MySQL数据库——SQL优化(2/3)-order by 优化、group by 优化
目录
order by 优化
概述
测试
优化原则
group by 优化
测试
优化原则
order by 优化
概述
MySQL的排序,有两种方式:
- Using filesort : 通过表的索引或全表扫描,读取满足条件的数据行,然后在排序缓冲区sortbuffer中完成排序操作,所有不是通过索引直接返回排序结果的排序都叫 FileSort 排序。
- Using index : 通过有序索引顺序扫描直接返回有序数据,这种情况即为 using index,不需要额外排序,操作效率高。
对于以上的两种排序方式,Using index的性能高,而Using filesort的性能低,我们在优化排序
操作时,尽量要优化为 Using index。
测试
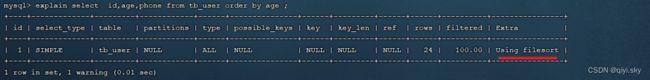
假设现在在tb_user表中根据年龄或电话号码来排序: (age和phone均无索引)
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by age ;explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by age, phone ; 由于 age, phone 都没有索引,所以此时再排序时,出现Using filesort, 排序性能较低。
由于 age, phone 都没有索引,所以此时再排序时,出现Using filesort, 排序性能较低。
创建索引
-- 创建索引
create index idx_user_age_phone_aa on tb_user(age,phone);创建索引后,根据age和phone进行升序排序:
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by age,phone;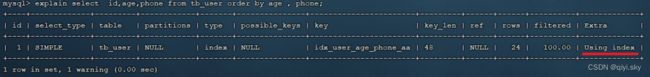
建立索引之后,再次进行排序查询,就由原来的Using filesort,变为了 Using index,性能就是比较高的了。
再根据age和phone进行降序排序:
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by age desc ,phone desc;也出现 Using index, 但是此时Extra中出现了 Backward index scan,这个代表反向扫描索引,因为在MySQL中我们创建的索引,默认索引的叶子节点是从小到大排序的,而此时我们查询排序时,是从大到小,所以,在降序排序扫描时,就是反向扫描,就会出现 Backward index scan。
在MySQL8版本中,支持降序索引,我们也可以创建降序索引。
根据phone,age进行升序排序,phone在前,age在后:
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by phone , age;排序时,也需要满足最左前缀法则,否则也会出现 filesort。
因为在创建索引的时候, age是第一个字段,phone是第二个字段,所以排序时也该按照这个顺序来,否则就会出现 Using filesort。
根据age, phone进行降序一个升序,一个降序:
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by age asc , phone desc ;因为创建索引时,如果未指定顺序,默认都是按照升序排序的,而查询时,一个升序,一个降序,此时就会出现Using filesort。
为了解决上述的问题,我们可以创建一个索引,这个联合索引中 age 升序排序,phone 倒序排序。
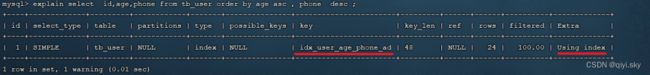
创建联合索引(age 升序排序,phone 倒序排序) :
create index idx_user_age_phone_ad on tb_user(age asc ,phone desc);这时执行SQL语句就达到我们的预期了:
优化原则
由上述的测试,我们得出order by优化原则:
- 根据排序字段建立合适的索引,多字段排序时,也遵循最左前缀法则。
- 尽量使用覆盖索引。
- 多字段排序, 一个升序一个降序,此时需要注意联合索引在创建时的规则(ASC/DESC)。
- 如果不可避免的出现filesort,大数据量排序时,可以适当增大排序缓冲区大小sort_buffer_size(默认256k)。
group by 优化
分组操作,我们主要来看看索引对于分组操作的影响。
测试
在没有索引的情况下,执行如下SQL,查询执行计划:
explain select profession , count(*) from tb_user group by profession ; 与order by优化类似,Using temporary也是效率比较低的,我们要利用索引将其变为Using index。
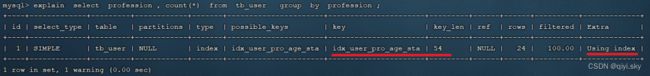
我们针对于 profession , age, status 创建一个联合索引:
create index idx_user_pro_age_sta on tb_user(profession , age , status);然后再执行前面相同的SQL查看执行计划:
explain select profession , count(*) from tb_user group by profession ; 同样,如果仅仅根据age分组,就会出现 Using temporary ;
而如果是根据profession,age两个字段同时分组,则不会出现 Using temporary。
原因是对于分组操作,在联合索引中,也是符合最左前缀法则的。
优化原则
所以,在分组操作中,我们需要通过以下两点进行优化,以提升性能:
- 在分组操作时,可以通过索引来提高效率。
- 分组操作时,索引的使用也是满足最左前缀法则的。
END
学习自:黑马程序员——MySQL数据库课程