图解顺序表+单链表
文章目录
- 一 图解顺序表
-
- 顺序表的概念
- 顺序表的实现
-
- 1 抽象对应的类
- 2 类的方法去实现顺序表
-
- 2.1 顺序表的打印
- 2.2 顺序表的新增元素
- 2.3判定是否包含某个元素
- 2.4 获取顺序表的长度
- 2.5 查找某个元素对应的位置
- 2.6 获取pos位置的元素
- 2.8 把pos位置改成value
- 2.9 删除第一次出现的关键字key
- 2.10 清空顺序表
- 顺序表缺陷
- 二 图解单链表
-
- 概念
- 链表的分类
- 节点
-
- 头结点与尾节点
- 单链表常用实现方法
-
- 1 抽象类
- 2 在单链表中进行实现方法
-
- 2.1 实例化一个单链表
- 2.2 遍历单链表
- 2.3 头插法
- 2.4 尾插法
- 2.5查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
- 2.6 求单链表的长度
- 2.7删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
- 2.8删除所有值为key的节点
- 2.9任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
- 2.10清空单链表
- 顺序表与单链表总结:
一 图解顺序表
顺序表的概念
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。(以下我们所要进行描述的是动态顺序表,动态为数据分配一个内存空间)
顺序表的实现
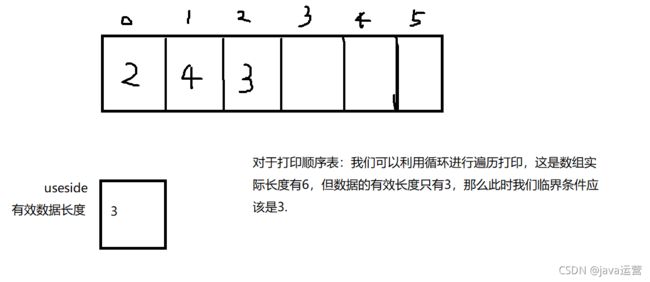
在Java类与对象中,我们了解到。java是一门面向对象的编程语言,对于如何对一组数据进行增删查改。我们可以把他们放到一个类里面,通过实例化对象。直接进行相应的调用操作即可,不用过多的关心类里面是怎么实现的。对于一个动态顺序表,我们可以定义一个数组来存储这些数据,用useside来表示数组里面实际的有效数据的长度,这样我们就可以得到类的成员属性,通过对应的方法来实现。接下来我们通过图片以及代码结合,理解一下什么是顺序表。
1 抽象对应的类
class ordly {
public int[] elem;
public int useside;//表示数据的有效长度
public ordly(){
this.elem=new int[6];
}
}
2 类的方法去实现顺序表
对于类的调用者来说就是提供了相应的接口去实现
2.1 顺序表的打印
// 打印顺序表(代码实现)
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < useside; i++) {
System.out.println(elem[i]+" ");
}
}
2.2 顺序表的新增元素
// 在 pos 位置新增元素(代码实现)
public boolean isfull(){
return this.useside==elem.length;
}
public void add(int pos, int data) {
if (pos<0||pos>useside){
System.out.println("输入pos位置不合法");
return;
}
if (isfull()){//判断是否需要扩容
elem= Arrays.copyOf(elem,2*elem.length);
}
for (int i=useside-1;i>=pos;i--){
elem[i+1]=elem[i];
}
elem[pos]=data;
useside++;
}
2.3判定是否包含某个元素
// 判定是否包含某个元素(代码实现)
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
if(useside==0){
System.out.println("这是一个空顺序表");
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < useside; i++) {
if (elem[i]==toFind){
return true;
}
}
return false;//循环走完还没找到,说明没有这个数据
}
2.4 获取顺序表的长度
// 获取顺序表长度
public int size() {
return useside;
}
2.5 查找某个元素对应的位置
方法与是否包含一个数的方法类似
// 查找某个元素对应的位置(代码实现)
public int search(int toFind) {
if (useside==0){
System.out.println("空顺序表,没有你所要找的数据");
}
for (int i = 0; i < useside; i++) {
if (elem[i]==toFind){
return i;
}
}
return -1;//没有找到
}
2.6 获取pos位置的元素
// 获取 pos 位置的元素(代码实现)
public int getPos(int pos) {
if (pos<0||pos>useside){
System.out.println("输入位置不合法");
return -1;
}
if (useside==0){
System.out.println("这是一个空顺序表");
return -2;
}
return elem[pos];
}
2.8 把pos位置改成value
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
public void setPos(int pos, int value) {
if (pos<0||pos>useside){
System.out.println("输入位置不合法");
return;
}
if (useside==0){
System.out.println("这是一个空链表");
return;
}
elem[pos]=value;
}
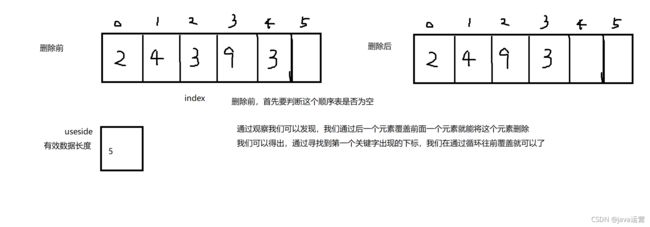
2.9 删除第一次出现的关键字key
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) {
if (useside==0){
System.out.println("这是一个空顺序表,没有你要删除的数据");
return;
}
int index=search(toRemove);
if (index==-1){
System.out.println("没有你要删除的元素");
}
for (int i = index; i <useside-1 ; i++) {
elem[i]=elem[i+1];
}
useside--;
}
2.10 清空顺序表
public void clear() {
useside=0;
}
这里要特别提及一下这里的清空顺序表以及删除某个元素的顺序表的操作针对的简单类型,对于引用类型。我们不是这样做的,对于这一块的源码,以及对于引用操作类型的处理,可以参考我码云上的代码,希望对你有所帮助。
码云地址
顺序表缺陷
1 对于顺序表的插入以及删除,复杂度为O(N)。
2 对于扩容处理,拷贝数组,释放旧空间,会有不小的消耗
3 对于扩容处理,还存在在浪费空间
缺陷的解决:引进链表,解决这一问题。
二 图解单链表
概念
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的 。
链表的分类
单向带头循环 单向带头不循环
单向不带头循环 单向不带头不循环
双向带头循环 双向带头不循环
双向不带头循环 双向不带头不循环
对于单链表而言,我们主要着重于单向不带头不循环。
节点
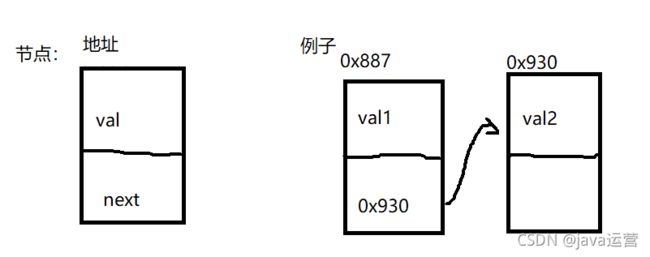
对于单链表而言,不是利用数组来描述,我们用节点来描述链表,对于节点是由两部分组成的val(一个值,为整型)和next(引用类型,用来指向下一个地址)组成的具体如图表示:
头结点与尾节点
在单链表中,我们会将第一个作为头节点,注意在单向不带头不循环链表中这个头结点是可以变的(头结点也就意味着是单链表的第一位),对于尾节点的next是null,例子如图:

单链表常用实现方法
1 抽象类
对于节点是一种类,里面会包含val以及next两者成员属性。
单链表是一种类,里面会包含节点,以及对单链表进行操作的基本实现方法
class nodelist{//节点
public int val;
public nodelist next;
public nodelist(int val){
this.val=val;
}
}
class singlelist{//单链表
nodelist head;
}
2 在单链表中进行实现方法
2.1 实例化一个单链表
public void creat(){
nodelist list=new nodelist(10);
nodelist list1=new nodelist(20);
nodelist list2=new nodelist(35);
nodelist list3=new nodelist(20);
nodelist list4=new nodelist(23);
list.next=list1;
list1.next=list2;
list2.next=list3;
list3.next=list4;
head=list;
}
2.2 遍历单链表
//对单链表打印
public void display(){
nodelist cur=head;//由于头结点没有改变,所以不能移动,此时创建一个等于head的头结点,代替head进行遍历
while (cur!=null){
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur=cur.next;//此时cur就往后移动
}
}
2.3 头插法
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
nodelist first=new nodelist(data);
first.next=head;
head=first;
}
2.4 尾插法
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
nodelist last=new nodelist(data);
nodelist cur=head;
while (cur.next!=null){
cur=cur.next;
}
cur.next=last;//到达尾节点之后,把null换成last的地址
}
2.5查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
对于这个,我们可以采用遍历单链表,查找是否会有于key相等的值。
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
if (head==null){//单链表为空
return false;
}
nodelist cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
return true;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
return false;
}
2.6 求单链表的长度
//得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
if (head==null){
return -1;//表示单链表为空的情况
}
int count=0;
nodelist cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
count++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return count;
}
2.7删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
boolean ret=contains(key);
if (ret==false){//判断单链表是否包含你要找的元素,调用contains(key)
System.out.println("没有你要删除的数据");
return;
}
if (head.val==key){//但删除的是头结点时
head=head.next;
return;
}
nodelist cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
if (cur.next.val==key){
cur.next=cur.next.next;
return;
}else{
cur=cur.next;
}
}
}
2.8删除所有值为key的节点
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
boolean ret=contains(key);//判断是否含有要删除的关键字key
if (ret==false){
System.out.println("没有你要删除的元素");
return;
}
nodelist cur=head;
nodelist prve=head.next;
while (prve!=null){
if (prve.val==key){
cur.next=prve.next;
prve=prve.next;
}else{
cur=cur.next;
prve=prve.next;
}
}
if (head.val==key){//如果头结点也是等于key
head=head.next;
}
}
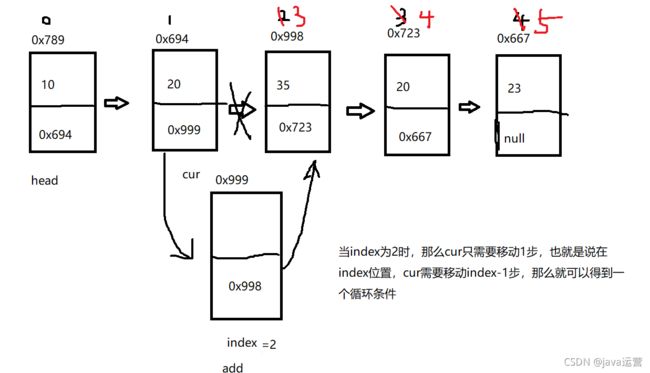
2.9任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
nodelist add=new nodelist(data);
if (index==0){//头插法
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index==size()){//尾插法
addLast(data);
return;
}
nodelist cur =head;
while (index-1!=0){
cur=cur.next;
}
add.next=cur.next;
cur.next=add;
}
2.10清空单链表
public void clear(){
//暴力清空 head=null;
while (head!=null){
nodelist cur=head.next;
head=null;
head=cur;
}
}
单链表源码地址
顺序表与单链表总结:
对于顺序表与单链表我们应该要懂得操作的原理是什么,如何进行操作,可以通过画图来理解,从而加深自己对于单链表与顺序表的理解与应用,之后就可以通过一些练习来巩固,发散自己的思维,从而提升自我的编程能力,具体的题目,可以看一下我之后的刷题文章记录。