Linux内核音频子系统ALSA、ASOC及其示例分析
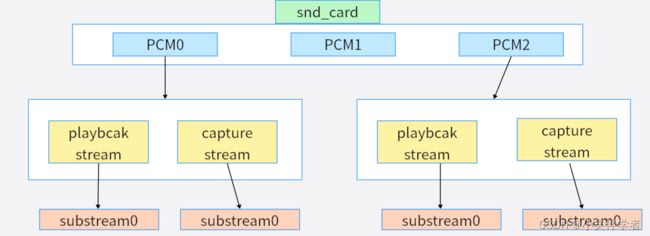
1.音频子系统总框架
ALSA 是Advanced Linux Sound Architecture 的缩写,目前已经成为了linux的主流音频体系结构在内核设备驱动层,ALSA提供了alsa-driver,同时在应用层,ALSA为我们提供了alsa-lib,应用程序只要调用alsa-lib提供的API,即可以完成对底层音频硬件的控制。
ALSA-lib:向应用层提供API接口;
alsa-driver: 音频硬件设备驱动,由三大部分组成:Machine,Platform,Codec。
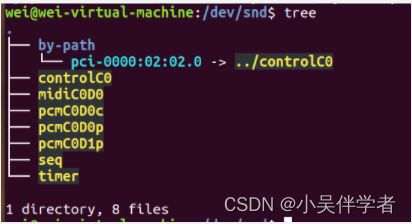
进入系统,查看/dev/snd 文件夹中的内容:dev文件夹中是系统的设备文件,即设备的驱动程序。
其中主要的两个设备:PCM,ControlC0。PCM主要复杂ADC、DAC,Control主要让用户空间的应用程序(alsa-lib)可以访问和控制codec芯片中的多路开关,滑动控件等。
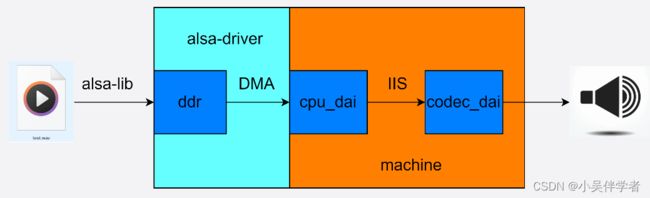
2.ALSA框架
其中cpu_dai代表cpu的数字音频接口,IIS是飞利浦公司提出的一种用于数字音频设备之间进行音频数据传输的总线,用于主控制器和音频 CODEC 芯片之间传输音频数据。
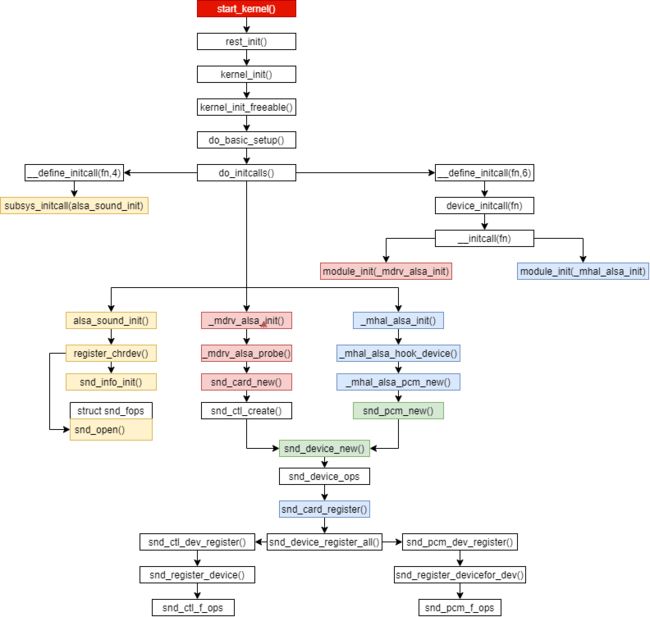
2.1ALSA初始化
初始化过程如下:
首先调用alsa_sound_init初始化声卡对应字符设备,且主设备号为116:
static int __init alsa_sound_init(void)
{
snd_major = major;
snd_ecards_limit = cards_limit;
//获取字符设备主设备号,即声卡的主设备号,其他声卡设备都是其下的次设备号
if (register_chrdev(major, "alsa", &snd_fops)) {
pr_err("ALSA core: unable to register native major device number %d\n", major);
return -EIO;
}
//创建 snd_proc_root 目录为 /proc/sound
if (snd_info_init() < 0) {
unregister_chrdev(major, "alsa");
return -ENOMEM;
}
snd_info_minor_register();
#ifndef MODULE
pr_info("Advanced Linux Sound Architecture Driver Initialized.\n");
#endif
return 0;
}Linux系统上的 /proc 目录是一种文件系统,即 proc文件系统。与其它常见的文件系统不同的是,/proc是一种伪文件系统(也即虚拟文件系统),存储的是当前内核运行状态的一系列特殊文件,用户可以通过这些文件查看有关系统硬件及当前正在运行进程的信息,甚至可以通过更改其中某些文件来改变内核的运行状态。
int __init snd_info_init(void)
{
struct proc_dir_entry *p;
//1、创建 alsa proc root entry;
p = proc_mkdir("asound", NULL);
if (p == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
snd_proc_root = p;
#ifdef CONFIG_SND_OSSEMUL
{
struct snd_info_entry *entry;
if ((entry = snd_info_create_module_entry(THIS_MODULE, "oss", NULL)) == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
entry->mode = S_IFDIR | S_IRUGO | S_IXUGO;
if (snd_info_register(entry) < 0) {
snd_info_free_entry(entry);
return -ENOMEM;
}
snd_oss_root = entry;
}
#endif
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SND_SEQUENCER)
{
struct snd_info_entry *entry;
if ((entry = snd_info_create_module_entry(THIS_MODULE, "seq", NULL)) == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
entry->mode = S_IFDIR | S_IRUGO | S_IXUGO;
if (snd_info_register(entry) < 0) {
snd_info_free_entry(entry);
return -ENOMEM;
}
snd_seq_root = entry;
}
#endif
snd_info_version_init(); //3、创建 file: /proc/asound/version
snd_minor_info_init(); //4、创建 file: /proc/asound/devices
snd_minor_info_oss_init();
snd_card_info_init(); //5、创建 file: /proc/asound/cards
return 0;
}其中该字符设备对应的ops为 snd_fops:
static const struct file_operations snd_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = snd_open,
.llseek = noop_llseek,
};snd_open 函数中利用次设备号根据全局数组 snd_minors 找到相应的次设备 file_operations 并替换,最后调用相应次设备的 open 函数:
static int snd_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
unsigned int minor = iminor(inode);//获取声卡下对应的次设备
struct snd_minor *mptr = NULL;
const struct file_operations *new_fops;
int err = 0;
if (minor >= ARRAY_SIZE(snd_minors))
return -ENODEV;
mutex_lock(&sound_mutex);
mptr = snd_minors[minor];//获取到具体的声卡设备,即次设备比如 control、pcm 设备等
if (mptr == NULL) {
mptr = autoload_device(minor);
if (!mptr) {
mutex_unlock(&sound_mutex);
return -ENODEV;
}
}
//获取次设备的 f_ops 文件结构体
new_fops = fops_get(mptr->f_ops);
mutex_unlock(&sound_mutex);
if (!new_fops)
return -ENODEV;
//用次设备的 file_operations 替换
replace_fops(file, new_fops);
//执行该次设备的文件 open 函数
if (file->f_op->open)
err = file->f_op->open(inode, file);
return err;
}其中snd_minors为全局数组,每一个元素都保存了声卡下某个逻辑设备的上下文信息,他在逻辑身边建立阶段被填充,在逻辑设备被使用时就可以从该结构中得到相应的信息,PCM设备也不例外,也使用该结构体:
struct snd_minor {
int type; /* SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_XXX */
int card; /* card number */
int device; /* device number */
const struct file_operations *f_ops; /* file operations */
void *private_data; /* private data for f_ops->open */
struct device *dev; /* device for sysfs */
struct snd_card *card_ptr; /* assigned card instance */
};
全局数组
static struct snd_minor *snd_minors[SNDRV_OS_MINORS];
设备类型:
#define SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_CONTROL SNDRV_MINOR_CONTROL
#define SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_HWDEP SNDRV_MINOR_HWDEP
#define SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_RAWMIDI SNDRV_MINOR_RAWMIDI
#define SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_PLAYBACK SNDRV_MINOR_PCM_PLAYBACK
#define SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_CAPTURE SNDRV_MINOR_PCM_CAPTURE
#define SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_SEQUENCER SNDRV_MINOR_SEQUENCER
#define SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_TIMER SNDRV_MINOR_TIMER
#define SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_COMPRESS SNDRV_MINOR_COMPRESS创建对应的class文件:
static int __init init_soundcore(void)
{
int rc;
rc = init_oss_soundcore();
if (rc)
return rc;
//创建全局 sound_class
sound_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "sound");
if (IS_ERR(sound_class)) {
cleanup_oss_soundcore();
return PTR_ERR(sound_class);
}
sound_class->devnode = sound_devnode;
return 0;
}
subsys_initcall(init_soundcore); 2.2声卡结构体及其创建、注册
2.2声卡结构体及其创建、注册
内核中使用结构体snd_card来描述一张声卡:
struct snd_card {
int number; /* number of soundcard (index to
snd_cards) */
char id[16]; /* id string of this card */
char driver[16]; /* driver name */
char shortname[32]; /* short name of this soundcard */
char longname[80]; /* name of this soundcard */ //会在具体驱动中设置,主要反映在/proc/asound/cards中
char mixername[80]; /* mixer name */
char components[128]; /* card components delimited with
space */
struct module *module; /* top-level module */
void *private_data; /* private data for soundcard */ //声卡的私有数据,可以在创建声卡时通过参数指定数据的大小
void (*private_free) (struct snd_card *card); /* callback for freeing of
private data */
struct list_head devices; /* devices */ //记录该声卡下所有逻辑设备的链表
struct device ctl_dev; /* control device */
unsigned int last_numid; /* last used numeric ID */
struct rw_semaphore controls_rwsem; /* controls list lock */
rwlock_t ctl_files_rwlock; /* ctl_files list lock */
int controls_count; /* count of all controls */
int user_ctl_count; /* count of all user controls */
struct list_head controls; /* all controls for this card */ //记录该声卡下所有控制单元的链表
struct list_head ctl_files; /* active control files */ //用于管理该card下的active的control设备
struct mutex user_ctl_lock; /* protects user controls against
concurrent access */
struct snd_info_entry *proc_root; /* root for soundcard specific files */
struct snd_info_entry *proc_id; /* the card id */
struct proc_dir_entry *proc_root_link; /* number link to real id */
struct list_head files_list; /* all files associated to this card */
struct snd_shutdown_f_ops *s_f_ops; /* file operations in the shutdown
state */
spinlock_t files_lock; /* lock the files for this card */
int shutdown; /* this card is going down */
struct completion *release_completion;
struct device *dev; /* device assigned to this card */ //和card相关的设备
struct device card_dev; /* cardX object for sysfs */ //card用于在sys中显示,用于代表该card
const struct attribute_group *dev_groups[4]; /* assigned sysfs attr */
bool registered; /* card_dev is registered? */
#ifdef CONFIG_PM
unsigned int power_state; /* power state */
struct mutex power_lock; /* power lock */
wait_queue_head_t power_sleep;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_SND_MIXER_OSS) || defined(CONFIG_SND_MIXER_OSS_MODULE)
struct snd_mixer_oss *mixer_oss;
int mixer_oss_change_count;
#endif
};
使用函数snd_card_new创建一个声卡:
int snd_card_new(struct device *parent, int idx, const char *xid,
struct module *module, int extra_size,
struct snd_card **card_ret)
{
struct snd_card *card;
int err;
if (snd_BUG_ON(!card_ret))
return -EINVAL;
*card_ret = NULL;
if (extra_size < 0)
extra_size = 0;
/* 1. 分配snd_card和private_data的空间
在snd_card后面的空间分配,card->private_data指向该空间
*/
card = kzalloc(sizeof(*card) + extra_size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!card)
return -ENOMEM;
if (extra_size > 0)
card->private_data = (char *)card + sizeof(struct snd_card);
if (xid)/* (2). 为 card->id 赋值 */
strlcpy(card->id, xid, sizeof(card->id));
err = 0;
mutex_lock(&snd_card_mutex);
if (idx < 0) /* first check the matching module-name slot */
idx = get_slot_from_bitmask(idx, module_slot_match, module);
if (idx < 0) /* if not matched, assign an empty slot */
idx = get_slot_from_bitmask(idx, check_empty_slot, module);
if (idx < 0)
err = -ENODEV;
else if (idx < snd_ecards_limit) {
if (test_bit(idx, snd_cards_lock))
err = -EBUSY; /* invalid */
} else if (idx >= SNDRV_CARDS)
err = -ENODEV;
if (err < 0) {
mutex_unlock(&snd_card_mutex);
dev_err(parent, "cannot find the slot for index %d (range 0-%i), error: %d\n",
idx, snd_ecards_limit - 1, err);
kfree(card);
return err;
}
set_bit(idx, snd_cards_lock); /* lock it */
if (idx >= snd_ecards_limit)
snd_ecards_limit = idx + 1; /* increase the limit */
mutex_unlock(&snd_card_mutex);
card->dev = parent; /* (3). 赋值parent */
card->number = idx; /* (4). 分配snd_card的序号 */
card->module = module;/* (5). 赋值module */
/* 2、初始化结构体和变量 */
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&card->devices);
init_rwsem(&card->controls_rwsem);
rwlock_init(&card->ctl_files_rwlock);
mutex_init(&card->user_ctl_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&card->controls);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&card->ctl_files);
spin_lock_init(&card->files_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&card->files_list);
#ifdef CONFIG_PM
mutex_init(&card->power_lock);
init_waitqueue_head(&card->power_sleep);
#endif
/* 设置设备文件节点的名字 */
device_initialize(&card->card_dev);
card->card_dev.parent = parent;
card->card_dev.class = sound_class;
card->card_dev.release = release_card_device;
card->card_dev.groups = card->dev_groups;
card->dev_groups[0] = &card_dev_attr_group;
err = kobject_set_name(&card->card_dev.kobj, "card%d", idx);
if (err < 0)
goto __error;
/* the control interface cannot be accessed from the user space until */
/* snd_cards_bitmask and snd_cards are set with snd_card_register */
/* 创建一个control设备 */
err = snd_ctl_create(card);
if (err < 0) {
dev_err(parent, "unable to register control minors\n");
goto __error;
}
/* 生成声卡的proc文件 */
err = snd_info_card_create(card);
if (err < 0) {
dev_err(parent, "unable to create card info\n");
goto __error_ctl;
}
*card_ret = card;
return 0;
__error_ctl:
snd_device_free_all(card);
__error:
put_device(&card->card_dev);
return err;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(snd_card_new);card_ret返回申请到的snd_card,然后使用函数snd_card_register()函数注册该声卡:
int snd_card_register(struct snd_card *card)
{
int err;
/* 合法性判断,如果此处card不存在,panic。 */
if (snd_BUG_ON(!card))
return -EINVAL;
/* 1、根据card的registered判断是否已经注册,如果注册继续。否则调用device_add添加设备,
设置registered标志。创建声卡的sysfs设备节点。其中card->card_dev在创建声卡结构体的时候被赋值。
card->card_dev.class = sound_class;
sound_class在sound模块被加载的时候创建
设备节点:/dev/snd/cartd%i
*/
if (!card->registered) {
err = device_add(&card->card_dev);
if (err < 0)
return err;
card->registered = true;
}
/* 2、调用snd_device_register_all注册所有card的设备,包括pcm, control等 */
if ((err = snd_device_register_all(card)) < 0)
return err;
mutex_lock(&snd_card_mutex);
/* 3、添加当前的声卡到声卡数组 */
if (snd_cards[card->number]) {
/* already registered */
mutex_unlock(&snd_card_mutex);
return 0;
}
if (*card->id) {
/* make a unique id name from the given string */
char tmpid[sizeof(card->id)];
memcpy(tmpid, card->id, sizeof(card->id));
snd_card_set_id_no_lock(card, tmpid, tmpid);
} else {
/* create an id from either shortname or longname */
const char *src;
src = *card->shortname ? card->shortname : card->longname;
snd_card_set_id_no_lock(card, src,
retrieve_id_from_card_name(src));
}
snd_cards[card->number] = card;
mutex_unlock(&snd_card_mutex);
init_info_for_card(card); /* 4、注册声卡的proc文件 */
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SND_MIXER_OSS)
if (snd_mixer_oss_notify_callback)
snd_mixer_oss_notify_callback(card, SND_MIXER_OSS_NOTIFY_REGISTER);
#endif
return 0;
}其中snd_cards是全局数组,用来存储注册成功的声卡:
struct snd_card *snd_cards[SNDRV_CARDS];
/* number of supported soundcards */
#ifdef CONFIG_SND_DYNAMIC_MINORS
#define SNDRV_CARDS CONFIG_SND_MAX_CARDS
#else
#define SNDRV_CARDS 8 /* don't change - minor numbers */
#endif
其中函数snd_device_register_all()会注册所有挂接到该声卡下的设备:
int snd_device_register_all(struct snd_card *card)
{
struct snd_device *dev;
int err;
if (snd_BUG_ON(!card))
return -ENXIO;
/* 遍历注册所有的snd_device,调用__snd_device_register函数完成注册 */
list_for_each_entry(dev, &card->devices, list) {
err = __snd_device_register(dev);
if (err < 0)
return err;
}
return 0;
}
static int __snd_device_register(struct snd_device *dev)
{
if (dev->state == SNDRV_DEV_BUILD) {
if (dev->ops->dev_register) {
int err = dev->ops->dev_register(dev); //调用各自的注册函数
if (err < 0)
return err;
}
dev->state = SNDRV_DEV_REGISTERED;
}
return 0;
}2.3PCM设备的创建
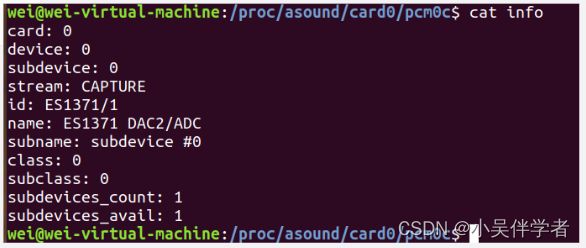
PCM是英文Pulse-code modulation(脉冲编码调制)的缩写,中文译名是脉冲编码调制。我们知道在现实生活中,人耳听到的声音是模拟信号,PCM就是要把声音从模拟转换成数字信号的一种技术。通常,播放音乐时,应用程序从存储介质中读取音频数据(MP3、WMA、AAC......),经过解码后,最终送到音频驱动程序中的就是PCM数据,反过来,在录音时,音频驱动不停地把采样所得的PCM数据送回给应用程序,由应用程序完成压缩、存储等任务。所以,音频驱动的两大核心任务就是:
(1)playback :如何把用户空间的应用程序发过来的PCM数据,转化为人耳可以辨别的模拟音频;D-A(数模转换)。
(2)capture :把mic拾取到得模拟信号,经过采样、量化,转换为PCM信号送回给用户空间的应用程序 A-D(模数转换)。
pcm所对应的结构体为snd_pcm:
struct snd_pcm {
struct snd_card *card; //PCM device 说挂载的声卡
struct list_head list; //一个Card可能有多个PCM 实例,PCM 实例列表
int device; /* device number */ //PCM 实例的索引
unsigned int info_flags;
unsigned short dev_class;
unsigned short dev_subclass;
char id[64];
char name[80];
struct snd_pcm_str streams[2]; //PCM的playback和capture stream
struct mutex open_mutex;
wait_queue_head_t open_wait;
void *private_data; //private_data一般为芯片专用信息
void (*private_free) (struct snd_pcm *pcm); //用来释放private_data
bool internal; /* pcm is for internal use only */
bool nonatomic; /* whole PCM operations are in non-atomic context */
#if defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS) || defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS_MODULE)
struct snd_pcm_oss oss;
#endif
};通过调用snd_pcm_new()函数创建某一个声卡下的PCM设备,其中,参数device 表示目前创建的是该声卡下的第几个pcm,第一个pcm设备从0开始。参数playback_count 表示该pcm将会有几个playback substream。参数capture_count 表示该pcm将会有几个capture substream。
int snd_pcm_new(struct snd_card *card, const char *id, int device,
int playback_count, int capture_count, struct snd_pcm **rpcm)
{
return _snd_pcm_new(card, id, device, playback_count, capture_count,
false, rpcm);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(snd_pcm_new);static int _snd_pcm_new(struct snd_card *card, const char *id, int device,
int playback_count, int capture_count, bool internal,
struct snd_pcm **rpcm)
{
struct snd_pcm *pcm;
int err;
static struct snd_device_ops ops = {
.dev_free = snd_pcm_dev_free,
.dev_register = snd_pcm_dev_register,
.dev_disconnect = snd_pcm_dev_disconnect,
};
if (snd_BUG_ON(!card))
return -ENXIO;
if (rpcm)
*rpcm = NULL;
pcm = kzalloc(sizeof(*pcm), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pcm)
return -ENOMEM;
pcm->card = card;
pcm->device = device;
pcm->internal = internal;
mutex_init(&pcm->open_mutex);
init_waitqueue_head(&pcm->open_wait);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pcm->list);
if (id)
strlcpy(pcm->id, id, sizeof(pcm->id));
//如果有,建立playback stream,相应的substream也同时建立
if ((err = snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK, playback_count)) < 0) {
snd_pcm_free(pcm);
return err;
}
//如果有,建立capture stream,相应的substream也同时建立
if ((err = snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE, capture_count)) < 0) {
snd_pcm_free(pcm);
return err;
}
//把该pcm挂到声卡中,参数ops中的dev_register字段指向了函数snd_pcm_dev_register,这个回调函数会在声卡的注册阶段被调用
if ((err = snd_device_new(card, SNDRV_DEV_PCM, pcm, &ops)) < 0) {
snd_pcm_free(pcm);
return err;
}
if (rpcm)
*rpcm = pcm;
return 0;
}
int snd_device_new(struct snd_card *card, enum snd_device_type type,
void *device_data, struct snd_device_ops *ops)
{
struct snd_device *dev;
struct list_head *p;
if (snd_BUG_ON(!card || !device_data || !ops))
return -ENXIO;
dev = kzalloc(sizeof(*dev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dev)
return -ENOMEM;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->list);
dev->card = card;
dev->type = type; //类型为pcm
dev->state = SNDRV_DEV_BUILD;
dev->device_data = device_data; //把pcm赋值
dev->ops = ops;
/* insert the entry in an incrementally sorted list */
list_for_each_prev(p, &card->devices) {
struct snd_device *pdev = list_entry(p, struct snd_device, list);
if ((unsigned int)pdev->type <= (unsigned int)type)
break;
}
list_add(&dev->list, p);
return 0;
}当调用snd_card_register()函数时,通过snd_device_register_all()函数会通过调用自身的注册函数将自身进行注册,也就是说新建好pcm,并且将其挂载在对应的声卡下后,调用snd_card_register()函数,也会调用snd_pcm_dev_register()函数对pcm进行注册:
static int snd_pcm_dev_register(struct snd_device *device)
{
int cidx, err;
struct snd_pcm_substream *substream;
struct snd_pcm_notify *notify;
struct snd_pcm *pcm;
if (snd_BUG_ON(!device || !device->device_data))
return -ENXIO;
pcm = device->device_data;
if (pcm->internal)
return 0;
mutex_lock(®ister_mutex);
err = snd_pcm_add(pcm);
if (err)
goto unlock;
for (cidx = 0; cidx < 2; cidx++) {
int devtype = -1;
if (pcm->streams[cidx].substream == NULL)
continue;
switch (cidx) {
case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK:
devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_PLAYBACK;
break;
case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE:
devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_CAPTURE;
break;
}
/* register pcm */
//针对capture和playback两种pcm的ops进行注册
err = snd_register_device(devtype, pcm->card, pcm->device,
&snd_pcm_f_ops[cidx], pcm,
&pcm->streams[cidx].dev);
if (err < 0) {
list_del_init(&pcm->list);
goto unlock;
}
for (substream = pcm->streams[cidx].substream; substream; substream = substream->next)
snd_pcm_timer_init(substream);
}
list_for_each_entry(notify, &snd_pcm_notify_list, list)
notify->n_register(pcm);
unlock:
mutex_unlock(®ister_mutex);
return err;
}其中snd_pcm_f_ops说明了针对capture和playback的ops:
const struct file_operations snd_pcm_f_ops[2] = {
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.write = snd_pcm_write,
.write_iter = snd_pcm_writev,
.open = snd_pcm_playback_open,
.release = snd_pcm_release,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.poll = snd_pcm_playback_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_playback_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,
.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,
.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,
.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,
},
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = snd_pcm_read,
.read_iter = snd_pcm_readv,
.open = snd_pcm_capture_open,
.release = snd_pcm_release,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.poll = snd_pcm_capture_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_capture_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,
.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,
.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,
.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,
}
};
通过调用snd_register_device()函数对设备进行注册:
int snd_register_device(int type, struct snd_card *card, int dev,
const struct file_operations *f_ops,
void *private_data, struct device *device)
{
int minor;
int err = 0;
struct snd_minor *preg;
if (snd_BUG_ON(!device))
return -EINVAL;
//创建一个snd_minor
preg = kmalloc(sizeof *preg, GFP_KERNEL);
if (preg == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
preg->type = type;
preg->card = card ? card->number : -1;
preg->device = dev;
preg->f_ops = f_ops;
preg->private_data = private_data;
preg->card_ptr = card;
mutex_lock(&sound_mutex);
minor = snd_find_free_minor(type, card, dev);//找到一个次设备号
if (minor < 0) {
err = minor;
goto error;
}
preg->dev = device;
device->devt = MKDEV(major, minor);//主设备号为116
err = device_add(device);//会在/dev/snd/目录下创建pcm逻辑设备的设备文件,如pcmC0D0c..
if (err < 0)
goto error;
/* snd_minor为struct snd_minor *类型的全局数组,用于保存系统中的snd_minor
之后可以次设备号为下标在该数组中找到对应的snd_minor
*/
snd_minors[minor] = preg;
error:
mutex_unlock(&sound_mutex);
if (err < 0)
kfree(preg);
return err;
}2.4Control设备的创建
Control接口主要让用户空间的应用程序(alsa-lib)可以访问和控制音频codec芯片中的多路开关,滑动控件等。对于Mixer(混音)来说,Control接口显得尤为重要,从ALSA 0.9.x版本开始,所有的mixer工作都是通过control接口的API来实现的。在ALSA中,control用snd_kcontrol结构体描述。创建一个新的control至少需要实现 snd_kcontrol_new中的info、get和put这3个成员函数,snd_kcontrol_new结构体的定义如下:
struct snd_kcontrol_new {
snd_ctl_elem_iface_t iface; /* interface identifier */
unsigned int device; /* device/client number */
unsigned int subdevice; /* subdevice (substream) number */
const unsigned char *name; /* ASCII name of item */ /* 名称 */
unsigned int index; /* index of item */ /* 同名control,通过index区分 */
unsigned int access; /* access rights */ /* 访问权限 */
unsigned int count; /* count of same elements */ /* 元素的数量 */
snd_kcontrol_info_t *info; //用于获得该control的详细信息
snd_kcontrol_get_t *get; //获取control的目前值
snd_kcontrol_put_t *put; //用于把应用程序的控制值设置到control中
union {
snd_kcontrol_tlv_rw_t *c;
const unsigned int *p;
} tlv;
unsigned long private_value;
};
typedef int (snd_kcontrol_info_t) (struct snd_kcontrol * kcontrol, struct snd_ctl_elem_info * uinfo);
typedef int (snd_kcontrol_get_t) (struct snd_kcontrol * kcontrol, struct snd_ctl_elem_value * ucontrol);
typedef int (snd_kcontrol_put_t) (struct snd_kcontrol * kcontrol, struct snd_ctl_elem_value * ucontrol);设置好snd_kcontrol_new就可以调用snd_ctl_new1函数用于创建一个snd_kcontrol,之后调用snd_ctl_add函数用于将创建的snd_kcontrol添加到对应的card中。
struct snd_kcontrol *snd_ctl_new1(const struct snd_kcontrol_new *ncontrol,
void *private_data)
{
struct snd_kcontrol *kctl;
unsigned int count;
unsigned int access;
int err;
if (snd_BUG_ON(!ncontrol || !ncontrol->info))
return NULL;
count = ncontrol->count;
if (count == 0)
count = 1;
access = ncontrol->access;
if (access == 0)
access = SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_ACCESS_READWRITE;
access &= (SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_ACCESS_READWRITE |
SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_ACCESS_VOLATILE |
SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_ACCESS_INACTIVE |
SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_ACCESS_TLV_READWRITE |
SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_ACCESS_TLV_COMMAND |
SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_ACCESS_TLV_CALLBACK);
//创建snd_kcontrol
err = snd_ctl_new(&kctl, count, access, NULL);
if (err < 0)
return NULL;
/* The 'numid' member is decided when calling snd_ctl_add(). */
/* 根据snd_kcontrol_new初始化snd_kcontrol */
kctl->id.iface = ncontrol->iface;
kctl->id.device = ncontrol->device;
kctl->id.subdevice = ncontrol->subdevice;
if (ncontrol->name) {
strlcpy(kctl->id.name, ncontrol->name, sizeof(kctl->id.name));
if (strcmp(ncontrol->name, kctl->id.name) != 0)
pr_warn("ALSA: Control name '%s' truncated to '%s'\n",
ncontrol->name, kctl->id.name);
}
kctl->id.index = ncontrol->index;
kctl->info = ncontrol->info;
kctl->get = ncontrol->get;
kctl->put = ncontrol->put;
kctl->tlv.p = ncontrol->tlv.p;
kctl->private_value = ncontrol->private_value;
kctl->private_data = private_data;
return kctl;
}int snd_ctl_add(struct snd_card *card, struct snd_kcontrol *kcontrol)
{
struct snd_ctl_elem_id id;
unsigned int idx;
unsigned int count;
int err = -EINVAL;
if (! kcontrol)
return err;
if (snd_BUG_ON(!card || !kcontrol->info))
goto error;
id = kcontrol->id;
if (id.index > UINT_MAX - kcontrol->count)
goto error;
down_write(&card->controls_rwsem);
if (snd_ctl_find_id(card, &id)) {
up_write(&card->controls_rwsem);
dev_err(card->dev, "control %i:%i:%i:%s:%i is already present\n",
id.iface,
id.device,
id.subdevice,
id.name,
id.index);
err = -EBUSY;
goto error;
}
if (snd_ctl_find_hole(card, kcontrol->count) < 0) {
up_write(&card->controls_rwsem);
err = -ENOMEM;
goto error;
}
//把snd_kcontrol挂入snd_card的controls链表
list_add_tail(&kcontrol->list, &card->controls);
card->controls_count += kcontrol->count;
kcontrol->id.numid = card->last_numid + 1;
card->last_numid += kcontrol->count;
id = kcontrol->id;
count = kcontrol->count;
up_write(&card->controls_rwsem);
for (idx = 0; idx < count; idx++, id.index++, id.numid++)
snd_ctl_notify(card, SNDRV_CTL_EVENT_MASK_ADD, &id);
return 0;
error:
snd_ctl_free_one(kcontrol);
return err;
}在snd_card_new()函数中,会调用snd_ctl_create()函数创建声卡的Control逻辑设备:
int snd_ctl_create(struct snd_card *card)
{
//这个snd_device_ops不同类型的逻辑设备,其回调函数是不一样的
static struct snd_device_ops ops = {
.dev_free = snd_ctl_dev_free,
.dev_register = snd_ctl_dev_register,
.dev_disconnect = snd_ctl_dev_disconnect,
};
int err;
if (snd_BUG_ON(!card))
return -ENXIO;
if (snd_BUG_ON(card->number < 0 || card->number >= SNDRV_CARDS))
return -ENXIO;
//初始化Control逻辑设备的device
snd_device_initialize(&card->ctl_dev, card);
//设置Control逻辑设备device的name
dev_set_name(&card->ctl_dev, "controlC%d", card->number);
//创建Control逻辑设备的snd_device
err = snd_device_new(card, SNDRV_DEV_CONTROL, card, &ops);
if (err < 0)
put_device(&card->ctl_dev);
return err;
}在注册声卡的时候,snd_ctl_dev_register()函数会被调用:
static int snd_ctl_dev_register(struct snd_device *device)
{
struct snd_card *card = device->device_data;
return snd_register_device(SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_CONTROL, card, -1,
&snd_ctl_f_ops, card, &card->ctl_dev);
}Control设备对应的ops为snd_ctl_ops,为一个全局的变量:
static const struct file_operations snd_ctl_f_ops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = snd_ctl_read,
.open = snd_ctl_open,
.release = snd_ctl_release,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.poll = snd_ctl_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = snd_ctl_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = snd_ctl_ioctl_compat,
.fasync = snd_ctl_fasync,
};例如在用户空间中通过ioctl来控制底层设备:
static long snd_ctl_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
struct snd_ctl_file *ctl;
struct snd_card *card;
struct snd_kctl_ioctl *p;
void __user *argp = (void __user *)arg;
int __user *ip = argp;
int err;
ctl = file->private_data;
card = ctl->card;
if (snd_BUG_ON(!card))
return -ENXIO;
switch (cmd) {
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_PVERSION:
return put_user(SNDRV_CTL_VERSION, ip) ? -EFAULT : 0;
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_CARD_INFO:
return snd_ctl_card_info(card, ctl, cmd, argp);
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_ELEM_LIST:
return snd_ctl_elem_list(card, argp);
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_ELEM_INFO:
return snd_ctl_elem_info_user(ctl, argp); //获取control的详细信息
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_ELEM_READ:
return snd_ctl_elem_read_user(card, argp); //读取control的当前值
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_ELEM_WRITE:
return snd_ctl_elem_write_user(ctl, argp); //把应用程序的控制值设置到control中
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_ELEM_LOCK:
return snd_ctl_elem_lock(ctl, argp);
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_ELEM_UNLOCK:
return snd_ctl_elem_unlock(ctl, argp);
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_ELEM_ADD:
return snd_ctl_elem_add_user(ctl, argp, 0);
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_ELEM_REPLACE:
return snd_ctl_elem_add_user(ctl, argp, 1);
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_ELEM_REMOVE:
return snd_ctl_elem_remove(ctl, argp);
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_SUBSCRIBE_EVENTS:
return snd_ctl_subscribe_events(ctl, ip);
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_TLV_READ:
return snd_ctl_tlv_ioctl(ctl, argp, SNDRV_CTL_TLV_OP_READ);
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_TLV_WRITE:
return snd_ctl_tlv_ioctl(ctl, argp, SNDRV_CTL_TLV_OP_WRITE);
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_TLV_COMMAND:
return snd_ctl_tlv_ioctl(ctl, argp, SNDRV_CTL_TLV_OP_CMD);
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_POWER:
return -ENOPROTOOPT;
case SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_POWER_STATE:
#ifdef CONFIG_PM
return put_user(card->power_state, ip) ? -EFAULT : 0;
#else
return put_user(SNDRV_CTL_POWER_D0, ip) ? -EFAULT : 0;
#endif
}
down_read(&snd_ioctl_rwsem);
list_for_each_entry(p, &snd_control_ioctls, list) {
err = p->fioctl(card, ctl, cmd, arg);
if (err != -ENOIOCTLCMD) {
up_read(&snd_ioctl_rwsem);
return err;
}
}
up_read(&snd_ioctl_rwsem);
dev_dbg(card->dev, "unknown ioctl = 0x%x\n", cmd);
return -ENOTTY;
}3.ASOC框架
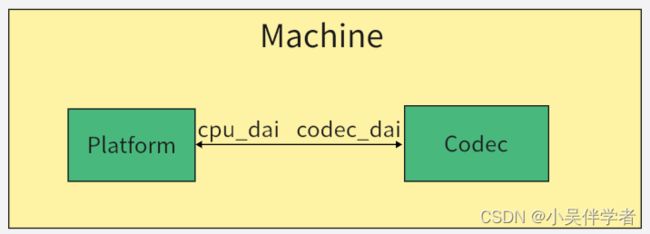
ASoC--ALSA System on Chip ,是建立在标准ALSA驱动层上,为了更好地支持嵌入式处理器和移动设备中的音频Codec的一套软件体系。ASoC被分为Machine、Platform和Codec三大部分,其中的Machine驱动负责Platform和Codec之间的耦合以及部分和设备或板子特定的代码,再次引用上一节的内容:Machine驱动负责处理机器特有的一些控件和音频事件(例如,当播放音频时,需要先行打开一个放大器);单独的Platform和Codec驱动是不能工作的,它必须由Machine驱动把它们结合在一起才能完成整个设备的音频处理工作。
通常一个声卡设备,大概包含以下几个物理设备或者外设:
Codec:音频编解码控制器,包括模拟麦或者spk。
AMIC/SPK/DMIC:纯硬件电路。麦克风或者spk,软件无需干预;
DMA:对于硬件设备的数据量,大多情况都是通过DMA搬运来提高效率;
cpu:整个soc平台,主要提供音频通信接口来实现和codec传输。比如(I2S/PDM等);
DAI:音频接口,抽象概念,比如I2S等。
Card:抽象概念,声卡;
capture:抽象概念;表示录音设备;
Playback:抽象概念,表示软件设备。
3.1ASOC中的Machine
主要是将cpu_dai与codec_dai进行连接,然后创建了对应的PCM,注册了声卡。将platform与codec进行联系。
3.2ASOC中的platform
Platform驱动的主要作用是完成音频数据的管理,最终通过CPU的数字音频接口(DAI)把音频数据传送给Codec进行处理,最终由Codec输出驱动耳机或者是喇叭的音信信号。在具体实现上,ASoC有把Platform驱动分为两个部分:snd_soc_platform_driver 和snd_soc_dai_driver。其中,platform_driver负责管理音频数据,把音频数据通过dma或其他操作传送至cpu dai中,dai_driver则主要完成cpu一侧的dai的参数配置,同时也会通过一定的途径把必要的dma等参数与snd_soc_platform_driver进行交互。
通常ASOC把snd_soc_platform_driver注册为一个系统的platform_driver,我们需要做的是:
(1)定义一个snd_soc_platform_driver结构的实例;
(2)在platform_driver的probe回调中利用ASOC的API:snd_soc_register_platform()注册上面定义的实例;
(3)实现snd_soc_platform_driver的各个回调函数;
snd_soc_register_platform() 该函数用于注册一个snd_soc_platform,只有注册以后,它才可以被Machine驱动使用。它的代码已经清晰地表达了它的实现过程:
int snd_soc_register_platform(struct device *dev,
const struct snd_soc_platform_driver *platform_drv)
{
struct snd_soc_platform *platform;
int ret;
dev_dbg(dev, "ASoC: platform register %s\n", dev_name(dev));
platform = kzalloc(sizeof(struct snd_soc_platform), GFP_KERNEL); //分配platform结构体
if (platform == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
ret = snd_soc_add_platform(dev, platform, platform_drv); //向soc添加platform
if (ret)
kfree(platform);
return ret;
}struct snd_soc_platform {
struct device *dev;
const struct snd_soc_platform_driver *driver;
struct list_head list; //链表,用于将platform挂载到platform_list中
struct snd_soc_component component; //component单元,连接platform和codec的桥梁
};/**
* snd_soc_add_platform - Add a platform to the ASoC core
* @dev: The parent device for the platform
* @platform: The platform to add
* @platform_driver: The driver for the platform
*/
int snd_soc_add_platform(struct device *dev, struct snd_soc_platform *platform,
const struct snd_soc_platform_driver *platform_drv)
{
int ret;
ret = snd_soc_component_initialize(&platform->component,
&platform_drv->component_driver, dev); //初始化component
if (ret)
return ret;
platform->dev = dev;
platform->driver = platform_drv; //初始化driver
if (platform_drv->probe)
platform->component.probe = snd_soc_platform_drv_probe;
if (platform_drv->remove)
platform->component.remove = snd_soc_platform_drv_remove;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_FS
platform->component.debugfs_prefix = "platform";
#endif
mutex_lock(&client_mutex);
snd_soc_component_add_unlocked(&platform->component);
list_add(&platform->list, &platform_list); //将初始化的platform添加到链表platform_list中
mutex_unlock(&client_mutex);
dev_dbg(dev, "ASoC: Registered platform '%s'\n",
platform->component.name);
return 0;
}定义了三个全局的链表用来匹配:
static LIST_HEAD(platform_list);
static LIST_HEAD(codec_list);
static LIST_HEAD(component_list);static int snd_soc_component_initialize(struct snd_soc_component *component,
const struct snd_soc_component_driver *driver, struct device *dev)
{
struct snd_soc_dapm_context *dapm;
component->name = fmt_single_name(dev, &component->id);
if (!component->name) {
dev_err(dev, "ASoC: Failed to allocate name\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
component->dev = dev;
component->driver = driver;
component->probe = component->driver->probe;
component->remove = component->driver->remove;
if (!component->dapm_ptr)
component->dapm_ptr = &component->dapm;
dapm = component->dapm_ptr;
dapm->dev = dev;
dapm->component = component;
dapm->bias_level = SND_SOC_BIAS_OFF;
dapm->idle_bias_off = true;
if (driver->seq_notifier)
dapm->seq_notifier = snd_soc_component_seq_notifier;
if (driver->stream_event)
dapm->stream_event = snd_soc_component_stream_event;
component->controls = driver->controls;
component->num_controls = driver->num_controls;
component->dapm_widgets = driver->dapm_widgets;
component->num_dapm_widgets = driver->num_dapm_widgets;
component->dapm_routes = driver->dapm_routes;
component->num_dapm_routes = driver->num_dapm_routes;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&component->dai_list); //初始化component中的dai_list,dai_list主要是用于挂载cpu_dai和codec_dai
mutex_init(&component->io_mutex);
return 0;
}3.3ASOC中的CODEC
在移动设备中,Codec的作用可以归结为4种,分别是:
(1)对PCM等信号进行D/A转换,把数字的音频信号转换为模拟信号;
(2)对Mic、Linein或者其他输入源的模拟信号进行A/D转换,把模拟的声音信号转变CPU能够处理的数字信号;
(3)对音频通路进行控制,比如播放音乐,收听调频收音机,又或者接听电话时,音频信号在codec内的流通路线是不一样的;
(4)对音频信号做出相应的处理,例如音量控制,功率放大,EQ控制等等;
ASoC对Codec驱动的一个基本要求是:驱动程序的代码必须要做到平台无关性,以方便同一个Codec的代码不经修改即可用在不同的平台上。
描述Codec的最主要的几个数据结构分别是:snd_soc_codec,snd_soc_codec_driver,snd_soc_dai,snd_soc_dai_driver,其中的snd_soc_dai和snd_soc_dai_driver在ASoC的Platform驱动中也会使用到,Platform和Codec的DAI通过snd_soc_dai_link结构,在Machine驱动中进行绑定连接。
/* SoC Audio Codec device */
struct snd_soc_codec {
struct device *dev; /* 指向Codec设备的指针 */
const struct snd_soc_codec_driver *driver; /* 指向该codec的驱动的指针 */
struct list_head list;
struct list_head card_list;
/* runtime */
unsigned int cache_bypass:1; /* Suppress access to the cache */
unsigned int suspended:1; /* Codec is in suspend PM state */
unsigned int cache_init:1; /* codec cache has been initialized */
/* codec IO */
void *control_data; /* codec control (i2c/3wire) data */ /* 该指针指向的结构用于对codec的控制,通常和read,write字段联合使用 */
hw_write_t hw_write;
void *reg_cache;
/* component */
struct snd_soc_component component;
/* dapm */
struct snd_soc_dapm_context dapm;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_FS
struct dentry *debugfs_reg;
#endif
};/* codec driver */
struct snd_soc_codec_driver {
/* driver ops */
int (*probe)(struct snd_soc_codec *); /* codec驱动的probe函数,由snd_soc_instantiate_card回调 */
int (*remove)(struct snd_soc_codec *);
int (*suspend)(struct snd_soc_codec *); /* 电源管理 */
int (*resume)(struct snd_soc_codec *); /* 电源管理 */
struct snd_soc_component_driver component_driver;
/* Default control and setup, added after probe() is run */
const struct snd_kcontrol_new *controls;
int num_controls;
const struct snd_soc_dapm_widget *dapm_widgets;
int num_dapm_widgets;
const struct snd_soc_dapm_route *dapm_routes;
int num_dapm_routes;
/* codec wide operations */
int (*set_sysclk)(struct snd_soc_codec *codec,
int clk_id, int source, unsigned int freq, int dir);
int (*set_pll)(struct snd_soc_codec *codec, int pll_id, int source,
unsigned int freq_in, unsigned int freq_out);
/* codec IO */
struct regmap *(*get_regmap)(struct device *);
unsigned int (*read)(struct snd_soc_codec *, unsigned int);
int (*write)(struct snd_soc_codec *, unsigned int, unsigned int);
unsigned int reg_cache_size;
short reg_cache_step;
short reg_word_size;
const void *reg_cache_default;
/* codec bias level */
int (*set_bias_level)(struct snd_soc_codec *,
enum snd_soc_bias_level level);
bool idle_bias_off;
bool suspend_bias_off;
void (*seq_notifier)(struct snd_soc_dapm_context *,
enum snd_soc_dapm_type, int);
bool ignore_pmdown_time; /* Doesn't benefit from pmdown delay */
};struct snd_soc_dai {
const char *name;//描述dai的名称
int id;
struct device *dev;
/* driver ops */
struct snd_soc_dai_driver *driver; //指向snd_soc_dai_driver,这个结构里描述了cpu_dai的支持类型和各种对cpu_dai进行操作的api
/* DAI runtime info */
unsigned int capture_active:1; /* stream is in use */
unsigned int playback_active:1; /* stream is in use */
unsigned int symmetric_rates:1;
unsigned int symmetric_channels:1;
unsigned int symmetric_samplebits:1;
unsigned int active;
unsigned char probed:1;
struct snd_soc_dapm_widget *playback_widget; //cpu_dai播放时使用的dma
struct snd_soc_dapm_widget *capture_widget; //cpu_dai录制时使用的dma
/* DAI DMA data */
void *playback_dma_data;
void *capture_dma_data;
/* Symmetry data - only valid if symmetry is being enforced */
unsigned int rate;
unsigned int channels;
unsigned int sample_bits;
/* parent platform/codec */
struct snd_soc_codec *codec; //指向所关联的codec设备
struct snd_soc_component *component; //指向所关联的component
/* CODEC TDM slot masks and params (for fixup) */
unsigned int tx_mask;
unsigned int rx_mask;
struct list_head list;
};struct snd_soc_dai_driver {
/* DAI description */
const char *name; //DAI驱动名字
unsigned int id;
unsigned int base;
/* DAI driver callbacks */
int (*probe)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai); /* dai驱动的probe函数,由snd_soc_instantiate_card回调 */
int (*remove)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai);
int (*suspend)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai); /* 电源管理 */
int (*resume)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai);
/* compress dai */
bool compress_dai;
/* DAI is also used for the control bus */
bool bus_control;
/* ops */
const struct snd_soc_dai_ops *ops; /* 指向本dai的snd_soc_dai_ops结构 */
/* DAI capabilities */
struct snd_soc_pcm_stream capture; /* 描述capture的能力 */
struct snd_soc_pcm_stream playback; /* 描述playback的能力 */
unsigned int symmetric_rates:1;
unsigned int symmetric_channels:1;
unsigned int symmetric_samplebits:1;
/* probe ordering - for components with runtime dependencies */
int probe_order;
int remove_order;
};
struct snd_soc_dai_ops {
/*
* DAI clocking configuration, all optional.
* Called by soc_card drivers, normally in their hw_params.
*/
int (*set_sysclk)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai,
int clk_id, unsigned int freq, int dir);
int (*set_pll)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai, int pll_id, int source,
unsigned int freq_in, unsigned int freq_out);
int (*set_clkdiv)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai, int div_id, int div);
int (*set_bclk_ratio)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai, unsigned int ratio);
/*
* DAI format configuration
* Called by soc_card drivers, normally in their hw_params.
*/
int (*set_fmt)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai, unsigned int fmt);
int (*xlate_tdm_slot_mask)(unsigned int slots,
unsigned int *tx_mask, unsigned int *rx_mask);
int (*set_tdm_slot)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai,
unsigned int tx_mask, unsigned int rx_mask,
int slots, int slot_width);
int (*set_channel_map)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai,
unsigned int tx_num, unsigned int *tx_slot,
unsigned int rx_num, unsigned int *rx_slot);
int (*set_tristate)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai, int tristate);
/*
* DAI digital mute - optional.
* Called by soc-core to minimise any pops.
*/
int (*digital_mute)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai, int mute);
int (*mute_stream)(struct snd_soc_dai *dai, int mute, int stream);
/*
* ALSA PCM audio operations - all optional.
* Called by soc-core during audio PCM operations.
*/
int (*startup)(struct snd_pcm_substream *,
struct snd_soc_dai *);
void (*shutdown)(struct snd_pcm_substream *,
struct snd_soc_dai *);
int (*hw_params)(struct snd_pcm_substream *,
struct snd_pcm_hw_params *, struct snd_soc_dai *);
int (*hw_free)(struct snd_pcm_substream *,
struct snd_soc_dai *);
int (*prepare)(struct snd_pcm_substream *,
struct snd_soc_dai *);
/*
* NOTE: Commands passed to the trigger function are not necessarily
* compatible with the current state of the dai. For example this
* sequence of commands is possible: START STOP STOP.
* So do not unconditionally use refcounting functions in the trigger
* function, e.g. clk_enable/disable.
*/
int (*trigger)(struct snd_pcm_substream *, int,
struct snd_soc_dai *);
int (*bespoke_trigger)(struct snd_pcm_substream *, int,
struct snd_soc_dai *);
/*
* For hardware based FIFO caused delay reporting.
* Optional.
*/
snd_pcm_sframes_t (*delay)(struct snd_pcm_substream *,
struct snd_soc_dai *);
};Codec驱动的代码要做到平台无关性,要使得Machine驱动能够使用该Codec,Codec驱动的首要任务就是确定snd_soc_codec和snd_soc_dai的实例,并把它们注册到系统中,注册后的codec和dai才能为Machine驱动所用。比如sound/soc/codecs中的wm8960.c,其适用的是i2c总线。
static const struct i2c_device_id wm8960_i2c_id[] = {
{ "wm8960", 0 },
{ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(i2c, wm8960_i2c_id);
static const struct of_device_id wm8960_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "wlf,wm8960", },
{ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, wm8960_of_match);
static struct i2c_driver wm8960_i2c_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "wm8960",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.of_match_table = wm8960_of_match,
},
.probe = wm8960_i2c_probe,
.remove = wm8960_i2c_remove,
.id_table = wm8960_i2c_id,
};
module_i2c_driver(wm8960_i2c_driver);在设备树中有以下内容:
当匹配到设备,则会进行probe:
static int wm8960_i2c_probe(struct i2c_client *i2c,
const struct i2c_device_id *id)
{
struct wm8960_data *pdata = dev_get_platdata(&i2c->dev);
struct wm8960_priv *wm8960;
int ret;
int repeat_reset = 10;
wm8960 = devm_kzalloc(&i2c->dev, sizeof(struct wm8960_priv),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (wm8960 == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
wm8960->mclk = devm_clk_get(&i2c->dev, "mclk");
if (IS_ERR(wm8960->mclk)) {
if (PTR_ERR(wm8960->mclk) == -EPROBE_DEFER)
return -EPROBE_DEFER;
}
wm8960->regmap = devm_regmap_init_i2c(i2c, &wm8960_regmap);
if (IS_ERR(wm8960->regmap))
return PTR_ERR(wm8960->regmap);
if (pdata)
memcpy(&wm8960->pdata, pdata, sizeof(struct wm8960_data));
else if (i2c->dev.of_node)
wm8960_set_pdata_from_of(i2c, &wm8960->pdata);
do {
ret = wm8960_reset(wm8960->regmap);
repeat_reset--;
} while (repeat_reset > 0 && ret != 0);
if (ret != 0) {
dev_err(&i2c->dev, "Failed to issue reset\n");
return ret;
}
if (wm8960->pdata.shared_lrclk) {
ret = regmap_update_bits(wm8960->regmap, WM8960_ADDCTL2,
0x4, 0x4);
if (ret != 0) {
dev_err(&i2c->dev, "Failed to enable LRCM: %d\n",
ret);
return ret;
}
}
/* Latch the update bits */
regmap_update_bits(wm8960->regmap, WM8960_LINVOL, 0x100, 0x100);
regmap_update_bits(wm8960->regmap, WM8960_RINVOL, 0x100, 0x100);
regmap_update_bits(wm8960->regmap, WM8960_LADC, 0x100, 0x100);
regmap_update_bits(wm8960->regmap, WM8960_RADC, 0x100, 0x100);
regmap_update_bits(wm8960->regmap, WM8960_LDAC, 0x100, 0x100);
regmap_update_bits(wm8960->regmap, WM8960_RDAC, 0x100, 0x100);
regmap_update_bits(wm8960->regmap, WM8960_LOUT1, 0x100, 0x100);
regmap_update_bits(wm8960->regmap, WM8960_ROUT1, 0x100, 0x100);
regmap_update_bits(wm8960->regmap, WM8960_LOUT2, 0x100, 0x100);
regmap_update_bits(wm8960->regmap, WM8960_ROUT2, 0x100, 0x100);
i2c_set_clientdata(i2c, wm8960);
ret = snd_soc_register_codec(&i2c->dev,
&soc_codec_dev_wm8960, &wm8960_dai, 1);
return ret;
}可见,Codec驱动的第一个步骤就是定义snd_soc_codec_driver和snd_soc_dai_driver的实例,然后调用snd_soc_register_codec函数对Codec进行注册。进入snd_soc_register_codec函数看看:
/**
* snd_soc_register_codec - Register a codec with the ASoC core
*
* @codec: codec to register
*/
int snd_soc_register_codec(struct device *dev,
const struct snd_soc_codec_driver *codec_drv,
struct snd_soc_dai_driver *dai_drv,
int num_dai)
{
struct snd_soc_codec *codec;
struct snd_soc_dai *dai;
int ret, i;
dev_dbg(dev, "codec register %s\n", dev_name(dev));
codec = kzalloc(sizeof(struct snd_soc_codec), GFP_KERNEL);//申请一个snd_soc_codec实例
if (codec == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
codec->component.dapm_ptr = &codec->dapm;
codec->component.codec = codec;
ret = snd_soc_component_initialize(&codec->component,
&codec_drv->component_driver, dev); 给codec中component初始化
if (ret)
goto err_free;
if (codec_drv->controls) {
codec->component.controls = codec_drv->controls;
codec->component.num_controls = codec_drv->num_controls;
}
if (codec_drv->dapm_widgets) {
codec->component.dapm_widgets = codec_drv->dapm_widgets;
codec->component.num_dapm_widgets = codec_drv->num_dapm_widgets;
}
if (codec_drv->dapm_routes) {
codec->component.dapm_routes = codec_drv->dapm_routes;
codec->component.num_dapm_routes = codec_drv->num_dapm_routes;
}
//初始化codec结构体
if (codec_drv->probe)
codec->component.probe = snd_soc_codec_drv_probe;
if (codec_drv->remove)
codec->component.remove = snd_soc_codec_drv_remove;
if (codec_drv->write)
codec->component.write = snd_soc_codec_drv_write;
if (codec_drv->read)
codec->component.read = snd_soc_codec_drv_read;
codec->component.ignore_pmdown_time = codec_drv->ignore_pmdown_time;
codec->dapm.idle_bias_off = codec_drv->idle_bias_off;
codec->dapm.suspend_bias_off = codec_drv->suspend_bias_off;
if (codec_drv->seq_notifier)
codec->dapm.seq_notifier = codec_drv->seq_notifier;
if (codec_drv->set_bias_level)
codec->dapm.set_bias_level = snd_soc_codec_set_bias_level;
codec->dev = dev;
codec->driver = codec_drv;
codec->component.val_bytes = codec_drv->reg_word_size;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_FS
codec->component.init_debugfs = soc_init_codec_debugfs;
codec->component.debugfs_prefix = "codec";
#endif
if (codec_drv->get_regmap)
codec->component.regmap = codec_drv->get_regmap(dev);
for (i = 0; i < num_dai; i++) {
fixup_codec_formats(&dai_drv[i].playback);
fixup_codec_formats(&dai_drv[i].capture);
}
ret = snd_soc_register_dais(&codec->component, dai_drv, num_dai, false); //注册codec dai,将dai介入component->dai_list中
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(dev, "ASoC: Failed to register DAIs: %d\n", ret);
goto err_cleanup;
}
list_for_each_entry(dai, &codec->component.dai_list, list)
dai->codec = codec;
mutex_lock(&client_mutex);
snd_soc_component_add_unlocked(&codec->component); //将codec中的component加入全局变量component_list中
list_add(&codec->list, &codec_list);
mutex_unlock(&client_mutex);
dev_dbg(codec->dev, "ASoC: Registered codec '%s'\n",
codec->component.name);
return 0;
err_cleanup:
snd_soc_component_cleanup(&codec->component);
err_free:
kfree(codec);
return ret;
}