Spring Boot读取配置文件值 (@ConfigurationProperties注解或@Value注解)
如何使用Java读取到properties文件中的内容,并且把它封装到JavaBean中,以供随时使用
传统方法:
public class getProperties {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
//properties读数据
Properties properties = new Properties();
//本地读取配置文件写法
try (Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("src/main/resources/examine.properties"), "UTF-8")) {
properties.load(reader);
}
//根据key单独获取value,#请勿使用这类文字
String notUse = properties.getProperty("notuse");
}
}
1. 使用@ConfigurationProperties注解
一、Spring Boot一种配置配置绑定:
@ConfigurationProperties + @Component
假设有配置文件application.properties
mycar.brand=BYD
mycar.price=100000
只有在容器中的组件,才会拥有SpringBoot提供的强大功能,所以需要@component
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class Car {
private String brand;
private int price;
...
}
这样Car的实例已经绑定了brand为BYD,price为100000
二、Spring Boot另一种配置配置绑定:
@EnableConfigurationProperties + @ConfigurationProperties
- 开启Car配置绑定功能
- 把这个Car这个组件自动注册到容器中
@EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class)
public class MyConfig {
...
}
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class Car {
private String brand;
private int price;
}
这样Car的实例已经绑定了brand为BYD,price为100000
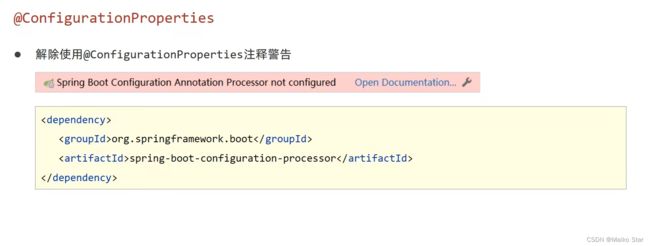
三、解除使用@ConfigurationProperties注解警告
如果有报错/警告,可以参考下面内容:
2. 使用 @Value注解
一、@Value注解介绍
当使用@Value注解读取配置文件的值时,首先需要在需要读取配置值的字段上使用@Value注解,并传入配置文件中的键作为参数。然后,Spring Boot会自动将配置文件中对应键的值注入到该字段中。
二、@Value注解案例
下面是一个详细的示例,假设有一个配置文件application.properties,其中包含了一个名为app.name的配置项:
app.name=My Application在需要读取该配置项的类中,可以通过@Value注解读取配置文件的值:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyApp {
@Value("${app.name}")
private String applicationName;
public void printApplicationName() {
System.out.println("Application Name: " + applicationName);
}
}在上述示例中,@Value("${app.name}")表示要读取配置文件中app.name的值,并将其注入到applicationName字段中。然后,可以在printApplicationName()方法中打印该值。
当应用启动时,Spring Boot会自动加载配置文件,并将配置文件中的值注入到相应的字段中。可以在其他组件或服务中使用MyApp类,并调用printApplicationName()方法来获取和使用配置文件中的值。
注意:要确保配置文件正确命名为application.properties,并放置在Spring Boot应用的classpath下,例如src/main/resources目录。