gin全解
文章目录
- 介绍
- 安装
- 快速开始(三种启动方式)
- 参数
-
- 获取querystring参数
-
- 其他不常用方法
- 表单参数(form参数)
-
- 其他不常用方法
- 获取path参数
- 参数绑定
- 文件上传
-
- 单个文件
- 多个文件
- 请求(ctx.Request)
- 响应
-
- gin.H{}
- 字符串响应
- JSON/YAML/TOML/ProtoBuf响应
- 重定向
-
- http重定向
- 路由重定向
- 同步异步
- 视图响应
- 文件响应(静态文件+文件响应)
- 路由
-
- 普通路由
- 路由组
- 路由原理
- Gin中间件
-
- Next()
- Abort()
- 定义中间件
- 注册中间件
-
- 为全局路由注册
- 为某个路由单独注册
- 为路由组注册中间件
- 小例子
- 报错后的顺序
- 提前返回的顺序
- 中间件注意事项
-
- gin默认中间件
- gin中间件中使用goroutine
- 中间件推荐
-
- 跨域中间件
- jwt中间件
- 日志中间件
-
- 基于zap的中间件
- 在gin项目中使用zap
- 会话控制
-
- Cookie
- Session=Cookie+存储
- Token
- 参数验证
-
- 自定义验证
- 自定义验证v10
-
- 变量验证
- 结构体验证
- 标签
- 合理的拆分目录
-
- 单app单router
- 单app多router
-
- 目录结构
- routers/shop.go
- main.go
- 多app多router
-
- 目录结构
- app/shop/router.go
- routers/routers.go
- main.go
- gin使用Air实现实时热重载
- [部署Go Web应用的N+1种方法](https://blog.csdn.net/General_zy/article/details/124908517)
- go日志库log/zap/logrus
- orm框架
介绍
Gin 是一个用 Go (Golang) 编写的 Web 框架。 它具有类似 martini 的 API,性能要好得多,多亏了 httprouter,速度提高了 40 倍。 如果您需要性能和良好的生产力,您一定会喜欢 Gin。
安装
要求:Go 1.13 及以上版本
go get -u github.com/gin-gonic/gin
快速开始(三种启动方式)
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
engine.GET("/", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.JSON(200, gin.H{"msg": "OK2"})
})
// 方法1
//engine.Run(":8000")
// 方法2
//http.ListenAndServe(":8000", engine)
// 方法3
server := &http.Server{
Addr: ":8000",
Handler: engine,
ReadTimeout: 10 * time.Second,
WriteTimeout: 10 * time.Second,
MaxHeaderBytes: 1 << 20,
}
server.ListenAndServe()
}
参数
获取querystring参数
querystring指的是URL中?后面携带的参数。- URL参数可以通过
DefaultQuery()或Query()方法获取。 - DefaultQuery()若参数不存在,返回默认值,Query()若参数不存在,返回空串。
func main() {
//Default返回一个默认的路由引擎
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/user/search", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 可以添加默认值
username := c.DefaultQuery("username", "Generalzy")
//username := c.Query("username")
// 获取address信息
address := c.Query("address")
//输出json结果给调用方
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "ok",
"username": username,
"address": address,
})
})
r.Run()
}
http://localhost:8080/user/search?username=Generalzy&address=中国
其他不常用方法
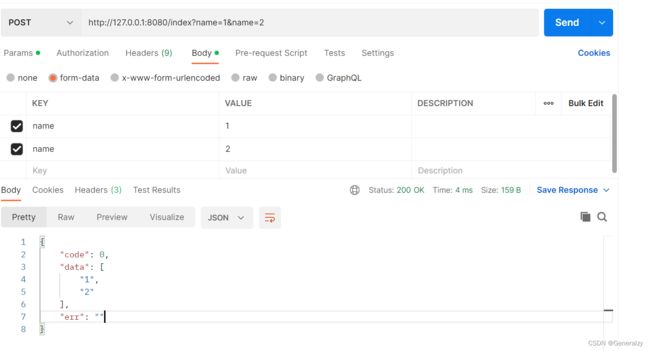
- GetQueryArray()获取列表
func Index(ctx *gin.Context) {
if val,ok:=ctx.GetQueryArray("name");ok{
fmt.Println(val)
ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK,gin.H{
"code":0,
"err":"",
"data":val,
})
}else{
ctx.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest,gin.H{
"code":1,
"err":"params error",
"data":[]interface{}{},
})
}
}
// http://127.0.0.1:8080/index?name=1&name=2
{
"code": 0,
"data": [
"1",
"2"
],
"err": ""
}
表单参数(form参数)
- 表单传输为post请求,http常见的传输格式为四种:
- application/json
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- application/xml
- multipart/form-data
- 表单参数可以通过PostForm()方法获取,该方法默认解析的是x-www-form-urlencoded
或from-data格式的参数 - 同样,
PostForm()若参数不存在返回空串,DefaultPostForm()若参数不存在返回默认值
func main() {
//Default返回一个默认的路由引擎
r := gin.Default()
r.POST("/user/search", func(c *gin.Context) {
// DefaultPostForm取不到值时会返回指定的默认值
//username := c.DefaultPostForm("username", "德玛西亚")
username := c.PostForm("username")
address := c.PostForm("address")
//输出json结果给调用方
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "ok",
"username": username,
"address": address,
})
})
r.Run(":8080")
}
其他不常用方法
- GetPostFormArray()与GetQueryArray()类型
获取path参数
请求的参数通过URL路径传递,例如:/user/search/德玛西亚/北京
func main() {
//Default返回一个默认的路由引擎
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/user/search/:username/:address", func(c *gin.Context) {
username := c.Param("username")
address := c.Param("address")
//输出json结果给调用方
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "ok",
"username": username,
"address": address,
})
})
r.Run(":8080")
}
参数绑定
为了能够更方便的获取请求相关参数,提高开发效率,可以基于请求的Content-Type识别请求数据类型并利用反射机制自动提取请求中QueryString、form表单、JSON、XML等参数到结构体中。 下面的示例代码演示了.ShouldBind()强大的功能,它能够基于请求自动提取JSON、form表单和QueryString类型的数据,并把值绑定到指定的结构体对象。
- 模型绑定可以将请求体绑定给一个类型,目前支持绑定的类型有 JSON, XML 和标准表单数据。
- 使用绑定方法时,Gin 会根据请求头中 Content-Type 来自动判断需要解析的类型。如果你明确绑定的类型,可以不用自动推断,而用
BindWith(&login, binding.Form)方法。
// Binding from JSON
type Login struct {
User string `form:"user" json:"user" binding:"required"`
Password string `form:"password" json:"password" binding:"required"`
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
// 绑定JSON的示例 ({"user": "q1mi", "password": "123456"})
router.POST("/loginJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {
var login Login
if err := c.ShouldBind(&login); err == nil {
fmt.Printf("login info:%#v\n", login)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"user": login.User,
"password": login.Password,
})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
}
})
// 绑定form表单示例 (user=q1mi&password=123456)
router.POST("/loginForm", func(c *gin.Context) {
var login Login
// ShouldBind()会根据请求的Content-Type自行选择绑定器
if err := c.ShouldBind(&login); err == nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"user": login.User,
"password": login.Password,
})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
}
})
// 绑定QueryString示例 (/loginQuery?user=q1mi&password=123456)
router.GET("/loginForm", func(c *gin.Context) {
var login Login
// ShouldBind()会根据请求的Content-Type自行选择绑定器
if err := c.ShouldBind(&login); err == nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"user": login.User,
"password": login.Password,
})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
}
})
// Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080
router.Run(":8080")
}
ShouldBind会按照下面的顺序解析请求中的数据完成绑定:
- 如果是
GET请求,只使用Form绑定引擎(query)(tag为form)。 - 如果是
POST请求,首先检查content-type是否为JSON或XML(tag为json),然后再使用Form(form-data)。 - 针对不同的绑定,gin提供了不同的tag,使用时建议查看具体绑定接口提供的
tag和方法防止无效绑定,比如:绑定给uri的要用uri:username,绑定给json的要用json:username,绑定给form的要用form:username…
了解:
URI数据解析和绑定
if err := c.ShouldBindUri(&login); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
Query数据解析和绑定
err := c.BindQuery(&p)
文件上传
- multipart/form-data格式用于文件上传
- gin文件上传与原生的net/http方法类似,不同在于gin把原生的request封装到c.Request
中
单个文件
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
// 处理multipart forms提交文件时默认的内存限制是32 MiB
// 可以通过下面的方式修改
// router.MaxMultipartMemory = 8 << 20 // 8 MiB
router.POST("/upload", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 单个文件
file, err := c.FormFile("f1")
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{
"message": err.Error(),
})
return
}
// 打印文件名
log.Println(file.Filename)
// 文件存储位置
dst := fmt.Sprintf("C:/tmp/%s", file.Filename)
// 上传文件到指定的目录
c.SaveUploadedFile(file, dst)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": fmt.Sprintf("'%s' uploaded!", file.Filename),
})
})
router.Run()
}
多个文件
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
// 处理multipart forms提交文件时默认的内存限制是32 MiB
// 可以通过下面的方式修改
// router.MaxMultipartMemory = 8 << 20 // 8 MiB
router.POST("/upload", func(c *gin.Context) {
// Multipart form
form, _ := c.MultipartForm()
files := form.File["file"]
for index, file := range files {
log.Println(file.Filename)
dst := fmt.Sprintf("C:/tmp/%s_%d", file.Filename, index)
// 上传文件到指定的目录
c.SaveUploadedFile(file, dst)
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": fmt.Sprintf("%d files uploaded!", len(files)),
})
})
router.Run()
}
请求(ctx.Request)
type Context struct {
// 封装了htpp的Request
Request *http.Request
// 继承了http的ResponseWriter接口
Writer ResponseWriter
...
}
-
请求头
ctx.Request.Header.Get() ctx.GetHeader() -
请求参数
-
cookies
-
上传文件
响应
- 响应头
- 附加cookie
- 字符串响应
gin.H{}
// H is a shortcut for map[string]interface{}
type H map[string]any
字符串响应
// String writes the given string into the response body.
func (c *Context) String(code int, format string, values ...any) {
c.Render(code, render.String{Format: format, Data: values})
}
func Index(ctx *gin.Context) {
ctx.String(http.StatusOK,"我是你%s大爷","二")
}
JSON/YAML/TOML/ProtoBuf响应
// JSON serializes the given struct as JSON into the response body.
// It also sets the Content-Type as "application/json".
func (c *Context) JSON(code int, obj any) {
c.Render(code, render.JSON{Data: obj})
}
// YAML serializes the given struct as YAML into the response body.
func (c *Context) YAML(code int, obj any) {
c.Render(code, render.YAML{Data: obj})
}
// TOML serializes the given struct as TOML into the response body.
func (c *Context) TOML(code int, obj interface{}) {
c.Render(code, render.TOML{Data: obj})
}
// ProtoBuf serializes the given struct as ProtoBuf into the response body.
func (c *Context) ProtoBuf(code int, obj any) {
c.Render(code, render.ProtoBuf{Data: obj})
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": fmt.Sprintf("%d files uploaded!", len(files)),
})
重定向
http重定向
r.GET("/test", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.Redirect(http.StatusMovedPermanently, "http://www.sogo.com/")
})
路由重定向
r.GET("/test", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 指定重定向的URL
c.Request.URL.Path = "/test2"
r.HandleContext(c)
})
r.GET("/test2", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"hello": "world"})
})
同步异步
goroutine机制可以方便的实现异步处理
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
engine.HandleMethodNotAllowed = true // 开启方法不允许校验
engine.GET("/long_async", func(context *gin.Context) {
// Copy 返回可以在请求范围之外安全使用的当前上下文的副本。当必须将上下文传递给 goroutine 时,必须使用它。
// goroutine中只能使用上下文的副本
// 1. 异步
cp := context.Copy()
go func() {
time.Sleep(5 * time.Second)
// 注意:goroutine中必须使用上下文副本
log.Println("done! in path", cp.Request.URL.Path)
}()
})
engine.GET("/long_sync", func(context *gin.Context) {
// 同步:可以使用原始上下文,context
time.Sleep(5 * time.Second)
log.Println("done! int path", context.Request.URL.Path)
})
engine.Run(":8000")
}
视图响应
先要使用LoadHTMLTemplates加载模板文件
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
// 加载模板文件
//engine.LoadHTMLGlob("html/*")
engine.LoadHTMLFiles("html/index.html", "html/user.html")
// url: http://127.0.0.1:8000
engine.GET("/index.html", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{"name": "张三"})
})
engine.GET("/user.html", func(context *gin.Context) {
var User struct{
User string `json:"user"`
Age int `json:"age"`
}
User.User = "李四"
User.Age = 18
data, _ := json.Marshal(&User)
m := make(map[string]any)
json.Unmarshal(data, &m)
context.HTML(http.StatusOK, "user.html", m)
})
engine.Run(":8000")
}
文件响应(静态文件+文件响应)
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
// url: http://127.0.0.1:8000/index/user.html
//engine.Static("/index", "./html")
// url: http://127.0.0.1:8000/index/index.html
//engine.StaticFS("/index", gin.Dir("./html", false))
// url: http://127.0.0.1:8000/index
engine.StaticFile("/index", "./html/index.html")
// 设置返回头并返回数据
fileContentDisposition := "attachment;filename=\"" + attachmentName + "\""
c.Header("Content-Type", "application/zip") // 这里是压缩文件类型 .zip
c.Header("Content-Disposition", fileContentDisposition)
c.Data(http.StatusOK, contentType, fileContent)
// fileContent是文件的字节流
ctx.DataFromReader(200, response.ContentLength, "application/octet-stream", fileContent, nil)
// 传入路径的文件下载
c.File("local/file.go")
engine.Run(":8000")
}
路由
普通路由
r.GET("/index", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
r.GET("/login", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
r.POST("/login", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
此外,还有一个可以匹配所有请求方法的Any方法如下:
r.Any("/test", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
为没有配置处理函数的路由添加处理程序,默认情况下它返回404代码,下面的代码为没有匹配到路由的请求都返回views/404.html页面。
r.NoRoute(func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusNotFound, "views/404.html", nil)
})
路由组
可以将拥有共同URL前缀的路由划分为一个路由组。习惯性一对{}包裹同组的路由,这只是为了看着清晰。
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
userGroup := r.Group("/user")
{
userGroup.GET("/index", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
userGroup.GET("/login", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
userGroup.POST("/login", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
}
shopGroup := r.Group("/shop")
{
shopGroup.GET("/index", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
shopGroup.GET("/cart", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
shopGroup.POST("/checkout", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
}
r.Run()
}
路由组也是支持嵌套的,例如:
shopGroup := r.Group("/shop")
{
shopGroup.GET("/index", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
shopGroup.GET("/cart", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
shopGroup.POST("/checkout", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
// 嵌套路由组
xx := shopGroup.Group("xx")
xx.GET("/oo", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
}
通常我们将路由分组用在划分业务逻辑或划分API版本时。
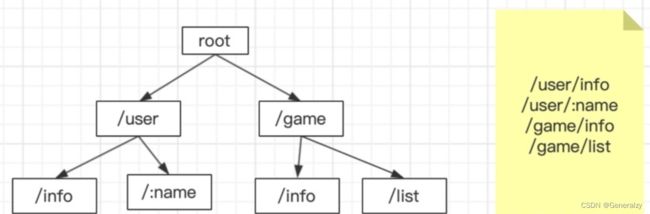
路由原理
-
Gin框架中的路由使用的是httprouter这个库。
-
其基本原理就是构造一个路由地址的前缀树。
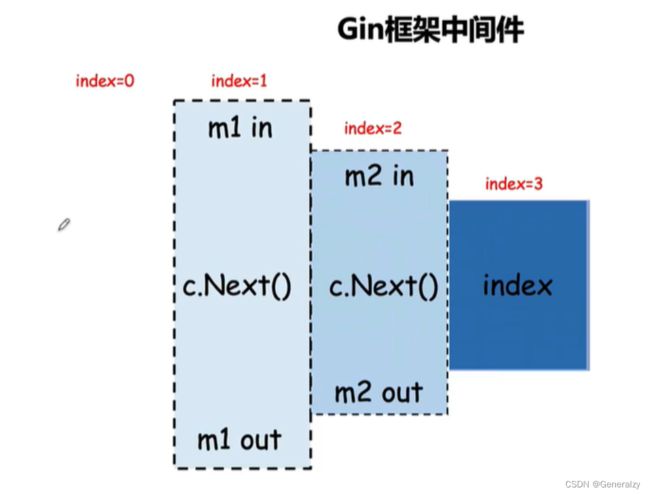
Gin中间件
Gin框架允许开发者在处理请求的过程中,加入用户自己的钩子(Hook)函数。这个钩子函数就叫中间件,中间件适合处理一些公共的业务逻辑,比如登录认证、权限校验、数据分页、记录日志、耗时统计等。
Next()
Abort()
定义中间件
Gin中的中间件必须是一个gin.HandlerFunc类型。
// StatCost 是一个统计耗时请求耗时的中间件
func StatCost() gin.HandlerFunc {
return func(c *gin.Context) {
start := time.Now()
// 可以通过c.Set在请求上下文中设置值,后续的处理函数能够取到该值
c.Set("name", "123")
// 调用该请求的剩余处理程序
c.Next()
// 不调用该请求的剩余处理程序
// c.Abort()
// 计算耗时
cost := time.Since(start)
log.Println(cost)
}
}
注册中间件
在gin框架中,可以为每个路由添加任意数量的中间件
为全局路由注册
func main() {
// 新建一个没有任何默认中间件的路由
r := gin.New()
// 注册一个全局中间件
r.Use(StatCost())
r.GET("/test", func(c *gin.Context) {
name := c.MustGet("name").(string) // 从上下文取值
log.Println(name)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "Hello world!",
})
})
r.Run()
}
为某个路由单独注册
// 给/test2路由单独注册中间件(可注册多个)
r.GET("/test2", StatCost(), func(c *gin.Context) {
name := c.MustGet("name").(string) // 从上下文取值
log.Println(name)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "Hello world!",
})
})
为路由组注册中间件
shopGroup := r.Group("/shop", StatCost())
{
shopGroup.GET("/index", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
...
}
或
shopGroup := r.Group("/shop")
shopGroup.Use(StatCost())
{
shopGroup.GET("/index", func(c *gin.Context) {...})
...
}
小例子
func InitMiddleWare(e *gin.Engine){
e.Use(RequestResponseMiddleWare(),AuthMiddleWare())
}
func AuthMiddleWare()gin.HandlerFunc{
return func(ctx *gin.Context) {
token:=ctx.GetHeader("token")
if len(token)!=0{
fmt.Printf("request通过认证,token为:%s \n",token)
ctx.Next()
fmt.Printf("response通过认证,token为:%s \n",token)
}else{
// 不再向后执行
ctx.Abort()
// 响应错误信息
ctx.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest,gin.H{
"code":1,
"err":http.StatusText(http.StatusBadRequest),
})
// 结束本次请求
return
}
}
}
func RequestResponseMiddleWare() gin.HandlerFunc{
return func(ctx *gin.Context) {
fmt.Printf("请求到达,地址为:%s \n",ctx.RemoteIP())
// 下一步
ctx.Next()
// 回到此处
fmt.Printf("响应到达,地址为:%s \n",ctx.RemoteIP())
}
}
请求到达,地址为:127.0.0.1
request通过认证,token为:1
response通过认证,token为:1
响应到达,地址为:127.0.0.1
报错后的顺序
func Index(ctx *gin.Context) {
panic("故意的")
}
请求到达,地址为:127.0.0.1
request通过认证,token为:1
提前返回的顺序
任何write操作都会向response的缓冲区写入数据,请求结束时才会返回。
func RequestResponseMiddleWare() gin.HandlerFunc{
return func(ctx *gin.Context) {
fmt.Printf("请求到达,地址为:%s \n",ctx.RemoteIP())
// 下一步
// ctx.Next()
ctx.String(200,"提前返回")
return
// 回到此处
fmt.Printf("响应到达,地址为:%s \n",ctx.RemoteIP())
}
}
请求到达,地址为:127.0.0.1
request通过认证,token为:1
response通过认证,token为:1
请求到达,地址为:127.0.0.1
request通过认证,token为:1
2023/01/26 21:21:57 Key: 'User.Username' Error:Field validation for 'Username' failed on the 'required' tag
Key: 'User.Password' Error:Field validation for 'Password' failed on the 'required' tag
response通过认证,token为:1
响应到达,地址为:127.0.0.1
中间件注意事项
gin默认中间件
gin.Default()默认使用了Logger和Recovery中间件,其中:
Logger中间件将日志写入gin.DefaultWriter,即使配置了GIN_MODE=release。Recovery中间件会recover任何panic。如果有panic的话,会写入500响应码。
如果不想使用上面两个默认的中间件,可以使用gin.New()新建一个没有任何默认中间件的路由。
gin中间件中使用goroutine
当在中间件或handler中启动新的goroutine时,不能使用原始的上下文(c *gin.Context),必须使用其只读副本(ctx.Copy())。
中间件推荐
跨域中间件
gin-cors gin跨域的官方中间件。
- 安装
go get github.com/gin-contrib/cors
- 典型案例
package main
import (
"time"
"github.com/gin-contrib/cors"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
// CORS for https://foo.com and https://github.com origins, allowing:
// - PUT and PATCH methods
// - Origin header
// - Credentials share
// - Preflight requests cached for 12 hours
router.Use(cors.New(cors.Config{
AllowOrigins: []string{"https://foo.com"},
AllowMethods: []string{"PUT", "PATCH"},
AllowHeaders: []string{"Origin"},
ExposeHeaders: []string{"Content-Length"},
AllowCredentials: true,
AllowOriginFunc: func(origin string) bool {
return origin == "https://github.com"
},
MaxAge: 12 * time.Hour,
}))
router.Run()
}
- Using DefaultConfig as start point
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
// - No origin allowed by default
// - GET,POST, PUT, HEAD methods
// - Credentials share disabled
// - Preflight requests cached for 12 hours
config := cors.DefaultConfig()
config.AllowOrigins = []string{"http://google.com"}
// config.AllowOrigins = []string{"http://google.com", "http://facebook.com"}
// config.AllowAllOrigins = true
router.Use(cors.New(config))
router.Run()
}
- 默认允许全部
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
// same as
// config := cors.DefaultConfig()
// config.AllowAllOrigins = true
// router.Use(cors.New(config))
router.Use(cors.Default())
router.Run()
}
jwt中间件
gin-jwt 用于Gin框架的JWT中间件
go get github.com/appleboy/gin-jwt/v2
日志中间件
基于zap的中间件
// GinLogger 接收gin框架默认的日志
func GinLogger(logger *zap.Logger) gin.HandlerFunc {
return func(c *gin.Context) {
start := time.Now()
path := c.Request.URL.Path
query := c.Request.URL.RawQuery
c.Next()
cost := time.Since(start)
logger.Info(path,
zap.Int("status", c.Writer.Status()),
zap.String("method", c.Request.Method),
zap.String("path", path),
zap.String("query", query),
zap.String("ip", c.ClientIP()),
zap.String("user-agent", c.Request.UserAgent()),
zap.String("errors", c.Errors.ByType(gin.ErrorTypePrivate).String()),
zap.Duration("cost", cost),
)
}
}
// GinRecovery recover掉项目可能出现的panic
func GinRecovery(logger *zap.Logger, stack bool) gin.HandlerFunc {
return func(c *gin.Context) {
defer func() {
if err := recover(); err != nil {
// Check for a broken connection, as it is not really a
// condition that warrants a panic stack trace.
var brokenPipe bool
if ne, ok := err.(*net.OpError); ok {
if se, ok := ne.Err.(*os.SyscallError); ok {
if strings.Contains(strings.ToLower(se.Error()), "broken pipe") || strings.Contains(strings.ToLower(se.Error()), "connection reset by peer") {
brokenPipe = true
}
}
}
httpRequest, _ := httputil.DumpRequest(c.Request, false)
if brokenPipe {
logger.Error(c.Request.URL.Path,
zap.Any("error", err),
zap.String("request", string(httpRequest)),
)
// If the connection is dead, we can't write a status to it.
c.Error(err.(error)) // nolint: errcheck
c.Abort()
return
}
if stack {
logger.Error("[Recovery from panic]",
zap.Any("error", err),
zap.String("request", string(httpRequest)),
zap.String("stack", string(debug.Stack())),
)
} else {
logger.Error("[Recovery from panic]",
zap.Any("error", err),
zap.String("request", string(httpRequest)),
)
}
c.AbortWithStatus(http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
}()
c.Next()
}
}
这样我们就可以在gin框架中使用我们上面定义好的两个中间件来代替gin框架默认的Logger()和Recovery()了。
r := gin.New()
r.Use(GinLogger(), GinRecovery())
在gin项目中使用zap
再加入日志切割:
package logger
import (
"gin_zap_demo/config"
"net"
"net/http"
"net/http/httputil"
"os"
"runtime/debug"
"strings"
"time"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/natefinch/lumberjack"
"go.uber.org/zap"
"go.uber.org/zap/zapcore"
)
var lg *zap.Logger
// InitLogger 初始化Logger
func InitLogger(cfg *config.LogConfig) (err error) {
writeSyncer := getLogWriter(cfg.Filename, cfg.MaxSize, cfg.MaxBackups, cfg.MaxAge)
encoder := getEncoder()
var l = new(zapcore.Level)
err = l.UnmarshalText([]byte(cfg.Level))
if err != nil {
return
}
core := zapcore.NewCore(encoder, writeSyncer, l)
lg = zap.New(core, zap.AddCaller())
zap.ReplaceGlobals(lg) // 替换zap包中全局的logger实例,后续在其他包中只需使用zap.L()调用即可
return
}
func getEncoder() zapcore.Encoder {
encoderConfig := zap.NewProductionEncoderConfig()
encoderConfig.EncodeTime = zapcore.ISO8601TimeEncoder
encoderConfig.TimeKey = "time"
encoderConfig.EncodeLevel = zapcore.CapitalLevelEncoder
encoderConfig.EncodeDuration = zapcore.SecondsDurationEncoder
encoderConfig.EncodeCaller = zapcore.ShortCallerEncoder
return zapcore.NewJSONEncoder(encoderConfig)
}
func getLogWriter(filename string, maxSize, maxBackup, maxAge int) zapcore.WriteSyncer {
lumberJackLogger := &lumberjack.Logger{
Filename: filename,
MaxSize: maxSize,
MaxBackups: maxBackup,
MaxAge: maxAge,
}
return zapcore.AddSync(lumberJackLogger)
}
// GinLogger 接收gin框架默认的日志
func GinLogger() gin.HandlerFunc {
return func(c *gin.Context) {
start := time.Now()
path := c.Request.URL.Path
query := c.Request.URL.RawQuery
c.Next()
cost := time.Since(start)
lg.Info(path,
zap.Int("status", c.Writer.Status()),
zap.String("method", c.Request.Method),
zap.String("path", path),
zap.String("query", query),
zap.String("ip", c.ClientIP()),
zap.String("user-agent", c.Request.UserAgent()),
zap.String("errors", c.Errors.ByType(gin.ErrorTypePrivate).String()),
zap.Duration("cost", cost),
)
}
}
// GinRecovery recover掉项目可能出现的panic,并使用zap记录相关日志
func GinRecovery(stack bool) gin.HandlerFunc {
return func(c *gin.Context) {
defer func() {
if err := recover(); err != nil {
// Check for a broken connection, as it is not really a
// condition that warrants a panic stack trace.
var brokenPipe bool
if ne, ok := err.(*net.OpError); ok {
if se, ok := ne.Err.(*os.SyscallError); ok {
if strings.Contains(strings.ToLower(se.Error()), "broken pipe") || strings.Contains(strings.ToLower(se.Error()), "connection reset by peer") {
brokenPipe = true
}
}
}
httpRequest, _ := httputil.DumpRequest(c.Request, false)
if brokenPipe {
lg.Error(c.Request.URL.Path,
zap.Any("error", err),
zap.String("request", string(httpRequest)),
)
// If the connection is dead, we can't write a status to it.
c.Error(err.(error)) // nolint: errcheck
c.Abort()
return
}
if stack {
lg.Error("[Recovery from panic]",
zap.Any("error", err),
zap.String("request", string(httpRequest)),
zap.String("stack", string(debug.Stack())),
)
} else {
lg.Error("[Recovery from panic]",
zap.Any("error", err),
zap.String("request", string(httpRequest)),
)
}
c.AbortWithStatus(http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
}()
c.Next()
}
}
然后定义日志相关配置:
type LogConfig struct {
Level string `json:"level"`
Filename string `json:"filename"`
MaxSize int `json:"maxsize"`
MaxAge int `json:"max_age"`
MaxBackups int `json:"max_backups"`
}
在项目中先从配置文件加载配置信息,再调用logger.InitLogger(config.Conf.LogConfig)即可完成logger实例的初识化。其中,通过r.Use(logger.GinLogger(), logger.GinRecovery(true))注册我们的中间件来使用zap接收gin框架自身的日志,在项目中需要的地方通过使用zap.L().Xxx()方法来记录自定义日志信息。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"gin_zap_demo/config"
"gin_zap_demo/logger"
"net/http"
"os"
"go.uber.org/zap"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
// load config from config.json
if len(os.Args) < 1 {
return
}
if err := config.Init(os.Args[1]); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// init logger
if err := logger.InitLogger(config.Conf.LogConfig); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("init logger failed, err:%v\n", err)
return
}
gin.SetMode(config.Conf.Mode)
r := gin.Default()
// 注册zap相关中间件
r.Use(logger.GinLogger(), logger.GinRecovery(true))
r.GET("/hello", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 假设你有一些数据需要记录到日志中
var (
name = "q1mi"
age = 18
)
// 记录日志并使用zap.Xxx(key, val)记录相关字段
zap.L().Debug("this is hello func", zap.String("user", name), zap.Int("age", age))
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello liwenzhou.com!")
})
addr := fmt.Sprintf(":%v", config.Conf.Port)
r.Run(addr)
}
会话控制
Cookie
// 设置
ctx.SetCookie()
// 获取
ctx.Cookie()
// 删除
ctx.SetCookie(maxAge=-1)
Session=Cookie+存储
Token
参数验证
- 用gin框架的数据验证,可以不用解析数据,减少if else,会简洁许多。
- form用于标记请求参数的入参,json用于反序列化
type User struct {
Username string `json:"username" binding:"required" form:"username"`
Password string `json:"password" binding:"required" form:"password"`
}
func Index(ctx *gin.Context) {
user:=new(User)
if err:=ctx.ShouldBind(user);err!=nil{
log.Println(err)
}else{
fmt.Println(user)
}
ctx.String(200,"OK")
}
自定义验证
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"gopkg.in/go-playground/validator.v10"
)
/*
对绑定解析到结构体上的参数,自定义验证功能
比如我们需要对URL的接受参数进行判断,判断用户名是否为root如果是root通过否则
返回false
*/
type Login struct {
User string `uri:"user" validate:"required,checkName"`
Pssword string `uri:"password"`
}
// 自定义验证函数
func checkName(fl validator.FieldLevel) bool {
if fl.Field().String() != "root" {
return false
}
return true
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
validate := validator.New()
//注册自定义函数,与struct tag关联起来
err := validate.RegisterValidation("checkName", checkName)
r.GET("/:user/:password", func(c *gin.Context) {
var login Login
//注册自定义函数,与struct tag关联起来
err := validate.RegisterValidation("checkName", checkName)
if err := c.ShouldBindUri(&login); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
err = validate.Struct(login)
if err != nil {
for _, err := range err.(validator.ValidationErrors) {
fmt.Println(err)
}
return
}
fmt.Println("success")
})
r.Run()
}
自定义验证v10
go get github.com/go-playground/validator/v10
Web 框架 gin 的默认验证器,gin将其validate标签改为了binding标签
func (v *defaultValidator) lazyinit() {
v.once.Do(func() {
v.validate = validator.New()
v.validate.SetTagName("binding")
})
}
变量验证
Var 方法使用 tag(标记)验证方式验证单个变量。
func (*validator.Validate).Var(field interface{}, tag string) error
- 它接收一个 interface{} 空接口类型的 field 和一个 string 类型的 tag,返回校验报错信息(ValidationErrors)
- 如果是验证数组、slice 和 map,可能会包含多个错误。
func main() {
validate := validator.New()
// 验证变量
email := "admin#admin.com"
email := ""
err := validate.Var(email, "required,email")
if err != nil {
validationErrors := err.(validator.ValidationErrors)
fmt.Println(validationErrors)
// output: Key: '' Error:Field validation for '' failed on the 'email' tag
// output: Key: '' Error:Field validation for '' failed on the 'required' tag
return
}
}
结构体验证
func (*validator.Validate).Struct(s interface{}) error
func main() {
validate = validator.New()
type User struct {
ID int64 `json:"id" validate:"gt=0"`
Name string `json:"name" validate:"required"`
Gender string `json:"gender" validate:"required,oneof=man woman"`
Age uint8 `json:"age" validate:"required,gte=0,lte=130"`
Email string `json:"email" validate:"required,email"`
}
user := &User{
ID: 1,
Name: "frank",
Gender: "boy",
Age: 180,
Email: "[email protected]",
}
err = validate.Struct(user)
if err != nil {
validationErrors := err.(validator.ValidationErrors)
// output: Key: 'User.Age' Error:Field validation for 'Age' failed on the 'lte' tag
fmt.Println(validationErrors)
return
}
}
注册一个函数,获取结构体字段的名称:
validate.RegisterTagNameFunc(func(field reflect.StructField) string {
return field.Tag.Get("json")
})
标签
| 关键字 | 针对对象 | 功能 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| required | 属性,结构,文件 | 标示必须存在(0时验证失败) |
validate:"required" |
| omitempty | 属性,结构,文件 | omitempty要么不传,传的话就要大于5 | validate:"omitempty,gt=5" |
| len | 字符串,数组,时间间隔,文件长度 | 标示长度,size,间隔,大小 | validate:"len=1" |
| min | 字符串,数字,数组,时间间隔 | 标示最小 | validate:"min=1" |
| max | 字符串,数字,数组,时间 | 标示最大 | validate:"max=7" |
| eq | 字符串,数组,时间间隔,布尔值 | 标示相等,正对数组是长度 | validate:"eq=3" |
| ne | 字符串,数组,时间间隔,布尔值 | 标示不相等 | validate:"ne=" |
| lt | 字符串,数字,数组,时间 | 小于 | validate:"lt=3" |
| lte | 字符串,数字,数组,时间 | 小于等于 | validate:"lte=3" |
| gt | 字符串,数字,数组,时间 | 大于 | validate:"gt=3" |
| gte | 字符串,数字,数组,时间 | 大于等于 | validate:"gte=3" |
| eqfield | 同级属性 | 等于 | validate:"eqfield=MaxString" |
| eqcsfield | 内部属性 | 等于 | validate:"eqcsfield=Inner.EqCSFieldString" |
| necsfield | 内部属性 | 不等于 | validate:"necsfield=Inner.NeCSFieldString" |
| gtcsfield | 内部属性 | 大于 | validate:"gtcsfield=Inner.GtCSFieldString" |
| ltcsfield | 内部属性 | 小于 | validate:"ltcsfield=Inner.LtCSFieldString" |
| ltecsfield | 内部属性 | 小于等于 | validate:"ltecsfield=Inner.LteCSFieldString" |
| nefield | 同级属性 | 不等于 | validate:"nefield=EqFieldString" |
| gtfield | 同级属性 | 大于 | validate:"gtfield=MaxString" |
| gtefield | 同级属性 | 大于等于 | validate:"gtefield=MaxString" |
| ltfield | 同级属性 | 小于 | validate:"ltfield=MaxString" |
| ltefield | 同级属性 | 小于等于 | validate:"ltefield=MaxString" |
| alpha | 字符串 | "^[a-zA-Z]+$" |
validate:"alpha" |
| alphanum | 字符串 | "^[a-zA-Z0-9]+$" |
validate:"alphanum" |
| numeric | 字符串 | "^[-+]?[0-9]+(?:\\.[0-9]+)?$" |
validate:"numeric" |
| number | 字符串 | "^[0-9]+$" |
validate:"number" |
| hexadecimal | 字符串 | "^(0[xX])?[0-9a-fA-F]+$" |
validate:"hexadecimal" |
| hexcolor | 字符串 | "^#(?:[0-9a-fA-F]{3}|[0-9a-fA-F]{6})$" |
validate:"hexcolor" |
| rgb | 字符串 | 复杂正则不展示 | validate:"rgb" |
| rgba | 字符串 | 复杂正则不展示 | |
| hsl | 字符串 | 复杂正则不展示 | |
| hsla | 字符串 | 复杂正则不展示 | |
| 字符串 | 复杂正则不展示 | validate:"email" |
|
| url | 字符串 | url规则 | validate:"url" |
| uri | 字符串 | uri规则 | validate:"uri" |
| base64 | 字符串 | "^(?:[A-Za-z0-9+\\/]{4})*(?:[A-Za-z0-9+\\/]{2}==|[A-Za-z0-9+\\/]{3}=|[A-|Za-z0-9+\\/]{4})$" |
validate:"base64" |
| contains | 字符串 | 包含 | validate:"contains=purpose" |
| containsany | 字符串 | 包含任意一个 | validate:"containsany=!@#$" |
| excludes | 字符串 | 不包含 | validate:"excludes=text" |
| excludesall | 字符串 | 不包含任意一个 | validate:"excludesall=!@#$" |
| excludesrune | 字符串 | 不包含某个rune类型 | validate:"excludesrune=☻" |
| isbn | 字符串 | 两个isbn | validate:"isbn" |
| isbn10 | 字符串 | "^(?:[0-9]{9}X|[0-9]{10})$" |
validate:"isbn10" |
| isbn13 | 字符串 | ^(?:(?:97(?:8|9))[0-9]{10})$" |
validate:"isbn13" |
| uuid | 字符串 | "^[0-9a-f]{8}-[0-9a-f]{4}-[0-9a-f]{4}-[0-9a-f]{4}-[0-9a-f]{12}$" |
validate:"uuid" |
| uuid3 | 字符串 | "^[0-9a-f]{8}-[0-9a-f]{4}-3[0-9a-f]{3}-[0-9a-f]{4}-[0-9a-f]{12}$" |
validate:"uuid3" |
| uuid4 | 字符串 | "^[0-9a-f]{8}-[0-9a-f]{4}-4[0-9a-f]{3}-[89ab][0-9a-f]{3}-[0-9a-f]{12}$" |
validate:"uuid4" |
| uuid5 | 字符串 | "^[0-9a-f]{8}-[0-9a-f]{4}-5[0-9a-f]{3}-[89ab][0-9a-f]{3}-[0-9a-f]{12}$" |
validate:"uuid5" |
| ascii | 字符串 | "^[\x00-\x7F]*$" |
validate:"ascii" |
| printascii | 字符串 | ^[\x20-\x7E]*$" |
validate:"printascii" |
| multibyte | 字符串 | "[^\x00-\x7F]" |
validate:"multibyte" |
| datauri | 字符串 | ^data:((?:\w+\/(?:([^;]|;[^;]).)+)?) |
validate:"datauri" |
| latitude | 字符串 | "^[-+]?([1-8]?\\d(\\.\\d+)?|90(\\.0+)?)$" |
validate:"latitude" |
| longitude | 字符串 | "^[-+]?(180(\\.0+)?|((1[0-7]\\d)|([1-9]?\\d))(\\.\\d+)?)$" |
validate:"longitude" |
| ssn | 字符串 | ^[0-9]{3}[ -]?(0[1-9]|[1-9][0-9])[ -]?([1-9][0-9]{3}|[0-9][1-9][0-9]{2}|[0-9]{2}[1-9][0-9]|[0-9]{3}[1-9])$ |
validate:"ssn" |
| ip | 字符串 | ip规则 | validate:"ip" |
| ipv4 | 字符串 | ipv4规则 | validate:"ipv4" |
| ipv6 | 字符串 | ipv6规则 | validate:"ipv6" |
| cidr | 字符串 | ip规则 | validate:"cidr" |
| cidrv4 | 字符串 | ipv4规则 | validate:"cidrv4" |
| cidrv6 | 字符串 | ipv6规则 | validate:"cidrv6" |
| tcp_addr | 字符串 | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"tcp_addr" |
| tcp4_addr | 字符串 | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"tcp4_addr" |
| tcp6_addr | 字符串 | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"tcp6_addr" |
| udp_addr | 字符串 | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"udp_addr" |
| udp4_addr | 字符串 | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"udp4_addr" |
| udp6_addr | 字符串 | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"udp6_addr" |
| ip_addr | 字符串 | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"ip_addr" |
| ip4_addr | 字符串 | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"ip4_addr" |
| ip6_addr | 字符串 | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"ip6_addr" |
| unix_addr | 字符串 | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"unix_addr" |
| mac | 字符串 | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"mac" |
| iscolor | 字符串 | 颜色校验所有颜色规则 | validate:"iscolor" |
| oneof | OneOfString | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"oneof=red green" |
| oneof | OneOfInt | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"oneof=5 63" |
| unique | UniqueSlice | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"unique" |
| unique | UniqueArray | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"unique" |
| unique | UniqueMap | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"unique" |
| json | JSONString | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"json" |
| lowercase | LowercaseString | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"lowercase" |
| uppercase | UppercaseString | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"uppercase" |
| datetime | Datetime | 对应规则按需验证 | validate:"datetime=2006-01-02" |
合理的拆分目录
单app单router
单app多router
目录结构
gin_demo
├── go.mod
├── go.sum
├── main.go
└── routers
├── blog.go
└── shop.go
routers/shop.go
routers/shop.go中添加一个LoadShop的函数,将shop相关的路由注册到指定的路由器:
func LoadShop(e *gin.Engine) {
e.GET("/hello", helloHandler)
e.GET("/goods", goodsHandler)
e.GET("/checkout", checkoutHandler)
...
}
main.go
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
routers.LoadBlog(r)
routers.LoadShop(r)
if err := r.Run(); err != nil {
fmt.Println("startup service failed, err:%v\n", err)
}
}
多app多router
目录结构
gin_demo
├── apps
│ ├── blog
│ │ ├── handler.go
│ │ └── router.go
│ └── shop
│ ├── handler.go
│ └── router.go
├── go.mod
├── go.sum
├── main.go
└── routers
└── routers.go
app/shop/router.go
app/shop/router.go用来定义shop相关路由信息,具体内容如下:
func Routers(e *gin.Engine) {
e.GET("/goods", goodsHandler)
e.GET("/checkout", checkoutHandler)
}
routers/routers.go
routers/routers.go中根据需要定义Include函数用来注册子app中定义的路由,Init函数用来进行路由的初始化操作:
type Option func(*gin.Engine)
var options = []Option{}
// 注册app的路由配置
func Include(opts ...Option) {
options = append(options, opts...)
}
// 初始化
func Init() *gin.Engine {
r := gin.New()
for _, opt := range options {
opt(r)
}
return r
}
main.go
func main() {
// 加载多个APP的路由配置
routers.Include(shop.Routers, blog.Routers)
// 初始化路由
r := routers.Init()
if err := r.Run(); err != nil {
fmt.Println("startup service failed, err:%v\n", err)
}
}
gin使用Air实现实时热重载
部署Go Web应用的N+1种方法
go日志库log/zap/logrus
orm框架
参考:Gorm全解