么就跟随我一起,开始我们的 LeetCode 高频 SQL 之旅吧!
- 博客主页:知识汲取者的博客
- LeetCode高频SQL100题专栏:LeetCode高频SQL100题_知识汲取者的博客-CSDN博客
- Gitee地址:知识汲取者 (aghp) - Gitee.com
- 题目来源:高频 SQL 50 题(基础版) - 学习计划 - 力扣(LeetCode)全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
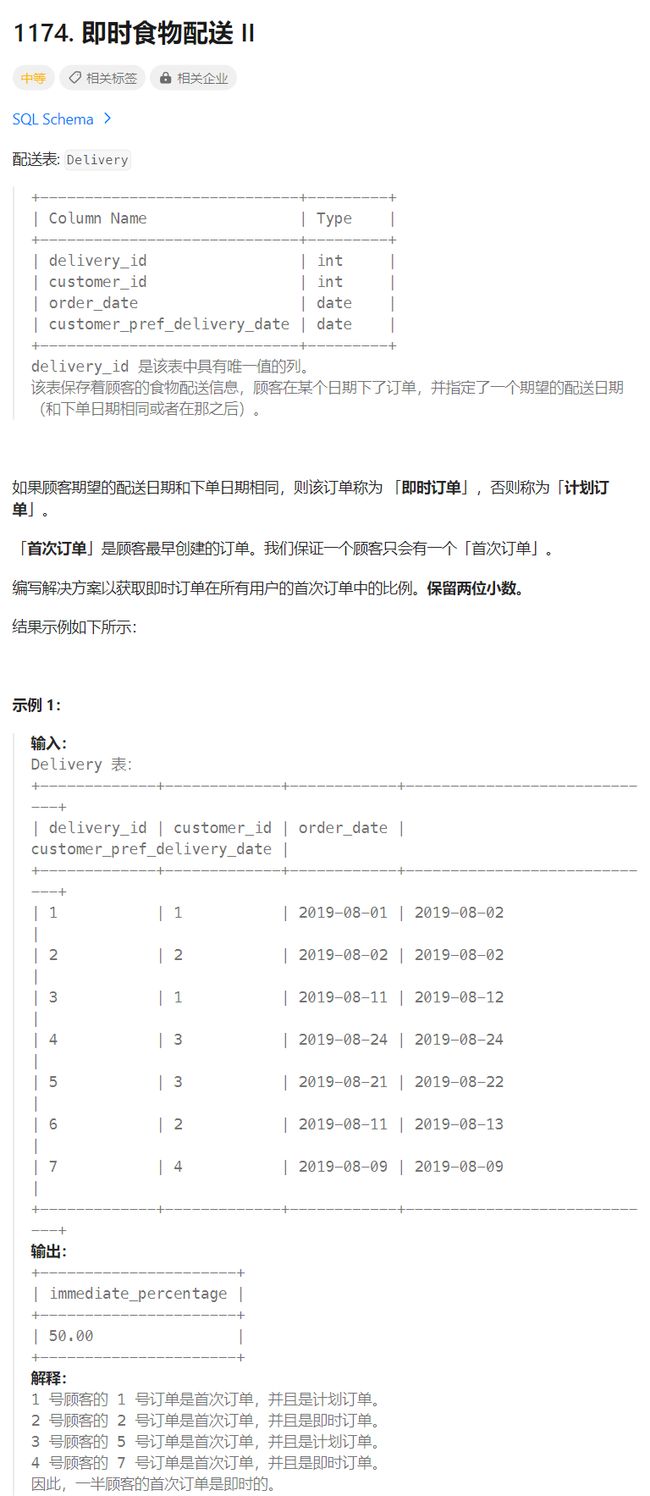
即时食物配送II
题目
题目来源:1174.即时食物配送II
题解
-
考察知识点:
子查询、min、group by、round、sum、count除了
min以外几个在之前的文章中都有介绍了-
min(column_name):返回不同列值当中的最小值这个一般可以搭配
group by或distinct使用,本题中是搭配 group by 进行使用
-
1)首先审题,我们明确题目是让我们查询 用户首次订单中即时订单的占比,这里需要理解首次订单和即时订单的含义,首次订单是指用户最早下的单,即时订单是指预定时间(order_date)和实际时间(customer_pref_delivery_date)相等的订单。
所以我们首先需要确定用户所有的首次订单,这里我们使用 group by 和 min 得到
select customer_id, min(order_date)
from delivery
group by customer_id;
| customer_id | min(order_date) |
| ----------- | --------------- |
| 1 | 2019-08-01 |
| 2 | 2019-08-02 |
| 3 | 2019-08-21 |
| 4 | 2019-08-09 |
2)只要我们得到上面那张表,后面操作起来就简单多了。
上面那张表就是用户第一次下单的记录,我们需要利用子查询过滤出第一次查询的记录,这里选择使用 in,这个in是两列同时满足才成立,这样就能够过滤出首次用户下单的记录了
select round(sum(order_date = customer_pref_delivery_date)*100 / count(*), 2) immediate_percentage
from Delivery
where (customer_id, order_date) in (
select customer_id, min(order_date)
from delivery
group by customer_id
);
当然还有一种写法,利用avg函数计算比率
select round(avg(order_date = customer_pref_delivery_date)*100, 2) immediate_percentage
from Delivery
where (customer_id, order_date) in (
select customer_id, min(order_date)
from delivery
group by customer_id
);
游戏玩法分析IV
题目
题目来源:550.游戏玩法分析IV
题解
-
考察知识点:
子查询、min、round、avg、group by、左连接、datediffdatediff(date_1, date_2):计算 date_1 - date_2 的插值
其它的知识点在之前的文章中都有详细讲过,这里就不再过多赘述了
1)审题,我们是要计算第一天登录之后第二天也登陆的人数占总人数的比例,所以我们首先要确定第一天登录的人数是多少,同时需要指导第一天登录的日期,按照下方的SQL,我们可以得到第一天登录的人数有哪些
select player_id, min(event_date) first_time
from Activity
group by player_id
当然这里也可以使用distinct,关于两者的比较可以看这篇文章:SQL去重是用DISTINCT好,还是GROUP BY好? - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
| player_id | first_time |
| --------- | ---------- |
| 1 | 2016-03-01 |
| 2 | 2017-06-25 |
| 3 | 2016-03-02 |
2)现在我们得到首次查询时间,我们只需要进行应该左连接,同时利用datediff函数来获取第一天登录用户第二天的登录情况
select *
from (
select player_id, min(event_date) first_time
from Activity
group by player_id
) l
left join Activity r
on l.player_id = r.player_id and datediff(r.event_date, l.first_time) = 1;
| player_id | first_time | player_id | device_id | event_date | games_played |
| --------- | ---------- | --------- | --------- | ---------- | ------------ |
| 1 | 2016-03-01 | 1 | 2 | 2016-03-02 | 6 |
| 2 | 2017-06-25 | null | null | null | null |
| 3 | 2016-03-02 | null | null | null | null |
3)上面的查询我们可以通过 r.event_data 来判断第二天的登录情况,现在我们需要基于上表进行应该计算统计
select round(avg(r.event_date is not null), 2) fraction
from (
select player_id, min(event_date) first_time
from Activity
group by player_id
) l
left join Activity r
on l.player_id = r.player_id and datediff(r.event_date, l.first_time) = 1;
当然还有一种写法,但是性能是没有上面那一种快,毕竟计算量增大了,不信的可以使用 explain 测试一下
select round(sum(if(r.event_date is not null, 1, 0)) / count(*), 2) fraction
from (
select player_id, min(event_date) first_time
from Activity
group by player_id
) l
left join Activity r
on l.player_id = r.player_id and datediff(r.event_date, l.first_time) = 1;
看这这个SQL挺复杂的,是否还有一种更简洁的写法呢?比如说不使用子查询?
这里提供一种扣友的答案:
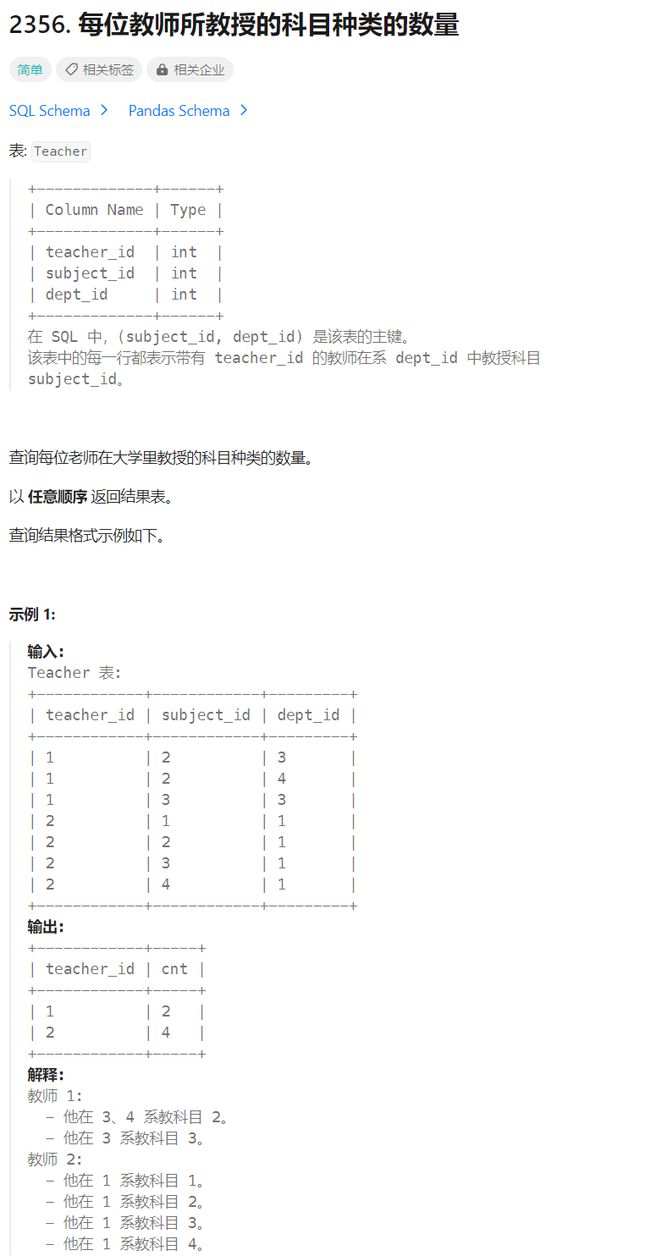
每位教师所教授的科目种类的数量
题目
题目来源:2356.每位教师所教授的科目种类的数量
题解
- 考察知识点:
group by、count、distinct
select teacher_id, count(distinct subject_id) cnt
from Teacher
group by teacher_id;
查询近30天活跃用户数
题目
题目来源:1141.查询近30天活跃用户数
题解
- 考察知识点:
count、distinct、datediff、group by
select activity_date day, count(distinct user_id) active_users
from Activity
where datediff('2019-07-27', activity_date) >= 0 and datediff('2019-07-27', activity_date) < 30
group by activity_date;
当然还可以这样写:
select activity_date day, count(distinct user_id) active_users
from Activity
where date_add(activity_date, interval 29 day)>='2019-07-27' and activity_date<='2019-07-27'
group by activity_date;
还可以这样写(这种写法性能更高):
select activity_date day, count(distinct user_id) active_users
from Activity
where activity_date between '2019-06-28' and '2019-07-27'
group by activity_date;
销售分析III
题目
题目来源:1084.销售分析III
题解
- 考察知识点:
between and、left join、min、max
1)要实现效果,需要先使用左连接
select s.product_id, p.product_name
from Product p left join Sales s on p.product_id = s.product_id
where sale_date between '2019-01-01' and '2019-03-31';
| product_id | product_name |
| ---------- | ------------ |
| 1 | S8 |
| 2 | G4 |
2)可以看到,上表中多出了product_id为2的一列,这是因为我们还没有确保当前产品是否全部在时间段内,所以还需要进行一个过滤。
我的想法是直接利用子查询查询出所有满足的product_id,然后利用 in 进行一个过滤
select product_id
from Sales
group by product_id
having min(sale_date) >= '2019-01-01' and max(sale_date) <= '2019-03-31';
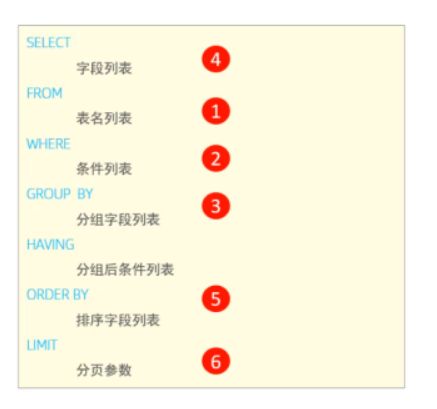
执行报如下错误,这是因为MySQL中where条件中不能使用聚合函数,这和MySQL的解析执行过程有关
You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'where min(sale_date) >= '2019-01-01' and max(sale_date) <= '2019-03-31';
# SELE' at line 15
进行修改,将聚合函数放到 having 中(只要聚合函数在④也就是select执行条件后面,都是可以的)
select product_id
from Sales
group by product_id
having min(sale_date) >= '2019-01-01' and max(sale_date) <= '2019-03-31';
| product_id |
| ---------- |
| 1 |
最终的结果
select s.product_id , p.product_name
from Sales s left join Product p on s.product_id = p.product_id
group by s.product_id
having min(sale_date) >= '2019-01-01' and max(sale_date) <= '2019-03-31';