第三章JVM之自动内存管理
文章目录
- 内存结构总览
- 程序计数器(寄存器)
-
-
- 各种码之间的关系
- 程序计数器的特点
-
- 虚拟机栈
-
-
- 虚拟机栈溢出
-
- 本地方法栈
- 堆Heap
-
-
- 堆内存溢出
- 堆内存诊断
-
- 方法区
-
-
- 永久代和元空间对方法区的实现
- 方法区溢出演示
- 运行时常量池
-
- StringTable
-
- 直接内存
-
-
- 直接内存的回收原理
-
内存结构总览
- JVM将执行Java程序的过程中会把所管理的内存划分为若干个不同的数据区域
程序计数器(寄存器)
0: getstatic #20 // PrintStream out = System.out;
3: astore_1 // --
4: aload_1 // out.println(1);
5: iconst_1 // --
6: invokevirtual #26 // --
9: aload_1 // out.println(2);
10: iconst_2 // --
11: invokevirtual #26 // --
14: aload_1 // out.println(3);
15: iconst_3 // --
16: invokevirtual #26 // --
19: aload_1 // out.println(4);
20: iconst_4 // --
21: invokevirtual #26 // --
24: aload_1 // out.println(5);
25: iconst_5 // --
26: invokevirtual #26 // --
29: return
- 上面的代码是二进制字节码
- 注释表示的是对应的Java代码的意思
- 我们JVM的程序计数器是用来记住下一条JVM指令(二进制字节码)的执行地址
- 物理上实现PC是通过寄存器(读取速度最快)实现
各种码之间的关系
机器码
- 各种用二进制编码方式表示的指令,叫做机器指令码;刚开始,人们就用它编写程序,这就是机器语言。
- 机器语言虽然能够被计算机理解和接受,但是和人们的语言差别太大,不易被人们理解和记忆,并且用它编程容易出差错。
- 用它编写的程序一经输入计算机,CPU直接读取运行,因此和其它语言编的程序相比,执行速度最快。
- 机器指令与CPU紧密相关,所以不同种类的CPU所对应的机器指令也就不同。
指令
- 由于机器码是由0和1组成的二进制序列,可读性实在太差,于是,人们发明了指令。
- 指令就是把机器码中特定的0和1序列,简化成对应的指令,一般为英文简写,如mov、inc等,可读性好。
- 由于不同的硬件平台,执行同一个操作,对应的机器码可能不同,所以不同的硬件平台的同一种指令(比如mov),对应的机器码也可能不同。
指令集
- 不同的硬件平台,各自支持的指令是有差别的。因此每个平台所支持的指令,称之为对应平台的指令集。
- 如常见的,X86指令集对应X86的架构平台,ARM指令集对应的是ARM架构的平台。
汇编语言
- 由于指令的可读性还是太差,于是人们发明了汇编语言。
- 在汇编语言中,用助记符(Mnemonics)代替机器操作指令码,用地址符(Symbol)或标号(label)代替指令或者操作数的地址。
- 在不同的硬件平台,汇编语言对应着不同的机器语言指令集,通过汇编过程转换成机器指令。由于计算机只认识指令码,所以用汇编语言编写的程序还必须翻译成机器指令码,计算机才能识别和执行。
高级语言
- 为了使计算机用户编写程序更容易些,后来就出现了各种高级计算机语言。高级语言比机器语言、汇编语言更接近人的语言。
- 当计算机执行高级语言编写的程序时,仍然需要把程序解释和编译成机器的指令码,完成这个过程的程序就叫做解释程序或者编译程序。
字节码
- 字节码是一种中间状态(中间码)的二进制代码,它比机器码更抽象,需要直译器转译后才能成为机器码。
- 字节码主要为了实现特定软件运行和软件环境,与硬件环境无关。
- 字节码的实现方式是通过编译器和虚拟机器。编译器将源码文件编译成字节码,特定平台上的虚拟机器将字节码转译为可以直接执行的指令。
程序计数器的特点
作用:是记录下一条 JVM指令的执行地址行号。
特点:
-
是线程私有的
- 我们的Java是支持多线程的,采用时间片的方式为线程来分配CPU
- 所以我们每个线程会分配一个程序计数器
-
不会存在内存溢出——唯一不会发生的区域
虚拟机栈
Java Virtual Machine Stacks (Java 虚拟机栈)
- 每个线程运行需要的内存空间,称为虚拟机栈,每个线程对应一个虚拟机栈,它的生命周期与线程相同
- 每个栈由多个栈帧(Frame)组成,对应着每次调用方法时所占用的内存
- 存储局部变量表、操作数栈、动态链接、方法出口等信息
- 局部变量表:存放了编译期可知的各种基本类型(boolean、byte、char、short、int、float、long、double)、对象引用(reference 类型)和 returnAddress 类型(指向了一条字节码指令的地址)
- 局部变量表所需的内存空间在编译器就会完成分配,这些数据类型在局部变量表中的存储空间以局部变量槽来表示,其中64位的long和double类型的数据会占用两个变量槽,其余的数据类型只会占一个
- 每个线程只能有一个活动栈帧,对应着当前正在执行的方法,也就是最上面的那个栈帧
问题解析
垃圾回收是否管理栈内存
- 因为我们栈空间里都是栈帧,在方法执行的时候调入内存,在方法执行接触
栈内存分配越大越好吗
- 不是越大越好,因为我们知道一个线程分配一个虚拟机栈,所以如果栈空间越大,我们的物理内存是有限的,就会导致我们的能开启的线程数就会减少
- 通过
-Xxs(栈大小) 设置我们的虚拟机栈的大小 - 在创建线程的时候申请内存时因为无法获得足够的内存而出现OutOfMemoryError
方法内的局部变量是否是线程安全的
- 看是否我们方法内的局部变量,没有逃离方法的作用范围,它就是线程安全的
- 如果局部变量引用了对象,并逃离了方法的作用访问
**
* 局部变量的线程安全问题
*/
public class Demo1_17 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(4);
sb.append(5);
sb.append(6);
new Thread(()->{
m2(sb);
}).start();
}
public static void m1() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(1);
sb.append(2);
sb.append(3);
System.out.println(sb.toString());
//线程安全的,因为我们的sb对象只在m1这个范围内执行 也就是说只会在一个栈帧中,只会是一个线程私有
}
public static void m2(StringBuilder sb) {
sb.append(1);
sb.append(2);
sb.append(3);
System.out.println(sb.toString());
//可能是线程不安全的,因为这个sb局部变量,是一个参数,可能会被其他线程调用
//这个传递参数还必须的对象,因为在Java中我们的参数是传值操作,如果是基本类型,只会传对应的值,而不会影响本来的数据
}
public static StringBuilder m3() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(1);
sb.append(2);
sb.append(3);
return sb;
//可能是返回的结果,可能被其他的线程拿到这个对象来进行修改
}
}
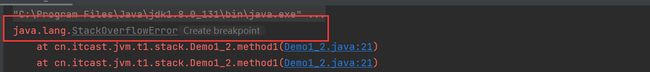
虚拟机栈溢出
- 栈帧过多导致栈内存溢出——比如递归没有结束条件
- 栈帧过大导致栈内存溢出
- 两种虚拟机栈溢出的情况是由JVM规范规定的
- 如果线程请求栈深度大于虚拟机栈所允许的深度,抛出StackOverflowError
- 如果Java虚拟机栈容量可以动态扩展,当栈扩展无法申请到足够的内存,会抛出OutOfMemoryError异常
- HotSpot的选择是不支持扩展
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.stack;
/**
* 演示栈内存溢出 java.lang.StackOverflowError
* -Xss256k
*/
public class Demo1_2 {
private static int count;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
method1();
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(count);
}
}
private static void method1() {
count++;
method1();//通过递归来造成栈内存溢出
}
}
线程运行诊断
案例一:cpu 占用过多
解决方法:Linux 环境下运行某些程序的时候,可能导致 CPU 的占用过高,这时需要定位占用 CPU 过高的线程
- top 命令,Linux top命令用于实时显示 process 的动态。我们来通过top查看哪个进程的CPU占有率高
- ps H -eo pid, tid(线程id), %cpu | grep (刚才通过 top 查到的进程号) 通过 ps 命令进一步查看是哪个线程占用 CPU 过高
- ps可以当前进程的状态
- H可以用来打印这个进程所有线程对CPU的占用率
- eo pid,tid,%cpu来规定显示哪几个信息
- jstack 进程 id 通过查看进程中的线程的 tid ,刚才通过 ps 命令看到的 tid 来对比定位,注意 jstack 查找出的线程 id 是 16 进制的,需要转换。
- 还可以查看线程之间死锁的问题
本地方法栈
- 一些带有 native 关键字的方法就是需要 JAVA 去调用本地的C或者C++方法,因为 JAVA 有时候没法直接和操作系统底层交互,所以需要用到本地方法栈,服务于带 native 关键字的方法。
为什么使用Native Method
java使用起来非常方便,然而有些层次的任务用java实现起来不容易,或者在对程序的效率很在意时,问题就来了。与java环境外交互
有时Java应用需要与Java外面的环境交互,这是本地方法存在的主要原因。你可以想想Java需要与一些底层系统,如操作系统或某些硬件交换信息时的情况。本地方法正是这样的一种交流机制:它为我们提供了一个非常简洁的接口,而且我们无需区了解Java应用之外的繁琐细节。
与操作系统交互(比如线程最后要回归于操作系统线程)
JVM支持着java语言本身和 运行库,它是java程序赖以生存的平台,它由一个解释器(解释字节码)和一些连接到本地代码的库组成。然而不管怎样,它毕竟不是一个完整的系统,它经常依赖于一些底层系统的支持。这些底层系统常常是强大的操作系统。通过使用本地方法,我们得以用java实现了jre的与底层系统的交互,甚至JVM的一部分就是用C写的。还有,如果我们要使用一些java语言本身没有提供封装的操作系统特性时,我们也需要使用本地方法。
Sun‘s Java
Sun的解释器是用C实现的,这使得它能像一些普通的C一样与外部交互。jre大部分是用java实现的,它也通过一些本地方法与外界交互。例如:类java.lang.Thread的setPriority()方法是用Java实现的,但是它实现调用的事该类里的本地方法setPriority().这个本地方法是用C实现的,并被植入JVM内部,在Windows 95的平台上,这个本地方法最终将调用Win32 setpriority()API。这是一个本地方法的具体实现由JVM直接提供,更多的情况是本地方法由外部的动态链接库(external dynamic link library)提供,然后被JVM调用。
堆Heap
Heap 堆
- 通过new关键字创建的对象,数组都会被放在堆内存
- JVM规范中说是所有的对象实例和数组都放在堆中
- 但是在实现的时候,是几乎,因为编译技术的进步和逃逸分析技术的发展
特点
- 它是线程共享,堆内存中的对象都需要考虑线程安全问题
- 有垃圾回收机制——回收的就是堆中的垃圾
- 根据JVM规范,Java堆可以处于物理上不连续的内存空间,但是在逻辑上是要被视为连续的
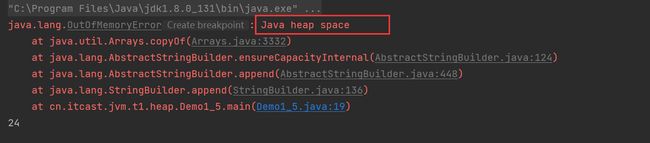
堆内存溢出
- java.lang.OutofMemoryError :java heap space. 堆内存溢出
- 可以使用
-Xmx来指定堆内存最大值-Xms指定堆内存的最小值。
public class Demo1_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
try {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
String a = "hello";
while (true) {
list.add(a); // hello, hellohello, hellohellohellohello ...
a = a + a; // hellohellohellohello
i++;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
- 我们的list集合在try范围内是一只有效的,而我们的字符串是对象,存储在堆中,因为list一直有效,所以这些字符串是不能被回收的
堆内存诊断
jps 工具
查看当前系统中有哪些 java 进程
jmap 工具
查看堆内存占用情况 jmap - heap 进程id
jconsole 工具
图形界面的,多功能的监测工具,可以连续监测
jvisualvm 工具
- 这个用于我们来查看当前堆内存的使用情况非常方便
- 发现进行了一次FULL GC堆内存占用减少了很多
方法区
定义
- 方法区也是各个线程共享的内存区域,用于存储类信息,常量,静态变量,即时编译器编译后的代码缓存等数据
JVM规范对方法区的定义
The Java Virtual Machine has a method area that is shared among all Java Virtual Machine threads. The method area is analogous to the storage area for compiled code of a conventional language or analogous to the “text” segment in an operating system process.
It stores per-class structures such as the run-time constant pool, field and method data, and the code for methods and constructors, including the special methods ( used in class and instance initialization and interface initialization.
- 重要的是方法区里存储了运行时常量池,字段,方法数据以及方法和构造方法的代码,包括特殊方法,用于类和实例初始化以及接口初始化方法
The method area is created on virtual machine start-up. Although the method area is logically part of the heap, simple implementations may choose not to either garbage collect or compact it. This specification does not mandate the location of the method area or the policies used to manage compiled code. The method area may be of a fixed size or may be expanded as required by the computation and may be contracted if a larger method area becomes unnecessary. The memory for the method area does not need to be contiguous.
- 方法区域是在虚拟机启动时创建的。尽管方法区域在逻辑上是堆的一部分,但简单的实现可能不会选择垃圾收集或压缩它。此规范不强制指定方法区的位置或用于管理已编译代码的策略(比如Hotspot中元空间和永久代两种不同的方式对方法区的实现)。方法区域可以具有固定的大小,或者可以根据计算的需要进行扩展,并且如果不需要更大的方法区域,则可以收缩。方法区域的内存不需要是连续的!
A Java Virtual Machine implementation may provide the programmer or the user control over the initial size of the method area, as well as, in the case of a varying-size method area, control over the maximum and minimum method area size.
The following exceptional condition is associated with the method area:
- If memory in the method area cannot be made available to satisfy an allocation request, the Java Virtual Machine throws an
OutOfMemoryError.****
永久代和元空间对方法区的实现
- 1.6方法区跟其实在物理上是跟我们的堆在一块区域,只是概念上的不同,都是占用JVM管理的内存
- 1.8以后废弃了永久代,用元空间来实现,我们的方法区放到外面的本地内存中去,不占用JVM的内存空间,而方法区中的StringTable放到我们的堆中
- 1.8 以前会导致永久代内存溢出
- 1.8 之后会导致元空间内存溢出
1、常量池:俗称静态常量池,存在于*.class文件中,就是一张表,虚拟机指令根据这张表找到要执行的类名、类方法、参数类型、字面量等信息
常量池:虚拟机指令:
2、运行时常量池:类被加载时,其常量池信息会被放入运行时常量池,并把里面的符号地址变为真实地址。
3、StringTable 串池:运行时常量池的 一部分,储存字符串常量
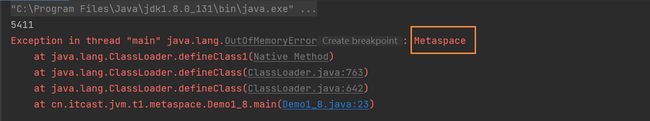
方法区溢出演示
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.metaspace;
import jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.ClassWriter;
import jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes;
/**
* 演示元空间内存溢出 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Metaspace
* 在JDK1.8的环境下演示
* -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=8m
*/
public class Demo1_8 extends ClassLoader { // 可以用来加载类的二进制字节码
public static void main(String[] args) {
int j = 0;
try {
Demo1_8 test = new Demo1_8();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++, j++) {
// ClassWriter 作用是生成类的二进制字节码
ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(0);
// 版本号, public, 类名, 包名, 父类, 接口
cw.visit(Opcodes.V1_8, Opcodes.ACC_PUBLIC, "Class" + i, null, "java/lang/Object", null);
// 返回 byte[]
byte[] code = cw.toByteArray();
// 执行了类的加载
test.defineClass("Class" + i, code, 0, code.length); // Class 对象
}
} finally {
System.out.println(j);
}
}
}
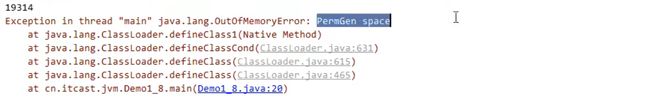
package cn.itcast.jvm;
import com.sun.xml.internal.ws.org.objectweb.asm.ClassWriter;
import com.sun.xml.internal.ws.org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes;
/**
* 演示永久代内存溢出 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space
* 这是在我们的JDK1.6环境下运行
* -XX:MaxPermSize=8m
*/
public class Demo1_8_1_6 extends ClassLoader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int j = 0;
try {
Demo1_8_1_6 test = new Demo1_8_1_6();
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++, j++) {
ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(0);
cw.visit(Opcodes.V1_6, Opcodes.ACC_PUBLIC, "Class" + i, null, "java/lang/Object", null);
byte[] code = cw.toByteArray();
test.defineClass("Class" + i, code, 0, code.length);
}
} finally {
System.out.println(j);
}
}
}
实际开发中可能出现方法区的溢出
- Spring
- Mybatis
- 这些框架中都用了字节码技术 比如这里面都会用到cglib动态代理 使用字节码技术来动态生成字节码,完成动态的类加载
运行时常量池
// 二进制字节码(类基本信息,常量池,类方法定义,包含了虚拟机指令)
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("hello world");
}
}
我们将class文件反编译后的内容
Classfile /E:/JAVA代码/jvm/out/production/jvm/cn/itcast/jvm/t5/HelloWorld.class
Last modified 2022-11-12; size 567 bytes
MD5 checksum 8efebdac91aa496515fa1c161184e354
Compiled from "HelloWorld.java"
public class cn.itcast.jvm.t5.HelloWorld
minor version: 0
major version: 52
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_SUPER
- 这是我们类的基本信息 类的路径,上次修改时间 签名 类的修饰符
Constant pool:
#1 = Methodref #6.#20 // java/lang/Object."":()V
#2 = Fieldref #21.#22 // java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#3 = String #23 // hello world
#4 = Methodref #24.#25 // java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#5 = Class #26 // cn/itcast/jvm/t5/HelloWorld
#6 = Class #27 // java/lang/Object
#7 = Utf8
#8 = Utf8 ()V
#9 = Utf8 Code
#10 = Utf8 LineNumberTable
#11 = Utf8 LocalVariableTable
#12 = Utf8 this
#13 = Utf8 Lcn/itcast/jvm/t5/HelloWorld;
#14 = Utf8 main
#15 = Utf8 ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
#16 = Utf8 args
#17 = Utf8 [Ljava/lang/String;
#18 = Utf8 SourceFile
#19 = Utf8 HelloWorld.java
#20 = NameAndType #7:#8 // "":()V
#21 = Class #28 // java/lang/System
#22 = NameAndType #29:#30 // out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#23 = Utf8 hello world
#24 = Class #31 // java/io/PrintStream
#25 = NameAndType #32:#33 // println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#26 = Utf8 cn/itcast/jvm/t5/HelloWorld
#27 = Utf8 java/lang/Object
#28 = Utf8 java/lang/System
#29 = Utf8 out
#30 = Utf8 Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#31 = Utf8 java/io/PrintStream
#32 = Utf8 println
#33 = Utf8 (Ljava/lang/String;)V
- 这就是我们的常量池
public cn.itcast.jvm.t5.HelloWorld();
descriptor: ()V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC
Code:
stack=1, locals=1, args_size=1
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."":()V
4: return
LineNumberTable:
line 4: 0
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 5 0 this Lcn/itcast/jvm/t5/HelloWorld;
public static void main(java.lang.String[]);
descriptor: ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATIC
Code:
stack=2, locals=1, args_size=1
0: getstatic #2 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
3: ldc #3 // String hello world
5: invokevirtual #4 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
8: return
LineNumberTable:
line 6: 0
line 7: 8
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 9 0 args [Ljava/lang/String;
}
- 类方法定义,包括了虚拟机指令
在上面的例子中我们能看出来
- 常量池:就是一张表,虚拟机指令根据这张常量表找到要执行的类名,方法名,参数类型,字面量等信息
- 运行时常量池,常量池是 *.class 文件中的,当该类被加载,它的常量池信息就会放入运行时常量
池,并把里面的符号地址变为真实地址 (#1 #2 这些都是符号地址,运行的时候需要变成真的运行内存地址)
StringTable
- 运行常量池的一部分,存储字符串常量
String s1 = "a";
String s2 = "b";
String s3 = "a" + "b";// javac 在编译期间的优化,结果已经在编译期确定为ab
String s4 = s1 + s2;// new StringBuilder().append("a").append("b").toString() new String("ab")
String s5 = "ab";
String s6 = s4.intern();
// 问
System.out.println(s3 == s4); //false
System.out.println(s3 == s5);//true
System.out.println(s3 == s6);//true
String x2 = new String("c") + new String("d");
String x1 = "cd";
x2.intern();
System.out.println(x1 == x2); //1.6false 1.8false
String x2 = new String("c") + new String("d");
x2.intern();
String x1 = "cd";
System.out.println(x1 == x2); //1.6false 1.8true
- 常量池中的字符串仅是符号,第一次用到时才变为对象 利用串池的机制,来避免重复创建字符串对象
- 字符串变量拼接的原理是 StringBuilder (1.8)
- 字符串常量拼接的原理是编译期优化
- 可以使用 intern 方法,主动将串池中还没有的字符串对象放入串池
- 1.8 将这个字符串对象尝试放入串池,如果有则并不会放入,方法的返回值是在池中字符串对象的位置.如果没有则放入串池, 会把串池中的对象返回
- 1.6 将这个字符串对象尝试放入串池,如果有则并不会放入,方法的返回值是在池中字符串对象的位置.如果没有会把此对象复制一份,放入串池, 会把串池中的对象返回
字符串的延迟加载
/**
* 演示字符串字面量也是【延迟】成为对象的
*/
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = args.length;
System.out.println(); // 字符串个数 2275
System.out.print("1");
System.out.print("2");
System.out.print("3");
System.out.print("4");
System.out.print("5");
System.out.print("6");
System.out.print("7");
System.out.print("8");
System.out.print("9");
System.out.print("0");
System.out.print("1"); // 字符串个数 2285
System.out.print("2");
System.out.print("3");
System.out.print("4");
System.out.print("5");
System.out.print("6");
System.out.print("7");
System.out.print("8");
System.out.print("9");
System.out.print("0");
System.out.print(x); // 字符串个数
}
}
- 字符串字面量是执行到对应语句才会将延迟成为对象,放入常量池中
StringTable 位置
- jdk1.6 StringTable 位置是在永久代中,1.8 StringTable 位置是在堆中。
- 为什么要这样
- 因为我们永久代的回收效率很低,只有FULL GC才会触发永久代的回收(FULL GC在老年代空间不足才会触发)
- StringTable存储着我们的字符串常量,我们的字符串常量在程序中应用的次数很多,所以要及时对StringTable进行回收
StringTable的垃圾回收
-Xmx10m 指定堆内存大小
-XX:+PrintStringTableStatistics 打印字符串常量池信息
-XX:+PrintGCDetails
-verbose:gc 打印 gc 的次数,耗费时间等信息
StringTable 性能调优
StringTable的底层是一个哈希表
- 调整 -XX:StringTableSize=桶个数(至少1009以上),如果桶的个数比较多,数据比较分散,发生哈希冲撞的机率也比较低,所以可以适当增加哈希表桶的个数,来减少字符串放入串池所需要的时间
- 考虑将字符串对象是否入池 (因为入池,重复的字符串只需要对一个字符串的重复运用就行)
直接内存
Direct Memory
- 常见于 NIO 操作时,用于数据缓冲区
- 分配回收成本较高,但读写性能高
- 不受 JVM 内存回收管理
private static void io() {
long start = System.nanoTime();
try (FileInputStream from = new FileInputStream(FROM);
FileOutputStream to = new FileOutputStream(TO);
) {
byte[] buf = new byte[_1Mb];//Java的缓冲区
while (true) {
int len = from.read(buf);
if (len == -1) {
break;
}
to.write(buf, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("io 用时:" + (end - start) / 1000_000.0);
}
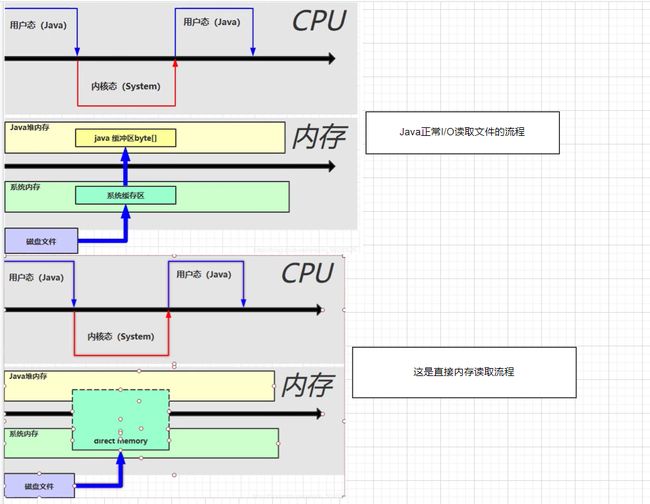
- Java这种I/O,因为有一个系统缓冲区和Java缓冲区(堆内存),从磁盘读取文件,需要先将数据放到系统缓冲区,然后在放入到我们的Java缓冲区(byte数组),系统缓存区是被我们的操作系统管理的,所以也会涉及到内核态和用户态的转换
- 利用缓冲区分次读取
- 因为 java 不能直接操作文件管理,需要切换到内核态,使用本地方法进行操作,然后读取磁盘文件,会在系统内存中创建一个缓冲区,将数据读到系统缓冲区, 然后在将系统缓冲区数据,复制到 java 堆内存中。缺点是数据存储了两份,在系统内存中有一份,java 堆中有一份,造成了不必要的复制。
private static void directBuffer() {
long start = System.nanoTime();
try (FileChannel from = new FileInputStream(FROM).getChannel();
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream(TO).getChannel();
) {
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_1Mb);//分配的是直接缓冲区
while (true) {
int len = from.read(bb);
if (len == -1) {
break;
}
bb.flip();
to.write(bb);
bb.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("directBuffer 用时:" + (end - start) / 1000_000.0);
}
- 直接内存是操作系统和 Java 代码都可以访问的一块区域,无需将代码从系统内存复制到 Java 堆内存,从而提高了效率。
- 所以这种在读我们大文件的时候,效率比较高
直接内存的回收原理
public class Code_06_DirectMemoryTest {
public static int _1GB = 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchFieldException,IllegalAccessException
{
// method();
method1();
}
// 演示 直接内存 是被 unsafe 创建与回收
private static void method1() throws IOException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Field field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
field.setAccessible(true);
Unsafe unsafe = (Unsafe)field.get(Unsafe.class);
long base = unsafe.allocateMemory(_1GB);//分配直接内存 返回值是直接内存的地址
unsafe.setMemory(base,_1GB, (byte)0);
System.in.read();
unsafe.freeMemory(base);
System.in.read();
}
// 演示 直接内存被 释放
private static void method() throws IOException {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_1GB);
System.out.println("分配完毕");
System.in.read();
System.out.println("开始释放");
byteBuffer = null;
System.gc(); // 手动 gc
System.in.read();
}
}
直接内存的回收不是通过 JVM 的垃圾回收来释放的,而是通过unsafe.freeMemory 来手动释放。
第一步:allocateDirect 的实现
public static ByteBuffer allocateDirect(int capacity) {
return new DirectByteBuffer(capacity);
}
底层是创建了一个 DirectByteBuffer 对象。
第二步:DirectByteBuffer 类
DirectByteBuffer(int cap) { // package-private
super(-1, 0, cap, cap);
boolean pa = VM.isDirectMemoryPageAligned();
int ps = Bits.pageSize();
long size = Math.max(1L, (long)cap + (pa ? ps : 0));
Bits.reserveMemory(size, cap);
long base = 0;
try {
base = unsafe.allocateMemory(size); // 使用了unsafe allocateMemory来进行直接内存的申请
} catch (OutOfMemoryError x) {
Bits.unreserveMemory(size, cap);
throw x;
}
unsafe.setMemory(base, size, (byte) 0);//和allocateMemory一起使用
if (pa && (base % ps != 0)) {
// Round up to page boundary
address = base + ps - (base & (ps - 1));
} else {
address = base;
}
cleaner = Cleaner.create(this, new Deallocator(base, size, cap));
// 通过虚引用,来实现直接内存的释放,this为虚引用的实际对象, 第二个参数是一个回调,实现了 runnable 接口,run 方法 中通过 unsafe 释放内存。
att = null;
}
这里调用了一个 Cleaner 的 create 方法,且后台线程还会对虚引用的对象监测,如果虚引用的实际对象(这里是 DirectByteBuffer )被回收以后,就会调用 Cleaner 的 clean 方法,来清除直接内存中占用的内存。
public void clean() {
if (remove(this)) {
try {
// 都用函数的 run 方法, 释放内存
this.thunk.run();
} catch (final Throwable var2) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
if (System.err != null) {
(new Error("Cleaner terminated abnormally", var2)).printStackTrace();
}
System.exit(1);
return null;
}
});
}
}
}
可以看到关键的一行代码, this.thunk.run(),thunk 是 Runnable 对象。run 方法就是回调 Deallocator 中的 run 方法,
public void run() {
if (address == 0) {
// Paranoia
return;
}
// 释放内存
unsafe.freeMemory(address);
address = 0;
Bits.unreserveMemory(size, capacity);
}
直接内存的回收机制总结
-
使用了 Unsafe 类来完成直接内存的分配回收,回收需要主动调用freeMemory 方法
-
ByteBuffer 的实现内部使用了 Cleaner(虚引用)来检测 ByteBuffer 。一旦ByteBuffer 被垃圾回收,那么会由 ReferenceHandler(守护线程) 来调用 Cleaner 的 clean 方法调用 freeMemory 来释放内存
注意
/**
* -XX:+DisableExplicitGC 显示的GC失效
*/
private static void method() throws IOException {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_1GB);
System.out.println("分配完毕");
System.in.read();
System.out.println("开始释放");
byteBuffer = null;
System.gc(); // 手动 gc 失效
System.in.read();
}
一般用 jvm 调优时,会加上下面的参数:
-XX:+DisableExplicitGC // 静止显示的 GC
意思就是禁止我们手动的 GC,比如手动 System.gc() 无效,它是一种 full gc,会回收新生代、老年代,会造成程序执行的时间比较长。所以我们就通过 unsafe 对象调用 freeMemory 的方式释放内存。