selinux源码分析
首先来一幅lsm的逻辑图:

上幅图来至:Linux Security Module Framework一文,很清晰的描述了LSM的逻辑,从用户空间到系统调用再到selinux模块接口。
selinux驱动模块位置:
\linux-4.5-rc1\security
1.selinux核心驱动的加载
1)selinux文件节点的创建:
在selinuxfs.c文件中,__initcall(init_sel_fs)驱动模块的加载,会注册文件节点。这些节点作为内核与用户空间通信的接口。其核心API调用顺序为:
init_sel_fs->register_filesystem->sel_mount->sel_fill_super
在sel_fill_super函数中定义了一个结构体数组:
static struct tree_descr selinux_files[] = {
[SEL_LOAD] = {"load", &sel_load_ops, S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR},
[SEL_ENFORCE] = {"enforce", &sel_enforce_ops, S_IRUGO|S_IWUSR},
[SEL_CONTEXT] = {"context", &transaction_ops, S_IRUGO|S_IWUGO},
[SEL_ACCESS] = {"access", &transaction_ops, S_IRUGO|S_IWUGO},
[SEL_CREATE] = {"create", &transaction_ops, S_IRUGO|S_IWUGO},
[SEL_RELABEL] = {"relabel", &transaction_ops, S_IRUGO|S_IWUGO},
[SEL_USER] = {"user", &transaction_ops, S_IRUGO|S_IWUGO},
[SEL_POLICYVERS] = {"policyvers", &sel_policyvers_ops, S_IRUGO},
[SEL_COMMIT_BOOLS] = {"commit_pending_bools", &sel_commit_bools_ops, S_IWUSR},
[SEL_MLS] = {"mls", &sel_mls_ops, S_IRUGO},
[SEL_DISABLE] = {"disable", &sel_disable_ops, S_IWUSR},
[SEL_MEMBER] = {"member", &transaction_ops, S_IRUGO|S_IWUGO},
[SEL_CHECKREQPROT] = {"checkreqprot", &sel_checkreqprot_ops, S_IRUGO|S_IWUSR},
[SEL_REJECT_UNKNOWN] = {"reject_unknown", &sel_handle_unknown_ops, S_IRUGO},
[SEL_DENY_UNKNOWN] = {"deny_unknown", &sel_handle_unknown_ops, S_IRUGO},
[SEL_STATUS] = {"status", &sel_handle_status_ops, S_IRUGO},
[SEL_POLICY] = {"policy", &sel_policy_ops, S_IRUGO},
[SEL_VALIDATE_TRANS] = {"validatetrans", &sel_transition_ops,
S_IWUGO},
/* last one */ {""}
};
会根据上面的结构体数组,生成相应的文件节点。节点位置位于:
sys/fs/selinux/ 目录下
2)hooks驱动的加载
hook是处理各种操作check的核心地方,驱动加载调用顺序
security_initcall(selinux_init)->security_add_hooks
结构体数据selinux_hooks,定义了各种操作的入口函数:
static struct security_hook_list selinux_hooks[] = {
LSM_HOOK_INIT(binder_set_context_mgr, selinux_binder_set_context_mgr),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(binder_transaction, selinux_binder_transaction),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(binder_transfer_binder, selinux_binder_transfer_binder),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(binder_transfer_file, selinux_binder_transfer_file),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(ptrace_access_check, selinux_ptrace_access_check),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(ptrace_traceme, selinux_ptrace_traceme),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(capget, selinux_capget),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(capset, selinux_capset),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(capable, selinux_capable),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(quotactl, selinux_quotactl),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(quota_on, selinux_quota_on),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(syslog, selinux_syslog),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(vm_enough_memory, selinux_vm_enough_memory),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(netlink_send, selinux_netlink_send),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(bprm_set_creds, selinux_bprm_set_creds),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(bprm_committing_creds, selinux_bprm_committing_creds),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(bprm_committed_creds, selinux_bprm_committed_creds),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(bprm_secureexec, selinux_bprm_secureexec),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sb_alloc_security, selinux_sb_alloc_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sb_free_security, selinux_sb_free_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sb_copy_data, selinux_sb_copy_data),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sb_remount, selinux_sb_remount),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sb_kern_mount, selinux_sb_kern_mount),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sb_show_options, selinux_sb_show_options),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sb_statfs, selinux_sb_statfs),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sb_mount, selinux_mount),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sb_umount, selinux_umount),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sb_set_mnt_opts, selinux_set_mnt_opts),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sb_clone_mnt_opts, selinux_sb_clone_mnt_opts),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sb_parse_opts_str, selinux_parse_opts_str),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(dentry_init_security, selinux_dentry_init_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_alloc_security, selinux_inode_alloc_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_free_security, selinux_inode_free_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_init_security, selinux_inode_init_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_create, selinux_inode_create),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_link, selinux_inode_link),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_unlink, selinux_inode_unlink),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_symlink, selinux_inode_symlink),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_mkdir, selinux_inode_mkdir),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_rmdir, selinux_inode_rmdir),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_mknod, selinux_inode_mknod),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_rename, selinux_inode_rename),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_readlink, selinux_inode_readlink),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_follow_link, selinux_inode_follow_link),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_permission, selinux_inode_permission),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_setattr, selinux_inode_setattr),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_getattr, selinux_inode_getattr),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_setxattr, selinux_inode_setxattr),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_post_setxattr, selinux_inode_post_setxattr),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_getxattr, selinux_inode_getxattr),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_listxattr, selinux_inode_listxattr),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_removexattr, selinux_inode_removexattr),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_getsecurity, selinux_inode_getsecurity),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_setsecurity, selinux_inode_setsecurity),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_listsecurity, selinux_inode_listsecurity),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_getsecid, selinux_inode_getsecid),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(file_permission, selinux_file_permission),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(file_alloc_security, selinux_file_alloc_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(file_free_security, selinux_file_free_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(file_ioctl, selinux_file_ioctl),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(mmap_file, selinux_mmap_file),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(mmap_addr, selinux_mmap_addr),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(file_mprotect, selinux_file_mprotect),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(file_lock, selinux_file_lock),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(file_fcntl, selinux_file_fcntl),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(file_set_fowner, selinux_file_set_fowner),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(file_send_sigiotask, selinux_file_send_sigiotask),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(file_receive, selinux_file_receive),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(file_open, selinux_file_open),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_create, selinux_task_create),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(cred_alloc_blank, selinux_cred_alloc_blank),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(cred_free, selinux_cred_free),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(cred_prepare, selinux_cred_prepare),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(cred_transfer, selinux_cred_transfer),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(kernel_act_as, selinux_kernel_act_as),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(kernel_create_files_as, selinux_kernel_create_files_as),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(kernel_module_request, selinux_kernel_module_request),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_setpgid, selinux_task_setpgid),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_getpgid, selinux_task_getpgid),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_getsid, selinux_task_getsid),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_getsecid, selinux_task_getsecid),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_setnice, selinux_task_setnice),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_setioprio, selinux_task_setioprio),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_getioprio, selinux_task_getioprio),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_setrlimit, selinux_task_setrlimit),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_setscheduler, selinux_task_setscheduler),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_getscheduler, selinux_task_getscheduler),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_movememory, selinux_task_movememory),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_kill, selinux_task_kill),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_wait, selinux_task_wait),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(task_to_inode, selinux_task_to_inode),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(ipc_permission, selinux_ipc_permission),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(ipc_getsecid, selinux_ipc_getsecid),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(msg_msg_alloc_security, selinux_msg_msg_alloc_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(msg_msg_free_security, selinux_msg_msg_free_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(msg_queue_alloc_security,
selinux_msg_queue_alloc_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(msg_queue_free_security, selinux_msg_queue_free_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(msg_queue_associate, selinux_msg_queue_associate),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(msg_queue_msgctl, selinux_msg_queue_msgctl),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(msg_queue_msgsnd, selinux_msg_queue_msgsnd),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(msg_queue_msgrcv, selinux_msg_queue_msgrcv),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(shm_alloc_security, selinux_shm_alloc_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(shm_free_security, selinux_shm_free_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(shm_associate, selinux_shm_associate),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(shm_shmctl, selinux_shm_shmctl),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(shm_shmat, selinux_shm_shmat),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sem_alloc_security, selinux_sem_alloc_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sem_free_security, selinux_sem_free_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sem_associate, selinux_sem_associate),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sem_semctl, selinux_sem_semctl),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sem_semop, selinux_sem_semop),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(d_instantiate, selinux_d_instantiate),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(getprocattr, selinux_getprocattr),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(setprocattr, selinux_setprocattr),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(ismaclabel, selinux_ismaclabel),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(secid_to_secctx, selinux_secid_to_secctx),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(secctx_to_secid, selinux_secctx_to_secid),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(release_secctx, selinux_release_secctx),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_invalidate_secctx, selinux_inode_invalidate_secctx),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_notifysecctx, selinux_inode_notifysecctx),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_setsecctx, selinux_inode_setsecctx),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inode_getsecctx, selinux_inode_getsecctx),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(unix_stream_connect, selinux_socket_unix_stream_connect),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(unix_may_send, selinux_socket_unix_may_send),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_create, selinux_socket_create),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_post_create, selinux_socket_post_create),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_bind, selinux_socket_bind),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_connect, selinux_socket_connect),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_listen, selinux_socket_listen),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_accept, selinux_socket_accept),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_sendmsg, selinux_socket_sendmsg),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_recvmsg, selinux_socket_recvmsg),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_getsockname, selinux_socket_getsockname),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_getpeername, selinux_socket_getpeername),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_getsockopt, selinux_socket_getsockopt),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_setsockopt, selinux_socket_setsockopt),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_shutdown, selinux_socket_shutdown),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_sock_rcv_skb, selinux_socket_sock_rcv_skb),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_getpeersec_stream,
selinux_socket_getpeersec_stream),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_getpeersec_dgram, selinux_socket_getpeersec_dgram),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sk_alloc_security, selinux_sk_alloc_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sk_free_security, selinux_sk_free_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sk_clone_security, selinux_sk_clone_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sk_getsecid, selinux_sk_getsecid),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(sock_graft, selinux_sock_graft),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inet_conn_request, selinux_inet_conn_request),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inet_csk_clone, selinux_inet_csk_clone),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(inet_conn_established, selinux_inet_conn_established),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(secmark_relabel_packet, selinux_secmark_relabel_packet),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(secmark_refcount_inc, selinux_secmark_refcount_inc),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(secmark_refcount_dec, selinux_secmark_refcount_dec),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(req_classify_flow, selinux_req_classify_flow),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(tun_dev_alloc_security, selinux_tun_dev_alloc_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(tun_dev_free_security, selinux_tun_dev_free_security),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(tun_dev_create, selinux_tun_dev_create),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(tun_dev_attach_queue, selinux_tun_dev_attach_queue),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(tun_dev_attach, selinux_tun_dev_attach),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(tun_dev_open, selinux_tun_dev_open),
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY_NETWORK_XFRM
LSM_HOOK_INIT(xfrm_policy_alloc_security, selinux_xfrm_policy_alloc),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(xfrm_policy_clone_security, selinux_xfrm_policy_clone),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(xfrm_policy_free_security, selinux_xfrm_policy_free),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(xfrm_policy_delete_security, selinux_xfrm_policy_delete),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(xfrm_state_alloc, selinux_xfrm_state_alloc),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(xfrm_state_alloc_acquire,
selinux_xfrm_state_alloc_acquire),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(xfrm_state_free_security, selinux_xfrm_state_free),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(xfrm_state_delete_security, selinux_xfrm_state_delete),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(xfrm_policy_lookup, selinux_xfrm_policy_lookup),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(xfrm_state_pol_flow_match,
selinux_xfrm_state_pol_flow_match),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(xfrm_decode_session, selinux_xfrm_decode_session),
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_KEYS
LSM_HOOK_INIT(key_alloc, selinux_key_alloc),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(key_free, selinux_key_free),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(key_permission, selinux_key_permission),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(key_getsecurity, selinux_key_getsecurity),
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_AUDIT
LSM_HOOK_INIT(audit_rule_init, selinux_audit_rule_init),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(audit_rule_known, selinux_audit_rule_known),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(audit_rule_match, selinux_audit_rule_match),
LSM_HOOK_INIT(audit_rule_free, selinux_audit_rule_free),
#endif
};
我们来看看LSM_HOOK_INIT这个的宏定义:
#define LSM_HOOK_INIT(HEAD, HOOK) \
{ .head = &security_hook_heads.HEAD, .hook = { .HEAD = HOOK } }
extern struct security_hook_heads security_hook_heads;
用LSM_HOOK_INIT(file_open, selinux_file_open)这个来看看上面的宏定义是干什么的:
{.head=&security_hook_heads.file_open,
.hook={.file_open=selinux_file_open}}
结合security_hook_list的定义就很清楚了,就是定义了各种check的接口。
2policy te镜像文件的加载
通过sys/fs/selinux/load 节点调用,写入te二进制镜像数据
代码截图如下:

其核心就是通过security_load_policy接口,对用户空间传进来的te镜像文件进行解析并加载。

上面截图,有三个重要的接口调用:
1.从传入的镜像数据中根本固定的语法格式,解析数据。具体代码,大家可以自行研究,这里不过多解读
2.对读取的数据进行检查,有可能写入的客体和权限是不支持的
3.根据读取的数据,加载安全上下文 sidtab
对于第二步,这里是和用户空间打交道最多的地方,secclass_map包含了所有系统能支持的客体和操作请求类型
3secclass_map的定义
在文件security\selinux\include\classmap.h
#define COMMON_FILE_SOCK_PERMS "ioctl", "read", "write", "create", \
"getattr", "setattr", "lock", "relabelfrom", "relabelto", "append"
#define COMMON_FILE_PERMS COMMON_FILE_SOCK_PERMS, "unlink", "link", \
"rename", "execute", "quotaon", "mounton", "audit_access", \
"open", "execmod"
#define COMMON_SOCK_PERMS COMMON_FILE_SOCK_PERMS, "bind", "connect", \
"listen", "accept", "getopt", "setopt", "shutdown", "recvfrom", \
"sendto", "name_bind"
#define COMMON_IPC_PERMS "create", "destroy", "getattr", "setattr", "read", \
"write", "associate", "unix_read", "unix_write"
/*
* Note: The name for any socket class should be suffixed by "socket",
* and doesn't contain more than one substr of "socket".
*/
struct security_class_mapping secclass_map[] = {
{ "security",
{ "compute_av", "compute_create", "compute_member",
"check_context", "load_policy", "compute_relabel",
"compute_user", "setenforce", "setbool", "setsecparam",
"setcheckreqprot", "read_policy", "validate_trans", NULL } },
{ "process",
{ "fork", "transition", "sigchld", "sigkill",
"sigstop", "signull", "signal", "ptrace", "getsched", "setsched",
"getsession", "getpgid", "setpgid", "getcap", "setcap", "share",
"getattr", "setexec", "setfscreate", "noatsecure", "siginh",
"setrlimit", "rlimitinh", "dyntransition", "setcurrent",
"execmem", "execstack", "execheap", "setkeycreate",
"setsockcreate", NULL } },
{ "system",
{ "ipc_info", "syslog_read", "syslog_mod",
"syslog_console", "module_request", NULL } },
{ "capability",
{ "chown", "dac_override", "dac_read_search",
"fowner", "fsetid", "kill", "setgid", "setuid", "setpcap",
"linux_immutable", "net_bind_service", "net_broadcast",
"net_admin", "net_raw", "ipc_lock", "ipc_owner", "sys_module",
"sys_rawio", "sys_chroot", "sys_ptrace", "sys_pacct", "sys_admin",
"sys_boot", "sys_nice", "sys_resource", "sys_time",
"sys_tty_config", "mknod", "lease", "audit_write",
"audit_control", "setfcap", NULL } },
{ "filesystem",
{ "mount", "remount", "unmount", "getattr",
"relabelfrom", "relabelto", "associate", "quotamod",
"quotaget", NULL } },
{ "file",
{ COMMON_FILE_PERMS,
"execute_no_trans", "entrypoint", NULL } },
{ "dir",
{ COMMON_FILE_PERMS, "add_name", "remove_name",
"reparent", "search", "rmdir", NULL } },
{ "fd", { "use", NULL } },
{ "lnk_file",
{ COMMON_FILE_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "chr_file",
{ COMMON_FILE_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "blk_file",
{ COMMON_FILE_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "sock_file",
{ COMMON_FILE_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "fifo_file",
{ COMMON_FILE_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "tcp_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS,
"node_bind", "name_connect",
NULL } },
{ "udp_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS,
"node_bind", NULL } },
{ "rawip_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS,
"node_bind", NULL } },
{ "node",
{ "recvfrom", "sendto", NULL } },
{ "netif",
{ "ingress", "egress", NULL } },
{ "netlink_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "packet_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "key_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "unix_stream_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, "connectto", NULL } },
{ "unix_dgram_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "sem",
{ COMMON_IPC_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "msg", { "send", "receive", NULL } },
{ "msgq",
{ COMMON_IPC_PERMS, "enqueue", NULL } },
{ "shm",
{ COMMON_IPC_PERMS, "lock", NULL } },
{ "ipc",
{ COMMON_IPC_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "netlink_route_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS,
"nlmsg_read", "nlmsg_write", NULL } },
{ "netlink_tcpdiag_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS,
"nlmsg_read", "nlmsg_write", NULL } },
{ "netlink_nflog_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "netlink_xfrm_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS,
"nlmsg_read", "nlmsg_write", NULL } },
{ "netlink_selinux_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "netlink_iscsi_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "netlink_audit_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS,
"nlmsg_read", "nlmsg_write", "nlmsg_relay", "nlmsg_readpriv",
"nlmsg_tty_audit", NULL } },
{ "netlink_fib_lookup_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "netlink_connector_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "netlink_netfilter_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "netlink_dnrt_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "association",
{ "sendto", "recvfrom", "setcontext", "polmatch", NULL } },
{ "netlink_kobject_uevent_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "netlink_generic_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "netlink_scsitransport_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "netlink_rdma_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "netlink_crypto_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "appletalk_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, NULL } },
{ "packet",
{ "send", "recv", "relabelto", "forward_in", "forward_out", NULL } },
{ "key",
{ "view", "read", "write", "search", "link", "setattr", "create",
NULL } },
{ "dccp_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS,
"node_bind", "name_connect", NULL } },
{ "memprotect", { "mmap_zero", NULL } },
{ "peer", { "recv", NULL } },
{ "capability2",
{ "mac_override", "mac_admin", "syslog", "wake_alarm", "block_suspend",
"audit_read", NULL } },
{ "kernel_service", { "use_as_override", "create_files_as", NULL } },
{ "tun_socket",
{ COMMON_SOCK_PERMS, "attach_queue", NULL } },
{ "binder", { "impersonate", "call", "set_context_mgr", "transfer",
NULL } },
{ NULL }
};
可以看出secclass_map是一个结构体数组,结构体第一个成员变量是客体名字,第二个成员变量是客体能支持的请求权限字符串
struct security_class_mapping {
const char *name;
const char *perms[sizeof(u32) * 8 + 1];
};
4 打开文件权限check实例
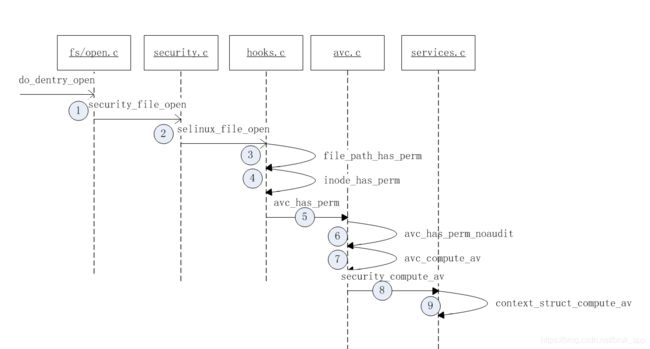
1 用户空间调用open打开某个文件,将会触发系统调用do_dentry_open,然后就开始了Open操作的权限check
在security.c文件里面包含了各种客体操作check 的入口函数,不同的check调用对应的函数,最终会指向hooks的回调函数
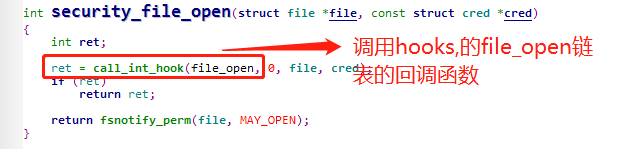
2.selinux_file_open
这个函数就是一个中转函数,重点是check av的赋值。代码如下
static inline u32 open_file_to_av(struct file *file)
{
u32 av = file_to_av(file);
if (selinux_policycap_openperm)
av |= FILE__OPEN;
return av;
}
这个FILE__OPEN和其它所有的file操作如,FILE_IOCTRL…查找了整个驱动源码没找到在什么地方定义的,真是见鬼了
3-4.
这两个函数调用,也主要是中转的。其中值得注意的是,inode是进行私有的话,就直播返回0,不再做检查。0代码许可,不为0的操作都是代码没有权限
5.avc_has_perm
看看这个函数完整的定义,包括参数和返回值的说明
/**
* avc_has_perm - Check permissions and perform any appropriate auditing.
* @ssid: source security identifier
* @tsid: target security identifier
* @tclass: target security class
* @requested: requested permissions, interpreted based on @tclass
* @auditdata: auxiliary audit data
*
* Check the AVC to determine whether the @requested permissions are granted
* for the SID pair (@ssid, @tsid), interpreting the permissions
* based on @tclass, and call the security server on a cache miss to obtain
* a new decision and add it to the cache. Audit the granting or denial of
* permissions in accordance with the policy. Return %0 if all @requested
* permissions are granted, -%EACCES if any permissions are denied, or
* another -errno upon other errors.
*/
int avc_has_perm(u32 ssid, u32 tsid, u16 tclass,
u32 requested, struct common_audit_data *auditdata)
{
struct av_decision avd;
int rc, rc2;
rc = avc_has_perm_noaudit(ssid, tsid, tclass, requested, 0, &avd);
rc2 = avc_audit(ssid, tsid, tclass, requested, &avd, rc, auditdata, 0);
if (rc2)
return rc2;
return rc;
}
其中avc_has_perm_noaudit就是开始检测权限了,而avc_audit则是根据检测的结果返回状态码,如果有权限操作则返回0,如果没有则调用slow_avc_audit,打印出各种属性。通常就是我们LOG中看到的avc报错LOG
6.avc_has_perm_noaudit

7-9是service根据安全上下文,读取policy的配置,然后将读取的结果在第6步里面与请求的操作作判断,然后返回是许可还是禁止操作。具体的代码就不再作介绍了。
