ceph cluster client(RBD)
- 前期准备
- 关闭防火墙、selinux,配置hosts文件,配置ceph.repo,配置NTP,创建用户和SSL免密登陆。
[root@ ceph1~]#systemctl stop firewalld
[root@ ceph1]# setenforce 0
[root@ ceph1~]# cat /etc/selinux/config
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled #关掉selinux
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
[root@ ceph1~]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/ceph.repo
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aishangwei/ceph-demo/master/ceph-deploy/ceph.repo
[root@ceph1 ~]# yum -y install ntpdate ntp
[root@ceph1 ~]# cat /etc/ntp.conf
server ntp1.aliyun.com iburst
[root@ceph1 ~]# systemctl restart ntpd
[root@ceph1 ~]# useradd ceph-admin
[root@ceph1 ~]# echo "ceph-admin" | passwd --stdin ceph-admin
Changing password for user ceph-admin.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@ceph1 ~]# echo "ceph-admin ALL = (root) NOPASSWD:ALL" | tee /etc/sudoers.d/ceph-admin
ceph-admin ALL = (root) NOPASSWD:ALL
[root@ceph1 ~]# cat /etc/sudoers.d/ceph-admin
ceph-admin ALL = (root) NOPASSWD:ALL
[root@ceph1 ~]# chmod 0440 /etc/sudoers.d/ceph-admin
[root@ceph1 ~]# cat /etc/hosts
192.168.48.132 ceph1
192.168.48.133 ceph2
192.168.48.134 ceph3
[root@ceph1 ~]#
[root@ceph1 ~]# sed -i 's/Default requiretty/#Default requiretty/' /etc/sudoers #配置sudo不需要tty
官方安装方法:http://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/start/quick-start-preflight/
注:以上在另外两台机上配置,步骤一样
2)使用ceph-deploy部署群集
[root@ceph1 ~]# su - ceph-admin
[ceph-admin@ceph1 ~]$ ssh-keygen
[ceph-admin@ceph1 ~]$ ssh-copy-id ceph-admin@ceph1
[ceph-admin@ceph1 ~]$ ssh-copy-id ceph-admin@ceph2
[ceph-admin@ceph1 ~]$ ssh-copy-id ceph-admin@ceph3
[ceph-admin@ceph1 sudoers.d]$ sudo yum install -y ceph-deploy python-pip
[ceph-admin@ceph1 ~]$ sudo mkdir my-cluster
[ceph-admin@ceph1 ~]$ sudo cd my-cluster/
[ceph-admin@ceph1 ~]$ ceph-deploy new ceph1 ceph2 ceph3 #部署节点
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ ls
ceph.conf ceph-deploy-ceph.log ceph.mon.keyring
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ cat ceph.conf #添加两行
[global]
fsid = 37e48ca8-8b87-40eb-9f64-cfdc0b659cf2
mon_initial_members = ceph1, ceph2, ceph3
mon_host = 192.168.48.132,192.168.48.133,192.168.48.134
auth_cluster_required = cephx
auth_service_required = cephx
auth_client_required = cephx
public network = 192.168.48.0/24
cluster network = 192.168.48.0/24
#安装ceph包、替代ceph-deploy install node1 node2,不过下面的命令需要在ceph2和ceph3上做
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ sudo yum -y install ceph ceph-radosgw
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ sudo yum -y install ceph ceph-radosgw
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ sudo yum -y install ceph ceph-radosgw
配置初始monitor(s)、并收集所有秘钥:
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ ceph-deploy mon create-initial
把配置信息拷贝到各节点
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ ceph-deploy admin ceph1 ceph2 ceph3
配置osd
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ for dev in /dev/sdb /dev/sdc /dev/sdd
> do
> ceph-deploy disk zap ceph1 $dev
> ceph-deploy osd create ceph1 --data $dev
> ceph-deploy disk zap ceph2 $dev
> ceph-deploy osd create ceph2 --data $dev
> ceph-deploy disk zap ceph3 $dev
> ceph-deploy osd create ceph3 --data $dev
> done
部署mgr,L版以后才需要部署
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ ceph-deploy mgr create ceph1 ceph3 ceph3
ceph-deploy gatherkeys ceph01
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ ceph mgr module enable dashboard
注如果报错,做如下配置
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ sudo chown -R ceph-admin /etc/ceph
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ ll /etc/ceph/
total 12
-rw------- 1 ceph-admin root 63 Dec 15 11:05 ceph.client.admin.keyring
-rw-r--r-- 1 ceph-admin root 308 Dec 15 11:15 ceph.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 ceph-admin root 92 Nov 27 04:20 rbdmap
-rw------- 1 ceph-admin root 0 Dec 15 10:49 tmpqjm9oQ
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ ceph mgr module enable dashboard
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ sudo netstat -tupln | grep 7000
tcp6 0 0 :::7000 :::* LISTEN 8298/ceph-mgr
在浏览器上访问http://192.168.48.132:7000/ #图形化界面就0k
![]()
这是监听的节点
到这集群部署完成,好开心啊
3)安装ceph块存储客户端
Ceph块设备,以前称为RADOS块设备,为客户机提供可靠的、分布式的和高性能的块存储磁盘。RADOS块设备利用 librbd库并以顺序的形式在Ceph集群中的多个osd上存储数据块。RBD是由Ceph的RADOS层支持的,因此每个块设备 都分布在多个Ceph节点上,提供了高性能和优异的可靠性。RBD有Linux内核的本地支持,这意味着RBD驱动程序从 过去几年就与Linux内核集成得很好。除了可靠性和性能之外,RBD还提供了企业特性,例如完整和增量快照、瘦配 置、写时复制克隆、动态调整大小等等。RBD还支持内存缓存,这大大提高了其性能:
![]()
任何普通的Linux主机(RHEL或基于debian的)都可以充当Ceph客户机。客户端通过网络与Ceph存储集群交互以存储或检 索用户数据。Ceph RBD支持已经添加到Linux主线内核中,从2.6.34和以后的版本开始。
[ceph-admin@ceph1 ceph]$ ll /etc/ceph/*
-rw------- 1 ceph-admin root 63 Dec 15 11:05 /etc/ceph/ceph.client.admin.keyring #这是root的秘钥
-rw-r--r-- 1 ceph-admin root 308 Dec 15 11:15 /etc/ceph/ceph.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 ceph-admin root 92 Nov 27 04:20 /etc/ceph/rbdmap
-rw------- 1 ceph-admin root 0 Dec 15 10:49 /etc/ceph/tmpqjm9oQ
创建ceph块client用户名和认知秘钥
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ ceph auth get-or-create client.rbd mon 'allow r' osd 'allow class-read object_prifix rbd_children, allow rwx POOL=rbd' | tee ./ceph.client.rbd.keyring
[client.rbd]
key = AQDmeBRcPXpMNBAAlSJxwDM9PbcH2UMgx2cAYQ==
或者
ceph auth get-or-create client.rbd mon ‘allow r’ osd ‘allow class-read object_prefix rbd_children, allow rwx pool=rbd’ |tee ./ceph.client.rbd.keyring
注:client.rbd为客户端名 mon之后的全为授权配置
#客户端配置解析
打开从新一个client 注:要能域名解析及配置hosts文件
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$scp ceph.client.rbd.keyring /etc/ceph/ceph.conf client:/etc/ceph/ceph.client.rbd.keyring
检查是否符合块设备环境要求
[root@client ceph]# uname -r
3.10.0-514.el7.x86_64
[root@client ceph]# modprobe rbd
[root@client ceph]# echo $?
0
[root@client ceph]#
安装ceph客户端
[root@client ceph]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/ceph.repo https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aishangwei/ceph-demo/master/ceph-deploy/ceph.repo
[root@client ~]# yum -y install ceph
[root@client ~]# cat /etc/ceph/ceph.client.rbd.keyring
[root@client ~]# ceph -s --name client.rbd
cluster:
id: 37e48ca8-8b87-40eb-9f64-cfdc0b659cf2
health: HEALTH_OK
services:
mon: 3 daemons, quorum ceph1,ceph2,ceph3
mgr: ceph3(active), standbys: ceph1
osd: 9 osds: 9 up, 9 in
data:
pools: 0 pools, 0 pgs
objects: 0 objects, 0B
usage: 9.05GiB used, 261GiB / 270GiB avail
pgs:
[root@client ~]#
客户端创建块设备及映射
*创建块设备
默认创建块设备,会直接创建在 rbd 池中,但使用 deploy 安装后,该rbd池并没有创建。
# 创建池和块
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ ceph osd lspools # 查看集群存储池
[ceph-admin@ceph1 my-cluster]$ ceph osd pool create rbd 512 # 512为 place group 数量,由于我们后续测试,也需要更多的pg,所以这里设置为50
在这里也能看到
![]()
确定 pg_num 取值是强制性的,因为不能自动计算。下面是几个常用的值:
• 少于 5 个 OSD 时可把 pg_num 设置为 128
• OSD 数量在 5 到 10 个时,可把 pg_num 设置为 512
• OSD 数量在 10 到 50 个时,可把 pg_num 设置为 4096
• OSD 数量大于 50 时,你得理解权衡方法、以及如何自己计算 pg_num 取值
# 客户端创建 块设备
[root@client ~]# rbd create rbd1 --size 10240 --name client.rbd
2 RBD配置使用
2.1 RBD挂载到本地操作系统
1)创建rbd使用的pool
# #pg_num 32 pgp_num 32
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo ceph osd pool create p_rbd 32 32
# 查看详细信息
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo ceph osd pool ls detail
# 查看状态
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo ceph pg stat
2) 创建一个块设备(10G)
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo rbd create --size 10240 image001 -p p_rbd
3) 查看块设备
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo rbd ls -p p_rbd
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo rbd info image001 -p p_rbd
# #从底层查看创建rbd后所创建的文件
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo rados -p p_rbd ls --all
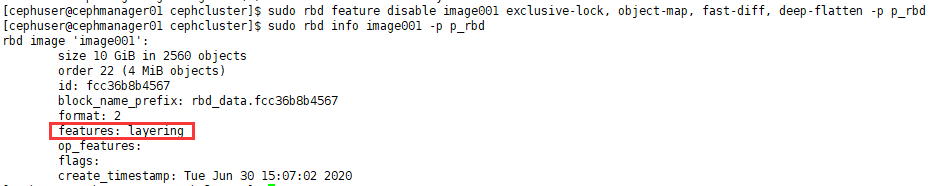
4) 禁用当前系统内核不支持的feature
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo rbd feature disable image001 exclusive-lock, object-map, fast-diff, deep-flatten -p p_rbd
# 确认features: layering
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo rbd info image001 -p p_rbd
5) 将块设备映射到系统内核
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo rbd map image001 -p p_rbd
# map成功后,会出现/dev/rbd0
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ lsblk
6) 格式化块设备镜像
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo mkfs.xfs /dev/rbd0
7) mount到本地
[root@cephmanager01 ~]# mount /dev/rbd0 /mnt
# 查看mount情况
[root@cephmanager01 ~]# df -h
# 写入数据
[root@cephmanager01 ~]# cd /mnt && echo 'hello world' > aa.txt
# 查看底层的存储组织方式
[root@cephmanager01 mnt]# rados -p p_rbd ls --all
#查看磁盘情况
[root@cephmanager01 mnt]# ceph df
8) 查看相关映射情况
[root@cephmanager01 mnt]# rbd showmapped
2.2 RBD挂载到客户端操作系统
服务器端:cephmanager01
客户端:192.168.10.57 CentOS7.5 64bit
2.2.1 客户端环境准备
确保内核高于2.6
确保加载了rbd模块
安装ceph-common
[客户端验证]
# 内核版本高于2.6
[root@localhost ~]# uname -r
# 加载rbd模块
[root@localhost ~]# modprobe rbd
# 取人加载rbd模块成功,返回0为成功
[root@localhost ~]# echo $?
# 按爪给你ceph-common
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y ceph-common
2.2.2 服务器配置
1)创建ceph块客户端认证
# 切换到cephuser的cluster目录
[root@cephmanager01 ~]# su - cephuser
[cephuser@cephmanager01 ~]$ cd cephcluster/
# 创建了对pool名为p_rbd的认证权限
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo ceph auth get-or-create client.rbd mon 'allow r' osd 'allow class-read object_prefix rbd_children, allow rwx pool=p_rbd' |tee ./ceph.client.rbd.keyring
# 查看权限
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo ceph auth get client.rbd
# 确保当前目录生产了ceph.client.rbd.keyring文件
2)拷贝配置文件到客户端并验证
# 拷贝ceph.conf和密钥文件到客户端
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo scp ceph.conf ceph.client.rbd.keyring [email protected]:/etc/ceph/
# 客户端验证,需要到客户端操作系统下执行,能返回id和服务器一样则验证成功
[root@localhost ceph]# ceph -s --name client.rbd
3)服务器端创建池
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo ceph osd lspools
# 这里借用上面创建的p_rbd
2.2.3 客户端配置
客户端执行
1)创建一个容量为10G的rbd块设备
[root@localhost ceph]# rbd create image002 --size 10240 --name client.rbd -p p_rbd
# 客户端查看查看image002块设
[root@localhost ceph]# rbd ls --name client.rbd -p p_rbd
# 查看image002块设备信息
[root@localhost ceph]# rbd --image image002 info --name client.rbd -p p_rbd
2)禁用当前系统内核不支持的feature
依然要先禁用当前系统内核不支持的feature,否则映射的时候会报错
[root@localhost ceph]# rbd feature disable image002 exclusive-lock object-map fast-diff deep-flatten --name client.rbd -p p_rbd
• layering: 分层支持
• exclusive-lock: 排它锁定支持对
• object-map: 对象映射支持(需要排它锁定(exclusive-lock))
• deep-flatten: 快照平支持(snapshot flatten support)
• fast-diff: 在client-node1上使用krbd(内核rbd)客户机进行快速diff计算(需要对象映射),我们将无法在CentOS内核3.10上映射块设备映像,因为该内核不支持对象映射(object-map)、深平(deep-flatten)和快速diff(fast-diff)(在内核4.9中引入了支持)。为了解决这个问题,我们将禁用不支持的特性,有几个选项可以做到这一点:
1)动态禁用
rbd feature disable image002 exclusive-lock object-map deep-flatten fast-diff --name client.rbd
2) 创建RBD镜像时,只启用 分层特性。
rbd create image003 --size 10240 --image-feature layering --name client.rbd
3)ceph 配置文件中禁用
rbd_default_features = 1
3) 客户端映射块设备
# 对image002进行映射
[root@localhost ceph]# rbd map --image image002 --name client.rbd -p p_rb
# 查看本机已经映射的rbd镜像
[root@localhost ceph]# rbd showmapped --name client.rbd
# 查看磁盘rbd0大小,这个时候可以看到在本地多了一个/dev/rbd0的磁盘
[root@localhost ceph]# lsblk
# 格式化rbd0
[root@localhost ceph]# mkfs.xfs /dev/rbd0
# 创建挂在目录并进行挂载
[root@localhost ceph]# mkdir /ceph_disk_rbd
[root@localhost ceph]# mount /dev/rbd0 /ceph_disk_rbd/
# 写入数据测试
[root@localhost ceph_disk_rbd]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/ceph_disk_rbd/file01 count=100 bs=1M
# 查看写入文件大小,确认是否100M
[root@localhost ceph_disk_rbd]# du -sh /ceph_disk_rbd/file0
4)配置开机自动挂载
/usr/local/bin/rbd-mount文件需要根据实际情况修改
# 如果不能连接raw.githubusercontent.com,请选择科学上网
[root@localhost ceph]# wget -O /usr/local/bin/rbd-mount https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aishangwei/ceph-demo/master/client/rbd-mount
内容如下:
#!/bin/bash
# Pool name where block device image is stored,根据实际情况修改
export poolname=rbd
# Disk image name,根据实际情况修改
export rbdimage=rbd1
# Mounted Directory,根据实际情况修改
export mountpoint=/mnt/ceph-disk1
# Image mount/unmount and pool are passed from the systemd service as arguments,根据实际情况修改
# Are we are mounting or unmounting
if [ "$1" == "m" ]; then
modprobe rbd
rbd feature disable $rbdimage object-map fast-diff deep-flatten
rbd map $rbdimage --id rbd --keyring /etc/ceph/ceph.client.rbd.keyring
mkdir -p $mountpoint
mount /dev/rbd/$poolname/$rbdimage $mountpoint
fi
if [ "$1" == "u" ]; then
umount $mountpoint
rbd unmap /dev/rbd/$poolname/$rbdimage
fi
[root@localhost ceph]# chmod +x /usr/local/bin/rbd-mount
[root@localhost ceph]# wget -O /etc/systemd/system/rbd-mount.service https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aishangwei/ceph-demo/master/client/rbd-mount.service
# 内容如下:
[Unit]
Description=RADOS block device mapping for $rbdimage in pool $poolname"
Conflicts=shutdown.target
Wants=network-online.target
After=NetworkManager-wait-online.service
[Service]
Type=oneshot
RemainAfterExit=yes
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/rbd-mount m
ExecStop=/usr/local/bin/rbd-mount u
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[root@localhost ceph]# systemctl daemon-reload
[root@localhost ceph]# systemctl enable rbd-mount.service
# 卸载手动挂载的目录,进行服务自动挂载测试
[root@localhost ceph]# umount /ceph_disk_rbd
[root@localhost ceph]# systemctl start rbd-mount.service
我环境的配置如图:
开机ceph自动map rbd块设备详细说明
1. 先下载init-rbdmap到/etc/init.d目录:
wget https://raw.github.com/ceph/ceph/a4ddf704868832e119d7949e96fe35ab1920f06a/src/init-rbdmap
-O /etc/init.d/rbdmap下载的原始文件有些错误,打开此文件:
vim /etc/init.d/rbdmap
#!/bin/bash
#chkconfig: 2345 80 60
#description: start/stop rbdmap
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: rbdmap
# Required-Start: $network
# Required-Stop: $network
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: Ceph RBD Mapping
# Description: Ceph RBD Mapping
### END INIT INFO
DESC="RBD Mapping"
RBDMAPFILE="/etc/ceph/rbdmap"
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
#. /etc/redhat-lsb/lsb_log_message,加入此行后不正长
do_map() {
if [ ! -f "$RBDMAPFILE" ]; then
log_warning_msg "$DESC : No $RBDMAPFILE found."
exit 0
fi
log_daemon_msg "Starting $DESC"
# Read /etc/rbdtab to create non-existant mapping
newrbd=
RET=0
while read DEV PARAMS; do
case "$DEV" in
""|\#*)
continue
;;
*/*)
;;
*)
DEV=rbd/$DEV
;;
esac
OIFS=$IFS
IFS=','
for PARAM in ${PARAMS[@]}; do
CMDPARAMS="$CMDPARAMS --$(echo $PARAM | tr '=' ' ')"
done
IFS=$OIFS
if [ ! -b /dev/rbd/$DEV ]; then
log_progress_msg $DEV
rbd map $DEV $CMDPARAMS
[ $? -ne "0" ] && RET=1
newrbd="yes"
fi
done < $RBDMAPFILE
log_end_msg $RET
# Mount new rbd
if [ "$newrbd" ]; then
log_action_begin_msg "Mounting all filesystems"
mount -a
log_action_end_msg $?
fi
}
do_unmap() {
log_daemon_msg "Stopping $DESC"
RET=0
# Unmap all rbd device
for DEV in /dev/rbd[0-9]*; do
log_progress_msg $DEV
# Umount before unmap
MNTDEP=$(findmnt --mtab --source $DEV --output TARGET | sed 1,1d | sort -r)
for MNT in $MNTDEP; do
umount $MNT || sleep 1 && umount -l $DEV
done
rbd unmap $DEV
[ $? -ne "0" ] && RET=1
done
log_end_msg $RET
}
case "$1" in
start)
do_map
;;
stop)
do_unmap
;;
reload)
do_map
;;
status)
rbd showmapped
;;
*)
log_success_msg "Usage: rbdmap {start|stop|reload|status}"
exit 1
;;
esac
exit 0运行会提示如下错误:
./rbdmap: line 34: log_progress_msg: command not found
./rbdmap: line 44: log_action_begin_msg: command not found
./rbdmap: line 46: log_action_end_msg: command not found解决方法是将log_*换成echo,或者直接注释掉。
然后chkconfig --add rbdmap; chkconfig rbdmap on就可以了。
有时候rbdmap服务不会自动启动,可以将rbdmap脚本中的函数拆分出来加入到/etc/init.d/ceph中:将其中的do_map加入到start)中,将do_unmap加入到stop中,将rbd showmapped加入到status)中。这样rbdmap就随ceph一起启动和停止了。
有兴趣的可以研究一下/etc/init.d/ceph脚本:
#!/bin/sh
# Start/stop ceph daemons
# chkconfig: 2345 60 80
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: ceph
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Required-Start: $remote_fs $named $network $time
# Required-Stop: $remote_fs $named $network $time
# Short-Description: Start Ceph distributed file system daemons at boot time
# Description: Enable Ceph distributed file system services.
### END INIT INFO
DESC="RBD Mapping"
RBDMAPFILE="/etc/ceph/rbdmap"
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
do_map() {
if [ ! -f "$RBDMAPFILE" ]; then
echo "$DESC : No $RBDMAPFILE found."
exit 0
fi
echo "Starting $DESC"
# Read /etc/rbdtab to create non-existant mapping
newrbd=
RET=0
while read DEV PARAMS; do
case "$DEV" in
""|\#*)
continue
;;
*/*)
;;
*)
DEV=rbd/$DEV
;;
esac
OIFS=$IFS
IFS=','
for PARAM in ${PARAMS[@]}; do
CMDPARAMS="$CMDPARAMS --$(echo $PARAM | tr '=' ' ')"
done
IFS=$OIFS
if [ ! -b /dev/rbd/$DEV ]; then
#log_progress_msg $DEV
rbd map $DEV $CMDPARAMS
[ $? -ne "0" ] && RET=1
newrbd="yes"
fi
done < $RBDMAPFILE
#echo $RET
# Mount new rbd
if [ "$newrbd" ]; then
echo "Mounting all filesystems"
mount -a
#log_action_end_msg $?
fi
}
do_unmap() {
echo "Stopping $DESC"
RET=0
# Unmap all rbd device
for DEV in /dev/rbd[0-9]*; do
#log_progress_msg $DEV
# Umount before unmap
MNTDEP=$(findmnt --mtab --source $DEV --output TARGET | sed 1,1d | sort -r)
for MNT in $MNTDEP; do
umount $MNT || sleep 1 && umount -l $DEV
done
rbd unmap $DEV
[ $? -ne "0" ] && RET=1
done
#log_end_msg $RET
}
# if we start up as ./mkcephfs, assume everything else is in the
# current directory too.
if [ `dirname $0` = "." ] && [ $PWD != "/etc/init.d" ]; then
BINDIR=.
SBINDIR=.
LIBDIR=.
ETCDIR=.
else
BINDIR=/usr/bin
SBINDIR=/usr/sbin
LIBDIR=/usr/lib64/ceph
ETCDIR=/etc/ceph
fi
usage_exit() {
echo "usage: $0 [options] {start|stop|restart|condrestart} [mon|osd|mds]..."
printf "\t-c ceph.conf\n"
printf "\t--valgrind\trun via valgrind\n"
printf "\t--hostname [hostname]\toverride hostname lookup\n"
exit
}
# behave if we are not completely installed (e.g., Debian "removed,
# config remains" state)
test -f $LIBDIR/ceph_common.sh || exit 0
. $LIBDIR/ceph_common.sh
EXIT_STATUS=0
# detect systemd
SYSTEMD=0
grep -qs systemd /proc/1/comm && SYSTEMD=1
signal_daemon() {
name=$1
daemon=$2
pidfile=$3
signal=$4
action=$5
[ -z "$action" ] && action="Stopping"
echo -n "$action Ceph $name on $host..."
do_cmd "if [ -e $pidfile ]; then
pid=`cat $pidfile`
if [ -e /proc/\$pid ] && grep -q $daemon /proc/\$pid/cmdline ; then
cmd=\"kill $signal \$pid\"
echo -n \$cmd...
\$cmd
fi
fi"
echo done
}
daemon_is_running() {
name=$1
daemon=$2
daemon_id=$3
pidfile=$4
do_cmd "[ -e $pidfile ] || exit 1 # no pid, presumably not running
pid=\`cat $pidfile\`
[ -e /proc/\$pid ] && grep -q $daemon /proc/\$pid/cmdline && grep -qwe -i.$daemon_id /proc/\$pid/cmdline && exit 0 # running
exit 1 # pid is something else" "" "okfail"
}
stop_daemon() {
name=$1
daemon=$2
pidfile=$3
signal=$4
action=$5
[ -z "$action" ] && action="Stopping"
echo -n "$action Ceph $name on $host..."
do_cmd "while [ 1 ]; do
[ -e $pidfile ] || break
pid=\`cat $pidfile\`
while [ -e /proc/\$pid ] && grep -q $daemon /proc/\$pid/cmdline ; do
cmd=\"kill $signal \$pid\"
echo -n \$cmd...
\$cmd
sleep 1
continue
done
break
done"
echo done
}
## command line options
options=
version=0
dovalgrind=
docrun=
allhosts=0
debug=0
monaddr=
dofsmount=1
dofsumount=0
verbose=0
while echo $1 | grep -q '^-'; do # FIXME: why not '^-'?
case $1 in
-v | --verbose)
verbose=1
;;
--valgrind)
dovalgrind=1
;;
--novalgrind)
dovalgrind=0
;;
--allhosts | -a)
allhosts=1;
;;
--restart)
docrun=1
;;
--norestart)
docrun=0
;;
-m )
[ -z "$2" ] && usage_exit
options="$options $1"
shift
MON_ADDR=$1
;;
--btrfs | --fsmount)
dofsmount=1
;;
--nobtrfs | --nofsmount)
dofsmount=0
;;
--btrfsumount | --fsumount)
dofsumount=1
;;
--conf | -c)
[ -z "$2" ] && usage_exit
options="$options $1"
shift
conf=$1
;;
--hostname )
[ -z "$2" ] && usage_exit
options="$options $1"
shift
hostname=$1
;;
*)
echo unrecognized option \'$1\'
usage_exit
;;
esac
options="$options $1"
shift
done
verify_conf
command=$1
[ -n "$*" ] && shift
get_local_name_list
get_name_list "$@"
# Reverse the order if we are stopping
if [ "$command" = "stop" ]; then
for f in $what; do
new_order="$f $new_order"
done
what="$new_order"
fi
for name in $what; do
type=`echo $name | cut -c 1-3` # e.g. 'mon', if $item is 'mon1'
id=`echo $name | cut -c 4- | sed 's/^\\.//'`
cluster=`echo $conf | awk -F'/' '{print $(NF)}' | cut -d'.' -f 1`
num=$id
name="$type.$id"
check_host || continue
binary="$BINDIR/ceph-$type"
cmd="$binary -i $id"
get_conf run_dir "/var/run/ceph" "run dir"
get_conf pid_file "$run_dir/$type.$id.pid" "pid file"
if [ "$command" = "start" ]; then
if [ -n "$pid_file" ]; then
do_cmd "mkdir -p "`dirname $pid_file`
cmd="$cmd --pid-file $pid_file"
fi
get_conf log_dir "" "log dir"
[ -n "$log_dir" ] && do_cmd "mkdir -p $log_dir"
get_conf auto_start "" "auto start"
if [ "$auto_start" = "no" ] || [ "$auto_start" = "false" ] || [ "$auto_start" = "0" ]; then
if [ -z "$@" ]; then
echo "Skipping Ceph $name on $host... auto start is disabled"
continue
fi
fi
if daemon_is_running $name ceph-$type $id $pid_file; then
echo "Starting Ceph $name on $host...already running"
do_map
continue
fi
get_conf copy_executable_to "" "copy executable to"
if [ -n "$copy_executable_to" ]; then
scp $binary "$host:$copy_executable_to"
binary="$copy_executable_to"
fi
fi
# conf file
cmd="$cmd -c $conf"
if echo $name | grep -q ^osd; then
get_conf osd_data "/var/lib/ceph/osd/ceph-$id" "osd data"
get_conf fs_path "$osd_data" "fs path" # mount point defaults so osd data
get_conf fs_devs "" "devs"
if [ -z "$fs_devs" ]; then
# try to fallback to old keys
get_conf tmp_btrfs_devs "" "btrfs devs"
if [ -n "$tmp_btrfs_devs" ]; then
fs_devs="$tmp_btrfs_devs"
fi
fi
first_dev=`echo $fs_devs | cut '-d ' -f 1`
fi
# do lockfile, if RH
get_conf lockfile "/var/lock/subsys/ceph" "lock file"
lockdir=`dirname $lockfile`
if [ ! -d "$lockdir" ]; then
lockfile=""
fi
get_conf asok "$run_dir/ceph-$type.$id.asok" "admin socket"
case "$command" in
start)
# Increase max_open_files, if the configuration calls for it.
get_conf max_open_files "32768" "max open files"
# build final command
wrap=""
runmode=""
runarg=""
[ -z "$docrun" ] && get_conf_bool docrun "0" "restart on core dump"
[ "$docrun" -eq 1 ] && wrap="$BINDIR/ceph-run"
[ -z "$dovalgrind" ] && get_conf_bool valgrind "" "valgrind"
[ -n "$valgrind" ] && wrap="$wrap valgrind $valgrind"
[ -n "$wrap" ] && runmode="-f &" && runarg="-f"
[ -n "$max_open_files" ] && files="ulimit -n $max_open_files;"
if [ $SYSTEMD -eq 1 ]; then
cmd="systemd-run -r bash -c '$files $cmd --cluster $cluster -f'"
else
cmd="$files $wrap $cmd --cluster $cluster $runmode"
fi
if [ $dofsmount -eq 1 ] && [ -n "$fs_devs" ]; then
get_conf pre_mount "true" "pre mount command"
get_conf fs_type "" "osd mkfs type"
if [ -z "$fs_type" ]; then
# try to fallback to to old keys
get_conf tmp_devs "" "btrfs devs"
if [ -n "$tmp_devs" ]; then
fs_type="btrfs"
else
echo No filesystem type defined!
exit 0
fi
fi
get_conf fs_opt "" "osd mount options $fs_type"
if [ -z "$fs_opt" ]; then
if [ "$fs_type" = "btrfs" ]; then
#try to fallback to old keys
get_conf fs_opt "" "btrfs options"
fi
if [ -z "$fs_opt" ]; then
if [ "$fs_type" = "xfs" ]; then
fs_opt="rw,noatime,inode64"
else
#fallback to use at least noatime
fs_opt="rw,noatime"
fi
fi
fi
[ -n "$fs_opt" ] && fs_opt="-o $fs_opt"
[ -n "$pre_mount" ] && do_cmd "$pre_mount"
if [ "$fs_type" = "btrfs" ]; then
echo Mounting Btrfs on $host:$fs_path
do_root_cmd_okfail "modprobe btrfs ; btrfs device scan || btrfsctl -a ; egrep -q '^[^ ]+ $fs_path' /proc/mounts || mount -t btrfs $fs_opt $first_dev $fs_path"
else
echo Mounting $fs_type on $host:$fs_path
do_root_cmd_okfail "modprobe $fs_type ; egrep -q '^[^ ]+ $fs_path' /proc/mounts || mount -t $fs_type $fs_opt $first_dev $fs_path"
fi
if [ "$ERR" != "0" ]; then
EXIT_STATUS=$ERR
continue
fi
fi
if [ "$type" = "osd" ]; then
get_conf update_crush "" "osd crush update on start"
if [ "${update_crush:-1}" = "1" -o "${update_crush:-1}" = "true" ]; then
# update location in crush
get_conf osd_location_hook "$BINDIR/ceph-crush-location" "osd crush location hook"
osd_location=`$osd_location_hook --cluster ceph --id $id --type osd`
get_conf osd_weight "" "osd crush initial weight"
defaultweight="$(df -P -k $osd_data/. | tail -1 | awk '{ print sprintf("%.2f",$2/1073741824) }')"
get_conf osd_keyring "$osd_data/keyring" "keyring"
do_cmd "timeout 30 $BINDIR/ceph -c $conf --name=osd.$id --keyring=$osd_keyring osd crush create-or-move -- $id ${osd_weight:-${defaultweight:-1}} $osd_location"
fi
fi
echo Starting Ceph $name on $host...
mkdir -p $run_dir
get_conf pre_start_eval "" "pre start eval"
[ -n "$pre_start_eval" ] && $pre_start_eval
get_conf pre_start "" "pre start command"
get_conf post_start "" "post start command"
[ -n "$pre_start" ] && do_cmd "$pre_start"
do_cmd_okfail "$cmd" $runarg
if [ "$ERR" != "0" ]; then
EXIT_STATUS=$ERR
fi
if [ "$type" = "mon" ]; then
# this will only work if we are using default paths
# for the mon data and admin socket. if so, run
# ceph-create-keys. this is the case for (normal)
# chef and ceph-deploy clusters, which is who needs
# these keys. it's also true for default installs
# via mkcephfs, which is fine too; there is no harm
# in creating these keys.
get_conf mon_data "/var/lib/ceph/mon/ceph-$id" "mon data"
if [ "$mon_data" = "/var/lib/ceph/mon/ceph-$id" -a "$asok" = "/var/run/ceph/ceph-mon.$id.asok" ]; then
echo Starting ceph-create-keys on $host...
cmd2="$SBINDIR/ceph-create-keys -i $id 2> /dev/null &"
do_cmd "$cmd2"
fi
fi
[ -n "$post_start" ] && do_cmd "$post_start"
[ -n "$lockfile" ] && [ "$?" -eq 0 ] && touch $lockfile
do_map
;;
stop)
get_conf pre_stop "" "pre stop command"
get_conf post_stop "" "post stop command"
[ -n "$pre_stop" ] && do_cmd "$pre_stop"
stop_daemon $name ceph-$type $pid_file
[ -n "$post_stop" ] && do_cmd "$post_stop"
[ -n "$lockfile" ] && [ "$?" -eq 0 ] && rm -f $lockfile
if [ $dofsumount -eq 1 ] && [ -n "$fs_devs" ]; then
echo Unmounting OSD volume on $host:$fs_path
do_root_cmd "umount $fs_path || true"
fi
do_unmap
;;
status)
if daemon_is_running $name ceph-$type $id $pid_file; then
echo -n "$name: running "
do_cmd "$BINDIR/ceph --admin-daemon $asok version 2>/dev/null" || echo unknown
elif [ -e "$pid_file" ]; then
# daemon is dead, but pid file still exists
echo "$name: dead."
EXIT_STATUS=1
else
# daemon is dead, and pid file is gone
echo "$name: not running."
EXIT_STATUS=3
fi
rbd showmapped
;;
ssh)
$ssh
;;
forcestop)
get_conf pre_forcestop "" "pre forcestop command"
get_conf post_forcestop "" "post forcestop command"
[ -n "$pre_forcestop" ] && do_cmd "$pre_forcestop"
stop_daemon $name ceph-$type $pid_file -9
[ -n "$post_forcestop" ] && do_cmd "$post_forcestop"
[ -n "$lockfile" ] && [ "$?" -eq 0 ] && rm -f $lockfile
;;
killall)
echo "killall ceph-$type on $host"
do_cmd "pkill ^ceph-$type || true"
[ -n "$lockfile" ] && [ "$?" -eq 0 ] && rm -f $lockfile
;;
force-reload | reload)
signal_daemon $name ceph-$type $pid_file -1 "Reloading"
;;
restart)
$0 $options stop $name
$0 $options start $name
;;
condrestart)
if daemon_is_running $name ceph-$type $id $pid_file; then
$0 $options stop $name
$0 $options start $name
else
echo "$name: not running."
fi
;;
cleanlogs)
echo removing logs
[ -n "$log_dir" ] && do_cmd "rm -f $log_dir/$type.$id.*"
;;
cleanalllogs)
echo removing all logs
[ -n "$log_dir" ] && do_cmd "rm -f $log_dir/* || true"
;;
*)
usage_exit
;;
esac
done
# activate latent osds?
if [ "$command" = "start" -a "$BINDIR" != "." ]; then
if [ "$*" = "" ] || echo $* | grep -q ^osd\$ ; then
ceph-disk activate-all
fi
fi
exit $EXIT_STATUS
2.3 快照配置
2.3.1 快照恢复
1、创建快照
本次快照以2.1章节的p_rbd/image001为例
# 确认image001
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo rbd ls -p p_rbd
# 查看映射情况
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ rbd showmapped
# 查看挂载情况
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ df -h
# 确认文件内容
[root@cephmanager01 mnt]# echo "snap test" > /mnt/cc.txt
[root@cephmanager01 mnt]# ls /mnt
2、创建快照并列出创建的快照
# 创建快照
[cephuser@cephmanager01 ~]$ sudo rbd snap create image001@image001_snap01 -p p_rbd
# 列出快照
[cephuser@cephmanager01 ~]$ sudo rbd snap list image001 -p p_rbd
# 或者用下面命令
[cephuser@cephmanager01 ~]$ sudo rbd snap ls p_rbd/image001
3、查看快照详细信息
[cephuser@cephmanager01 ~]$ sudo rbd info image001 -p p_rbd
4、删除/mnt/cc.txt,再恢复快照
[cephuser@cephmanager01 ~]$ sudo rbd snap rollback image001@image001_snap01 -p p_rbd
5、重新挂载文件系统,发现已经恢复到之前的状态了
[cephuser@cephmanager01 ~]$ sudo umount /mnt
[cephuser@cephmanager01 ~]$ sudo mount /dev/rbd0 /mnt
# 发现cc.txt依然存在
[cephuser@cephmanager01 ~]$ sudo ls /mnt/
2.3.1 快照克隆
本次快照以2.2章节的p_rbd/image003为例
1、克隆快照(快照必须处于被保护状态才能被克隆)
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo rbd snap protect image003@image003_snap01 -p p_rbd
# 创建将要被克隆的pool
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo ceph osd pool create p_clone 32 32
# 进行clone
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo rbd clone p_rbd/image003@image003_snap01 p_clone/image003_clone01
# 查看clone后的rbd
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo rbd ls -p p_clone
2、查看快照的children和parent关系
# 查看快照的children
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo rbd children image003@image003_snap01 -p p_rbd
# 确认 parent信息
[cephuser@cephmanager01 ~]$ sudo rbd info --image p_clone/image003_clone01
# 去掉快照的parent
[cephuser@cephmanager01 cephcluster]$ sudo rbd flatten p_clone/image003_clone01
3、删除快照
# 去掉快照保护
[cephuser@cephmanager01 ~]$ sudo rbd snap unprotect image003@image003_snap01 -p p_rbd
# 删除快照
[cephuser@cephmanager01 ~]$ sudo rbd snap remove image003@image003_snap01 -p p_rbd