多线程---并发容器的使用
多线程---并发容器的使用
- 1. 容器概览
- 2. 容器的使用
-
- 1. Map
-
- 1. HashTable
- 2. HashMap
- 3. SynchronizedHashMap
- 4. ConcurrentHashMap
- 2. Collection
-
- 1. ArrayList
- 2. Vector
- 3. LinkedList
- 4. ConcurrentLinkedQueue
- 3. 并发容器的使用
-
- 1. ConcurrentHashMap
- 2. CopyOnWriteArrayList
- 3. ConcurrentLinkedQueue
- 4. LinkedBlockingQueue
- 5. ArrayBlockingQueue
- 6. DelayQueue
- 7. SynchronousQueue
- 8. LinkedTransferQueue
- 3. 练习题
-
- 1. 使用LockSupport
- 2. 使用synchronized, notify,wait
-
- 使用CountDownLatch保证顺序
- 使用volatile+标识字段
- 3. 使用Lock.newCondition()
-
- 优化
- 4. 使用Exchanger
- 5. 使用TransferQueue队列
- 6. 使用CAS-1
- 7. 使用CAS-2
1. 容器概览
2. 容器的使用
1. Map
多线程环境下,几种Map的处理效率和线程安全问题
测试方案:准备10万条数据, 10个线程, 每个线程处理1万条数据, 并发执行。
数据准备
public class Constants {
public static final int COUNT = 1000000;
public static final int THREAD_COUNT = 100;
}
1. HashTable
HashTable是线程安全的, 因为里面加了很多synchronized, 每次put操作, 都会锁整个Map
public class T01_TestHashtable {
//HashMap是jdk1.0产生的, 最早出现, 里面的很多方法都加了synchronized锁, 所以效率比较低
static Hashtable<UUID, UUID> m = new Hashtable<>();
static int count = Constants.COUNT;
static UUID[] keys = new UUID[count];
static UUID[] values = new UUID[count];
static final int THREAD_COUNT = Constants.THREAD_COUNT;
//先准备好测试用例, 减少干扰因素
static {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
keys[i] = UUID.randomUUID();
values[i] = UUID.randomUUID();
}
}
/**
* 每个线程处理1万条数据,
*/
static class MyThread extends Thread {
int start;
int gap = count / THREAD_COUNT;
public MyThread(int start) {
this.start = start;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//从start开始, 到start+gap个结束
for (int i = start; i < start + gap; i++) {
m.put(keys[i], values[i]);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
//设置每个线程的起始值不一样
threads[i] =
new MyThread(i * (count / THREAD_COUNT));
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
t.start();
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
try {
//主线程等待每个线程都执行结束
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
//插入执行的时间
System.out.println(end - start);
System.out.println(m.size());
//-----------------------------------
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 10000000; j++) {
m.get(keys[10]);
}
});
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
t.start();
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
try {
//主线程需要等待所有子线程执行完
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
}
- 执行结果
写耗时: 290
1000000
读耗时: 29602
可以看到执行时间在300毫秒左右
2. HashMap
sun在HashTablede的基础上推出了无锁的HashMap
public class T02_TestHashMap {
//sun在HashTablede的基础上推出了无锁的HashMap
static HashMap<UUID, UUID> m = new HashMap<>();
static int count = Constants.COUNT;
static UUID[] keys = new UUID[count];
static UUID[] values = new UUID[count];
static final int THREAD_COUNT = Constants.THREAD_COUNT;
static {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
keys[i] = UUID.randomUUID();
values[i] = UUID.randomUUID();
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
int start;
int gap = count / THREAD_COUNT;
public MyThread(int start) {
this.start = start;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = start; i < start + gap; i++) {
//HashMap在resize(扩容)时, 可能会出现多个线程同时进行, 导致数据丢失甚至死锁情况
m.put(keys[i], values[i]);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] =
new MyThread(i * (count / THREAD_COUNT));
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
t.start();
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
System.out.println(m.size());
}
}
- 执行结果
写耗时: 171
814683
读耗时: 2005
可以看到即使执行成功, 总数也不是10万条, 因为设计到Map的resize扩容, 多线程环境下, 同时进入扩容操作, 会出现问题, 具体参考: https://www.jianshu.com/p/e2f75c8cce01
3. SynchronizedHashMap
相当于有锁版的HashMap, 锁的粒度比HashTable小了一些
public class T03_TestSynchronizedHashMap {
//相当于有锁版的HashMap, 锁的粒度比HashTable小了一些
static Map<UUID, UUID> m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<UUID, UUID>());
static int count = Constants.COUNT;
static UUID[] keys = new UUID[count];
static UUID[] values = new UUID[count];
static final int THREAD_COUNT = Constants.THREAD_COUNT;
static {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
keys[i] = UUID.randomUUID();
values[i] = UUID.randomUUID();
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
int start;
int gap = count / THREAD_COUNT;
public MyThread(int start) {
this.start = start;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = start; i < start + gap; i++) {
m.put(keys[i], values[i]);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] =
new MyThread(i * (count / THREAD_COUNT));
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
t.start();
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
System.out.println(m.size());
//-----------------------------------
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 10000000; j++) {
m.get(keys[10]);
}
});
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
t.start();
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
}
- 执行结果
写耗时: 334
1000000
读耗时: 29575
4. ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap并发插入的时候, 效率未必比其他Map高, 但是并发读取的时候效率很
/**
* ConcurrentHashMap并发插入的时候, 效率未必比其他Map高, 但是并发读取的时候效率很高
*/
public class T04_TestConcurrentHashMap {
//结合了JUC包里的一些锁
static Map<UUID, UUID> m = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
static int count = Constants.COUNT;
static UUID[] keys = new UUID[count];
static UUID[] values = new UUID[count];
static final int THREAD_COUNT = Constants.THREAD_COUNT;
static {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
keys[i] = UUID.randomUUID();
values[i] = UUID.randomUUID();
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
int start;
int gap = count/THREAD_COUNT;
public MyThread(int start) {
this.start = start;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=start; i<start+gap; i++) {
m.put(keys[i], values[i]);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
for(int i=0; i<threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] =
new MyThread(i * (count/THREAD_COUNT));
}
for(Thread t : threads) {
t.start();
}
for(Thread t : threads) {
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("写耗时: " + (end - start));
System.out.println(m.size());
//-----------------------------------
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(()->{
for (int j = 0; j < 10000000; j++) {
m.get(keys[10]);
}
});
}
for(Thread t : threads) {
t.start();
}
for(Thread t : threads) {
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("读耗时: " + (end - start));
}
}
写耗时: 160
1000000
读耗时: 1108
2. Collection
多线程环境下集合的使用, 由一个测试题引入
测试题:
有N张火车票,每张票都有一个编号
同时有10个窗口对外售票
请写一个模拟程序
1. ArrayList
/**
* 有N张火车票,每张票都有一个编号
* 同时有10个窗口对外售票
* 请写一个模拟程序
*
* 分析下面的程序可能会产生哪些问题?
* 重复销售?超量销售?
*
*
* @author cyc
*/
package com.cyc.juc.c_024_FromVectorToQueue;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class TicketSeller1ArrayList {
static List<String> tickets = new ArrayList<>();
static {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
//提前将票添加到集合中
tickets.add("票编号:" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
while (tickets.size() > 0) {
//有可能只剩了一张票, 但是多个线程都通过了这个判断, 然后多线程直接开始remove, 所以会导致超卖的情况
System.out.println("销售了--" + tickets.remove(0));
}
}).start();
}
}
}
执行结果
Exception in thread “Thread-7” java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: -1
at java.util.ArrayList.remove(ArrayList.java:505)
at com.cyc.juc.c_024_FromVectorToQueue.TicketSeller1ArrayList.lambda$main$0(TicketSeller1ArrayList.java:32)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
最后多个线程都进入了判断, 并开始卖最后一张票, 导致数组越界异常。
Queue和List对比
- Queue中提供了一些对线程友好的API offer, peek, poll
BlockingQueue
中的put方法和take方法可实现线程堵塞
2. Vector
/**
* 有N张火车票,每张票都有一个编号
* 同时有10个窗口对外售票
* 请写一个模拟程序
*
* 分析下面的程序可能会产生哪些问题?
*
* 使用Vector或者Collections.synchronizedXXX
* 分析一下,这样能解决问题吗?
*
* @author cyc
*/
package com.cyc.juc.c_024_FromVectorToQueue;
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class TicketSeller2Vector {
static Vector<String> tickets = new Vector<>();
static {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
tickets.add("票 编号:" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
while (tickets.size() > 0) {
System.out.println("销售了--" + tickets.remove(0));
}
}).start();
}
}
}
- 执行结果可以正常输出
但是如果在
while (tickets.size() > 0) {
System.out.println("销售了--" + tickets.remove(0));
}
之中还有其他业务逻辑需要执行, 假设执行10毫秒, 即代码如下
while (tickets.size() > 0) {
//所谓的线程安全 , 是调用size()和remove()方法时加锁了, 但是在执行完size()之前和remove()之后, 并没有加锁,
//这个过程就不是原子的
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("销售了--" + tickets.remove(0));
}
- 输出结果
Exception in thread "Thread-9" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Array index out of range: 0
at java.util.Vector.remove(Vector.java:834)
at com.cyc.juc.c_024_FromVectorToQueue.TicketSeller2Vector.lambda$main$0(TicketSeller2Vector.java:42)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
同样导致数据越界异常, 因为Vector的size和remove操作执行过程中不是原子的
- 优化
给tickets加锁, 并在代码中判断tickets.size()是否等于0
package com.cyc.juc.c_024_FromVectorToQueue;
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class TicketSeller2Vector {
static Vector<String> tickets = new Vector<>();
static {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
tickets.add("票 编号:" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
while (tickets.size() > 0) {
synchronized (tickets) {
//所谓的线程安全 , 是调用size()和remove()方法时加锁了, 但是在执行完size()之前和remove()之后, 并没有加锁,
//这个过程就不是原子的
if (tickets.size() <= 0) {
break;
}
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("销售了--" + tickets.remove(0));
}
}
}).start();
}
}
}
3. LinkedList
/**
* 有N张火车票,每张票都有一个编号
* 同时有10个窗口对外售票
* 请写一个模拟程序
*
* 分析下面的程序可能会产生哪些问题?
* 重复销售?超量销售?
*
* 使用Vector或者Collections.synchronizedXXX
* 分析一下,这样能解决问题吗?
*
* 就算操作A和B都是同步的,但A和B组成的复合操作也未必是同步的,仍然需要自己进行同步
* 就像这个程序,判断size和进行remove必须是一整个的原子操作
*
* @author cyc
*/
package com.cyc.juc.c_024_FromVectorToQueue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class TicketSeller3VoctorWithSynchronize {
static List<String> tickets = new LinkedList<>();
static {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
tickets.add("票 编号:" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
//给tickets对象加锁, 保证原子性, 实现线程安全
synchronized (tickets) {
if (tickets.size() <= 0) {
break;
}
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("销售了--" + tickets.remove(0));
}
}
}).start();
}
}
}
4. ConcurrentLinkedQueue
/**
* 有N张火车票,每张票都有一个编号
* 同时有10个窗口对外售票
* 请写一个模拟程序
*
* 分析下面的程序可能会产生哪些问题?
* 重复销售?超量销售?
*
* 使用Vector或者Collections.synchronizedXXX
* 分析一下,这样能解决问题吗?
*
* 就算操作A和B都是同步的,但A和B组成的复合操作也未必是同步的,仍然需要自己进行同步
* 就像这个程序,判断size和进行remove必须是一整个的原子操作
*
* 使用ConcurrentQueue提高并发性
*
* @author cyc
*/
public class TicketSeller4ConcurrentLinkedQueue {
//多线程的程序应多考虑使用队列
static Queue<String> tickets = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
static {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
tickets.add("票 编号:" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
String s = tickets.poll();
if (s == null) {
break;
} else {
System.out.println("销售了--" + s);
}
}
}).start();
}
}
}
执行结果正常, 并且速度也很快
3. 并发容器的使用
1. ConcurrentHashMap
/**
* 几种并发容器Map的使用
* ConcurrentSkipListMap参考 https://blog.csdn.net/sunxianghuang/article/details/52221913
*/
public class T01_ConcurrentMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();//高并发无序
// Map map = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>(); //高并发并且排序
//Map map = new Hashtable<>();
//Map map = new HashMap<>(); //Collections.synchronizedXXX
//TreeMap
Random r = new Random();
Thread[] threads = new Thread[100];
//倒数门栓
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threads.length);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//100个线程并发往map里各写入10000条数据
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) {
map.put("a" + r.nextInt(100000), "a" + r.nextInt(100000));
// map.put("a" + m.getAndIncrement(), "a" + m.getAndIncrement());
}
latch.countDown();
});
}
Arrays.asList(threads).forEach(t -> t.start());
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
System.out.println(map.size());
}
}
2. CopyOnWriteArrayList
/**
* 写时复制容器 copy on write
* 多线程环境下,写时效率低,读时效率高
* 适合写少读多的环境
* 因为每次写的时候都要复制一份,
*
* @author cyc
*/
package com.cyc.juc.c_025;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
public class T02_CopyOnWriteList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> lists =
// new ArrayList<>(); //这个会出并发问题!
// new Vector();
new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();//写的时候加锁, 读的时候不加锁
Random r = new Random();
Thread[] threads = new Thread[100];
for(int i=0; i<threads.length; i++) {
Runnable task = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0; i<1000; i++) {
lists.add("a" + r.nextInt(10000));
}
}
};
threads[i] = new Thread(task);
}
//写操作
runAndWriteComputeTime(threads);
for(int i=0; i<threads.length; i++) {
Runnable task = () -> {
for (String list : lists) {
String s = list;
}
};
threads[i] = new Thread(task);
}
//读操作
runAndReadComputeTime(threads);
System.out.println("list大小: "+lists.size());
}
private static void runAndReadComputeTime(Thread[] threads) {
long s1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
Arrays.asList(threads).forEach(t->t.start());
Arrays.asList(threads).forEach(t->{
try {
//主线程等待所有线程执行完
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
long s2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("读耗时: "+(s2 - s1));
}
static void runAndWriteComputeTime(Thread[] threads) {
long s1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
Arrays.asList(threads).forEach(t->t.start());
Arrays.asList(threads).forEach(t->{
try {
//主线程等待所有线程执行完
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
long s2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("写耗时: "+(s2 - s1));
}
}
- 先来测试同样为线程安全的collection容器Vector
输出结果
写耗时: 86
读耗时: 401
list大小: 100000
- 测试CopyOnWriteArrayList
输出结果
写耗时: 2769
读耗时: 41
list大小: 100000
可以看到CopyOnWriteArrayList写操作比较慢, 这正是由于每次写入都要进行复制操作 , 但是读数据非常快。
3. ConcurrentLinkedQueue
package com.cyc.juc.c_025;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
/**
* ConcurrentLinkedQueue并发队列, 先进先出
*/
public class T04_ConcurrentQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> strs = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
strs.offer("a" + i); //add
}
System.out.println(strs);
System.out.println(strs.size());
//poll取出, 并删除一个
System.out.println(strs.poll());
System.out.println(strs.size());
//peak 取出 , 不删除
System.out.println(strs.peek());
System.out.println(strs.size());
}
}
- 输出结果
[a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9]
10
a0
9
a1
9
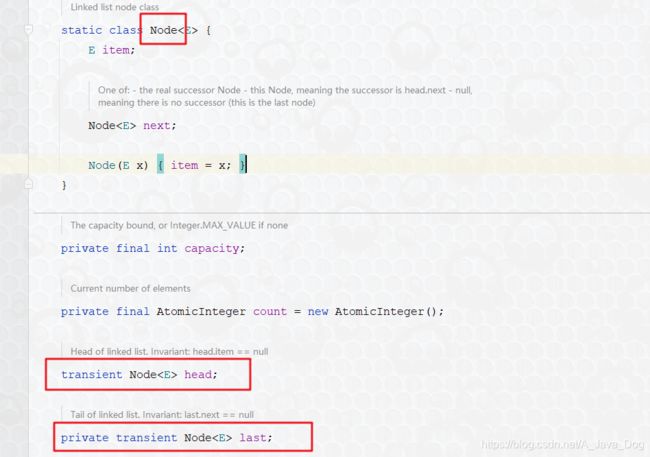
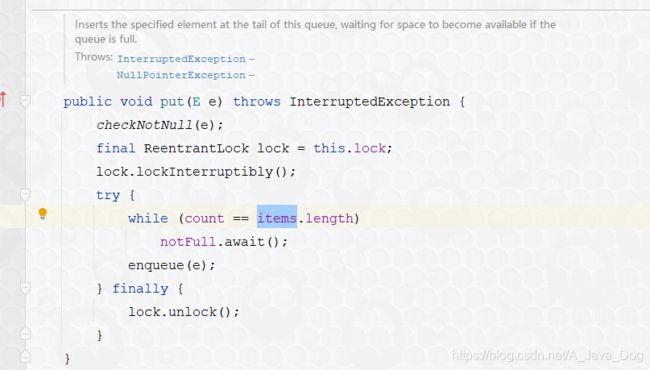
4. LinkedBlockingQueue
-
在生产和消费的时候,需要创建Node对象进行插入或移除,大批量数据的系统中,其对于GC的压力会比较大
-
LinkedBlockingQueue有默认的容量大小为:Integer.MAX_VALUE,当然也可以传入指定的容量大小
代码演示
/**
* BlockingQueue天生的阻塞队列
*/
public class T05_LinkedBlockingQueue {
//
static BlockingQueue<String> strs = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
static Random r = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
try {
strs.put("a" + i); //如果满了,就会等待
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(r.nextInt(1000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "p1").start();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
for (;;) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " take -" + strs.take()); //如果空了,就会等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "c" + i).start();
}
}
}
5. ArrayBlockingQueue
-
ArrayBlockingQueue内部维护了一个数组
在生产和消费的时候,是直接将枚举对象插入或移除的,不会产生或销毁任何额外的对象实例
插入操作
-
ArrayBlockingQueue在初始化的时候,必须传入一个容量大小的值
6. DelayQueue
package com.cyc.juc.c_025;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 按照等待时间长短排序执行 , 可以自定义执行优先级
* 用户: 按照时间进行调度,
*/
public class T07_DelayQueue {
static BlockingQueue<MyTask> tasks = new DelayQueue<>();
static Random r = new Random();
static class MyTask implements Delayed {
String name;
long runningTime;
MyTask(String name, long rt) {
this.name = name;
this.runningTime = rt;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
if (this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) < o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
return -1;
} else if (this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) > o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(runningTime - System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name + " " + runningTime;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
MyTask t1 = new MyTask("t1", now + 1000);
MyTask t2 = new MyTask("t2", now + 2000);
MyTask t3 = new MyTask("t3", now + 1500);
MyTask t4 = new MyTask("t4", now + 2500);
MyTask t5 = new MyTask("t5", now + 500);
tasks.put(t1);
tasks.put(t2);
tasks.put(t3);
tasks.put(t4);
tasks.put(t5);
System.out.println(tasks);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(tasks.take());
}
}
}
7. SynchronousQueue
/**
* 容量为0
* SynchronousQueue 同步Queue
* 常用作一个线程给另一个容器下单任务
* @author fei
*/
public class T08_SynchronusQueue { //容量为0
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<String> strs = new SynchronousQueue<>();
new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println(strs.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
strs.put("aaa"); //阻塞等待消费者消费
//必须有消费者进行消费才可以继续put,如果没有消费者, 则这里就会堵塞在这里
// strs.put("bbb");
//strs.add("aaa");
System.out.println(strs.size());
}
}
8. LinkedTransferQueue
package com.cyc.juc.c_025;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedTransferQueue;
/**
* 给线程传递任务
* 用于需要得到执行结果, 才能继续往下执行, 类似MQ的一个返回处理结果机制
* @author cyc
*/
public class T09_TransferQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
LinkedTransferQueue<String> strs = new LinkedTransferQueue<>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(strs.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
//和put的区别在于, 线程put完之后, 执行put的线程就可以走了,
// 而transfer, 执行transfer的线程必须原地等着, 阻塞住, 直到有线程取走transfer的值才行
//put是满了才等着, transfer是来了就得等着
strs.transfer("aaa");
//strs.put("aaa");
/*new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(strs.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();*/
}
}
3. 练习题
要求用线程顺序打印A1B2C3…Z26
1. 使用LockSupport
/**
* Locksupport park 当前线程阻塞(停止)
* unpark(Thread t)
*/
public class T02_00_LockSupport {
static Thread t1 = null, t2 = null;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for(char c : aC) {
System.out.print(c);
LockSupport.unpark(t2); //叫醒t2
LockSupport.park(); //t1阻塞
}
}, "t1");
t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for(char c : aI) {
//保证t1先执行
LockSupport.park(); //T2阻塞
System.out.print(c);
LockSupport.unpark(t1); //叫醒T1
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
输出结果
A1B2C3D4E5F6G7
2. 使用synchronized, notify,wait
public class T06_00_sync_wait_notify {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//新建一个需要被锁的对象
final Object o = new Object();
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (o) {
for(char c : aI) {
System.out.print(c);
try {
o.notify();//叫醒第二个线程
//这里为什么使用wait而不是sleep, wait可以释放锁, sleep不会释放锁
o.wait(); //让出锁
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//必须,否则无法停止程序, 因为两个线程最后会有一个是wait状态,
// 如果不进行o.notify(),则无法叫醒那个wait()的线程
o.notify();
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (o) {
for(char c : aC) {
System.out.print(c);
try {
o.notify();
o.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
o.notify();
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
保证执行顺序 , 先打印A, 再打印1, 然后依次B,2,C,3…
使用CountDownLatch保证顺序
package com.cyc.juc.c_026_00_interview.A1B2C3;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
/**
* 多线程保证执行顺序, 使A先输出, 再输出1
*/
public class T07_00_sync_wait_notify_sort {
private static CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Object o = new Object();
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
new Thread(()->{
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (o) {
for(char c : aI) {
System.out.print(c);
try {
//唤醒第二个线程
o.notify();
//让出锁
o.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
o.notify();
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (o) {
for(char c : aC) {
System.out.print(c);
//输出之后, 进行减1
latch.countDown();
try {
//唤醒第一个线程
o.notify();
//让出锁
o.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
o.notify();
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
使用volatile+标识字段
package com.cyc.juc.c_026_00_interview.A1B2C3;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
/**
* 多线程保证执行顺序, 使A先输出, 再输出1
*/
public class T07_00_sync_wait_notify_sort {
private static volatile boolean t2Started = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Object o = new Object();
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (o) {
while(!t2Started) {
try {
o.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
for(char c : aI) {
System.out.print(c);
try {
//唤醒第二个线程
o.notify();
//让出锁
o.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
o.notify();
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (o) {
for(char c : aC) {
System.out.print(c);
t2Started = true;
try {
//唤醒第一个线程
o.notify();
//让出锁
o.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
o.notify();
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
3. 使用Lock.newCondition()
/**
* 使用lock.newCondition()创建等待队列
* @author cyc
*/
public class T08_00_lock_condition {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
new Thread(()->{
try {
lock.lock();
for(char c : aI) {
System.out.print(c);
//唤醒一个等待在condition上的线程,将该线程从等待队列中转移到同步队列中
condition.signal();
//当前线程进入等待状态
condition.await();
}
condition.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
lock.lock();
for(char c : aC) {
System.out.print(c);
condition.signal();
condition.await();
}
condition.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
优化
/**
* Condition本质是锁资源上不同的等待队列
*/
public class T09_00_lock_condition_two {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
//condition实际上是一个等待队列
Condition conditionT1 = lock.newCondition();
Condition conditionT2 = lock.newCondition();
new Thread(()->{
try {
lock.lock();
for(char c : aI) {
System.out.print(c);
conditionT2.signal();
conditionT1.await();
}
conditionT2.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
lock.lock();
for(char c : aC) {
System.out.print(c);
conditionT1.signal();
conditionT2.await();
}
conditionT1.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
4. 使用Exchanger
package com.cyc.juc.c_026_00_interview.A1B2C3;
import java.util.concurrent.Exchanger;
public class T12_00_Exchanger_Not_Work {
private static Exchanger<String> exchanger = new Exchanger<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0; i<aI.length; i++) {
System.out.print(aI[i]);
try {
//Exchanger类中的exchange(String x) 方法具有阻塞的特点,也就是说此方法被调用后等待其他线程来获取数据,
// 如果没有其他线程取得数据,则就会一直阻塞等待下去。
exchanger.exchange("T1");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0; i<aC.length; i++) {
try {
exchanger.exchange("T2");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.print(aC[i]);
}
}).start();
}
}
5. 使用TransferQueue队列
package com.cyc.juc.c_026_00_interview.A1B2C3;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedTransferQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TransferQueue;
/**
* TransferQueue
*/
public class T13_TransferQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
TransferQueue<Character> queue = new LinkedTransferQueue<>();
new Thread(()->{
try {
for (char c : aI) {
//第一个线程作为消费者,去take , 如果没有, 则等待
System.out.print(queue.take());
queue.transfer(c);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
for (char c : aC) {
//将c交给对方去打印
queue.transfer(c);
System.out.print(queue.take());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
6. 使用CAS-1
package com.cyc.juc.c_026_00_interview.A1B2C3;
public class T03_00_cas {
enum ReadyToRun {T1, T2}
//保证线程之间的可见性, 当r有改动时, 可以立即通知其他线程进行更新缓存
static volatile ReadyToRun r = ReadyToRun.T1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
new Thread(() -> {
for (char c : aC) {
while (r != ReadyToRun.T1) {}
System.out.print(c);
r = ReadyToRun.T2;
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (char c : aI) {
while (r != ReadyToRun.T2) {}
System.out.print(c);
r = ReadyToRun.T1;
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
7. 使用CAS-2
package com.cyc.juc.c_026_00_interview.A1B2C3;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class T05_00_AtomicInteger {
static AtomicInteger threadNo = new AtomicInteger(1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
new Thread(() -> {
for (char c : aI) {
while (threadNo.get() != 1) {}
System.out.print(c);
threadNo.set(2);
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (char c : aC) {
while (threadNo.get() != 2) {}
System.out.print(c);
threadNo.set(1);
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}