fastp软件介绍
fastp软件介绍
- 1、软件介绍
- 2、重要参数解析
-
- 2.1 全部参数
- 2.2 使用示例
- 2.3 重要参数详解
-
- (1)UMI去除
- (2)质量过滤
- (3)长度过滤
- (4)低复杂度过滤
- (5)adapter过滤
- (6)通过质量值过滤每条read
- (7)ployG/ployX
- (8)PE数据的碱基校正(correction)
- (9)整体切除 【global trimming】
- 过滤reads顺序
- (10)输出文件切分
- (11)过表达序列分析 【overrepresented sequence analysis】
- 3、软件质控结果文件部分说明
-
- 3.1 Summary(整体结果)
- 3.2 Adapter
- 3.3 Insert size estimation
- 3.4 Before filtering
- 4、参考文件
1、软件介绍
在18年之前,fq质控用FASTQC等软件,去接头序列用cutadapt软件,数据过滤用Trimmomatic等软件。
后来海普洛斯的CTO开发了一款新软件fastp,整合了上述3个功能,实现了又快又好又个性化。
2、重要参数解析
2.1 全部参数
fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor
version 0.19.5
usage: fastp [options] ...
options:
-i, --in1 read1 input file name (string [=])
-o, --out1 read1 output file name (string [=])
-I, --in2 read2 input file name (string [=])
-O, --out2 read2 output file name (string [=])
-6, --phred64 indicate the input is using phred64 scoring (it'll be converted to phred33, so the output will still be phred33)
-z, --compression compression level for gzip output (1 ~ 9). 1 is fastest, 9 is smallest, default is 4. (int [=4])
--stdin input from STDIN. If the STDIN is interleaved paired-end FASTQ, please also add --interleaved_in.
--stdout stream passing-filters reads to STDOUT. This option will result in interleaved FASTQ output for paired-end input. Disabled by defaut.
--interleaved_in indicate that is an interleaved FASTQ which contains both read1 and read2. Disabled by defaut.
--reads_to_process specify how many reads/pairs to be processed. Default 0 means process all reads. (int [=0])
--dont_overwrite don' t overwrite existing files. Overwritting is allowed by default.
-V, --verbose output verbose log information (i.e. when every 1M reads are processed).
-A, --disable_adapter_trimming adapter trimming is enabled by default. If this option is specified, adapter trimming is disabled
-a, --adapter_sequence the adapter for read1. For SE data, if not specified, the adapter will be auto-detected. For PE data, this is used if R1/R2 are found not overlapped. (string [=auto])
--adapter_sequence_r2 the adapter for read2 (PE data only). This is used if R1/R2 are found not overlapped. If not specified, it will be the same as <adapter_sequence> (string [=auto])
--detect_adapter_for_pe by default, the auto-detection for adapter is for SE data input only, turn on this option to enable it for PE data.
-f, --trim_front1 trimming how many bases in front for read1, default is 0 (int [=0])
-t, --trim_tail1 trimming how many bases in tail for read1, default is 0 (int [=0])
-b, --max_len1 if read1 is longer than max_len1, then trim read1 at its tail to make it as long as max_len1. Default 0 means no limitation (int [=0])
-F, --trim_front2 trimming how many bases in front for read2. If it's not specified, it will follow read1's settings (int [=0])
-T, --trim_tail2 trimming how many bases in tail for read2. If it's not specified, it will follow read1's settings (int [=0])
-B, --max_len2 if read2 is longer than max_len2, then trim read2 at its tail to make it as long as max_len2. Default 0 means no limitation. If it's not specified, it will follow read1's settings (int [=0])
-g, --trim_poly_g force polyG tail trimming, by default trimming is automatically enabled for Illumina NextSeq/NovaSeq data
--poly_g_min_len the minimum length to detect polyG in the read tail. 10 by default. (int [=10])
-G, --disable_trim_poly_g disable polyG tail trimming, by default trimming is automatically enabled for Illumina NextSeq/NovaSeq data
-x, --trim_poly_x enable polyX trimming in 3' ends.
--poly_x_min_len the minimum length to detect polyX in the read tail. 10 by default. (int [=10])
-5, --cut_by_quality5 enable per read cutting by quality in front (5'), default is disabled (WARNING: this will interfere deduplication for both PE/SE data)
-3, --cut_by_quality3 enable per read cutting by quality in tail (3'), default is disabled (WARNING: this will interfere deduplication for SE data)
-W, --cut_window_size the size of the sliding window for sliding window trimming, default is 4 (int [=4])
-M, --cut_mean_quality the bases in the sliding window with mean quality below cutting_quality will be cut, default is Q20 (int [=20])
-Q, --disable_quality_filtering quality filtering is enabled by default. If this option is specified, quality filtering is disabled
-q, --qualified_quality_phred the quality value that a base is qualified. Default 15 means phred quality >=Q15 is qualified. (int [=15])
-u, --unqualified_percent_limit how many percents of bases are allowed to be unqualified (0~100). Default 40 means 40% (int [=40])
-n, --n_base_limit if one read's number of N base is >n_base_limit, then this read/pair is discarded. Default is 5 (int [=5])
-L, --disable_length_filtering length filtering is enabled by default. If this option is specified, length filtering is disabled
-l, --length_required reads shorter than length_required will be discarded, default is 15. (int [=15])
--length_limit reads longer than length_limit will be discarded, default 0 means no limitation. (int [=0])
-y, --low_complexity_filter enable low complexity filter. The complexity is defined as the percentage of base that is different from its next base (base[i] != base[i+1]).
-Y, --complexity_threshold the threshold for low complexity filter (0~100). Default is 30, which means 30% complexity is required. (int [=30])
--filter_by_index1 specify a file contains a list of barcodes of index1 to be filtered out, one barcode per line (string [=])
--filter_by_index2 specify a file contains a list of barcodes of index2 to be filtered out, one barcode per line (string [=])
--filter_by_index_threshold the allowed difference of index barcode for index filtering, default 0 means completely identical. (int [=0])
-c, --correction enable base correction in overlapped regions (only for PE data), default is disabled
--overlap_len_require the minimum length of the overlapped region for overlap analysis based adapter trimming and correction. 30 by default. (int [=30])
--overlap_diff_limit the maximum difference of the overlapped region for overlap analysis based adapter trimming and correction. 5 by default. (int [=5])
-U, --umi enable unique molecular identifer (UMI) preprocessing
--umi_loc specify the location of UMI, can be (index1/index2/read1/read2/per_index/per_read, default is none (string [=])
--umi_len if the UMI is in read1/read2, its length should be provided (int [=0])
--umi_prefix if specified, an underline will be used to connect prefix and UMI (i.e. prefix=UMI, UMI=AATTCG, final=UMI_AATTCG). No prefix by default (string [=])
--umi_skip if the UMI is in read1/read2, fastp can skip several bases following UMI, default is 0 (int [=0])
-p, --overrepresentation_analysis enable overrepresented sequence analysis.
-P, --overrepresentation_sampling one in (--overrepresentation_sampling) reads will be computed for overrepresentation analysis (1~10000), smaller is slower, default is 20. (int [=20])
-j, --json the json format report file name (string [=fastp.json])
-h, --html the html format report file name (string [=fastp.html])
-R, --report_title should be quoted with ' or ", default is "fastp report" (string [=fastp report])
-w, --thread worker thread number, default is 2 (int [=2])
-s, --split split output by limiting total split file number with this option (2~999), a sequential number prefix will be added to output name ( 0001.out.fq, 0002.out.fq...), disabled by default (int [=0])
-S, --split_by_lines split output by limiting lines of each file with this option(>=1000), a sequential number prefix will be added to output name ( 0001.out.fq, 0002.out.fq...), disabled by default (long [=0])
-d, --split_prefix_digits the digits for the sequential number padding (1~10), default is 4, so the filename will be padded as 0001.xxx, 0 to disable padding (int [=4])
-?, --help print this message
简书上有人以功能划分,重新归纳了参数如下,更加方便查看:
usage: fastp -i <in1> -o <out1> [-I <in1> -O <out2>] [options...]
options:
# I/O options 即输入输出文件设置
-i, --in1 read1 input file name (string)
-o, --out1 read1 output file name (string [=])
-I, --in2 read2 input file name (string [=])
-O, --out2 read2 output file name (string [=])
-6, --phred64 indicates the input is using phred64 scoring (it'll be converted to phred33, so the output will still be phred33)
-z, --compression compression level for gzip output (1 ~ 9). 1 is fastest, 9 is smallest, default is 2\. (int [=2])
--reads_to_process specify how many reads/pairs to be processed. Default 0 means process all reads. (int [=0])
# adapter trimming options 过滤序列接头参数设置
-A, --disable_adapter_trimming adapter trimming is enabled by default. If this option is specified, adapter trimming is disabled
-a, --adapter_sequence the adapter for read1\. For SE data, if not specified, the adapter will be auto-detected. For PE data, this is used if R1/R2 are found not overlapped. (string [=auto])
--adapter_sequence_r2 the adapter for read2 (PE data only). This is used if R1/R2 are found not overlapped. If not specified, it will be the same as (string [=])
# global trimming options 剪除序列起始和末端的低质量碱基数量参数
-f, --trim_front1 trimming how many bases in front for read1, default is 0 (int [=0])
-t, --trim_tail1 trimming how many bases in tail for read1, default is 0 (int [=0])
-F, --trim_front2 trimming how many bases in front for read2\. If it' s not specified, it will follow read1's settings (int [=0])
-T, --trim_tail2 trimming how many bases in tail for read2\. If it's not specified, it will follow read1's settings (int [=0])
# polyG tail trimming, useful for NextSeq/NovaSeq data polyG剪裁
-g, --trim_poly_g force polyG tail trimming, by default trimming is automatically enabled for Illumina NextSeq/NovaSeq data
--poly_g_min_len the minimum length to detect polyG in the read tail. 10 by default. (int [=10])
-G, --disable_trim_poly_g disable polyG tail trimming, by default trimming is automatically enabled for Illumina NextSeq/NovaSeq data
# polyX tail trimming
-x, --trim_poly_x enable polyX trimming in 3' ends.
--poly_x_min_len the minimum length to detect polyX in the read tail. 10 by default. (int [=10])
# per read cutting by quality options 划窗裁剪
-5, --cut_by_quality5 enable per read cutting by quality in front (5'), default is disabled (WARNING: this will interfere deduplication for both PE/SE data)
-3, --cut_by_quality3 enable per read cutting by quality in tail (3'), default is disabled (WARNING: this will interfere deduplication for SE data)
-W, --cut_window_size the size of the sliding window for sliding window trimming, default is 4 (int [=4])
-M, --cut_mean_quality the bases in the sliding window with mean quality below cutting_quality will be cut, default is Q20 (int [=20])
# quality filtering options 根据碱基质量来过滤序列
-Q, --disable_quality_filtering quality filtering is enabled by default. If this option is specified, quality filtering is disabled
-q, --qualified_quality_phred the quality value that a base is qualified. Default 15 means phred quality >=Q15 is qualified. (int [=15])
-u, --unqualified_percent_limit how many percents of bases are allowed to be unqualified (0~100). Default 40 means 40% (int [=40])
-n, --n_base_limit if one read's number of N base is >n_base_limit, then this read/pair is discarded. Default is 5 (int [=5])
# length filtering options 根据序列长度来过滤序列
-L, --disable_length_filtering length filtering is enabled by default. If this option is specified, length filtering is disabled
-l, --length_required reads shorter than length_required will be discarded, default is 15\. (int [=15])
# low complexity filtering
-y, --low_complexity_filter enable low complexity filter. The complexity is defined as the percentage of base that is different from its next base (base[i] != base[i+1]).
-Y, --complexity_threshold the threshold for low complexity filter (0~100). Default is 30, which means 30% complexity is required. (int [=30])
# filter reads with unwanted indexes (to remove possible contamination)
--filter_by_index1 specify a file contains a list of barcodes of index1 to be filtered out, one barcode per line (string [=])
--filter_by_index2 specify a file contains a list of barcodes of index2 to be filtered out, one barcode per line (string [=])
--filter_by_index_threshold the allowed difference of index barcode for index filtering, default 0 means completely identical. (int [=0])
# base correction by overlap analysis options 通过overlap来校正碱基
-c, --correction enable base correction in overlapped regions (only for PE data), default is disabled
# UMI processing
-U, --umi enable unique molecular identifer (UMI) preprocessing
--umi_loc specify the location of UMI, can be (index1/index2/read1/read2/per_index/per_read, default is none (string [=])
--umi_len if the UMI is in read1/read2, its length should be provided (int [=0])
--umi_prefix if specified, an underline will be used to connect prefix and UMI (i.e. prefix=UMI, UMI=AATTCG, final=UMI_AATTCG). No prefix by default (string [=])
--umi_skip if the UMI is in read1/read2, fastp can skip several bases following UMI, default is 0 (int [=0])
# overrepresented sequence analysis
-p, --overrepresentation_analysis enable overrepresented sequence analysis.
-P, --overrepresentation_sampling One in (--overrepresentation_sampling) reads will be computed for overrepresentation analysis (1~10000), smaller is slower, default is 20\. (int [=20])
# reporting options
-j, --json the json format report file name (string [=fastp.json])
-h, --html the html format report file name (string [=fastp.html])
-R, --report_title should be quoted with ' or ", default is "fastp report" (string [=fastp report])
# threading options 设置线程数
-w, --thread worker thread number, default is 3 (int [=3])
# output splitting options
-s, --split split output by limiting total split file number with this option (2~999), a sequential number prefix will be added to output name ( 0001.out.fq, 0002.out.fq...), disabled by default (int [=0])
-S, --split_by_lines split output by limiting lines of each file with this option(>=1000), a sequential number prefix will be added to output name ( 0001.out.fq, 0002.out.fq...), disabled by default (long [=0])
-d, --split_prefix_digits the digits for the sequential number padding (1~10), default is 4, so the filename will be padded as 0001.xxx, 0 to disable padding (int [=4])
# help
-?, --help print this message
2.2 使用示例
(1)最简单的使用示例
fastp -i in.fq -o out.fq # SE测序数据
fastp -i in.R1.fq -o out.R1.fq -I in.R2.fq -O out.R2.fq # PE测序书
fastp -i in.R1.fq.gz -I in.R2.fq.gz -o out.R1.fq.gz -O out.R2.fq.gz # 输入压缩文件,输出也为压缩文件
(2)结合常用参数的使用示例
fastp
-i *_R1_raw.fastq.gz # reads1 fastq
-I *_R2_raw.fastq.gz # reads2 fastq
-o *_R1_trim.fastq.gz # reads1 处理结果
-O *_R2_trim.fastq.gz # reads2 处理结果
--adapter_sequence=AGATCGGAAGAGCACACGTCTGAACTCCAGTCAC # reads1 接头序列
--adapter_sequence_r2=AGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGTGT # reads2 接头序列
--thread=4 # 设置线程数
--length_required=55 # 过滤过短序列,自定义55以下为短序列
--compression=4 # 压缩比例,1最快, 9最慢
--trim_poly_g # 开启polyG剪裁, 适用于Illumina NextSeq和NovaSeq系列数据
--cut_by_quality3 # 开启在3’端,也就是read末尾的剪裁
--correction # 通过overlap来校正碱基
--umi # 添加了umi技术的测序数据
--umi_loc per_read # 指定UMI所在的位置, per_read指在每个插入序列中
--umi_len 5 # UMI所占碱基长度
--umi_skip 3 # 去除UMI后,再去除3bp
-j *.trim.fastp.json # 适合程序读的JSON格式质控结果
-h *.trim.fastp.html # 适合人看的网页格式质控结果
2.3 重要参数详解
本部分内容来自参考文件:质控软件fastp常用参数说明_fastp参数_青灯照颦微的博客-CSDN博客;欢迎各位去读原文。
(1)UMI去除
分子标签(UMI),来自于相同的分子的标记,用于去重,错误校正。常用在ctDNA测序,illumina测序的UMI位于两个不同位置:index和read开头。
--umi 启用UMI处理参数;
--umi_loc 指定UMI的位置,可设置下面几种:
"index1": 第一个index作为UMI, 对双端数据,则作用于R1/R2;
"index2": 第二个index作为UMI, 对双端数据,则作用于R1/R2;
"read1": read1的头部作为UMI, 对双端数据,则作用于R1/R2;
"read2": read2的头部作为UMI, 对双端数据,则作用于R1/R2;
"pre_index", "index1_index2":
"pre_read": read1的头部定义'umi1', read2的头部定义'umi2', 'umi1_umi2'作为UMI, 作用于R1/R2
--umi_len UMI的长度,当指定UMI的位置为read1, read2,per_read时,应指定UMI长度;
--umi_prefix UMI设置前缀,例: UMI=AATTCCGG,prefix=ATC,即设置–umi_prefix=ATC,则被加在read_name行的UMI序列将会是ATC_AATTCCGG ;
--umi_skip UMI去除并加到read_name后,再去除(跳过)的碱基数;例:–umi_skip=4 表示去除UMI后再去除4bp。
fastp是将UMI提取后加在对应read的name行,如果UMI在read中,那么UMI会从read中移除,如果UMI在index中,会被保留。
(2)质量过滤
-q, --qualified_quality_phred 设置碱基质量值不小于多少时,该碱基为合格碱基,默认碱基质量值是15,即默认碱基质量>=15是合格碱基,<15为不合格碱基;
-u --unqualified_percent_limit 设置允许不合格碱基的占比为多少时,去掉这条read,默认是40,即默认不合格碱基占比>40%时,去掉该read;
-Q, --disable_quality_filtering 设置该参数则禁用默认质量过滤参数(-q, -u)。
(3)长度过滤
-l, --length_required 设置read的最小长度,默认是15,即长度<15的read被去掉;
--length_limit 设置read的最大长度, 默认为0是没有最大长度限制;
(4)低复杂度过滤
-Y, --complexity_threshold 设置read的复杂度过滤阈值,默认为30,即当read复杂度<30时,去掉该read。复杂度:
- 复杂度的定义为 一个碱基与其下一个相邻碱基不同的碱基个数占比;
- 例:一条长为51bp的read,有3个碱基与其下一个碱基不同
seq = 'AAAATTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGCCCC'
其复杂度为:complexity = 3/(51-1) = 6%
-y, --low_complexity_filter 设置该参数则禁用默认复杂度过滤参数(-Y)
(5)adapter过滤
-A, --disable_adapter_trimming 设置该参数则禁用默认adapter过滤参数;
-a, --adapter_sequence 指定引物序列(对应SE数据的引物序列 或 对应PE数据的R1的引物序列)。对单端(SE)数据,可通过自动检测前~1Mreads的尾巴,去识别adapter,若设置该参数,则表示禁用自动识别adapter;
--adapter_sequence_r2 指定R2引物序列(对PE数据的R2)。对双端(PE)数据,是通过两条reads的overlap去adapter(由于该方法比较稳定,通常不必设置引物序列)。如果为找到overlap,用使用这些序列去adapter(是否设置都先通过overlap去adapter?);
--detect_adapter_for_pe 默认对双端数据则默认不使用自动检测adapter(SE可自动检测),设置该参数,表示对双端数据也启用自动检测方法;
--adapter_fasta 接头序列文件(fasta格式),注意该fasta文件中的fasta序列长度至少6bp,否则会被跳过。
注:fastp首先去除自动化检测到的接头序列,或者使用–adapter_sequence |–adapter_sequence_r2指定的接头序列,然后去除由–adapter_fasta设置的接头序列。去除的接头序列分布可以在html/json文件中查看。
(6)通过质量值过滤每条read
下面参数是通过滑动窗的平均质量值切除reads。
-W, --cut_window_size 设置滑动窗口大小;
-M, --cut_mean_quality 设置滑动窗口的平均质量值阈值,低于这个阈值则被切除;
可对两端分别进行切除:
对5'端的参数,与Trimmomatic中的LEADING参数方法相似:
-5, --cut_front 是去除5'端低质量碱基,具体是指滑动窗从5'向末尾3’滑动,如果窗口内的碱基平均质量值低于阈值,则切除这些碱基,然后窗口继续滑动,直到达到阈值则不再去除;
--cut_front_window_size 是设置从5'端开始的滑动窗的大小,即每个滑动窗包含几个碱基;
--cut_front_mean_quality 设置从5'端开始的滑动窗平均质量值阈值,低于该阈值则切除这些碱基;
对3'端开始切除的参数与5'端类似,也与Trimmomatic中的TRAILING参数的方法类似:
-3, --cut_tail 是去除3'端低质量碱基,具体是指滑动窗从3'向起始5’滑动,如果窗口内的碱基平均质量值低于阈值,则切除这些碱基,然后窗口继续滑动,直到达到阈值则不再去除;
--cut_tail_window_size 是设置从3'端开始的滑动窗的大小;
--cut_tail_mean_quality 设置从3'端开始的滑动窗平均质量值阈值,低于该阈值则切除这些碱基;
还有切除序列的其他参数:
-r, --cut_right 是切除右侧序列,-3与-r参数的差别是,前者是先进行碱基去除,达到阈值则不再去除碱基,然后继续滑动窗口;后者是前者进行后,继续滑动滑动窗,直到发现窗口内碱基的平均质量值低于阈值,则切除该窗口及右侧所有碱基。也就是使用该参数,就没必要设置–cut_tail参数 。
(7)ployG/ployX
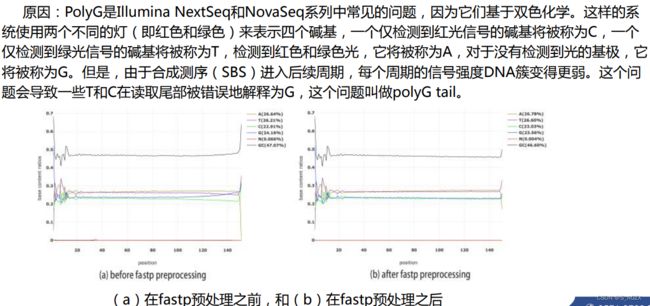
对Illumina的NextSeq/NovaSeq测序数据,常会用ployG发生(是因为这两个平台使用两个荧光信号,而没有信号时表示G)。fastp能够检测到ployG并去除(默认是NextSeq/NovaSeq平台,通过测序仪ID和fastq识别)
-g, --trim_poly_g 启用去除尾巴ployG;
--poly_g_min_len 设置去除尾巴’G’的最小长度,默认为10即尾巴ployG长度>10时,会被去除;
-G, --disable_trim_poly_g 禁用去除尾巴ployG;
-x, --polyX 启用去除polyX(polyA, polyT, polyC, polyG),若同时设置–trim_poly_g和–ployX,则先进行ployG尾巴去重,再进行ployX(这样设置有助于ployA尾巴在G尾巴之前时,去重ployA尾巴[常见于mRNA-Seq])。
(8)PE数据的碱基校正(correction)
fastp通过overlap进行分析,如果找到合适的overlap,当overlap区域的两个错配碱基中,一个碱基质量值较高,一个碱基质量值极低,该软件会将错配的两个碱基进行校正(?将低质量碱基校正为与高质量碱基互补的碱基)。对应的碱基质量值也校正为相同的值。
-c, --correction 对碱基校正,默认不启用该参数;使用该参数是基于检测overlap,overlap的可调参数有:
--overlap_len_require overlap的长度要求,默认是30,即默认overlap区域的长度不低于30bp;否则认为无overlap;
--overlap_diff_limit overlap中最大错配数,默认是5,即默认overlap时最多有5个错配;否则认为无overlap;
--overlap_diff_percent_limit overlap中最大错配数在重叠区的占比,默认是20,即默认最大错配数的碱基占比不高于20%;否则认为无overlap。
(9)整体切除 【global trimming】
整体切除一般是考虑到,illumina测序最后1个cycle或最后n个cycle测序质量较低,使用-t 1, --trim_tai1l=1参数将所有reads的末尾1bp去除;
-f, --trim_front1 对R1起始几bp进行去除,例如:-f 1或–trim_front1=1表示去除R1起始位置1bp碱基;
-t, --trim_tail1 对R1末尾几bp进行去除,例如:-t 2或–trim_tail1=2表示去除R1末尾位置1bp碱基;
-b, --max_len1 设置R1最大长度阈值,即R1的长度大于阈值,则在尾巴开始切除read直到与阈值相等,默认不切除。注意最大长度在最后一步处理;
-F, --trim_front2 与R1相似;不设置默认则与R1指定的参数相同;
-T, --trim_tail2 与R1相似;不设置默认则与R1指定的参数相同;
-B, --max_len2 设置R2最大长度,同-b参数。[注意最大长度在最后一步处理]
过滤reads顺序
## 过滤reads顺序:
1. 对UMI进行处理("--umi")
2. 整体切除的起始位置切除("-f", "-F")
# 比如UMI在5‘端却不知道序列时,可trim_front1 10 trim_front2 10来强制去除插入序列
3. 整体切除的尾巴位置切除("-t", "-T")
4. 5'端质量值切除("-cut_front")
5. 滑动窗切除("--cut_right")
6. 3'端质量值切除("--cut_tail")
7. ployG切除("--trim_ploy_g", 默认作用于'NovaSeq/NextSeq'的数据)
8. 根据overlap分析去adapter(PE数据)
9. 根据adapter序列去apapter("--adapter_sequence", "--adapter_sequence_r2", 对PE数据则跳过该步骤)
10. 去除polyX("--trim_poly_x")
11. 去除最大长度("--max_len")
(10)输出文件切分
可通过设置分割成几个文件或者设置每个文件的行数 ,两者不可同时设置。
-s, --split 指定最多分割成几个文件;
-S, --split_by_lines 指定分割后的每个文件最多几行;
-d, --split_prefix_digits 设置输出文件的前缀数字位数,例如:–split_prefix_digits=4 --split=3 --out1=out.fq , 则输出文件为0001.out.fq, 0002.out.fq, 0002.out.fq

(11)过表达序列分析 【overrepresented sequence analysis】
-p,--overrepresentation_analysis 启用该分析,默认仅统计序列长度为10bp, 20bp, 40bp, 100bp或 cycle -2 ;
-P, --overrepresentation_sampling 指定用于统计的reads数比例,默认20,即默认1/20的reads用于序列统计。例:设置-P 100 表示将1/100的reads用序列统计,设置-P 1 表示将所有reads用于统计(运行会很慢,默认20是平衡了速度和精确度)
不仅有过表达序统计结果,还有循环中(cycles)的分布情况,并用图展示检测到的过表达序列,以便找到最多的序列。

3、软件质控结果文件部分说明
本部分结果,主要来自于博客生信学习笔记:fastp质控处理生成的report结果解读_fastp结果解读_twocanis的博客-CSDN博客,欢迎去读原文。
3.1 Summary(整体结果)

General
版本号、序列循环数、质控之前的平均长度、质控之后的平均长度、插入片段的峰值
Before filtering
数据质控之前的(反应测序质量):总的reads长度、总碱基长度、Q20合格率、Q30合格率、GC含量
After filtering
质控之后的:内容同上
Filtering result
reads的通过率、低质量的reads、含太多N值的reads
3.2 Adapter
3.3 Insert size estimation

配对末端重叠分析,不同长度的Insert在reads中占的比例,相当于是DNA被打断后的长度分布。当插入片段大小<30或> 270,或包含太多错误,则不能被read读取,比如我这里就有28%的不可读reads)
3.4 Before filtering
质控之前的数据质量、碱基含量以及kmer分析等,可直接在网页上用鼠标拖动放大缩小以及查看具体数据细节,或进行图片保存等操作
(1)reads质量
在不同位置上的碱基质量分布,一般来讲质量应 >30 且波动较小为不错的数据

(2)碱基质量
read各个位置上碱基比例分布,这个是为了分析碱基的分离程度。
何为碱基分离?已知AT配对,CG配对,假如测序过程是比较随机的话(随机意味着好),那么在每个位置上A和T比例应该差不多,C和G的比例也应该差不多。
如下图所示,两者之间即使有偏差也不应该太大,最好平均在1%以内,如果过高,除非有合理的原因,比如某些特定的捕获测序所致,否则都需要注意是不是测序过程有什么偏差。

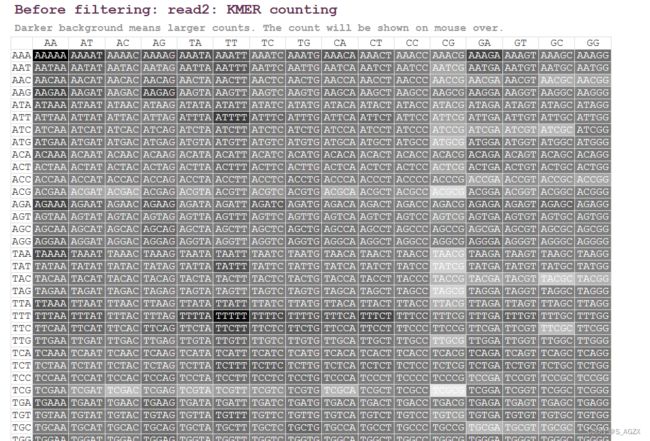
(3)KMER计数
fastp对5个碱基长度的所有组合的出现次数进行了统计,然后把它放在了一张表格中,表格的每一个元素为深背景白字,背景越深,则表示重复次数越多。这样,一眼望去,就可以发现有哪些异常的信息。鼠标可停留在某一具体组合上看出现次数和平均占比。
4、参考文件
1、GitHub - fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor
2、fastp参数说明
3、fastp: 一款超快速全功能的FASTQ文件自动化质控+过滤+校正+预处理软件 - 知乎
4、质控软件fastp常用参数说明_fastp参数_青灯照颦微的博客-CSDN博客
5、生信学习笔记:fastp质控处理生成的report结果解读_fastp结果解读_twocanis的博客-CSDN博客


