Spring事件监听机制源码分析
引言
在Spring中使用ApplicationListener和ApplicationEvent来实现事件的监听。每当ApplicationContext发布ApplicationEvent事件时,ApplicationListener的监听就会被触发。
使用场景
(1)一对多的情况下:一个对象发生改变同时需要改变其它对象
(2) 解除耦合:让耦合的双方都依赖于抽象,而不是依赖于具体。使得各自发生变化都不会影响对方
源码分析
1、容器初始化注册监听事件
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(XshApplicationListenerConfig.class);
(1)构造器
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
this();
this.register(componentClasses);
this.refresh();
}
(2) 初始化事件多播器applicationEventMulticaster
org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext#refresh
// 初始化事件多播器
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
// 先判断IOC容器中是否有现成的多播器,如果现成的多播器则使用现成的
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean("applicationEventMulticaster")) {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = (ApplicationEventMulticaster)beanFactory.getBean("applicationEventMulticaster", ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
} else {
// 如果没有现成的多播器则创建一个多播器
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
// 将多播器注册到IOC容器中
beanFactory.registerSingleton("applicationEventMulticaster", this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("No 'applicationEventMulticaster' bean, using [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
(3) 注册监听事件
// 注册事件
protected void registerListeners() {
// 获取系统中的存在的监听事件
Iterator var1 = this.getApplicationListeners().iterator();
// 将监听事件注册到多播器中
while(var1.hasNext()) {
ApplicationListener<?> listener = (ApplicationListener)var1.next();
this.getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
//获取自己实现ApplicationListener接口的所有组件名称
String[] listenerBeanNames = this.getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
String[] var7 = listenerBeanNames;
int var3 = listenerBeanNames.length;
//将这些监听事件注册到多播器中
for(int var4 = 0; var4 < var3; ++var4) {
String listenerBeanName = var7[var4];
this.getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
//判断是否有早期堆积的发布的事件,如果有则发布事件
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
Iterator var9 = earlyEventsToProcess.iterator();
while(var9.hasNext()) {
ApplicationEvent earlyEvent = (ApplicationEvent)var9.next();
this.getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
2、手动发布事件到全部监听publishEvent
annotationConfigApplicationContext.publishEvent(new ApplicationEvent("手动发布了一个事件") {
@Override
public Object getSource() {
return super.getSource();
}
});
(1)publishEvent
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
// 如果事件是ApplicationEvent类型的,则装备成ApplicationEvent
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
//否则将创建一个ApplicationEvent,将event作为事件的source
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent<?>) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
// 如果多播器是延迟初始化 并且早期堆积事件集合不为null,则将当前事件加入,等待多播器初始化后再注册监听中再播发
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
//否则立即将事件播发出去
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well...
//如果其父类不为空,则父类也将发布该事件
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
(2)multicastEvent
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
// 从多播器中获取线程池
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// 获取类型匹配的监听并且触发监听事件
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
//如果存在线程池,则放到线程池里异步执行
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
// 否则同步唤醒监听
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
(3)doInvokeListener
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
//调用监听事件
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass())) {
// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for
// -> let's suppress the exception and just log a debug message.
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
设计模式
使用到了观察者设计模式
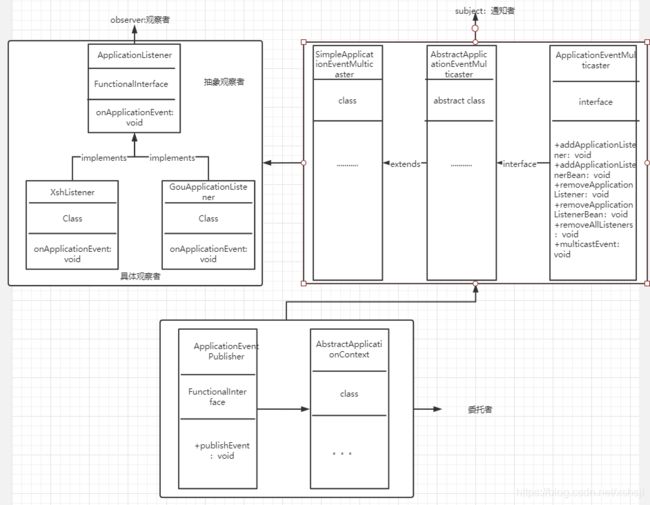
图解
通知者:
ApplicationEventMulticaster–最基本的抽象的通知者,定义了添加观察者、删除观察者、和通知观察者方法。
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster–实现了ApplicationEventMulticaster的抽象通知者,方便进行扩展,定义了一些具体的添加监听者到哪个集合中和进行缓存、具体的移除监听者
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster–继承了AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster的通知者,是具体通知者。
观察者:
ApplicationListener–抽象的观察者,定义了一个接口等通知者通知的时候进行事件处理。
XXXListener–具体的观察者,实现ApplicationListener的事件处理接口,是进行真正业务处理的
委托者–进行直接对外的发布事件,处理包装一下事件。如果不是ApplicationEvent类型的数据,将转成ApplicationEvent类型,以防事件发送失败。
流程
委托者ApplicationEventPublisher使用 publishEvent 发布一个事件,调用具体通知者ApplicationEventMulticaster多播器去触发具体观察者ApplicationListener的onApplicationEvent事件