TDengine 资深研发整理:基于 SpringBoot 多语言实现 API 返回消息国际化
作为一款在 Java 开发社区中广受欢迎的技术框架,SpringBoot 在开发者和企业的具体实践中应用广泛。具体来说,它是一个用于构建基于 Java 的 Web 应用程序和微服务的框架,通过简化开发流程、提供约定大于配置的原则以及集成大量常用库和组件,SpringBoot 能够帮助开发者更快速、更高效地构建应用程序。
为了帮助开发者更好地进行 SpringBoot 的开发,避免开发盲点,我们将 TDengine 资深研发所做的内部分享——《SpringBoot 多语言支持方案》进行了相关整理,给到有需要的开发者参考。
添加依赖
首先,SpringBoot 作为一个强大的 Java 开发脚手架工具框架,已经提供了多语言定义、解析底层工具,我们只需要在项目依赖中引入 spring-boot-starter 和 spring-boot-autoconfigure 两个包。
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-autoconfigure
分析 spring-boot-autoconfigure 的源码我们可以看到,在 MessageSourceAutoConfiguration 类中,默认已经自动装配了 MessageSource 对象。
添加多语言 message 配置文件
在 IDEA 中我们只需要在 resources 资源包上右键:新建–>资源包,在弹出窗口填写资源包名如:messages 选择区域设置,默认的有 en、zh_CN、zh_TC 选项。
添加完即可在 resources 包内看到绑定的多语言文件。
注意:在配置文件里查看编辑中文,需要在 IDEA 中修改 message 配置文件。
在配置文件中我们添加 message ,格式为:{code}={message}
METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED=Http method is not supported!
INTERFACE_NOT_FOUND=Interface does not exist!
UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE=Not supported MediaType!
ILLEGAL_REQUEST=Illegal request!
SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE=Server resources are unavailable!
SERVER_ERROR=Sorry, an internal server error occurred, please try again later.
INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR=Internal Server Error.
field.validity.check.failed=Field validity check failed!
bill.account.not-found=bill account not found!
grant.role-group.failed=grant role to group failed!
grant.role-user.failed=grant role to user failed!
add.user-group.failed=add user to group failed!
del.user-group.failed=delete user from group failed!
create.org.failed=create organization failed!
cannot.visit.org=you cannot visit this organization!
wrong.value.parameter=wrong value for parameter!
role.not-found=role not found!
role.update.failed=update role failed!
role.delete.failed=can not delete role!
account.in.arrears=The account is in arrears. Please recharge and try again!如何使用公共 jar 包内 i18n 资源文件
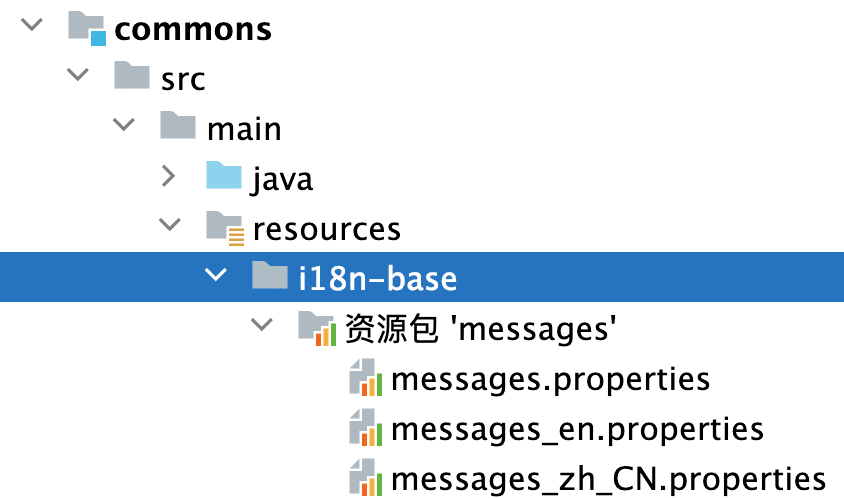
- 创建公共资源包 i18n 目录:在 commons 包里添加一个文件夹 i18n-base,这里可以通过一个文件夹避免资源包的覆盖。
- 依赖 commons 包的模块,在 yaml 配置文件中添加路径。
spring:
messages:
basename: i18n-base/messages,messages以上,我们的多语言框架支持配置、初始化已经完成,接下来就是如何在业务中使用了。
在模块中使用多语言消息
首先我们来看一个典型的 API 服务请求响应流程。客户端发出一个接口请求,会经过多个过滤器进行身份认证、API 接口鉴权认证、权限识别,验证通过后即可进入业务逻辑,最后通过接口返回。返回结果有两种:
- 过滤器认证失败直接返回包装结果 BaseApiResponse
- 认证通过进入业务逻辑,这里又包含两种情况:
- 业务异常,统一通过 GlobalExceptionHandler 拦截,最后由 ResponseAdvice 处理最终返回结果;
- 无异常,返回业务数据由 ResponseAdvice 处理最终返回结果。
一般来说,外层可以通过 ErrorHandler 捕获整个流程的异常,包括拦截器、框架层的调用出现的异常,最终由 ResponseAdvice 统一处理并最终返回结果。
整个流程如下图:
基于这个业务处理流程我们来封装异常信息国际化的逻辑,如下:
定义多语言 message 获取 LocaleMessageProvider
- 定义接口
public interface LocaleMessageProvider {
String get(String msgCode, Object... args);
}- 配置实现类
@Bean
public LocaleMessageProvider localeMessageProvider(MessageSource messageSource){
return (msgCode, args) -> {
Locale locale = LocaleContextHolder.getLocale();
return messageSource.getMessage(msgCode,args,locale);
};
}- 在返回结构体中使用 LocaleMessageProvider 获取 message;在 ResponseBodyAdvice 可以为每个 Response 对象设置 messageProvider。
BaseApiResponse.class
private LocaleMessageProvider messageProvider;
public String getmsg() {
String localeMsg = msg;
if (messageProvider != null){
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.msgCode)){
try {
localeMsg = messageProvider.get(this.msgCode, getArgs());
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(localeMsg)){
localeMsg = this.msgCode;
}
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(localeMsg)){
localeMsg = StringUtils.hasText(this.msgCode) ? this.msgCode : localeMsg;
}
return localeMsg;
}
public class ResponseAdvice implements ResponseBodyAdvice{
@Override
public Object beforeBodyWrite(Object body, @NotNull MethodParameter returnType,
@NotNull MediaType selectedContentType, @NotNull Class selectedConverterType,
@NotNull ServerHttpRequest request,
@NotNull ServerHttpResponse response) {
int code = ServiceInfoEnum.valueOf(key).getServiceCode() * 1000 + 200;
if (body instanceof BaseApiResponse) {
BaseApiResponse res = (BaseApiResponse) body;
res.setMessageProvider(messageProvider);
}
}
}在这里提出一个问题,SpringBoot 框架是如何处理语言设置的?在我们定义的 LocaleMessageProvider 里可以使用 LocaleContextHolder.getLocale() 来获取 Locale。
接下来我们继续遵循 LocaleContextHolder 的方法,可以先尝试从内部 localeContext 对象进行获取,获取不到的话则取 Locale 的缺省值。
org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder.java
public static Locale getLocale() {
return getLocale(getLocaleContext());
}
public static Locale getLocale(@Nullable LocaleContext localeContext) {
if (localeContext != null) {
Locale locale = localeContext.getLocale();
if (locale != null) {
return locale;
}
}
return (defaultLocale != null ? defaultLocale : Locale.getDefault());
}在 Locale 类中,我们看到缺省的 locale 最终从系统变量 user.language 获取,缺省是 en。
java.util.Locale.java
private static volatile Locale defaultLocale = initDefault();
private static Locale initDefault() {
String language, region, script, country, variant;
Properties props = GetPropertyAction.privilegedGetProperties();
language = props.getProperty("user.language", "en");
......//省略代码
}接下来我们看下 LocaleContextHolder 中的 Locale 是何时设置的,实际就是在 request 请求过滤器基类 RequestContextFilter 里,通过 request.getLocale() 获取到 request 的 locale,然后使用 LocaleContextHolder 设置到 LocaleContext 中。
RequestContextFilter.java
protected void doFilterInternal(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = new ServletRequestAttributes(request, response);
initContextHolders(request, attributes);
......//省略代码
}
private void initContextHolders(HttpServletRequest request, ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes) {
LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(request.getLocale(), this.threadContextInheritable);
......//省略代码
}最终我们看到在 Request 对象里,成功获取了“accept-lunguage” 请求。
org.apache.catalina.connector.Request.java
public Locale getLocale() {
if (!localesParsed) {
parseLocales();
}
if (locales.size() > 0) {
return locales.get(0);
}
return defaultLocale;
}
protected void parseLocales() {
......//省略代码
TreeMap> locales = new TreeMap<>();
Enumeration values = getHeaders("accept-language");
while (values.hasMoreElements()) {
String value = values.nextElement();
parseLocalesHeader(value, locales);
}
for (ArrayList list : locales.values()) {
for (Locale locale : list) {
addLocale(locale);
}
}
} 添加一个多语言消息
- 如果是异常消息,定义异常消息编码在代码中 exception 需使用 msgCode,如果是业务包装类型,那 BaseApiResponse 消息也要使用 msgCode
- 在 message 配置文件中添加对应的 {code}={message}
至此,我们的异常国际化配置就完成了,在客户端我们只需要在请求里添加一个 header:Accept-Language=zh-CN,就可以验证返回的结果。例如登录出错客户端接收到的信息为:
{
"code": 500,
"message": "用户名或者密码错误,请重新输入。",
"data":{}
}结语
以上就是基于 SpringBoot 多语言支持方案的完整分享内容,现在你可以操作体验了,希望本篇文章能带给你一些帮助。更多示例可参考:
- 异常中使用 messageCode
if (pricePlan.getClusterNum() >= 0 && appNum >= pricePlan.getClusterNum()) {
throw new CommonsException(HttpResponseStatus.PAYMENT_REQUIRED.code(),
"price.plan.limit.instance.number",
"instance number is over limit!");
}- 国际化文件中添加 message
#messages_en.properties
price.plan.limit.instance.number=instance number is over limit
#messages_zh_CN.properties
price.plan.limit.instance.number=实例数量超过限制如果你在实操过程中还遇到了其他技术问题,或者正面临着时序数据的处理难题,也可以添加小T vx:tdengine,和 TDengine 的技术研发人员进行直接沟通。
关于 TDengine
TDengine 核心是一款高性能、集群开源、云原生的时序数据库(Time Series Database,TSDB),专为物联网、工业互联网、电力、IT 运维等场景设计并优化,具有极强的弹性伸缩能力。同时它还带有内建的缓存、流式计算、数据订阅等系统功能,能大幅减少系统设计的复杂度,降低研发和运营成本,是一个高性能、分布式的物联网、工业大数据平台。当前 TDengine 主要提供两大版本,分别是支持私有化部署的 TDengine Enterprise 以及全托管的物联网、工业互联网云服务平台 TDengine Cloud,两者在开源时序数据库 TDengine OSS 的功能基础上有更多加强,用户可根据自身业务体量和需求进行版本选择。
了解更多 TDengine Database的具体细节,可在GitHub上查看相关源代码。