Spring 源码阅读 74:事务管理的原理 - BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 分析
本文通过对 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 类的分析,了解了 Spring 是如何通过 AOP 来完成事务的管理的,本文的内容需要你对 Spring 的 AOP 的实现原理有一定的了解。
基于 Spring Framework v5.2.6.RELEASE
概述
Spring 的事务管理基于 AOP 特性,因此,事务管理的增强逻辑需要一个 Advisor 来提供,这便是 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor,本文我们来分析它的原理。
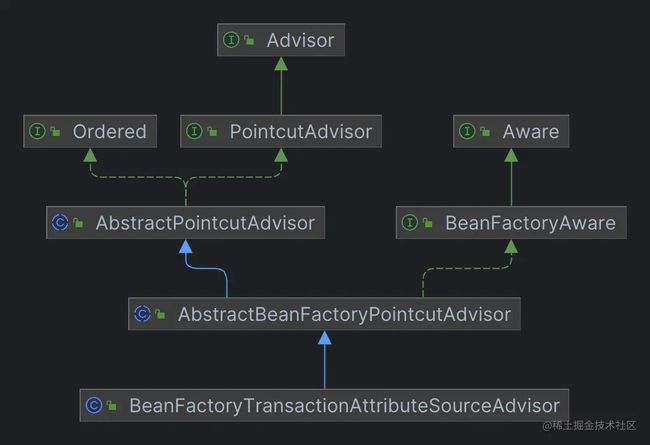
类关系
它是 PointcutAdvisor 的实现类,我们开发时配置的切面通过 Spring 解析后得到的也是一个 PointcutAdvisor,因此,它们的原理应该是相似的。所以,本文会通过以下几个方面来进行分析:
- Spring 创建它的具体过程
- 如何匹配被增强的类型
- 如何匹配被增强的方法
- 通过增强逻辑实现事务管理的具体原理
创建
它是在 Spring 解析配置的时候被创建的,以下是 ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration 中创建 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 的方法。
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
@Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor(
TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource, TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor) {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor);
if (this.enableTx != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
复制代码 方法中,通过无参构造方法创建了 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 对象,并初始化了一些属性。它并没有显式地声明构造方法,因此我们分别来看几个属性的设置。
transactionAttributeSource 属性
transactionAttributeSource 属性的值,来自方法参数,需要 Spring 来注入,这个值的来源是同一个配置类中的另外一个方法。
// org.springframework.transaction.annotation.ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration#transactionAttributeSource
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
}
复制代码其中,AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource 的构造方法如下。
public AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource() {
this(true);
}
复制代码再进入另外一个构造方法。
public AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource(boolean publicMethodsOnly) {
this.publicMethodsOnly = publicMethodsOnly;
if (jta12Present || ejb3Present) {
this.annotationParsers = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
this.annotationParsers.add(new SpringTransactionAnnotationParser());
if (jta12Present) {
this.annotationParsers.add(new JtaTransactionAnnotationParser());
}
if (ejb3Present) {
this.annotationParsers.add(new Ejb3TransactionAnnotationParser());
}
}
else {
this.annotationParsers = Collections.singleton(new SpringTransactionAnnotationParser());
}
}
复制代码AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource 的构造方法中,主要初始化了两个属性。
- publicMethodsOnly 的值,从上一段代码的方法调用
this(true)传入,它的值是true。 - annotationParsers 是一个列表,根据当前类加载器能够加载到的类型,添加不同的事物注解解析器,限于本文讨论的范围,我们只考虑 SpringTransactionAnnotationParser。
advice 属性
advice 属性的值,同样来自方法参数,它包含的是 Advisor 的增强逻辑,这里注入的值是 TransactionInterceptor 类型,来源也是用一配置类中的另一个方法。
// org.springframework.transaction.annotation.ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration#transactionInterceptor
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor(TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource) {
TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
if (this.txManager != null) {
interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
}
return interceptor;
}
复制代码它的构造方法也不包含任何逻辑,并且,注入了上一部分介绍了 transactionAttributeSource。除此之外,如果成员变量txManager不为空,则赋值给他的 transactionManager 属性。
transactionManager 是事务管理器,可以在当前配置类的父类中,找到它的来源。
TransactionManager
以下就是初始化成员变量txManager的方法。
@Autowired(required = false)
void setConfigurers(Collection configurers) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
return;
}
if (configurers.size() > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Only one TransactionManagementConfigurer may exist");
}
TransactionManagementConfigurer configurer = configurers.iterator().next();
this.txManager = configurer.annotationDrivenTransactionManager();
}
复制代码 方法添加了 @Autowired 注解,参数是 TransactionManagementConfigurer 类型的集合,Spring 会找到容器中所有的该类型的 Bean,组成一个集合,作为参数执行这个方法的逻辑。
当方法传入的集合中有且只有一个元素的时候,它的annotationDrivenTransactionManager会被执行,并将的到的结果赋值给txManager。
以下是 TransactionManagementConfigurer 接口的定义。
public interface TransactionManagementConfigurer {
TransactionManager annotationDrivenTransactionManager();
}
复制代码里面只有一个方法,返回 TransactionManager 类型的结果,一个配置类可以通过实现 TransactionManagementConfigurer 接口来自定义 TransactionManager 的创建逻辑。
pointcut 属性
除了配置方法中设置的值以外,BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 还有一个定义了初始值的属性pointcut,它表示切入点,负责匹配目标类和目标方法。
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor#pointcut
private final TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut pointcut = new TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut() {
@Override
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttributeSource getTransactionAttributeSource() {
return transactionAttributeSource;
}
};
复制代码pointcut属性的类型是 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut,并在初始化时实现了getTransactionAttributeSource方法。
进入 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 的构造方法。
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut#TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut
protected TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut() {
setClassFilter(new TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter());
}
复制代码构造方法中调用了setClassFilter方法给classFilter成员变量赋值,值是一个通过构造方法创建的 TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter 类型的实例。
TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter 是 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 的内部类,以下是它的源码。
private class TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter implements ClassFilter {
@Override
public boolean matches(Class clazz) {
if (TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ||
PlatformTransactionManager.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ||
PersistenceExceptionTranslator.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return false;
}
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.isCandidateClass(clazz));
}
}
复制代码我们都知道,在 Advisor 中,pointcut的主要作用是匹配目标类型和方法,以上的 ClassFilter 给 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 提供了一个类型匹配的具体逻辑。
在通过 Pointcut 进行目标类型和方法的匹配时,会先从 Pointcut 中获取一个 ClassFilter 或 MethodMatcher,然后通过它们的matches方法来判断。
TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 中,获取 ClassFilter 和 MethodMatcher 的方法定义在其父类 StaticMethodMatcherPointcut 中。
@Override
public ClassFilter getClassFilter() {
return this.classFilter;
}
@Override
public final MethodMatcher getMethodMatcher() {
return this;
}
复制代码其中,ClassFilter 就是在构造方法中初始化的 TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter,而 MethodMatcher 就是其自身。
下面分别来看一下,它是如何做目标类和方法的匹配的。
目标类型匹配
目标类型的匹配逻辑在 TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter 类的matches方法中。
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut.TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter#matches
@Override
public boolean matches(Class clazz) {
if (TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ||
PlatformTransactionManager.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ||
PersistenceExceptionTranslator.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return false;
}
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.isCandidateClass(clazz));
}
复制代码首先,确保目标类型不是 TransactionalProxy、PlatformTransactionManager 或者 PersistenceExceptionTranslator,然后,通过getTransactionAttributeSource方法,获取到transactionAttributeSource属性,通过他的isCandidateClass方法来判断。
// org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource#isCandidateClass
@Override
public boolean isCandidateClass(Class targetClass) {
for (TransactionAnnotationParser parser : this.annotationParsers) {
if (parser.isCandidateClass(targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
复制代码isCandidateClass方法的逻辑,就是遍历annotationParsers集合中的每一个 TransactionAnnotationParser 元素,执行过它们的isCandidateClass方法,进行判断。
根据之前的分析,我们这里只考虑集合中包含 SpringTransactionAnnotationParser 的情况,以下是它的isCandidateClass方法。
// org.springframework.transaction.annotation.SpringTransactionAnnotationParser#isCandidateClass
@Override
public boolean isCandidateClass(Class targetClass) {
return AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetClass, Transactional.class);
}
复制代码再进入 AnnotationUtils 的isCandidateClass方法。
// org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils#isCandidateClass(java.lang.Class, java.lang.Class)
public static boolean isCandidateClass(Class clazz, Class annotationType) {
return isCandidateClass(clazz, annotationType.getName());
}
// org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils#isCandidateClass(java.lang.Class, java.lang.String)
public static boolean isCandidateClass(Class clazz, String annotationName) {
if (annotationName.startsWith("java.")) {
return true;
}
if (AnnotationsScanner.hasPlainJavaAnnotationsOnly(clazz)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
复制代码如果类的名称是java.开头的,则返回true。然后,再 AnnotationsScanner 的hasPlainJavaAnnotationsOnly方法判断,除了此方法返回true的类型,其余情况都返回true。
// org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationsScanner#hasPlainJavaAnnotationsOnly(java.lang.Class)
static boolean hasPlainJavaAnnotationsOnly(Class type) {
return (type.getName().startsWith("java.") || type == Ordered.class);
}
复制代码名称以java.开头的情况前面已经判断过了,因此这里就是判断类型是否是 Ordered 类型。
总结下来,匹配类的逻辑就是,确保类不是 TransactionalProxy、PlatformTransactionManager、PersistenceExceptionTranslator、Ordered 这几种类型之一。
目标方法匹配
方法的匹配逻辑在 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 的matches方法中。
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class targetClass) {
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
复制代码匹配的逻辑依然是通过成员变量transactionAttributeSource的getTransactionAttribute方法,从方法获取事务相关的注解配置属性信息,如果获取到的结果不为空,则符合匹配条件。
AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource 中的getTransactionAttribute方法,继承自父类 AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource。
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource#getTransactionAttribute
@Override
@Nullable
public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class targetClass) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return null;
}
// First, see if we have a cached value.
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass);
TransactionAttribute cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached != null) {
// Value will either be canonical value indicating there is no transaction attribute,
// or an actual transaction attribute.
if (cached == NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE) {
return null;
}
else {
return cached;
}
}
else {
// We need to work it out.
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
// Put it in the cache.
if (txAttr == null) {
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE);
}
else {
String methodIdentification = ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method, targetClass);
if (txAttr instanceof DefaultTransactionAttribute) {
((DefaultTransactionAttribute) txAttr).setDescriptor(methodIdentification);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Adding transactional method '" + methodIdentification + "' with attribute: " + txAttr);
}
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr);
}
return txAttr;
}
}
复制代码首先判断方法不是在 Object 类中声明的,然后,从缓存中读取数据,如果缓存中没有数据,则执行获取注解配置信息的逻辑。因此,这个方法中重点要分析的逻辑是最外层的else语句块中的逻辑。
方法最终返回的txAttr是通过computeTransactionAttribute方法得到的,无论获取到的txAttr是否为空,都会将其添加到缓存集合attributeCache中,并最终作为结果返回。
computeTransactionAttribute的源码如下。
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource#computeTransactionAttribute
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class targetClass) {
// Don't allow no-public methods as required.
if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
return null;
}
// The method may be on an interface, but we need attributes from the target class.
// If the target class is null, the method will be unchanged.
Method specificMethod = AopUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
// First try is the method in the target class.
TransactionAttribute txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// Second try is the transaction attribute on the target class.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
if (specificMethod != method) {
// Fallback is to look at the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// Last fallback is the class of the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
}
return null;
}
复制代码方法的逻辑并不复杂,大致如下:
- 如果事务注解只对
public修饰的方法有效,但是当前的目标方法method不是public修饰的方法,直接返回空。 - 通过 AopUtils 的
getMostSpecificMethod方法,获取目标方法method的具体实现方法,也就是说,如果当前的目标方法是一个接口中定义的方法,则根据当前目标类型获取到类型中的实现方法specificMethod。 - 通过
findTransactionAttribute方法从specificMethod获取 TransactionAttribute,如果不为空,则作为结果返回。 - 通过
findTransactionAttribute方法从specificMethod所在的类型获取 TransactionAttribute,如果不为空,则作为结果返回。 - 如果
method和specificMethod不是同一个方法,则对method和它所在的类型执行3、4步的操作。 - 以上都得不到结果的情况下,返回空。
上面的步骤中,获取 TransactionAttribute 的findTransactionAttribute方法被多次调用,它的定义如下。
// org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource#findTransactionAttribute(java.lang.Class)
@Override
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttribute findTransactionAttribute(Class clazz) {
return determineTransactionAttribute(clazz);
}
// org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource#findTransactionAttribute(java.lang.reflect.Method)
@Override
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttribute findTransactionAttribute(Method method) {
return determineTransactionAttribute(method);
}
复制代码其中的具体逻辑交给了determineTransactionAttribute方法。
// org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource#determineTransactionAttribute
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttribute determineTransactionAttribute(AnnotatedElement element) {
for (TransactionAnnotationParser parser : this.annotationParsers) {
TransactionAttribute attr = parser.parseTransactionAnnotation(element);
if (attr != null) {
return attr;
}
}
return null;
}
复制代码主要的逻辑就是遍历annotationParsers集合中的注解解析器,来解析参数中传入的 AnnotatedElement,来获取 TransactionAttribute。前面我们提到过,这里的注解解析器,我们只考虑 SpringTransactionAnnotationParser,因此,进入它的parseTransactionAnnotation方法。
// org.springframework.transaction.annotation.SpringTransactionAnnotationParser#parseTransactionAnnotation(java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement)
@Override
@Nullable
public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement element) {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotationAttributes(
element, Transactional.class, false, false);
if (attributes != null) {
return parseTransactionAnnotation(attributes);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
复制代码逻辑非常简单,就是获取到方法或者类上的 Transactional 注解,然后将注解的属性封装成一个 TransactionAttribute 并返回。
总结下来就是,如果目标方法或者所在的类型,标记了 Transactional 注解,那么就会被负责事务管理的拦截器匹配到,并对其进行增强。
增强逻辑
了解了目标类型和方法的匹配,最后在看具体的增强逻辑。根据 Spring AOP 的机制,执行增强逻辑时,需要从 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 对象中,通过getAdvice方法,获取到增强逻辑的拦截器,再执行拦截器的invoke方法。
前文中已经介绍过,BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 的advice属性是在配置类中初始化的,它的类型是 TransactionInterceptor,它的主要继承关系如下。
可以确认,它实现了 MethodInterceptor 接口,并且它的invoke方法,就是增强逻辑所在的方法。
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor#invoke
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);
}
复制代码其中的核心逻辑是调用了定义在父类 TransactionAspectSupport 中的invokeWithinTransaction方法。
先分析方法的参数。其中,method和targetClass是目标方法和类型,相比起来,更值得注意的是第三个参数invocation,它的类型是 InvocationCallback。
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport.InvocationCallback
@FunctionalInterface
protected interface InvocationCallback {
Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable;
}
复制代码InvocationCallback 是一个函数式接口,其中的proceedWithInvocation方法,返回了一个 Object 结果。在调用方法时,这里传入的值是invocation::proceed,也就是说,这里的invocation参数传入的是目标方法的调用。了解完参数后,再看方法体。
这个方法的代码超过了 100 行,我们只分析其中的核心部分,完整的方法体代码可以到 TransactionAspectSupport 类的源码中查看。
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport#invokeWithinTransaction
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
// 省略部分代码
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
if (vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
// 省略部分代码
复制代码方法体中的内容,可以归纳为以下几个关键步骤:
- 通过
createTransactionIfNecessary方法,得到一个 TransactionInfo 类型的txInfo对象。从方法名称和返回的结果来看,这一步应该是根据需要创建了事务,并得到事务的信息。 - 然后,在
try语句中调用目标方法,并的到执行的返回值retVal。 - 如果执行目标方法的过程中出现了异常,则执行
completeTransactionAfterThrowing方法,处理异常的情况,再将异常抛出。 - 在finally语句块中执行
cleanupTransactionInfo方法,清除异常信息。 - 如果上述过程中没有出现异常,则执行
commitTransactionAfterReturning方法,提交事务。
从上述归纳中可以看出,最主要的步骤都是通过调用相应的方法来完成的,接下来,我们就逐一分析这些方法。
createTransactionIfNecessary 方法
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport#createTransactionIfNecessary
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
// If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name.
if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
@Override
public String getName() {
return joinpointIdentification;
}
};
}
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +
"] because no transaction manager has been configured");
}
}
}
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
复制代码其中,有一行关键的代码,如下:
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
复制代码这里对执行tm的getTransaction方法,获取食物状态,开启事务也是在这里完成的。tm的类型是 PlatformTransactionManager,它是一个事务管理器对象。事务管理器是在 Spring 的事务管理配置类中注册到 Spring 容器的,这一部分在前文已经介绍过。
事务管理器中会通过 JDBC 的方式,获取到数据库连接对象 Connection,通过调用setAutoCommit(false)将自动提交设置为false,就开启了事务。
目标方法的执行
开启事务之后,就可以开始执行目标方法了,由于目标方法执行时抛出的异常可能会导致事务会滚,因此,目标方法的调用被放在了try语句块中,方便对抛出的一场进行处理。
completeTransactionAfterThrowing 方法
如果目标方法跑出了一场,则会交给catch语句块中的completeTransactionAfterThrowing方法来处理。
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport#completeTransactionAfterThrowing
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
else {
// We don't roll back on this exception.
// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
}
复制代码这个方法的源码虽然不少,但是逻辑其实非常简单。首先,会判断当前抛出的异常是不是属于 Transaction 注解中rollbackFor属性配置的异常的范畴,如果是,则说明当前抛出的异常,是需要回滚的异常,此时,就会调用事务管理器的rollback方法进行回滚,否则,通过commit方法进行提交,不过这里的提交并不是直接提交事务,而是在提交前会判断事务信息,只在符合提交条件的情况下进行提交。
cleanupTransactionInfo 方法
在目标方法执行的finally语句块中会cleanupTransactionInfo方法,从方法名称可以看出它的作用是清理事务信息。
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport#cleanupTransactionInfo
protected void cleanupTransactionInfo(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {
if (txInfo != null) {
txInfo.restoreThreadLocalStatus();
}
}
复制代码它的作用其实就是将 ThreadLocal 中保存的当前事务的信息恢复到当前事务开启之前的状态。
commitTransactionAfterReturning 方法
最后,commitTransactionAfterReturning方法负责事务的提交。
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport#commitTransactionAfterReturning
protected void commitTransactionAfterReturning(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");
}
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
}
复制代码走到这一步,说明前面的流程实行的都很顺利,因此,直接告诉事务管理器提交事务就可以了。
总结
本文通过对 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 类的分析,了解了 Spring 是如何通过 AOP 来完成事务的管理的,本文的内容需要你对 Spring 的 AOP 的实现原理有一定的了解。
由于本文的重点是 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 对提供事务管理功能的分析,遇到涉及太多 Spring 的事务抽象相关的内容,没有做介绍,如果你对此感兴趣,可以搜索相关的文章了解其中的细节。