TCP/IP协议栈之LwIP-pbuf
一、概述
lwIP - A Lightweight TCP/IP stack
The focus of the lwIP TCP/IP implementation is to reduce resource usage while still having a full scale TCP. This makes lwIP suitable for use in embedded systems with tens of kilobytes of free RAM and room for around 40 kilobytes of code ROM.
Main features include:
- Protocols: IP, IPv6, ICMP, ND, MLD, UDP, TCP, IGMP, ARP, PPPoS, PPPoE
- DHCP client, DNS client (incl. mDNS hostname resolver), AutoIP/APIPA (Zeroconf), SNMP agent (v1, v2c, v3, private MIB support & MIB compiler)
- APIs: specialized APIs for enhanced performance, optional Berkeley-alike socket API
- Extended features: IP forwarding over multiple network interfaces, TCP congestion control, RTT estimation and fast recovery/fast retransmit
- Addon applications: HTTP(S) server, SNTP client, SMTP(S) client, ping, NetBIOS nameserver, mDNS responder, MQTT client, TFTP server
以上是LwIP官网的一段描述,LwIP全名:Lightweight IP,意思是轻量化的TCP/IP协议,是瑞典计算机科学院(SICS)的Adam Dunkels开发的一个小型开源的TCP/IP协议栈。LwIP的设计初衷是:用少量的资源消耗实现一个较为完整的TCP/IP协议栈,其中“完整”主要指的是TCP协议的完整性,实现的重点是在保持TCP协议主要功能的基础上减少对RAM的占用。此外LwIP既可以移植到操作系统上运行,也可以在无操作系统的情况下独立运行。
LwIP 具有主要特性:
- 支持ARP协议(以太网地址解析协议)。
- 支持ICMP协议(控制报文协议),用于网络的调试与维护。
- 支持IGMP协议(互联网组管理协议),可以实现多播数据的接收。
- 支持UDP协议(用户数据报协议)。
- 支持TCP协议(传输控制协议),包括阻塞控制、RTT估算、快速恢复和快速转发。
- 支持PPP协议(点对点通信协议),支持PPPoS和PPPoE。
- 支持DNS(域名解析)。
- 支持DHCP协议,动态分配IP地址。
- 支持IP协议,包括IPv4、IPv6协议,支持IP分片与重装功能,多网络接口下的数据包转发。
- 支持SNMP协议(简单网络管理协议)。
- 支持AUTOIP,自动IP地址配置。
- 提供专门的内部回调接口(Raw API),用于提高应用程序性能。
- 提供可选择的Socket API、NETCONN API(在多线程情况下使用) 。
LwIP在嵌入式中使用有以下优点:
- 资源开销低,即轻量化。LwIP内核有自己的内存管理策略和数据包管理策略,使得内核处理数据包的效率很高。另外,LwIP高度可剪裁,一切不需要的功能都可以通过宏编译选项去掉。LwIP的流畅运行需要40KB的代码ROM和几十KB的RAM,这让它非常适合用在内存资源受限的嵌入式设备中。
- 支持的协议较为完整。几乎支持TCP/IP中所有常见的协议,这在嵌入式设备中早已够用。
- 实现了一些常见的应用程序:DHCP客户端、DNS客户端、HTTP服务器、MQTT客户端、TFTP服务器、SNTP客户端等等。
- 同时提供了三种编程接口:RAW API、NETCONN API和Socket API。这三种API的执行效率、易用性、可移植性以及时空间的开销各不相同,用户可以根据实际需要,平衡利弊,选择合适的API进行网络应用程序的开发。
- 高度可移植。其源代码全部用C实现,用户可以很方便地实现跨处理器、跨编译器的移植。另外,它对内核中会使用到操作系统功能的地方进行了抽象,使用了一套自定义的API,用户可以通过自己实现这些API,从而实现跨操作系统的移植工作。
- 开源、免费,用户可以不用承担任何商业风险地使用它。
- 相比于嵌入式领域其它的TCP/IP协议栈,比如uC-TCP/IP、FreeRTOS-TCP等,LwIP的发展历史要更悠久一些,得到了更多的验证和测试。LwIP被广泛用在嵌入式网络设备中,国内一些物联网公司推出的物联网操作系统,其TCP/IP核心就是LwIP;物联网知名的WiFi模块ESP8266,其TCP/IP固件,使用的就是LwIP。
LwIP的不足:
LwIP尽管有如此多的优点,但它毕竟是为嵌入式而生,所以并没有很完整地实现TCP/IP协议栈。相比于Linux和Windows系统自带的TCP/IP协议栈,LwIP的功能不算完整和强大。但对于大多数物联网领域的网络应用程序,LwIP已经足够了。
二、网络数据包处理
1、TCP/IP是一种数据通信机制,因此,协议栈的实现本质上就是对数据包进行处理,为了实现高效的效率,LwIP数据包管理要提供一种高效处理的机制。协议栈各层能对数据包进行灵活的处理,同时减少数据在各层间传递时的时间与空间开销,这是提高协议栈工作效率的关键点。在BSD的实现中,一个描述数据包的结构体叫做mbuf,同样的在LwIP中,也有个类似的结构,称之为pbuf。
- LwIP与标准TCP/IP协议栈的区别
| 标准协议栈 | LwIP协议栈 |
|---|---|
| 严格分层 | 模糊分层 |
| 数据传输层层拷贝 | 数据传输直接操作 |
| 数据包私有 | 数据包共享 |
| 效率低 | 效率高 |
| 数据处理要求低 | 数据处理要求高 |
| 完整的TCP/IP协议 | 较完整TCP/IP协议 |
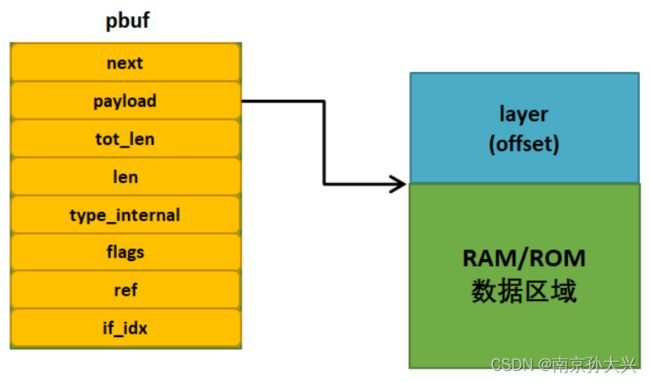
2、pbuf结构体就是一个描述协议栈中数据包的数据结构:
/** Main packet buffer struct */
struct pbuf
{
/** next pbuf in singly linked pbuf chain */
struct pbuf *next;
/** pointer to the actual data in the buffer */
void *payload;
/**
* total length of this buffer and all next buffers in chain
* belonging to the same packet.
*
* For non-queue packet chains this is the invariant:
* p->tot_len == p->len + (p->next? p->next->tot_len: 0)
*/
u16_t tot_len;
/** length of this buffer */
u16_t len;
/** a bit field indicating pbuf type and allocation sources
(see PBUF_TYPE_FLAG_*, PBUF_ALLOC_FLAG_* and PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK)
*/
u8_t type_internal;
/** misc flags */
u8_t flags;
/**
* the reference count always equals the number of pointers
* that refer to this pbuf. This can be pointers from an application,
* the stack itself, or pbuf->next pointers from a chain.
*/
LWIP_PBUF_REF_T ref;
/** For incoming packets, this contains the input netif's index */
u8_t if_idx;
};
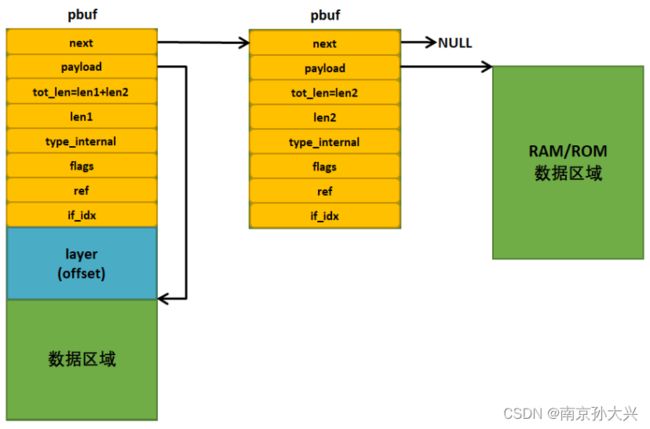
- next是一个pbuf类型的指针,指向下一个pbuf,因为网络中的数据包可能很大,而pbuf能管理的数据包大小有限,就会采用链表的形式将所有的pbuf包连接起来,这样子才能完整描述一个数据包,这些连接起来的pbuf包会组成一个链表,称之为pbuf链表。
- payload是一个指向数据区域的指针,指向该pbuf管理的数据区域起始地址,这里的数据区域可以是紧跟在pbuf结构体地址后面的RAM空间,也可以是ROM中的某个地址上,取决于pbuf的类型。
- tot_len中记录的是当前pbuf及其后续pbuf所有数据的长度,例如如果当前pbuf是pbuf链表上第一个数据结构,那么tot_len就记录着整个pbuf链表中所有pbuf中数据的长度;如果当前pbuf是链表上最后一个数据结构,那就记录着当前pbuf的长度。
- len表示当前pbuf中有效的数据长度。
- type_internal表示pbuf的类型,LwIP中有4种pbuf的类型,并且使用了一个枚举类型的数据结构定义他们。
- flags不同协议层表示内容不同。
- ref表示该pbuf被引用的次数,引用表示有其他指针指向当前pbuf,这里的指针可以是pbuf的next指针,也可以是其他任意形式的指针,初始化一个pbuf的时候,ref会被设置为1,因为该pbuf的地址一定会被返回一个指针变量,当有其他指针指向pbuf的时候,就必须调用相关函数将ref字段加1。
- if_idx用于记录传入的数据包中输入netif的索引,也就是netif中num字段。
3、pbuf的类型:
/**
* @ingroup pbuf
* Enumeration of pbuf types
*/
typedef enum
{
/** pbuf data is stored in RAM, used for TX mostly, struct pbuf and its payload
are allocated in one piece of contiguous memory (so the first payload byte
can be calculated from struct pbuf).
pbuf_alloc() allocates PBUF_RAM pbufs as unchained pbufs (although that might
change in future versions).
This should be used for all OUTGOING packets (TX).*/
PBUF_RAM = (PBUF_ALLOC_FLAG_DATA_CONTIGUOUS | PBUF_TYPE_FLAG_STRUCT_DATA_CONTIGUOUS | PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_HEAP),
/** pbuf data is stored in ROM, i.e. struct pbuf and its payload are located in
totally different memory areas. Since it points to ROM, payload does not
have to be copied when queued for transmission. */
PBUF_ROM = PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_MEMP_PBUF,
/** pbuf comes from the pbuf pool. Much like PBUF_ROM but payload might change
so it has to be duplicated when queued before transmitting, depending on
who has a 'ref' to it. */
PBUF_REF = (PBUF_TYPE_FLAG_DATA_VOLATILE | PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_MEMP_PBUF),
/** pbuf payload refers to RAM. This one comes from a pool and should be used
for RX. Payload can be chained (scatter-gather RX) but like PBUF_RAM, struct
pbuf and its payload are allocated in one piece of contiguous memory (so
the first payload byte can be calculated from struct pbuf).
Don't use this for TX, if the pool becomes empty e.g. because of TCP queuing,
you are unable to receive TCP acks! */
PBUF_POOL = (PBUF_ALLOC_FLAG_RX | PBUF_TYPE_FLAG_STRUCT_DATA_CONTIGUOUS | PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_MEMP_PBUF_POOL)
} pbuf_type;
- PBUF_RAM类型的pbuf空间是通过内存堆分配而来的,这种类型的pbuf在协议栈中使用得最多,一般协议栈中要发送的数据都是采用这种形式,在申请这种pbuf内存块的时候,协议栈会在管理的内存堆中根据需要的大小进行分配对应的内存空间,这种pbuf内存块包含数据空间以及pbuf数据结构区域,在连续的RAM内存空间中。内核申请这类型的pbuf时,也算上了协议首部的空间,当然是根据协议栈不同层次需要的首部进行申请,LwIP也使用一个枚举类型对不同的协议栈分层需要的首部大小进行定义。
/**
* @ingroup pbuf
* Enumeration of pbuf layers
*/
typedef enum
{
/** Includes spare room for transport layer header, e.g. UDP header.
* Use this if you intend to pass the pbuf to functions like udp_send().
*/
PBUF_TRANSPORT = PBUF_LINK_ENCAPSULATION_HLEN + PBUF_LINK_HLEN + PBUF_IP_HLEN + PBUF_TRANSPORT_HLEN,
/** Includes spare room for IP header.
* Use this if you intend to pass the pbuf to functions like raw_send().
*/
PBUF_IP = PBUF_LINK_ENCAPSULATION_HLEN + PBUF_LINK_HLEN + PBUF_IP_HLEN,
/** Includes spare room for link layer header (ethernet header).
* Use this if you intend to pass the pbuf to functions like ethernet_output().
* @see PBUF_LINK_HLEN
*/
PBUF_LINK = PBUF_LINK_ENCAPSULATION_HLEN + PBUF_LINK_HLEN,
/** Includes spare room for additional encapsulation header before ethernet
* headers (e.g. 802.11).
* Use this if you intend to pass the pbuf to functions like netif->linkoutput().
* @see PBUF_LINK_ENCAPSULATION_HLEN
*/
PBUF_RAW_TX = PBUF_LINK_ENCAPSULATION_HLEN,
/** Use this for input packets in a netif driver when calling netif->input()
* in the most common case - ethernet-layer netif driver. */
PBUF_RAW = 0
} pbuf_layer;
PBUF_RAM类型的pbuf:
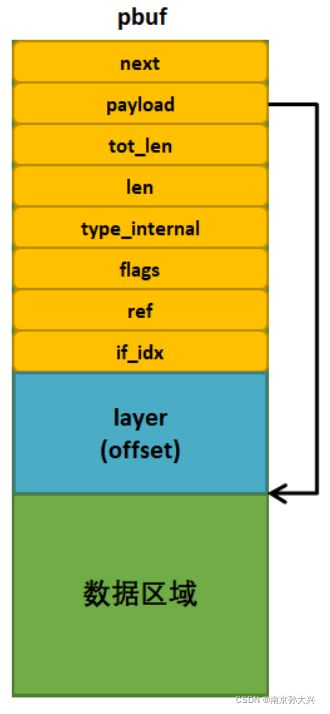
layer(offset)就是各层协议的首部,如TCP报文首部、IP首部、以太网帧首部等,预留出来的这些空间是为了在各个协议层中灵活地处理这些数据,当然layer的大小也可以是 0,具体是多少就与数据包的申请方式有关。
- PBUF_POOL类型的pbuf与PBUF_RAM类型的pbuf都是差不多的,其pbuf结构体与数据缓冲区也是存在于连续的内存块中,但它的空间是通过内存池分配的,这种类型的pbuf可以在极短的时间内分配得到,因为这是内存池分配策略的优势,在网卡接收数据的时候,LwIP一般就使用这种类型的pbuf来存储接收到的数据,申请PBUF_POOL类型时,协议栈会在内存池中分配适当的内存池个数以满足需要的数据区域大小。
- PBUF_ROM和PBUF_REF类型pbuf:
PBUF_ROM和PBUF_REF类型的pbuf基本是一样的,它们在内存池申请的pbuf不包含数据区域,只包含pbuf结构体,即MEMP_PBUF类型的POOL,这也是PBUF_ROM和PBUF_REF与前面两种类型的pbuf最大的差别。
PBUF_ROM类型的pbuf的数据区域存储在ROM中,是一段静态数据,而PBUF_REF类型的pbuf的数据区域存储在RAM空间中。申请这两种类型的pbuf时候也是只需要调用memp_malloc()函数从内存池中申请即可,申请内存的大小就是MEMP_PBUF,它只是一个pbuf结构体大小。
- 对于一个数据包,它可能会使用任意类型的pbuf进行描述,也可能使用多种不同的pbuf一起描述,就是采用多种pbuf描述一个数据包,但是无论怎么样描述,数据包的处理都是不变的,payload指向的始终是数据区域,采用链表的形式连接起来的数据包,其tot_len字段永远是记录当前及其后续pbuf的总大小。
- pbuf_alloc()
在不同层的协议中,layer字段的大小是不一样的,因为不一样的协议其首部大小是不同的,协议栈中各层首部的大小都会被预留出来,LwIP采用枚举类型的变量将各个层的首部大小记录下来,在申请的时候就把layer需要空间的大小根据协议进行分配。
struct pbuf *pbuf_alloc(pbuf_layer layer, u16_t length, pbuf_type type);
举个例子,假设TCP协议需要申请一个pbuf数据包,那么就会调用下面代码进行申请:
p = pbuf_alloc(PBUF_TRANSPORT, 1472, PBUF_RAM);
内核就会根据这句代码进行分配一个PBUF_RAM类型的pbuf,其数据区域大小是1472字节,并且会根据协议层次进行预留协议首部空间,由于是传输层,所以内核需要预留54个字节空间,即以太网帧首部长度PBUF_LINK_HLEN(14字节)、IP数据报首部长度PBUF_IP_HLEN(20字节)、TCP首部长度PBUF_TRANSPORT_HLEN(20字节)。当数据报往下层递交的时候,其他层
直接填充对应的协议首部即可,无需对数据进行拷贝等操作,这也是LwIP能快速处理的优势。
/* Initialize members of struct pbuf after allocation */
static void pbuf_init_alloced_pbuf(struct pbuf *p, void *payload, u16_t tot_len, u16_t len, pbuf_type type, u8_t flags)
{
p->next = NULL;
p->payload = payload;
p->tot_len = tot_len;
p->len = len;
p->type_internal = (u8_t)type;
p->flags = flags;
p->ref = 1;
p->if_idx = NETIF_NO_INDEX;
}
/**
* @ingroup pbuf
* Allocates a pbuf of the given type (possibly a chain for PBUF_POOL type).
*
* The actual memory allocated for the pbuf is determined by the
* layer at which the pbuf is allocated and the requested size
* (from the size parameter).
*
* @param layer header size
* @param length size of the pbuf's payload
* @param type this parameter decides how and where the pbuf
* should be allocated as follows:
*
* - PBUF_RAM: buffer memory for pbuf is allocated as one large
* chunk. This includes protocol headers as well.
* - PBUF_ROM: no buffer memory is allocated for the pbuf, even for
* protocol headers. Additional headers must be prepended
* by allocating another pbuf and chain in to the front of
* the ROM pbuf. It is assumed that the memory used is really
* similar to ROM in that it is immutable and will not be
* changed. Memory which is dynamic should generally not
* be attached to PBUF_ROM pbufs. Use PBUF_REF instead.
* - PBUF_REF: no buffer memory is allocated for the pbuf, even for
* protocol headers. It is assumed that the pbuf is only
* being used in a single thread. If the pbuf gets queued,
* then pbuf_take should be called to copy the buffer.
* - PBUF_POOL: the pbuf is allocated as a pbuf chain, with pbufs from
* the pbuf pool that is allocated during pbuf_init().
*
* @return the allocated pbuf. If multiple pbufs where allocated, this
* is the first pbuf of a pbuf chain.
*/
struct pbuf *pbuf_alloc(pbuf_layer layer, u16_t length, pbuf_type type)
{
struct pbuf *p;
u16_t offset = (u16_t)layer;
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_alloc(length=%"U16_F")\n", length));
switch (type)
{
case PBUF_REF: /* fall through */
case PBUF_ROM:
p = pbuf_alloc_reference(NULL, length, type);
break;
case PBUF_POOL:
{
struct pbuf *q, *last;
u16_t rem_len; /* remaining length */
p = NULL;
last = NULL;
rem_len = length;
do
{
u16_t qlen;
q = (struct pbuf *)memp_malloc(MEMP_PBUF_POOL);
if (q == NULL)
{
PBUF_POOL_IS_EMPTY();
/* free chain so far allocated */
if (p)
{
pbuf_free(p);
}
/* bail out unsuccessfully */
return NULL;
}
qlen = LWIP_MIN(rem_len, (u16_t)(PBUF_POOL_BUFSIZE_ALIGNED - LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(offset)));
pbuf_init_alloced_pbuf(q, LWIP_MEM_ALIGN((void *)((u8_t *)q + SIZEOF_STRUCT_PBUF + offset)), rem_len, qlen, type, 0);
LWIP_ASSERT("pbuf_alloc: pbuf q->payload properly aligned", ((mem_ptr_t)q->payload % MEM_ALIGNMENT) == 0);
LWIP_ASSERT("PBUF_POOL_BUFSIZE must be bigger than MEM_ALIGNMENT", (PBUF_POOL_BUFSIZE_ALIGNED - LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(offset)) > 0);
if (p == NULL)
{
/* allocated head of pbuf chain (into p) */
p = q;
}
else
{
/* make previous pbuf point to this pbuf */
last->next = q;
}
last = q;
rem_len = (u16_t)(rem_len - qlen);
offset = 0;
} while (rem_len > 0);
break;
}
case PBUF_RAM:
{
u16_t payload_len = (u16_t)(LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(offset) + LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(length));
mem_size_t alloc_len = (mem_size_t)(LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(SIZEOF_STRUCT_PBUF) + payload_len);
/* bug #50040: Check for integer overflow when calculating alloc_len */
if ((payload_len < LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(length)) || (alloc_len < LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(length)))
{
return NULL;
}
/* If pbuf is to be allocated in RAM, allocate memory for it. */
p = (struct pbuf *)mem_malloc(alloc_len);
if (p == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
pbuf_init_alloced_pbuf(p, LWIP_MEM_ALIGN((void *)((u8_t *)p + SIZEOF_STRUCT_PBUF + offset)), length, length, type, 0);
LWIP_ASSERT("pbuf_alloc: pbuf->payload properly aligned", ((mem_ptr_t)p->payload % MEM_ALIGNMENT) == 0);
break;
}
default:
LWIP_ASSERT("pbuf_alloc: erroneous type", 0);
return NULL;
}
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_alloc(length=%"U16_F") == %p\n", length, (void *)p));
return p;
}
- pbuf_free()
pbuf中ref字段就是记录pbuf数据包被引用的次数,在申请pbuf的时候,ref字段就被初始化为1,当释放pbuf的时候,先将ref减1,如果ref减1后为0,则表示能释放pbuf数据包,此外,能被内核释放的pbuf数据包只能是首节点或者其他地方未被引用过的节点。
LwIP的数据包释放函数会自动删除属于一个数据包中连同首节点在内所有pbuf,举个例子,假设一个数据包需要3个pbuf连接起来,那么在删除第一个pbuf的时候,内核会检测一下它下一个pbuf释放与首节点是否存储同一个数据包的数据,如果是那就将第二个节点也删除掉,同理第三个也会被删除。但如果删除某个pbuf链表的首节点时,链表中第二个节点的pbuf中ref字段不为0,则表示该节点还在其他地方被引用,那么第二个节点不与第一个节点存储同一个数据包,那么就不会删除第二个节点。
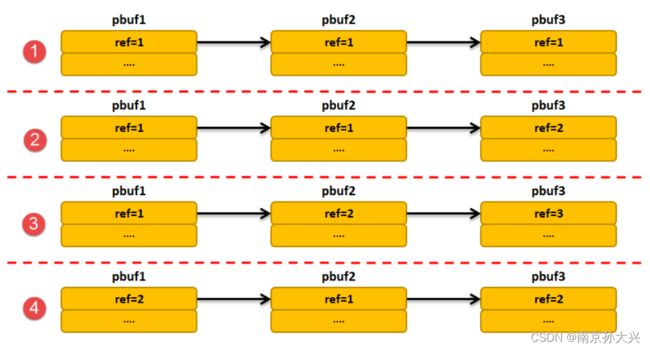
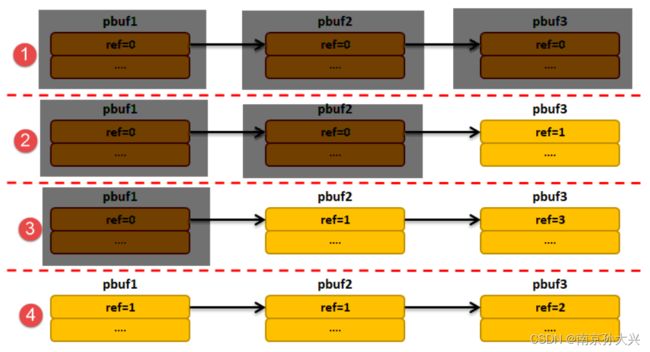
pbuf的释放要小心,如果pbuf是串成链表的话,pbuf在释放的时候,就会把pbuf的ref值减1,然后函数会判断ref减完之后是不是变成0,如果是0就会根据pbuf的类型调用内存池或者内存堆回收函数进行回收。然后这里就有个很危险的事,对于这个pbuf_free()函数,用户传递的参数必须是链表头指针,假如不是链表头而是指向链表中间的某个pbuf的指针,那就很容易出现问题,因为这个pbuf_free() 函数可不会帮我们检查是不是链表头,这样子势必会导致一部分pbuf没被回收,意味着一部分内存就这样被泄漏了,以后没办法用了。同时,还可能将一些尚未处理的数据回收了,这样子整个系统就乱套了。
/**
* @ingroup pbuf
* Dereference a pbuf chain or queue and deallocate any no-longer-used
* pbufs at the head of this chain or queue.
*
* Decrements the pbuf reference count. If it reaches zero, the pbuf is
* deallocated.
*
* For a pbuf chain, this is repeated for each pbuf in the chain,
* up to the first pbuf which has a non-zero reference count after
* decrementing. So, when all reference counts are one, the whole
* chain is free'd.
*
* @param p The pbuf (chain) to be dereferenced.
*
* @return the number of pbufs that were de-allocated
* from the head of the chain.
*
* @note MUST NOT be called on a packet queue (Not verified to work yet).
* @note the reference counter of a pbuf equals the number of pointers
* that refer to the pbuf (or into the pbuf).
*
* @internal examples:
*
* Assuming existing chains a->b->c with the following reference
* counts, calling pbuf_free(a) results in:
*
* 1->2->3 becomes ...1->3
* 3->3->3 becomes 2->3->3
* 1->1->2 becomes ......1
* 2->1->1 becomes 1->1->1
* 1->1->1 becomes .......
*
*/
u8_t pbuf_free(struct pbuf *p)
{
u8_t alloc_src;
struct pbuf *q;
u8_t count;
if (p == NULL)
{
LWIP_ASSERT("p != NULL", p != NULL);
/* if assertions are disabled, proceed with debug output */
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_LEVEL_SERIOUS, ("pbuf_free(p == NULL) was called.\n"));
return 0;
}
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_free(%p)\n", (void *)p));
PERF_START;
count = 0;
/* de-allocate all consecutive pbufs from the head of the chain that
* obtain a zero reference count after decrementing*/
while (p != NULL)
{
LWIP_PBUF_REF_T ref;
SYS_ARCH_DECL_PROTECT(old_level);
/* Since decrementing ref cannot be guaranteed to be a single machine operation
* we must protect it. We put the new ref into a local variable to prevent
* further protection. */
SYS_ARCH_PROTECT(old_level);
/* all pbufs in a chain are referenced at least once */
LWIP_ASSERT("pbuf_free: p->ref > 0", p->ref > 0);
/* decrease reference count (number of pointers to pbuf) */
ref = --(p->ref);
SYS_ARCH_UNPROTECT(old_level);
/* this pbuf is no longer referenced to? */
if (ref == 0)
{
/* remember next pbuf in chain for next iteration */
q = p->next;
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_free: deallocating %p\n", (void *)p));
alloc_src = pbuf_get_allocsrc(p);
#if LWIP_SUPPORT_CUSTOM_PBUF
/* is this a custom pbuf? */
if ((p->flags & PBUF_FLAG_IS_CUSTOM) != 0)
{
struct pbuf_custom *pc = (struct pbuf_custom *)p;
LWIP_ASSERT("pc->custom_free_function != NULL", pc->custom_free_function != NULL);
pc->custom_free_function(p);
}
else
#endif /* LWIP_SUPPORT_CUSTOM_PBUF */
{
/* is this a pbuf from the pool? */
if (alloc_src == PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_MEMP_PBUF_POOL)
{
memp_free(MEMP_PBUF_POOL, p);
/* is this a ROM or RAM referencing pbuf? */
}
else if (alloc_src == PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_MEMP_PBUF)
{
memp_free(MEMP_PBUF, p);
/* type == PBUF_RAM */
}
else if (alloc_src == PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_HEAP)
{
mem_free(p);
}
else
{
/* @todo: support freeing other types */
LWIP_ASSERT("invalid pbuf type", 0);
}
}
count++;
/* proceed to next pbuf */
p = q;
/* p->ref > 0, this pbuf is still referenced to */
/* (and so the remaining pbufs in chain as well) */
}
else
{
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_free: %p has ref %"U16_F", ending here.\n", (void *)p, (u16_t)ref));
/* stop walking through the chain */
p = NULL;
}
}
PERF_STOP("pbuf_free");
/* return number of de-allocated pbufs */
return count;
}
- pbuf_header()
pbuf_header()函数用于调整pbuf的payload指针(向前或向后移动一定字节数),在pbuf的数据区前可能会预留一些协议首部空间,而pbuf被创建时,payload指针是指向数据区的,为了实现对这些预留空间的操作,可以调用pbuf_header()函数使payload指针指向数据区前的首部字段,这就为各层对数据包首部的操作提供了方便。当然,进行这个操作的时候,len和tot_len字段值也会随之更新。
/**
* Adjusts the payload pointer to hide headers in the payload.
*
* Adjusts the ->payload pointer so that space for a header
* disappears in the pbuf payload.
*
* The ->payload, ->tot_len and ->len fields are adjusted.
*
* @param p pbuf to change the header size.
* @param header_size_decrement Number of bytes to decrement header size which
* decreases the size of the pbuf.
* If header_size_decrement is 0, this function does nothing and returns successful.
* @return non-zero on failure, zero on success.
*
*/
u8_t pbuf_remove_header(struct pbuf *p, size_t header_size_decrement)
{
void *payload;
u16_t increment_magnitude;
LWIP_ASSERT("p != NULL", p != NULL);
if ((p == NULL) || (header_size_decrement > 0xFFFF))
{
return 1;
}
if (header_size_decrement == 0)
{
return 0;
}
increment_magnitude = (u16_t)header_size_decrement;
/* Check that we aren't going to move off the end of the pbuf */
LWIP_ERROR("increment_magnitude <= p->len", (increment_magnitude <= p->len), return 1;);
/* remember current payload pointer */
payload = p->payload;
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(payload); /* only used in LWIP_DEBUGF below */
/* increase payload pointer (guarded by length check above) */
p->payload = (u8_t *)p->payload + header_size_decrement;
/* modify pbuf length fields */
p->len = (u16_t)(p->len - increment_magnitude);
p->tot_len = (u16_t)(p->tot_len - increment_magnitude);
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_remove_header: old %p new %p (%"U16_F")\n", (void *)payload, (void *)p->payload, increment_magnitude));
return 0;
}
/**
* Adjusts the payload pointer to reveal headers in the payload.
* @see pbuf_add_header.
*
* @param p pbuf to change the header size.
* @param header_size_increment Number of bytes to increment header size.
* @param force Allow 'header_size_increment > 0' for PBUF_REF/PBUF_ROM types
*
* @return non-zero on failure, zero on success.
*
*/
static u8_t pbuf_add_header_impl(struct pbuf *p, size_t header_size_increment, u8_t force)
{
u16_t type_internal;
void *payload;
u16_t increment_magnitude;
LWIP_ASSERT("p != NULL", p != NULL);
if ((p == NULL) || (header_size_increment > 0xFFFF))
{
return 1;
}
if (header_size_increment == 0)
{
return 0;
}
increment_magnitude = (u16_t)header_size_increment;
/* Do not allow tot_len to wrap as a result. */
if ((u16_t)(increment_magnitude + p->tot_len) < increment_magnitude)
{
return 1;
}
type_internal = p->type_internal;
/* pbuf types containing payloads? */
if (type_internal & PBUF_TYPE_FLAG_STRUCT_DATA_CONTIGUOUS)
{
/* set new payload pointer */
payload = (u8_t *)p->payload - header_size_increment;
/* boundary check fails? */
if ((u8_t *)payload < (u8_t *)p + SIZEOF_STRUCT_PBUF)
{
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_add_header: failed as %p < %p (not enough space for new header size)\n", (void *)payload, (void *)((u8_t *)p + SIZEOF_STRUCT_PBUF)));
/* bail out unsuccessfully */
return 1;
}
/* pbuf types referring to external payloads? */
}
else
{
/* hide a header in the payload? */
if (force)
{
payload = (u8_t *)p->payload - header_size_increment;
}
else
{
/* cannot expand payload to front (yet!)
* bail out unsuccessfully */
return 1;
}
}
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_add_header: old %p new %p (%"U16_F")\n", (void *)p->payload, (void *)payload, increment_magnitude));
/* modify pbuf fields */
p->payload = payload;
p->len = (u16_t)(p->len + increment_magnitude);
p->tot_len = (u16_t)(p->tot_len + increment_magnitude);
return 0;
}
static u8_t pbuf_header_impl(struct pbuf *p, s16_t header_size_increment, u8_t force)
{
if (header_size_increment < 0)
{
return pbuf_remove_header(p, (size_t) - header_size_increment);
}
else
{
return pbuf_add_header_impl(p, (size_t)header_size_increment, force);
}
}
/**
* Adjusts the payload pointer to hide or reveal headers in the payload.
* * Adjusts the ->payload pointer so that space for a header
* (dis)appears in the pbuf payload.
* * The ->payload, ->tot_len and ->len fields are adjusted.
* * @param p pbuf to change the header size.
* @param header_size_increment Number of bytes to increment header size which
* increases the size of the pbuf. New space is on the front.
* (Using a negative value decreases the header size.)
* If header_size_increment is 0, this function does nothing and returns successful.
* * PBUF_ROM and PBUF_REF type buffers cannot have their sizes increased, so
* the call will fail. A check is made that the increase in header size does
* not move the payload pointer in front of the start of the buffer.
* @return non-zero on failure, zero on success.
* */
u8_t pbuf_header(struct pbuf *p, s16_t header_size_increment)
{
return pbuf_header_impl(p, header_size_increment, 0);
}
- pbuf_chain()
函数用于连接两个pbuf(链表)为一个pbuf链表。
/**
* @ingroup pbuf
* Concatenate two pbufs (each may be a pbuf chain) and take over
* the caller's reference of the tail pbuf.
* * @note The caller MAY NOT reference the tail pbuf afterwards.
* Use pbuf_chain() for that purpose.
* * This function explicitly does not check for tot_len overflow to prevent
* failing to queue too long pbufs. This can produce invalid pbufs, so
* handle with care!
* * @see pbuf_chain()
*/
void pbuf_cat(struct pbuf *h, struct pbuf *t)
{
struct pbuf *p;
LWIP_ERROR("(h != NULL) && (t != NULL) (programmer violates API)", ((h != NULL) && (t != NULL)), return;);
/* proceed to last pbuf of chain */
for (p = h; p->next != NULL; p = p->next)
{
/* add total length of second chain to all totals of first chain */
p->tot_len = (u16_t)(p->tot_len + t->tot_len);
}
/* { p is last pbuf of first h chain, p->next == NULL } */
LWIP_ASSERT("p->tot_len == p->len (of last pbuf in chain)", p->tot_len == p->len);
LWIP_ASSERT("p->next == NULL", p->next == NULL);
/* add total length of second chain to last pbuf total of first chain */
p->tot_len = (u16_t)(p->tot_len + t->tot_len);
/* chain last pbuf of head (p) with first of tail (t) */
p->next = t;
/* p->next now references t, but the caller will drop its reference to t,
* so netto there is no change to the reference count of t.
*/
}
- pbuf_ref()
pbuf_ref函数用于将pbuf中的ref值加1。
/**
* @ingroup pbuf
* Increment the reference count of the pbuf.
*
* @param p pbuf to increase reference counter of
*
*/
void pbuf_ref(struct pbuf *p)
{
/* pbuf given? */
if (p != NULL)
{
SYS_ARCH_SET(p->ref, (LWIP_PBUF_REF_T)(p->ref + 1));
LWIP_ASSERT("pbuf ref overflow", p->ref > 0);
}
}
- pbuf_chain()
函数用于连接两个pbuf(链表)为一个pbuf链表。
/**
* @ingroup pbuf
* Chain two pbufs (or pbuf chains) together.
* * The caller MUST call pbuf_free(t) once it has stopped
* using it. Use pbuf_cat() instead if you no longer use t.
* * @param h head pbuf (chain)
* @param t tail pbuf (chain)
* @note The pbufs MUST belong to the same packet.
* @note MAY NOT be called on a packet queue.
* * The ->tot_len fields of all pbufs of the head chain are adjusted.
* The ->next field of the last pbuf of the head chain is adjusted.
* The ->ref field of the first pbuf of the tail chain is adjusted.
* */
void pbuf_chain(struct pbuf *h, struct pbuf *t)
{
pbuf_cat(h, t);
/* t is now referenced by h */
pbuf_ref(t);
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_chain: %p references %p\n", (void *)h, (void *)t));
}
- pbuf_dechain()
将第一个pbuf与链中剩余的pbuf分离开。
/**
* Dechains the first pbuf from its succeeding pbufs in the chain.
*
* Makes p->tot_len field equal to p->len.
* @param p pbuf to dechain
* @return remainder of the pbuf chain, or NULL if it was de-allocated.
* @note May not be called on a packet queue.
*/
struct pbuf *pbuf_dechain(struct pbuf *p)
{
struct pbuf *q;
u8_t tail_gone = 1;
/* tail */
q = p->next;
/* pbuf has successor in chain? */
if (q != NULL)
{
/* assert tot_len invariant: (p->tot_len == p->len + (p->next? p->next->tot_len: 0) */
LWIP_ASSERT("p->tot_len == p->len + q->tot_len", q->tot_len == p->tot_len - p->len);
/* enforce invariant if assertion is disabled */
q->tot_len = (u16_t)(p->tot_len - p->len);
/* decouple pbuf from remainder */
p->next = NULL;
/* total length of pbuf p is its own length only */
p->tot_len = p->len;
/* q is no longer referenced by p, free it */
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_dechain: unreferencing %p\n", (void *)q));
tail_gone = pbuf_free(q);
if (tail_gone > 0)
{
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_dechain: deallocated %p (as it is no longer referenced)\n", (void *)q));
}
/* return remaining tail or NULL if deallocated */
}
/* assert tot_len invariant: (p->tot_len == p->len + (p->next? p->next->tot_len: 0) */
LWIP_ASSERT("p->tot_len == p->len", p->tot_len == p->len);
return ((tail_gone > 0) ? NULL : q);
}
以上部分内容引自《[野火]LwIP应用开发实战指南》。