ESPIDF开发ESP32学习笔记【SPI与片外FLASH基础】
文章目录
- SPI
-
- SPI Master
-
- SPI传输时序
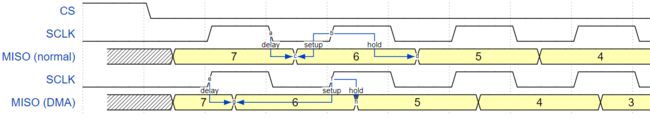
- Notes on Sending Mixed Transactions to the Same Device
- SPI传输模式
-
- 中断传输
- 轮询传输
- SPI使用
- 传输速率
- SPI Slave
-
- 从模式的基本配置
- 传输相关API与使用步骤
- 目前存在的DMA缺陷(摘自官网)
- Restrictions and Known Issues
- SPI使用例
- SPI FLASH组件
-
- FLASH设备的使用
-
- 初始化
- 访问FLASH
注意: 所有SPI相关的API都不能在中断服务函数或上下文切换期间使用,因为SPI相关的API都调用了互斥量,可能会造成系统错误
SPI
调用#include "driver/spi_master.h"或#include "driver/spi_slave.h"来使用API组件
ESP32集成了4个SPI外设
SPI0和SPI1通过总线仲裁器共享一条信号总线,用于在模组内部访问FLASH(SoC FLASH),不会对用户开放
SPI2和SPI3是通用SPI控制器,有时也被称为HSPI和VSPI。它们拥有独立的信号总线,每条总线都有三条片选(CS)信号,也就是说每个控制器都能驱动最多3个SPI从器件。这两个SPI控制器对用户开放
相关概念参考SPI协议,以下内容默认读者学习过SPI、QSPI基础知识。
表格翻译自官网
| 概念 | 定义 |
|---|---|
| Host | 作为SPI主设备使用的ESP32片上SPI外设,目前只能使用SPI2或SPI3 |
| Device | 片外SPI从设备 |
| Bus | SPI信号总线,通常包括MISO、MOSI、SCLK、多条CS线、可选的QUADWP和QUADHD线 |
| MISO | Master in Slave out |
| MOSI | Master in Slave out |
| SCLK | 同步时钟 |
| CS | 片选信号 |
| QUADWP | 写保护信号,当且仅当使用QSPI时启用 |
| QUADHD | 保持信号,当且仅当使用QSPI时启用 |
| Assertion | 启用某条信号线的行为;相反的行为称为de-assertion. |
| Transaction | 启动片选、传输数据、结束传输、断开片选这一系列传输过程称为一次传输。传输是原子性的,不能被中断 |
| Launch edge | 源寄存器触发launches信号到总线的时钟边沿 |
| Latch edge | 源寄存器触发latches in信号刀纵线的时钟边沿 |
对应的SPI-GPIO映射表如下所示
| 引脚对应的GPIO | SPI2 | SPI3 |
|---|---|---|
| CS0* | 15 | 5 |
| SCLK | 14 | 18 |
| MISO | 12 | 19 |
| MOSI | 13 | 23 |
| QUADWP | 2 | 22 |
| QUADHD | 4 | 21 |
SPI Master
ESP32内部的SPI控制器可设置为主模式(Master),基本特点如下
- 适应多线程环境
- 可配置DMA辅助传输
- 在同一信号线上自动分配时间处理来自不同设备的的多路数据
但是SPI控制器不是永远安全的,用户最好重构代码来让每个SPI外设在同一时间只被一个任务访问(避免临界区出现)或使用互斥量来处理临界区
临界区相关的处理参考RTOS部分
SPI传输时序
SPI的传输格式有以下五个组成部分
- 指令数据段
主机发送0-16位指令
- 地址数据段
主机发送0-64位地址
- 写入数据
主机向外设发送数据,允许附带可选的指令和地址数据,但这些数据无法从电器层面区分
- 空段
用于同步时序
- 读取数据
外设向主机发送数据
物理层传输属性由spi_bus_config_t结构体、spi_transaction_t结构体和spi_device_interface_config_t结构体设置
//spi_bus_config_t用于配置GPIO的SPI复用引脚和SPI控制器
//注意:如果不使用QSPI可以直接不初始化quadwp_io_num和quadhd_io_num,总线会自动关闭未被配置的信号线
//如果不使用某线应将其设置为-1
struct spi_bus_config_t={
.miso_io_num,//MISO信号线,可复用为QSPI的D0
.mosi_io_num,//MOSI信号线,可复用为QSPI的D1
.sclk_io_num,//SCLK信号线
.quadwp_io_num,//WP信号线,专用于QSPI的D2
.quadhd_io_num,//HD信号线,专用于QSPI的D3
.max_transfer_sz,//最大传输数据大小,单位字节,默认为4094
.intr_flags,//中断指示位
};
//spi_transaction_t用于配置SPI的数据格式
//注意:这个结构体只定义了一种SPI传输格式,如果需要多种SPI传输则需要定义多个结构体并进行实例化
struct spi_transaction_t={
.cmd,//指令数据,其长度在spi_device_interface_config_t中的command_bits设置
.addr,//地址数据,其长度在spi_device_interface_config_t中的address_bits设置
.length,//数据总长度,单位:比特
.rxlength,//接收到的数据总长度,应小于length,如果设置为0则默认设置为length
.flags,//SPI传输属性设置
.user,//用户定义变量,可以用来存储传输ID等注释信息
.tx_buffer,//发送数据缓存区指针
.tx_data,//发送数据
.rx_buffer,//接收数据缓存区指针,如果启用DMA则需要至少4个字节
.rx_data//如果设置了SPI_TRANS_USE_RXDATA,数据会被这个变量直接接收
};
//spi_device_interface_config_t用于配置SPI协议情况
//需要根据从设备的数据手册进行设置
struct spi_device_interface_config_t={
.command_bits,//默认控制位长度,设置为0-16
.address_bits,//默认地址位长度,设置为0-64
.dummy_bits,//在地址和数据位段之间插入的dummy位长度,用于匹配时序,一般可以保持默认
.clock_speed_hz,//时钟频率,设置的是80MHz的分频系数,单位为Hz
.mode,//SPI模式,设置为0-3
.duty_cycle_pos,//
.cs_ena_pretrans,//传输前CS信号的建立时间,只在半双工模式下有用
.cs_ena_posttrans,//传输时CS信号的保持时间
.input_delay_ns,//从机的最大合法数据传输时间
.spics_io_num,//设置GPIO复用为CS引脚
.queue_size,//传输队列大小,决定了等待传输数据的数量
.flags,//SPI设备属性设置
.pre_cb,//传输开始时的回调函数
.post_cb,//传输结束时的回调函数
};
SPI主机可以发起全双工/半双工的通信,全双工通信中,总传输数据长度由spi_device_interface_config_t::command_bits、spi_device_interface_config_t::address_bits、spi_transaction_t::length决定,spi_transaction_t::rxlength仅决定了缓存区接收数据的长度;但半双工通信中,读写不同步,总传输数据长度由只spi_transaction_t::length和spi_transaction_t::rxlength决定
指令和地址数据段是可选的,不是所有SPI设备都需要指令和/或数据,所以在spi_device_interface_config_t结构体中,如果设置command_bits和address_bits为0,就不会发送指令和数据
读写数据段也是可选的,如果rx_buffer设置为NULL,SPI_TRANS_USE_RXDATA没有定义,则读取数据段会被跳过;同理,如果tx_buffer设置为NULL,SPI_TRANS_USE_TXDATA没有定义,则写入数据段会被跳过
ESP32的驱动提供了两种传输方式:
- 中断传输:发送、接收时触发中断
- 轮询传输:轮询SPI设备状态,如果空闲则可以调用函数
两种模式也可以同时使用,但是实现代码较复杂
官网给出解释为
Notes on Sending Mixed Transactions to the Same Device
To reduce coding complexity, send only one type of transactions (interrupt or polling) to one Device. However, you still can send both interrupt and polling transactions alternately. The notes below explain how to do this.
The polling transactions should be initiated only after all the polling and interrupt transactions are finished.
Since an unfinished polling transaction blocks other transactions, please do not forget to call the function
spi_device_polling_end()afterspi_device_polling_start()to allow other transactions or to allow other Devices to use the bus. Remember that if there is no need to switch to other tasks during your polling transaction, you can initiate a transaction withspi_device_polling_transmit()so that it will be ended automatically.In-flight polling transactions are disturbed by the ISR operation to accommodate interrupt transactions. Always make sure that all the interrupt transactions sent to the ISR are finished before you call
spi_device_polling_start(). To do that, you can keep callingspi_device_get_trans_result()until all the transactions are returned.To have better control of the calling sequence of functions, send mixed transactions to the same Device only within a single task.
也就是说轮询模式下的两个API相当于开关,一个让CPU进入轮询状态,一个让CPU退出轮询状态,需要配合使用;中断模式下的API相当于一个指令,让SPI控制器在发送/接收完毕时发出中断告知CPU,CPU接收到中断后执行中断服务函数;轮询状态下应当保证没有中断,否则会影响实时性,但是中断状态下CPU可以干别的事
SPI传输模式
中断传输
中断传输期间,CPU可以执行其他任务。传输结束时,SPI外设触发中断,CPU调用任务处理函数进行处理
注意:一个任务可以排列多个传输序列,驱动程序会自动在中断服务程序(ISR)中对传输结果进行处理;但是中断传输会导致很多中断,如果设置中断任务太多还会影响日常任务运行降低实时性能
轮询传输
轮询传输会轮询SPI外设的状态寄存器(官网原文为状态位)直到传输完成
轮询传输可以节约ISR队列挂起等待和线程(任务)上下文切换所需时间,但是会导致CPU占用
使用API spi_device_polling_end()来进行轮询,这个API至少需要1us时间解除对其他任务的阻塞;官方推荐使用spi_device_acquire_bus()和spi_device_release_bus()来进行调度
SPI使用
- 设定并初始化GPIO复用为SPI
注意不使用的信号线要设置为-1
esp_err_t spi_bus_initialize(spi_host_device_t host,//SPI设备号
const spi_bus_config_t *bus_config,//总线GPIO设置
int dma_chan)//使用的DMA通道
//总线初始化API
//如果使能了DMA通道,所有传输和使用的数据接收缓冲区都应该在支持DMA访问的内存区域中申请
spi_host_device_t={
SPI1_HOST=0,
SPI2_HOST,
SPI3_HOST,
}
//dma_chan只能设置为0,1,2;设置为0则不启用DMA
- 使用spi_bus_add_device()设置SPI控制器设备
esp_err_t spi_bus_add_device(spi_host_device_t host,//SPI设备号
const spi_device_interface_config_t *dev_config,//数据格式设置
spi_device_handle_t *handle)//设备句柄
这个API会根据spi_device_interface_config_t结构体初始化一个SPI外设并规定具体的时序
注意不要过度使用:ESP32只有2个可用的SPI控制器,一个SPI控制器只有三个CS信号线,最多能控制6个从设备
全双工下,SPI最高速度可达80MHz,一般使用40Mhz;而半双工下,最高只能达到26MHz
-
设置一个或多个spi_transaction_t结构体来配置传输的数据格式
注意:需要等待当前传输完成后再发起新的传输
- 中断模式
使用
esp_err_t spi_device_queue_trans(spi_device_handle_t handle,//SPI设备句柄 spi_transaction_t *trans_desc,//要执行的传输 TickType_t ticks_to_wait)//等待时间,如果设置为MAX_DELAY则会等待到队满 //将要执行的传输放入SPI传输队列 esp_err_t spi_device_get_trans_result(spi_device_handle_t handle,//SPI设备句柄 spi_transaction_t **trans_desc,//之前执行的传输的指针 TickType_t ticks_to_wait)//等待时间 //获取此前由spi_device_queue_trans发起传输的结果来将一个传输加入待传输队列
可以通过spi_device_get_trans_result()查询传输结果;也可以将所有结果放入以下API,使用中断处理函数和FSM来设定各种传输结果对应的操作
esp_err_t spi_device_transmit(spi_device_handle_t handle,//SPI设备句柄 spi_transaction_t *trans_desc)//要执行的传输 //发起一次SPI传输,等待完成并返回结果,该函数和spi_device_queue_trans+spi_device_get_trans_result共同使用等价- 轮询模式
使用以下API来发起轮询模式的传输
esp_err_t spi_device_polling_transmit(spi_device_handle_t handle,//SPI设备句柄 spi_transaction_t *trans_desc)//要执行的传输 //发起一次轮询模式下的传输,等待完成后返回结果 //此函数和spi_device_polling_start+spi_device_polling_end共同使用等价如果需要再发送传输中间插入其他代码,可以使用以下两个API
esp_err_t spi_device_polling_start(spi_device_handle_t handle,//SPI设备句柄 spi_transaction_t *trans_desc,//要执行的传输 TickType_t ticks_to_wait)//等待时间 //立刻发起一次轮询模式传输 esp_err_t spi_device_polling_end(spi_device_handle_t handle,//SPI设备句柄 TickType_t ticks_to_wait)//等待时间 //使CPU保持轮询直到传输完成,这个任务直到成功完成才能结束且是非阻塞的——其他线程(任务)可以在传输期间占用CPU(当然会降低效率) -
发送/接收数据
可以使用
esp_err_t spi_device_acquire_bus(spi_device_handle_t device, TickType_t wait);//释放总线
和
void spi_device_release_bus(spi_device_handle_t dev);//释放总线
来让主设备一直占用总线,可以在两个API调用期间间断地发送数据
可以使用
esp_err_t spi_bus_remove_device(spi_device_handle_t handle)
//将设备从SPI总线上移除
和
esp_err_t spi_bus_free(spi_host_device_t host)
//释放总线
来解除目标设备对SPI总线的占用,并释放系统资源
传输速率
SPI传输速率与以下因素有关:
- 传输间隔
- SPI时钟频率(主要因素)
- SPI控制函数与回调函数的执行延迟
典型的传输间隔如下所示:
| 典型传输时间 (us) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 中断模式 | 轮询模式 | |
| 使用DMA | 24 | 8 |
| 不使用DMA | 22 | 7 |
SPI Slave
SPI从设备驱动负责处理ESP32作为从设备的情况
SPI2和SPI3也能独立地作为从设备使用,支持全双工四线SPI、半双工DSPI、半双工QSPI,支持收发64字节数据和使能DMA传输
从模式的基本配置
使用spi_slave_interface_config_t结构体来设置SPI从模式的物理接口
使用spi_slave_transaction_t结构体设置从模式下的数据格式和数据缓冲区大小等
使用spi_transaction_t结构体配置单独收取/单独发送等特殊情况的传输数据格式
结构体原型如下
//配置
spi_device_interface_config_t devcfg={
.command_bits=0,
.address_bits=0,
.dummy_bits=0,
.clock_speed_hz=5000000,
.duty_cycle_pos=128, //50% duty cycle
.mode=0,
.spics_io_num=GPIO_CS,
.cs_ena_posttrans=3,
//Keep the CS low 3 cycles after transaction, to stop slave from missing the last bit when CS has less propagation delay than CLK
.queue_size=3
};
//用于配置SPI从机接口的spi_slave_interface_config_t结构体
spi_slave_interface_config_t slvcfg={
.mode,//SPI模式,配置为0-3
.spics_io_num,//片选信号线复用IO
.queue_size,//传输队列大小,设置同时最多有多少挂起的传输
.flags,//接口属性,使用位或运算符|连接各属性参数
.post_setup_cb,//SPI寄存器加载新数据时调用的回调函数
.post_trans_cb//传输完成回调函数
};
//描述一次SPI传输的结构体
spi_slave_transaction_t
{
.length,//总数据长度
.trans_len,//传输数据长度
.tx_buffer,//数据发送缓冲区指针
.rx_buffer,//数据接收缓冲区指针
.user//用户定义变量,一般用于存储本次传输的ID
}
//注意:上述长度的单位是比特
//用于配置SPI总线的spi_bus_config_t结构体
spi_bus_config_t buscfg={
.mosi_io_num=GPIO_MOSI,
.miso_io_num=GPIO_MISO,
.sclk_io_num=GPIO_SCLK,
.quadwp_io_num = -1,
.quadhd_io_num = -1,
};
//未使用的参数应设置为-1
如果spi_slave_interface_config_t::rx_buffer=NULL,则跳过读取数据段;如果spi_slave_interface_config_t::tx_buffer=NULL,则跳过写入数据段
传输开始前,应当配置好一个或以上的spi_slave_transaction_t结构体
注意:如果传输的数据大于32字节,需要使能DMA通道1或通道2,如果不使用DMA,应将dma_chan参数设置为0
传输相关API与使用步骤
//所有形式的SPI设备都需要调用这个API来进行初始化
esp_err_t spi_bus_initialize(spi_host_device_t host,//SPI设备号
const spi_bus_config_t *bus_config,//总线GPIO设置
int dma_chan)//使用的DMA通道
//SPI从设备初始化
esp_err_t spi_slave_initialize(spi_host_device_t host,//SPI设备号
const spi_bus_config_t *bus_config,//SPI总线设置
const spi_slave_interface_config_t *slave_config,//SPI接口设置
int dma_chan)//使用的DMA通道
//卸载SPI从设备驱动
esp_err_t spi_slave_free(spi_host_device_t host)//SPI设备号
//发起SPI从设备队列传输数据
esp_err_t spi_slave_queue_trans(spi_host_device_t host,//SPI设备号
const spi_slave_transaction_t *trans_desc,//传输的数据
TickType_t ticks_to_wait)//等待时间
/* 将一条SPI消息挂到SPI传输队列,并等待发送 */
//获取队列传输数据的结果
esp_err_t spi_slave_get_trans_result(spi_host_device_t host,//SPI设备号
spi_slave_transaction_t **trans_desc,//传输数据指针
TickType_t ticks_to_wait)//等待时间
/* 在使用spi_slave_queue_trans到使用spi_slave_get_trans_result之间,CPU会轮询传输结果,使用该API获取结果 */
//发起一次SPI传输
esp_err_t spi_slave_transmit(spi_host_device_t host,//SPI设备号
spi_slave_transaction_t *trans_desc,//传输的数据
TickType_t ticks_to_wait)//等待时间
//该函数与连用spi_slave_queue_trans和spi_slave_get_trans_result效果相同
- 使用spi_bus_config_t结构体和spi_bus_initialize()函数创建SPI总线
- 使用spi_device_interface_config_t结构体和spi_bus_add_device()函数向SPI总线上添加新设备
- 使用spi_slave_queue_trans、spi_slave_get_trans_result、spi_slave_transmit三个API进行传输数据
- 如果需要卸载SPI从设备驱动,使用spi_slave_free
注意:如果使用了DMA,需要保证使用pvPortMallocCaps(size, MALLOC_CAP_DMA)为缓冲区开辟内存,这样可以保障DMA能够访问到这些缓冲区
DMA和初始化API的配置与主模式类似,驱动函数的使用方法也类似,在此不做介绍,关注API即可
目前存在的DMA缺陷(摘自官网)
Restrictions and Known Issues
If DMA is enabled, the rx buffer should be word-aligned (starting from a 32-bit boundary and having a length of multiples of 4 bytes). Otherwise, DMA may write incorrectly or not in a boundary aligned manner. The driver reports an error if this condition is not satisfied.
Also, a Host should write lengths that are multiples of 4 bytes. The data with inappropriate lengths will be discarded.
Furthermore, DMA requires SPI modes 1 and 3. For SPI modes 0 and 2, the MISO signal has to be launched half a clock cycle earlier to meet the timing. The new timing is as follows:
If DMA is enabled, a Device’s launch edge is half of an SPI clock cycle ahead of the normal time, shifting to the Master’s actual latch edge. In this case, if the GPIO matrix is bypassed, the hold time for data sampling is 68.75 ns and no longer a half of an SPI clock cycle. If the GPIO matrix is used, the hold time will increase to 93.75 ns. The Host should sample the data immediately at the latch edge or communicate in SPI modes 1 or 3. If your Host cannot meet these timing requirements, initialize your Device without DMA.
- 启用DMA时应当将收发缓存设定为字对齐模式(是4字节的倍数)
- 从机模式的DMA需要主机时钟的保持时间足够长才能工作,如果主机无法满足只能放弃使用DMA
SPI使用例
参考esp-idf/example/peripheral/spi/部分示例
SPI FLASH组件
以下内容部分摘自官网原文,黑体部分为强调和个人理解
SPI Flash 组件提供外部 flash 数据读取、写入、擦除和内存映射相关的 API 函数,同时也提供了更高层级的、面向分区的 API 函数(定义在分区表部分)
注意:ESP-IDF V4.0后饿FLASH API不再是原子的,如果 flash 操作地址有重叠,且写操作与读操作同时执行,读操作可能会返回一部分写入之前的数据,返回一部分写入之后的数据
FLASH设备的使用
初始化
设置方式类似基本的SPI API调用,具体步骤如下
- 调用spi_bus_initialize()初始化SPI总线
- 调用spi_bus_add_flash_device()将片外FLASH作为从设备挂载到SPI总线,并分配内存、填充esp_flash_t结构体、初始化CS信号线
- 调用esp_flash_init()与芯片进行通信(注意:目前多个FLASH芯片可以连接到同意总线,但尚不支持在同一个SPI总线上使用esp_flash_*和spi_device_*设备)
访问FLASH
一般来说应尽量避免对主SPI flash芯片直接使用原始SPI flash函数,如需对主SPI flash芯片进行操作应使用分区表API
使用以下API访问片外SPI FLASH
esp_err_t esp_flash_read(esp_flash_t *chip,//指向已识别FLASH对象地指针
void *buffer,//读取数据缓冲区指针,当保存在RAM且字对齐时具有更好的使用性能
uint32_t address,//待读取数据的FLASH地址,必须小于chip->size
uint32_t length);//待读取的数据长度
//将数据无对齐地从flash读取到RAM
//chip需要用esp_flash_init()初始化过才能使用
esp_err_t esp_flash_write(esp_flash_t *chip,//指向已识别FLASH对象地指针
const void *buffer,//写入数据缓冲区指针
uint32_t address,//待写入数据的FLASH地址
uint32_t length);//待写入的数据长度
//将数据无对齐地从RAM写入到 flash
esp_err_t esp_flash_write_encrypted(esp_flash_t *chip,//指向已识别FLASH对象地指针
uint32_t address,//待写入数据的FLASH地址
const void *buffer,//写入数据缓冲区指针
uint32_t length);//待写入的数据长度
//使用片上硬件FLASH加密外设,加密写入数据
//注意:地址和数据长度都应该是16位对齐
esp_err_t esp_flash_read_encrypted(esp_flash_t *chip,//指向已识别FLASH对象地指针
uint32_t address,//待读取数据的FLASH地址
void *out_buffer,//读取数据缓冲区指针
uint32_t length);//待读取的数据长度
//使用片上硬件FLASH加密外设,加密读取数据
esp_err_t esp_flash_erase_region(esp_flash_t *chip,
uint32_t start,//起始地址
uint32_t len);//擦除长度
//擦除 flash 中指定区域的数据
//注意:擦除的地址一定要和扇区对齐!!!
esp_err_t esp_flash_erase_chip(esp_flash_t *chip);//擦除整个 flash
esp_err_t esp_flash_get_size(esp_flash_t *chip,
uint32_t *out_size);
//根据FLASH ID检测FLASH容量(以字节为单位)
FLASH容量存储在引导程序映像头不烧录偏移量为0x1000的一个字段
默认情况下烧录引导程序时,esptool会自动检测SPI FLASH容量并使用正确容量更新引导程序的头部;但是也可以设置CONFIG_ESPTOOLPY_FLASHSIZE生成固定FLASH容量
struct esp_flash_t//描述片外FLASH的结构体,应当使用esp_flash_init()进行初始化
{
spi_flash_host_driver_t *host,//SPI驱动结构体句柄
const spi_flash_chip_t *chip_drv,//FLASH驱动“适配”结构体
const esp_flash_os_functions_t *os_func,
//RTOS钩子函数,使用esp_flash_init_os_functions()设置
os_func_data,
//RTOS钩子函数的参数
esp_flash_io_mode_t read_mode,//配置FLASH读取模式
uint32_t size,//FLASH容量,如果设置为0则会在初始化期间检测
uint32_t chip_id//检测FLASH ID
}
//SPI驱动结构体,配置主机驱动和上下文
//使用了c面向对象的方式,将方法(或者说是成员函数)用函数指针封装在结构体对象
//上面提到的那些API基本都被归纳进了这个结构体
struct spi_flash_host_driver_t
{
void *driver_data,//驱动数据
esp_err_t (*dev_config)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver),//设备驱动寄存器设置方法
esp_err_t (*common_command)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver, spi_flash_trans_t *t),
//用户定义传输指令方法
esp_err_t (*read_id)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver, uint32_t *id),//读取FLASH ID的方法
void (*erase_chip)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver),//全片擦除方法
void (*erase_sector)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver, uint32_t start_address),//扇区擦除方法
void (*erase_block)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver, uint32_t start_address),//块擦除方法
esp_err_t (*read_status)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver, uint8_t *out_sr),//读取FLASH状态方法
esp_err_t (*set_write_protect)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver, bool wp),//关闭写保护方法
void (*program_page)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver,
const void *buffer,
uint32_t address,
uint32_t length),
//按页写入FLASH并检查最大写入字节数方法
bool (*supports_direct_write)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver, const void *p),
//检查写入中是否需要申请新的页方法
bool (*supports_direct_read)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver, const void *p),
//检查读取中是否需要申请新的页方法
int max_write_bytes,//每页的最大写入字节数
esp_err_t (*read)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver,
void *buffer,
uint32_t address,
uint32_t read_len)
//从FLASH中读取数据并检查最大读取字节数方法
int max_read_bytes,//最大读取字节数
bool (*host_idle)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver),//检查SPI主机是否空闲方法
esp_err_t (*configure_host_io_mode)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver,
uint32_t command,
uint32_t addr_bitlen,
int dummy_bitlen_base,
esp_flash_io_mode_t io_mode),
//设置主机工作在不同的读取模式,响应补偿时间、设置IO模式方法
void (*poll_cmd_done)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver),//使硬件保持轮询直到操作完毕方法
esp_err_t (*flush_cache)(spi_flash_host_driver_t *driver,
uint32_t addr,
uint32_t size)
//清空主机(如SPI1)所用的缓存区方法
}
初始化外部FLASH的示例如下:
static esp_flash_t* example_init_ext_flash(void)
{
const spi_bus_config_t bus_config = {
.mosi_io_num = VSPI_IOMUX_PIN_NUM_MOSI,
.miso_io_num = VSPI_IOMUX_PIN_NUM_MISO,
.sclk_io_num = VSPI_IOMUX_PIN_NUM_CLK,
.quadwp_io_num = -1,
.quadhd_io_num = -1,
};
const esp_flash_spi_device_config_t device_config = {
.host_id = VSPI_HOST,
.cs_id = 0,
.cs_io_num = VSPI_IOMUX_PIN_NUM_CS,
.io_mode = SPI_FLASH_DIO,
.speed = ESP_FLASH_40MHZ
};
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "初始化外部SPI FLASH");
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "引脚设定:");
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "MOSI: %2d MISO: %2d SCLK: %2d CS: %2d",
bus_config.mosi_io_num, bus_config.miso_io_num,
bus_config.sclk_io_num, device_config.cs_io_num
);
//初始化SPI总线
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(spi_bus_initialize(VSPI_HOST, &bus_config, 1));
//将FLASH设备添加到SPI总线
esp_flash_t* ext_flash;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(spi_bus_add_flash_device(&ext_flash, &device_config));
//连接、检查FLASH并进行初始化
esp_err_t err = esp_flash_init(ext_flash);
if (err != ESP_OK)
{
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "连接外部FLASH失败: %s (0x%x)", esp_err_to_name(err), err);
return NULL;
}
//执行 输出ID和大小 任务
uint32_t id;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_flash_read_id(ext_flash, &id));
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Initialized external Flash, size=%d KB, ID=0x%x", ext_flash->size / 1024, id);
return ext_flash;
}