Qt-sqlite3数据库编程实例
一、需求和目的
Qt的数据库编程,Qt自带示例是书籍管理的,所以我们下面做个学生成绩查看。
二、程序设计
简化程序,数据库不进行严格设计,数据库表格只设计一张:姓名、学号、年龄、英语成绩、数学成绩、语文成绩、总成绩组成scores表。做一个简单的登录对话框,设计一个登录按钮,点击登录后进入scoreWindow,显示对应的成绩和学员信息。
仿照books的架构,我们将整个程序分为两大块:scoreWindow类、initdb,和books的功能相似,只是增加一个登录对话框,而对于table的重写暂时取消掉,主要是熟悉一下使用Qt进行数据库编程的流程。
这里我们不使用内存形式,使用文件形式展示sqlite3数据库中的数据。
三、源码展示
initdb.h:
#ifndef INITDB_H
#define INITDB_H
#include
void addScore(QSqlQuery &q, const QString &name, int num, int age, int english, int math, int chinese)
{
q.addBindValue(name);
q.addBindValue(num);
q.addBindValue(age);
q.addBindValue(english);
q.addBindValue(math);
q.addBindValue(chinese);
int total = math + english + chinese;
q.addBindValue(total);
q.exec();
}
QSqlError initDb()
{
QSqlDatabase db = QSqlDatabase::addDatabase("QSQLITE");
// db.setDatabaseName(":memory:");
db.setDatabaseName("./test.db");
if(!db.open())
return db.lastError();
QStringList tables = db.tables();
if(tables.contains("scores", Qt::CaseInsensitive))
return QSqlError();
QSqlQuery q;
if(!q.exec(QLatin1String("create table scores(id int primary key, name varchar, num int, age int,\
english int, math int, chinese int, total int)")))
return q.lastError();
if(!q.prepare(QLatin1String("insert into scores(name, num, age, english, math, chinese, total) \
values (?,?,?,?,?,?,?)")))
return q.lastError();
addScore(q, QLatin1String("james"), 1, 20, 80, 80, 80);
addScore(q, QLatin1String("jack"), 2, 20, 90, 90, 90);
addScore(q, QLatin1String("jim"), 3, 20, 100, 100, 100);
return QSqlError();
}
#endif // INITDB_H scorewindow.cpp
#include "scorewindow.h"
#include "ui_scorewindow.h"
#include "initdb.h"
#include
#include
scoreWindow::scoreWindow(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent),
ui(new Ui::scoreWindow)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
//judge is include sqlite driver
if(!QSqlDatabase::drivers().contains("QSQLITE"))
QMessageBox::critical(this, "Unable to load database",
"This pro needs the SQLITE driver");
//initialize the database
QSqlError err = initDb();
if(err.type() != QSqlError::NoError) {
showError(err);
return;
}
//create the data model
model = new QSqlRelationalTableModel(ui->scoreTable);
model->setEditStrategy(QSqlTableModel::OnManualSubmit);
model->setTable("scores");
//remeber the indexes of the columns
num = model->fieldIndex("num");
//set the ralations to the other database tables
model->setHeaderData(model->fieldIndex("name"), Qt::Horizontal, tr("姓名"));
model->setHeaderData(model->fieldIndex("age"), Qt::Horizontal, tr("年龄"));
model->setHeaderData(num, Qt::Horizontal, tr("学号"));
model->setHeaderData(model->fieldIndex("math"), Qt::Horizontal, tr("数学成绩"));
model->setHeaderData(model->fieldIndex("english"), Qt::Horizontal, tr("英语成绩"));
model->setHeaderData(model->fieldIndex("chinese"), Qt::Horizontal, tr("语文成绩"));
model->setHeaderData(model->fieldIndex("total"), Qt::Horizontal, tr("总成绩"));
//Populate the model
if(!model->select()) {
showError(model->lastError());
return;
}
//Set the model and hide the ID colum
ui->scoreTable->setModel(model);
ui->scoreTable->setColumnHidden(model->fieldIndex("id"), true);
ui->scoreTable->setSelectionMode(QAbstractItemView::SingleSelection);
}
scoreWindow::~scoreWindow()
{
delete ui;
}
void scoreWindow::showError(const QSqlError &err)
{
QMessageBox::critical(this, "Unable to init Database", "Error init database:"+ err.text());
} scorewindow.h:
#ifndef SCOREWINDOW_H
#define SCOREWINDOW_H
#include
#include
namespace Ui {
class scoreWindow;
}
class scoreWindow : public QMainWindow
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit scoreWindow(QWidget *parent = 0);
~scoreWindow();
private:
Ui::scoreWindow *ui;
void showError(const QSqlError &err);
QSqlRelationalTableModel *model;
int num;
};
#endif // SCOREWINDOW_H ui文件都是最基本的,没有进行复杂的处理。
四、结果展示
点击登录,直接显示表格信息。
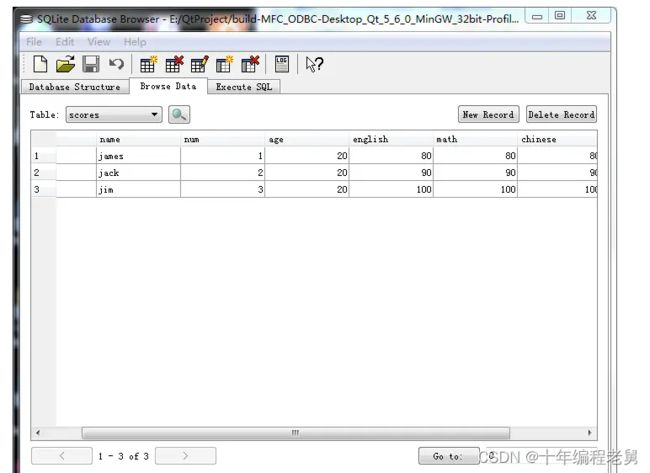
然后我们发现在工程文件夹下有一个test.db文件,这个就是我们的数据库文件,我们用专门的sqlite文件数据库查看软件直接打开该文件就可以看到数据库表格信息,我这里使用的是SQlite Database Browser2.0b1:
五、最后
之所以仿照books的设计方式是因为其设计方式更符合软件设计模式,这就像乐高积木,其每个积木的设计都符合一定的模式和规则,这样更方便组合成不同的形状,组合成不同的内容。
本次总结主要是熟悉Qt数据库编程流程,要灵活的运用可能还需要掌握其它的积木。