[代码随想录]二叉树篇
文章目录
- 1. 二叉树之层序遍历
-
- 1.1 144-二叉树的前序遍历
- 1.2 94-二叉树的中序遍历
- 1.3 145-二叉树的后序遍历
- 1.4 102-二叉树的层序遍历
- 1.5 107-二叉树的层序遍历II
- 1.6 199-二叉树的右视图
- 1.7* 637-二叉树的层平均值
- 1.8* 429-N叉树的层序遍历
- 1.9 515-在每个树行中找最大值
- 1.10* 116-填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- 1.11 117-填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
- 1.12 104-二叉树的最大深度
- 1.13 111-二叉树的最小深度
- 2. 二叉树之常见算法
-
- 2.1 226-翻转二叉树
- 2.2 101-对称二叉树
- 2.3* 222-完全二叉树的节点个数
- 2.4 110-平衡二叉树
- 2.5 257-二叉树的所有路径
- 2.6 404-左子叶之和
- 2.7* 513-找树左下角的值
- 2.8 112-路径总和
- 2.9* 106-从中序与后续遍历序列构造二叉树
- 2.10* 105-从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 2.11* 654-最大二叉树
- 2.12 617-合并二叉树
- 2.13* 236-二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 3. 二叉搜索树
-
- 3.1 700-二叉搜索树中的搜索
- 3.2* 98-验证二叉搜索树
- 3.3 530-二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
- 3.4 501-二叉搜索树中的众数
- 3.5* 235-二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- 3.6* 701-二叉搜索树中的插入操作
- 3.7* 450-删除二叉搜索树中的节点
- 3.8* 669-修剪二叉搜索树
- 3.9 108-将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
- 3.10 538-把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
1. 二叉树之层序遍历
1.1 144-二叉树的前序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void Recursion(TreeNode* root,vector<int>& ans)
{
if(root == nullptr)
return;
ans.push_back(root->val);
Recursion(root->left,ans);
Recursion(root->right,ans);
}
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans;
Recursion(root,ans);
return ans;
}
};
迭代难度更大
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while(cur || !st.empty())
{
while(cur) //第一趟把左列节点放入栈和ans
{
ans.push_back(cur->val);
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
TreeNode* tmp = st.top(); //对应着左下角的节点
st.pop();
cur = tmp->right; //开始右
}
return ans;
}
};
1.2 94-二叉树的中序遍历
class Solution {
public:
void Recursion(TreeNode* root,vector<int>& ans)
{
if(root == nullptr)
return;
Recursion(root->left,ans);
ans.push_back(root->val);
Recursion(root->right,ans);
}
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans;
Recursion(root,ans);
return ans;
}
};
迭代法
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> ans;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while(cur || !st.empty())
{
while(cur)
{
//ans.push_back(cur->val); 并不是最左边的数据放在第一个
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
TreeNode* tmp = st.top();
ans.push_back(tmp->val);
st.pop();
cur = tmp->right;
}
}
};
1.3 145-二叉树的后序遍历
145
class Solution
{
public:
void Recursion(TreeNode*& root,vector<int>& ans)
{
if(root==nullptr)
return;
Recursion(root->left,ans);
Recursion(root->right,ans);
ans.push_back(root->val);
}
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<int> ans;
Recursion(root,ans);
return ans;
}
};
迭代法
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
TreeNode* prev = nullptr;
while(cur || !st.empty())
{
while(cur)
{
st.push(cur);
cur=cur->left;
}
TreeNode* top = s.top();
if(!top->right || top->right == prev)
{
ans.push_back(top->val);
prev = top;
st.pop();
}
else
cur = top->right; //当左走完之后这一步可以走到右
}
return ans;
}
};
1.4 102-二叉树的层序遍历
102
class Solution {
public:
void Recursion(vector<vector<int>>& ans,TreeNode* root,int level)
{
if(!root)
return;
if(ans.size() <= level) //ans的层数不够,加层数
ans.push_back(vector<int>());
ans[level].push_back(root->val);
Recursion(ans,root->left,level+1);
Recursion(ans,root->right,level+1);
}
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
Recursion(ans,root,0);
return ans;
}
};
1.5 107-二叉树的层序遍历II
107
上一题reverse一下就可以了
class Solution {
public:
void Recursion(vector<vector<int>>& ans,TreeNode* root,int level)
{
if(!root)
return;
if(ans.size() <= level)
ans.push_back(vector<int>());
ans[level].push_back(root->val);
Recursion(ans,root->left,level+1);
Recursion(ans,root->right,level+1);
}
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
Recursion(ans,root,0);
reverse(ans.begin(),ans.end());
return ans;
}
};
也引入一下这题(上一题)的非递归写法
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL)
que.push(root); //先放一个根节点
vector<vector<int>> result;
while (!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
vector<int> vec;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
vec.push_back(node->val); //从前往后一个一个取
if (node->left)
que.push(node->left); //push进去当前层的下一层节点
if (node->right)
que.push(node->right); //同理
}
result.push_back(vec); //加入一层
}
reverse(result.begin(), result.end()); // 在这里反转一下数组即可
return result;
}
};
1.6 199-二叉树的右视图
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
vector<int> ans;
if(root) //加入第一个节点
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size;i++)
{
TreeNode* tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(i == (size-1)) //如果是位于尾部
ans.push_back(tmp->val);
if(tmp->left)
que.push(tmp->left);//加入下一层数据
if(tmp->right)
que.push(tmp->right);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
1.7* 637-二叉树的层平均值
637
class Solution {
public:
vector<double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
vector<double> ans;
if(root)
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
TreeNode* tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
sum+=tmp->val;
if(tmp->left)
que.push(tmp->left);
if(tmp->right)
que.push(tmp->right);
}
ans.push_back(sum/size);
}
return ans;
}
};
1.8* 429-N叉树的层序遍历
429
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if(root)
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
vector<int> tmp_v;
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
tmp_v.push_back(node->val);
for(int j = 0; j < node->children.size(); ++j) //下一层节点加入que
if(node->children[j])
que.push(node->children[j]);
}
ans.push_back(tmp_v);
}
return ans;
}
};
1.9 515-在每个树行中找最大值
515
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if(root)
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
int max = INT_MIN;
for(int i = 0; i < size;++i)
{
TreeNode* tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(tmp->val>max)
max = tmp->val;
if(tmp->left)
que.push(tmp->left);
if(tmp->right)
que.push(tmp->right);
}
ans.push_back(max);
}
return ans;
}
};
1.10* 116-填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
116
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node* next;
Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next)
: val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if(!root)
return nullptr;
Node* leftest = root;
while(leftest->left) //如果该节点还有子节点,则说明可以进入循环处理其孩子
{
Node* cur = leftest;
while(cur) //处理cur所有的子节点连接
{
cur->left->next = cur->right; //下一层的next连接
if(cur->next)
cur->right->next = cur->next->left; //下一层隔支连接
cur = cur->next;
}
leftest = leftest->left; //下一层最左边开始
}
return root;
}
};
若使用普通的层序遍历那么空间复杂度会达到N
而这种方式空间复杂度为1
1.11 117-填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
117
上一题是完全二叉树
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node* next;
Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next)
: val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if(root && (root->left || root->right)) //root存在并且必须有一个孩子
{
if(root->left && root->right) //如果有左有右,则连接孩子
root->left->next = root->right;
//准备让孩子隔支连接
Node* child = root->right ? root->right : root->left;
Node* brodady = root->next; //向右移动以便用孩子连接child
while(brodady && !(brodady->left||brodady->right)) //直到brodady走到尽头,也要找到有孩子的brodady
brodady = brodady->next;
child->next = brodady ? (brodady->left ? brodady->left : brodady->right) : nullptr;
connect(root->right); //先向右初始化出NULL
connect(root->left);
}
return root;
}
};
1.12 104-二叉树的最大深度
104
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)
return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
1.13 111-二叉树的最小深度
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)
return 0;
if(!root->left && !root->right)
return 1;
int min_depth = INT_MAX;
if(root->left)
min_depth = min(minDepth(root->left),min_depth);
if(root->right)
min_depth = min(minDepth(root->right),min_depth);
return min_depth+1;
}
};
2. 二叉树之常见算法
2.1 226-翻转二叉树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)
return nullptr;
swap(root->left,root->right);
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
return root;
}
};
2.2 101-对称二叉树
101
递归
class Solution {
public:
bool Recursion(TreeNode* left,TreeNode* right)
{
if(!left&&right || left&&!right) //如果长短不一
return false;
if(!left && !right) //如果都没有后续了
return true;
if(left->val != right->val)
return false;
return Recursion(left->left,right->right) &&
Recursion(left->right,right->left);
//对称的两个节点比较
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
return Recursion(root->left,root->right);
}
};
迭代(栈)
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
st.push(root->left);
st.push(root->right);
while (!st.empty())
{
TreeNode* leftNode = st.top();
st.pop();
TreeNode* rightNode = st.top();
st.pop();
if (!leftNode && !rightNode) //左右节点都不存在,相当于对称,循环至下一次判断
continue;
//左右不一样长 || 左右节点的值不一样
if ((!leftNode || !rightNode || (leftNode->val != rightNode->val)))
return false;
st.push(leftNode->left);
st.push(rightNode->right);
st.push(leftNode->right);
st.push(rightNode->left);
}
return true;
}
};
2.3* 222-完全二叉树的节点个数
222
递归遍历 O(N)
class Solution {
public:
void Recursion(TreeNode* root,int& count)
{
if(!root)
return;
count++;
Recursion(root->left,count);
Recursion(root->right,count);
}
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
int count = 0;
Recursion(root,count);
return count;
}
};
精简版递归
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
return 1 + countNodes(root->left)
+ countNodes(root->right);
}
};
最优
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root)
{
if (!root)
return 0;
int level = 0;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur->left)
{
level++;
cur = cur->left;
}
int low = 1 << level; // 层序遍历第low位为最深层最左侧节点序号 4
int high = (1 << (level + 1)) - 1; //层序遍历第high位为最深层最右侧节点序号 7
while (low < high)
{
int mid = (high - low + 1) / 2 + low; //+1防止low+0 ,mid为两节点中间部分一个节点,偏右
if (exists(root, level, mid))
low = mid;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
return low;
}
bool exists(TreeNode* root, int level, int mid) //6
{
int bits = 1 << (level - 1); //上一层的第一位序列
TreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur && bits > 0)
{
if (bits & mid) //0010 0110 0010 当不再同一树时判断后就进入循环
cur = cur->right;
else
cur = cur->left;
bits >>= 1; //bits是最左节点,往上靠
}
return cur != nullptr;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(logN*logN)
空间复杂度:O(1)
2.4 110-平衡二叉树
class Solution {
public:
int Recursion(TreeNode* root)
{
if(!root)
return 0;
int left = Recursion(root->left);
if(left == -1)
return -1;
int right = Recursion(root->right);
if(right == -1)
return -1;
if(abs(left-right) > 1)
return -1; //执行后,以后的结果都为-1,递归其实已经可以看作结束了
return left>right?left+1:right+1; //每一层都会记录层数+1
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root)
{
if(Recursion(root) == -1)
return false;
return true;
}
};
2.5 257-二叉树的所有路径
class Solution {
public:
void Recursion(TreeNode* root,vector<string>& vs,string s) //s传的是临时拷贝份
{
if(root&&!root->left&&!root->right) //无子,此时不加->
{
s+=(to_string(root->val));
vs.push_back(s);
return;
}
if(!root)
return;
s+=(to_string(root->val)+"->");
Recursion(root->left,vs,s);
Recursion(root->right,vs,s);
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string> vs;
string s;
Recursion(root,vs,s);
return vs;
}
};
2.6 404-左子叶之和
class Solution {
public:
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root)
return 0;
int leftValue = 0;
if (root->left && !root->left->left && !root->left->right) //左子存在且为叶
leftValue = root->left->val;
return leftValue + sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
}
};
2.7* 513-找树左下角的值
513
dfs
class Solution {
public:
void Recursion(TreeNode* cur,int curdep,int& maxdep,int& ans)
{
if(!cur->left&&!cur->right)
{
if(curdep>maxdep)
{
maxdep = dep;
ans = cur->val;
}
return;
}
if(cur->left) //cur->left在前面使得更早的占用ans,以防被right占用
Recursion(cur->left,dep+1,maxdep,ans);
if(cur->right)
Recursion(cur->right,dep+1,maxdep,ans);
}
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = root->val;
int maxdep = 0;
Recursion(root,0,maxdep,ans);
return ans;
}
};
bfs
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty())
{
TreeNode* cur = que.front();
que.pop();
if(cur->right)
que.push(cur->right);
if(cur->left)
que.push(cur->left);
ans = cur->val;
}
return ans;
}
};
2.8 112-路径总和
112
class Solution {
public:
bool Recursion(TreeNode* cur,int sum,int target)
{
if(!cur)
return false;
if(!cur->left&&!cur->right&&sum+cur->val == target)
return true;
return Recursion(cur->left,sum+cur->val,target)
||Recursion(cur->right,sum+cur->val,target);
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
return Recursion(root,0,targetSum);
}
};
2.9* 106-从中序与后续遍历序列构造二叉树
106
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* Recursion(vector<int>& inorder,vector<int>& postorder,int& rootindex,int left,int right)
{
if(left > right)
return nullptr;
TreeNode* cur = new TreeNode(postorder[rootindex]); //cur为当前根节点
int mid = 0;
for(mid = inorder.size()-1 ; mid >=0 ; --mid)
if(inorder[mid] == postorder[rootindex])
break;
//此时mid为inorder的根坐标
rootindex--; //跳到下一个根
//因为是后序所以先right,否则会出现构建出相反的树,并且大概率导致rootindex<0而导致的越栈
cur->right = Recursion(inorder,postorder,rootindex,mid+1,right);
cur->left = Recursion(inorder,postorder,rootindex,left,mid-1);
return cur;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
int rootindex = postorder.size() - 1;
return Recursion(inorder,postorder,rootindex,0,rootindex);
}
};
2.10* 105-从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* Recursion(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder,int& rootindex,int left , int right)
{
if(left > right)
return nullptr;
TreeNode* cur = new TreeNode(preorder[rootindex]);
int mid = 0;
for(mid = 0 ; mid < inorder.size() ; ++mid)
if(inorder[mid] == preorder[rootindex])
break;
rootindex++;
cur->left = Recursion(preorder,inorder,rootindex,left,mid-1);
cur->right = Recursion(preorder,inorder,rootindex,mid+1,right);
return cur;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int rootindex = 0;
return Recursion(preorder,inorder,rootindex,0,preorder.size()-1);
}
};
2.11* 654-最大二叉树
654
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* Recursion(vector<int>& nums,int left,int right)
{
if(left > right)
return nullptr;
int mid = left; //坐标
int max = 0; //最大值
for(int i = mid ; i <= right ; ++i)
{
if(nums[i] > max)
{
mid = i; //mid就是根的坐标
max = nums[i]; //最大值就是根
}
}
TreeNode* cur = new TreeNode(max); //构建根
cur->left = Recursion(nums,left,mid-1);
cur->right = Recursion(nums,mid+1,right);
return cur;
}
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) {
return Recursion(nums,0,nums.size()-1);
}
};
2.12 617-合并二叉树
617
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
if(!root1)
return root2; //如果两个节点都不存在,也会返回nullptr(root2)
if(!root2)
return root1;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(root1->val+root2->val);
root->left = mergeTrees(root1->left,root2->left);
root->right = mergeTrees(root1->right,root2->right);
return root;
}
};
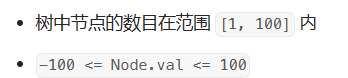
2.13* 236-二叉树的最近公共祖先
236
![]()
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(!root)
return nullptr;
if(root == p || root == q)
return root;
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
if(left&&right)
return root;
else if(!left&&right)
return right;
else if(left&&!right)
return left;
else
return nullptr;
}
};
3. 二叉搜索树
3.1 700-二叉搜索树中的搜索
700
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if(!root)
return nullptr;
if(val < root->val)
return searchBST(root->left,val);
else if(val > root->val)
return searchBST(root->right,val);
else
return root;
}
};
3.2* 98-验证二叉搜索树
98
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root,TreeNode* minNode = nullptr,TreeNode* maxNode = nullptr) {
if(!root)
return true;
if((minNode && root->val <= minNode->val) || //右树用来判断是否比父小
(maxNode && root->val >= maxNode->val)) //左树用来判断是否比父大
return false; //不符合就false
return isValidBST(root->left,minNode,root) && //对于左树,最大的就是根
isValidBST(root->right,root,maxNode); //对于右树,最小的就是根
}
};
更直观的方法
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root)
{
if(!root)
return true;
if(root->left)
{
TreeNode* tmp = root->left;
if(tmp->val>=root->val) //先判断和父的关系是否满足
return false;
while(tmp->right) //在判断自己的右孩子是否和自己对应
{ //左孩子会通过递归(和父的关系)进行判断
tmp = tmp->right;
if(tmp->val>=root->val)
return false;
}
}
if(root->right)
{
TreeNode* tmp = root->right;
if(tmp->val<=root->val)
return false;
while(tmp->left)
{
tmp = tmp->left;
if(tmp->val<=root->val)
return false;
}
}
return isValidBST(root->left) && isValidBST(root->right);
}
};
3.3 530-二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
530
递归
class Solution {
public:
void Recursion(TreeNode* root,TreeNode*& prev,int& mindif)
{
if(!root)
return;
Recursion(root->left,prev,mindif);
if(prev)
mindif = min(mindif,abs(root->val-prev->val));
prev = root; //prev就是更深层的
Recursion(root->right,prev,mindif);
}
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root)
{
int mindif = INT_MAX;
TreeNode* prev = nullptr;
Recursion(root,prev,mindif); //类似于采取中序遍历寻找mindif
return mindif;
}
};
完全遍历
class Solution {
public:
void Recursion(TreeNode* root,int& min)
{
if(!root)
return;
int tmp;
if(root->left)
{
TreeNode* left = root->left;
while(left)
{
tmp =abs(root->val-left->val);
if(tmp<min)
min = tmp;
left = left->right;
}
}
if(root->right)
{
TreeNode* right = root->right;
while(right)
{
tmp = abs(root->val-right->val);
if(tmp<min)
min = tmp;
right = right->left;
}
}
Recursion(root->left,min);
Recursion(root->right,min);
}
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root)
{
int min = 100000;
Recursion(root,min);
return min;
}
};
3.4 501-二叉搜索树中的众数
501
hash通解,即非二叉树也可解
class Solution {
public:
void Init_um_Recursion(TreeNode* root,unordered_map<int,int>& um)
{
if(!root)
return;
um[root->val]++;
Init_um_Recursion(root->left,um);
Init_um_Recursion(root->right,um);
}
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
unordered_map<int,int> um;
Init_um_Recursion(root,um);
vector<int> ans;
int max = INT_MIN;
for(auto& e : um) //算出最多的出现次数
if(e.second > max)
max = e.second;
for(auto& e : um)
if(e.second == max)
ans.push_back(e.first);
return ans;
}
};
针对
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int samenum = 0;
int count = 0;
int maxcount = 0;
void Get_ret(TreeNode* root,vector<int>& ret)
{
if(!root)
return;
Get_ret(root->left,ret);
ret.push_back(root->val);
if(samenum == root->val) //即使samenum初始值就和val相同也无所谓
count++;
else
{
samenum = root->val;
count=1; //避免samenum初始就和val相同而导致的错误计数,也方便使用
}
if(maxcount < count)
maxcount = count;
Get_ret(root->right,ret);
}
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans;
vector<int> ret;
Get_ret(root,ret);
int left = 0;
int right = maxcount-1; //left到right 可看作是窗口
while(right < ret.size())
{
if(ret[left] == ret[right])
{
ans.push_back(ret[left]);
left = right+1;
right = left+maxcount-1;
}
else
{
left++;
right++;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
3.5* 235-二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
235
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q)
{
if(!root)
return nullptr;
if(root->val > p->val && root->val > q->val) //都在根右边
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
else if(root->val<p->val&&root->val<q->val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
return root;
}
};
3.6* 701-二叉搜索树中的插入操作
701
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if(!root)
return new TreeNode(val);
if(val > root->val)
root->right = insertIntoBST(root->right,val);
else if(val < root->val)
root->left = insertIntoBST(root->left,val);
return root;
}
};
3.7* 450-删除二叉搜索树中的节点
450
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* findMin(TreeNode* node)
{
while (node->left)
node = node->left;
return node;
}
TreeNode* deleteNode(TreeNode* root, int key) {
if (!root)
return root;
if (key < root->val)
root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key);
else if (key > root->val)
root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key);
else
{
if (!root->left)
{
TreeNode* temp = root->right;
delete root;
return temp;
}
else if (!root->right)
{
TreeNode* temp = root->left;
delete root;
return temp;
}
TreeNode* temp = findMin(root->right); //temp就是要替代的节点
root->val = temp->val;
root->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->val);
}
return root;
}
};
3.8* 669-修剪二叉搜索树
669
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high)
{
if(!root)
return nullptr; //间接删除
if(root->val<low) //范围全在右子树上
return trimBST(root->right,low,high);
if(root->val>high)
return trimBST(root->left,low,high);
root->left = trimBST(root->left,low,high);
root->right = trimBST(root->right,low,high);
return root;
}
};
3.9 108-将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
108
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* Recursion(vector<int>& nums,int left,int right)
{
if(left>right)
return nullptr;
int mid = left+((right-left)>>1); // >>1 可看作是 /2,默认左偏
TreeNode* newnode = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
newnode->left = Recursion(nums,left,mid-1);
newnode->right = Recursion(nums,mid+1,right);
return newnode;
}
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums)
{
return Recursion(nums,0,nums.size()-1);
}
};
3.10 538-把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
538
class Solution {
public:
void Recursion(TreeNode* root,int& val)
{
if(!root)
return;
Recursion(root->right,val);
val+=root->val;
root->val = val;
Recursion(root->left,val);
}
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {
int val = 0;
Recursion(root,val);
return root;
}
};
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/d1834885da2444d78c3eb409153eadda.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/9c4e9dcce58e4600aecc4c98fb240d7c.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/474ddd638c494c768aa60d02967fcab2.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/535993473f1e44398ac508302e0d8e57.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/065c128ad606421a842541d819dc5a61.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第6张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/8922583ac41741b3963f5c4dbe3ba6c4.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第7张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/9f66b61f76274267ab7433012a43b53e.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第8张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/7bc7f5689f1c45b09deb8c67bfbf40d2.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第9张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/766e80a5c5a24f26a5945e57d9bab03a.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第10张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/0106136b81ed446c9ab2bcdcc7d1d21f.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第11张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/48af099f0fec4292892eca4e6d4cf886.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第12张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c8036d6eba4b4316bd5f6f21142ee2cb.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第13张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/00573873502e452a82877085780abb8d.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第14张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/120724baae33481f8010cd8a1286b5d1.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第15张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f3825b54dfd246d5b43a8bf9a6d4f084.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第16张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f33749c0c19b4834ad752cf3b68436dc.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第17张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/25816e17643a402880660cf965ea9a45.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第18张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/9a15718a8888443387d2acc2f849692d.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第19张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/7a81452df03746c18fd7e148aacb9a6a.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第20张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/80f4f4cb1fba44d3bd24ae431ffcd3fb.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第21张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/d70b5b0fab2547aba4bd147896d016a7.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第22张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e04cf810fa624282a50b538aacd34a78.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第23张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/bf40d6c5d38c4151af095183eb969df7.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第24张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/fb42c43e2279453caa72483dfa77a4a3.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第25张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c440561f474041e282b90038274eca2a.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第26张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/031816fbd6e34ea0ac386ec802a0f52b.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第27张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/78c32b4f34484735ad328bb04b2eceef.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第28张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/6792834952d6429cadf063bc4268c0f1.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第29张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/5655e0bb1c1b4e2a83e3c6e3e90981d9.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第30张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ac627c601822437bb33a9c87786a2318.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第31张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/348835a48c16439d8c27f3e71e88b61f.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第32张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/eb7155348f2b4dc6b8dc2c07fa30e848.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第33张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/69cba0a5c66a4cdcb4c23aacce078022.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第34张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/333044795cb242c8be685d78af5f617b.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第35张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/4732d8a1b7974f219b2ddc7762a254ed.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第36张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c1d655a73f3a4f96b62ab70d53e47404.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第37张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/14daf50c137b47b6aed8b9faf5a63a07.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第38张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/470eef8b1d1941b9a0a8ed9e4760d45f.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第39张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/88fad98fc1ac45ebb118d45246761712.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第40张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/5a82e81db1154847a46f745648906d3d.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第41张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/209a64145ffc4554ab8765e539613662.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第42张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/27fde79de5bd4212aa2e5593f61c0928.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第43张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/dfb1820a2c63476b8e8d067bff1b93ee.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第44张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/26f34bcadb3a4d05839c8534cb962248.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第45张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/6f7baac61d644f93bc2b5aade5521a2e.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第46张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/2fa8e8cd4b184e7491b7a8674120de68.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第47张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/6e724423eeea4ee3937633ff55c856c4.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第48张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/fd5f8edb0c554787bca352eb67eec710.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第49张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/7999d2841fd443e9bd426e2e09709de0.png)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第50张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/22b8df99208544909d6941872ded5c19.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第51张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/0a8efd67934844b59e762c59dbad8b8f.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第52张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/929671ba92ab42998f46b5f7c0c9fc44.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第53张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b5cf316214454390a20b7c0021cd51ce.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第54张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/7ef1655714d146aea48fd121947e8c64.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第55张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ed155574ac6b4fe1a8246d6b0786c972.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第56张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ec89ddea5701444cbeceb41c356feba0.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第57张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/105f5106c1e54dde9918d91ec9731be7.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第58张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/2bf0b2028c5b4df7affc7aa52ffc7d8a.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第59张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f414a7d5aeb44082a760f5cacab981d6.jpg)
![[代码随想录]二叉树篇_第60张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/948967be9fdc4667bc93e8670736205c.jpg)