java HashMap到ConcurrentHashMap(1.8版本为主)
又是一年加薪季,大佬们互相交换资源,小菜鸡们互相换坑。回首自己四年多的职业生涯,搭配社会发展、996、内卷、程序员发展、人生目标等各种话题,秃然想好好努力卷一下,好歹多挣点钱回家转型啊。于是网上整理了一些面试大纲,配合一些博客,整理出了一个复习计划,同时整理成博客,方便自己后续复习。
整个计划分为十个部分(集合、多线程、网络、Spring和Mybatis、MySQL、JVM、Kafka、Redis、Zookeeper、分布式),有缺漏或不正确的地方,欢迎指正。
先看看集合的接口实现框架图
HashMap
简述:
键值对、无序、线程不安全
底层实现是数组+链表+红黑树
put过程:
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node[] tab; Node p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
} put流程图:
resize扩容过程:
final Node[] resize() {
Node[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node[] newTab = (Node[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
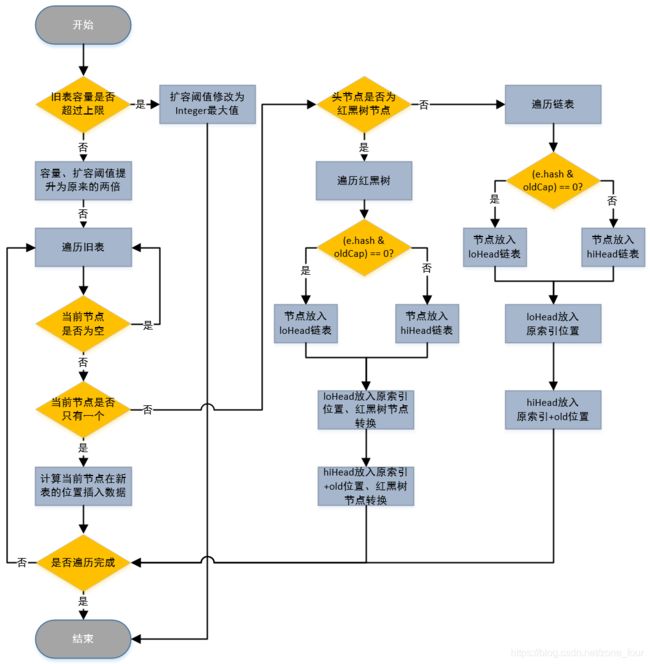
} 扩容流程图:
简单的描述两个点:
- hash方法中(h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16)是指高16位参与运算。前面是key转为hash变成总长32位的二进制数然后赋值给h,后面是h这个32位的哈希值整体右移16位。两个结果做异或运算,得出一个高位和低位都参与的哈希值。
- 索引位置(n-1) & hash,说这个之前,要先说下HashMap的初始化容器的时候计算容量的方法。
/**
* Returns a power of two size for the given target capacity.
*/
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
传入cap以后,先减一(防止cap等于2的幂次方的情况),然后无符号右移1位,然后无符号右移2位....五次操作,覆盖32位哈希值,最后+1得到最终的容器大小,也就是2的幂次方。
回到计算索引位置,通过n-1的哈希,有效数字都是1,区别只是多少个1,比如64-1 = 63 = 11 1111,hash值和11 1111 与运算 以后,得到索引就是在n-1区间内的平均分布值了,类似于取余。
有点忘记的可以看下面的hash模拟
hash模拟:
ConcurrentHashMap
简述:
java1.5版本,hashMap开发者之一的道格利提交了同时进行的包(concurrent)包,里面包含了线程和并发的一些工具类。其中加瓦.工具.同时进行的.同时进行的HashMap(java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap)实现了线程安全,成为了多线程并发中可以安全使用的HashMap。
键值对、无序、线程安全
是目前多线程常用的线程安全的集合。
put过程:
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node[] tab = table;;) {
Node f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
} put流程图:
扩容流程:
private final void transfer(Node[] tab, Node[] nextTab) {
int n = tab.length, stride;
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
if (nextTab == null) { // initiating
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node[] nt = (Node[])new Node[n << 1];
nextTab = nt;
} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
nextTable = nextTab;
transferIndex = n;
}
int nextn = nextTab.length;
ForwardingNode fwd = new ForwardingNode(nextTab);
boolean advance = true;
boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab
for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
Node f; int fh;
while (advance) {
int nextIndex, nextBound;
if (--i >= bound || finishing)
advance = false;
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
i = -1;
advance = false;
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
bound = nextBound;
i = nextIndex - 1;
advance = false;
}
}
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc;
if (finishing) {
nextTable = null;
table = nextTab;
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);
return;
}
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return;
finishing = advance = true;
i = n; // recheck before commit
}
}
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
advance = true; // already processed
else {
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node ln, hn;
if (fh >= 0) {
int runBit = fh & n;
Node lastRun = f;
for (Node p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
int b = p.hash & n;
if (b != runBit) {
runBit = b;
lastRun = p;
}
}
if (runBit == 0) {
ln = lastRun;
hn = null;
}
else {
hn = lastRun;
ln = null;
}
for (Node p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
if ((ph & n) == 0)
ln = new Node(ph, pk, pv, ln);
else
hn = new Node(ph, pk, pv, hn);
}
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
TreeBin t = (TreeBin)f;
TreeNode lo = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode hi = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
for (Node e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {
int h = e.hash;
TreeNode p = new TreeNode
(h, e.key, e.val, null, null);
if ((h & n) == 0) {
if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
lo = p;
else
loTail.next = p;
loTail = p;
++lc;
}
else {
if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
hi = p;
else
hiTail.next = p;
hiTail = p;
++hc;
}
}
ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin(lo) : t;
hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin(hi) : t;
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
。。。。。
扩容流程太长,而且网上博客到处都有,不乏讲解清晰、简单明了的文章,所以我就偷懒了。
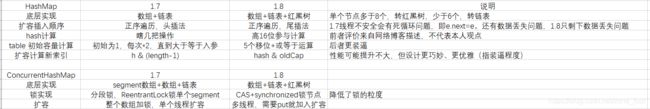
HashMap和concurrentHash 1.8的优化
TreeMap
LinkedHashMap
HashTable
List
ArrayList
LinkedList
Vector
CopyOnWriteArrayList
set
HashSet
TreeSet
LinkedHashSet
总结:
其他的集合不多赘叙了,建议先看HashMap源码,再看concurrentHashMap源码,过程为:先粗略看,然后细看,不懂就网上找解析对比着看,看完自己画个流程图或者自己写个巩固下。看完这两个集合的源码,其他集合的源码上手也就快了。
集合分为Map、List、Set三类,大三类又细分到hash、Linked、Tree,本质上就是各种底层集合的组合,了解数组、链表、二叉树,或者通过这些集合去了解,都是挺好的。
开头说的整理网上的大缸~下面几篇都是我看过比较好的文章,推荐给菜鸡朋友们,大佬请忽略。
hashMap
源码解析https://blog.csdn.net/ywlmsm1224811/article/details/91388815讲的清晰详细,没看过的可以看看
面试问题https://blog.csdn.net/v123411739/article/details/106324537这个本人挺牛的,文笔还很逗比,其他文章也有值得看看的
concurrentHashMap
源码解析https://blog.csdn.net/xingxiupaioxue/article/details/88062163整体不错
扩容部分https://blog.csdn.net/ZOKEKAI/article/details/90051567扩容流程的图画的挺好,因为他的图,我自己都不想丢脸继续画了
PS:先粗糙结尾了,等有时间再补充细节吧~
我要我偷偷的学习,然后惊艳所有面试官!