SpringBoot--Web开发
狂神视频
- spring:开源框架,轻量级框架,为了解决企业级应用开发的复杂性而创建的。
1、web开发静态资源处理
使用SpringBoot的步骤:
-
创建一个SpringBoot应用,选择我们需要的模块,SpringBoot就会默认将我们的需要的模块自动配置好
-
手动在配置文件中配置部分配置项目就可以运行起来了
-
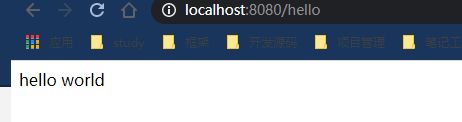
写一个controller层测试一下
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello world";
}
}
1.1、第一种静态资源映射规则
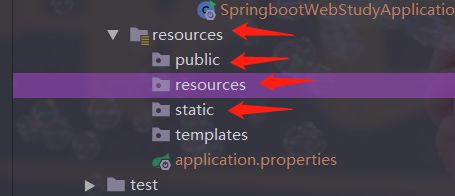
我们猜测静态资源是放置在static文件中的
现在来看看源码:
- SpringBoot中,SpringMVC的web配置都在WebMvcAutoConfiguration 这个配置类里面;代码页面一直按Shift出现搜索页面,找到WebMvcAutoConfiguration,进去找到WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter
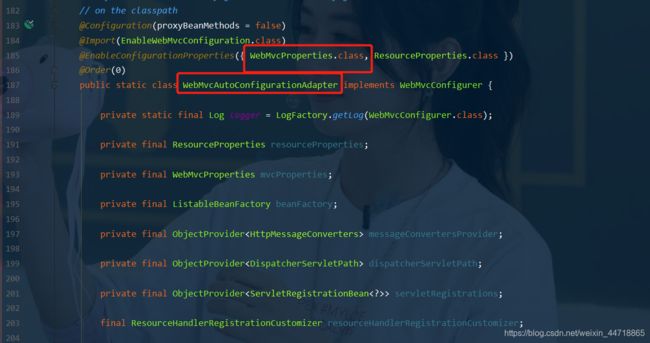
- 我们可以继续往下看看 WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter 中有很多配置方法;
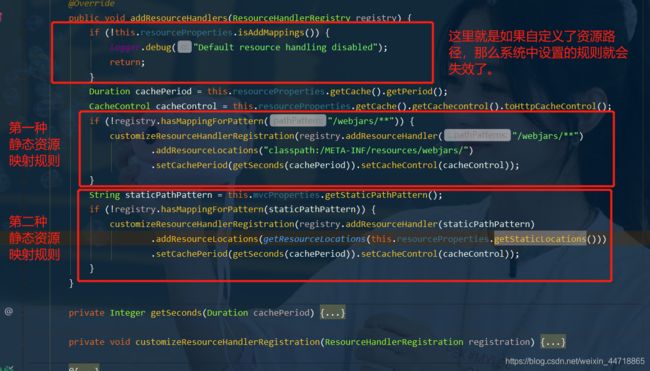
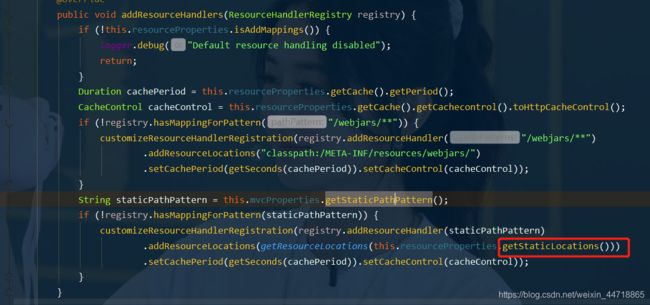
- 有一个方法:addResourceHandlers 添加资源处理
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
//如果静态资源已经被自定义了,就直接return了
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
// 已禁用默认资源处理
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
// 缓存控制
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
// webjars 配置:这是第一种获取静态资源的方式
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/")
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
// 静态资源配置:第二种获取静态资源的方式
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern)
.addResourceLocations(getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()))
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}
读一下源代码:比如所有的 /webjars/** , 都需要去 classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/ 找对应的资源;
webjars官网
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.6.0</version>
</dependency>
导入完毕,查看webjars目录结构,并访问Jquery.js文件
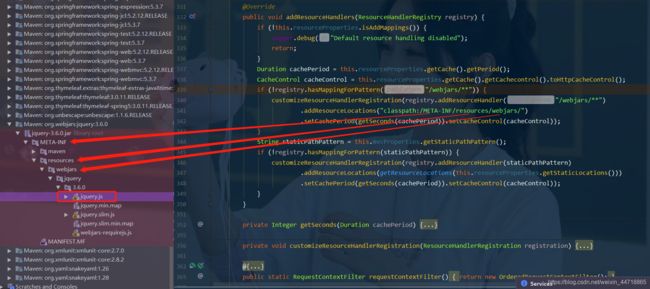
重新启动项目,访问:只要是静态资源,SpringBoot就会去对应的路径寻找资源,我们这里访问:
http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.js
1.2、第二种静态资源映射规则
- 那我们项目中要是使用自己的静态资源该怎么导入呢?我们看下一行代码;
- 刚刚的WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter 类中的addResourceHandlers 方法源码中有一段代码,找到getStaticLocations方法,点击进去这个方法里面查看代码,发现里面的代码返回的就是下一行代码中的静态资源staticPathPattern

getStaticLocations方法进去之后的代码:

- 我们去找staticPathPattern发现第二种映射规则 :/** , 访问当前的项目任意资源,它会去找 ResourceProperties 这个类
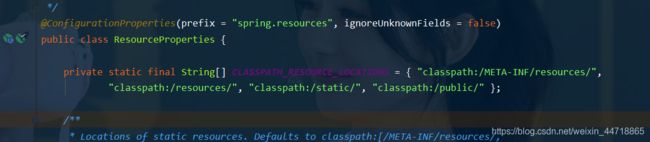
- 回到WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java类中查找ResourceProperties类,点击进去查看代码:发现有四个位置都可以。ResourceProperties 可以设置和我们静态资源有关的参数;这里面指向了它会去寻找资源的文件夹,即下面数组的内容。

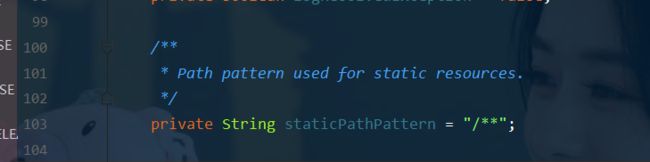
- 回到WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java类中查看getStaticLocation方法
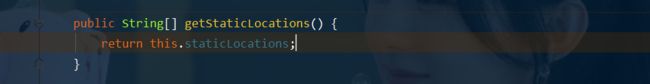
- 继续点击staticLocations进去查看可以看到有一个数组

- 继续点击这个数组属性进去可以看到内容跟上面的一样有四个位置存放静态资源;这里可以设置和我们静态资源有关的参数;这里面指向了它会去寻找资源的文件夹,即下面数组的内容。
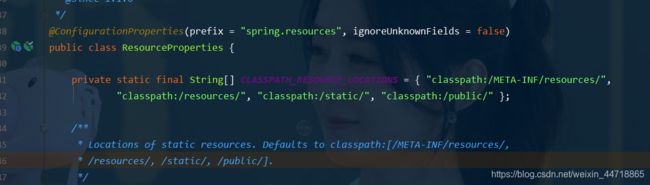
- 所以得出结论,以下四个目录存放的静态资源可以被我们识别:
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/"
"classpath:/resources/"
"classpath:/static/"
"classpath:/public/"
- 我们可以在resources根目录下新建对应的文件夹,都可以存放我们的静态文件;比如在public文件夹中新建文件1.js里面写了hello;
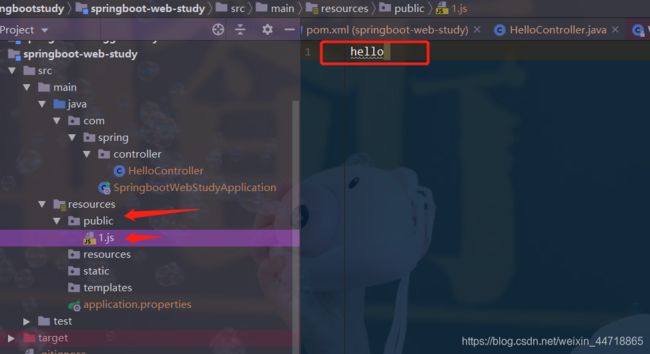
- 我们访问 http://localhost:8080/1.js , 他就会去这些文件夹中寻找对应的静态资源文件;
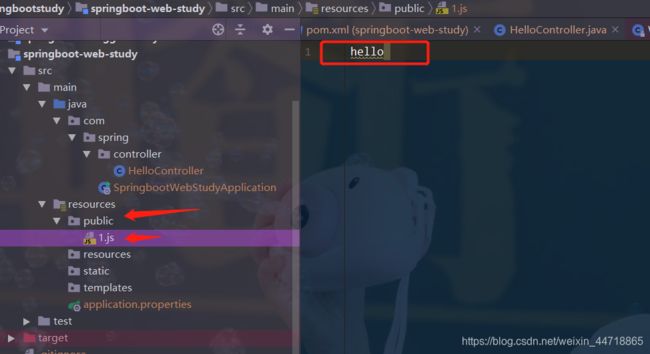
- 四个位置都可以放静态资源,那么他们是否有优先级?测试一下:public:hello1;resources:hello2;static:hell3;下都建一个1.js;内容分别为hello1,hello2,hell3,hello4;启动项目访问看看http://localhost:8080/1.js
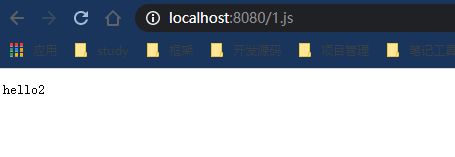
说明优先级是resources文件夹下的resources文件夹下的优先级是最高的。 - 删除resources文件夹下的resources文件夹下的文件,然后测试看看结果是hello3,也就是static文件夹下的文件
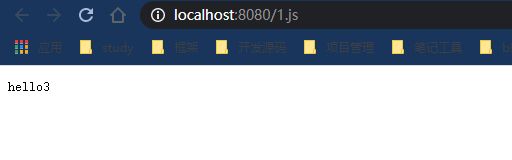
- 然后删掉static文件夹下的文件启动测试看结果是hello1,也就是public文件夹下的文件。
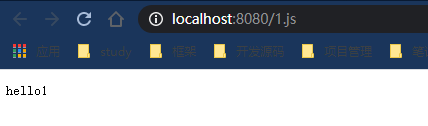
- 如上的测试可以看出优先级是resources>static>public。
1.3、自定义静态资源路径
我们也可以自己通过配置文件来指定一下,哪些文件夹是需要我们放静态资源文件的,在application.properties中配置;
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/coding/,classpath:/kuang/
一旦自己定义了静态文件夹的路径,原来的自动配置就都会失效了!
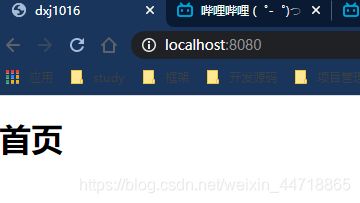
2、首页
- 到WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java类中搜索welcom可以看到WelcomePageHandlerMapping,getWelcomePage,getIndexHtml,源码如下:
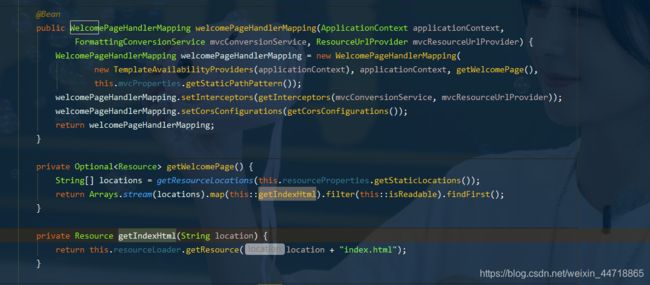
- 看到上面代码,通过@Bean注解注入bean中,bean里面有个WelcomePageHandlerMapping欢迎页的处理映射,这个映射可以从自定义的this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern()中获取;也可以从getWelcomePage获取,从哪里获得呢,从下面代码this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()中获得,也就是从静态资源的目录获取,获取什么呢?会从geIndexHtml中获取,geIndexHtml这个返回在静态资源下找到一个叫index.html的文件就会将这个文件的内容映射到首页。
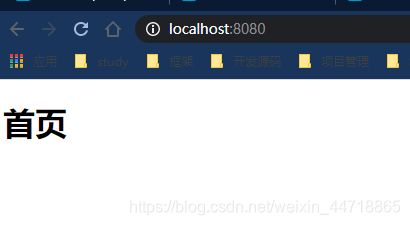
- 在静态资源路径下添加一个文件,比如这里我在public下创建一个index.html文件,内容如下:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>首页h1>
body>
html>
3、thymeleaf模板引擎
3.1、thymeleaf概述
3.2、引入Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf 官网
Thymeleaf 在Github 的主页
Spring官方文档:找到我们对应的版本
找到对应的pom依赖:可以适当点进源码看下本来的包!
<!--thymeleaf-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
3.3、Thymeleaf分析
我们去找一下Thymeleaf的自动配置类:ThymeleafProperties
idea代码页面双击shift然后搜索ThymeleafProperties
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.thymeleaf"
)
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING;
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
private boolean checkTemplate = true;
private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true;
private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/";
private String suffix = ".html";
private String mode = "HTML";
private Charset encoding;
}
- 我们可以在其中看到默认的前缀和后缀!
- 我们只需要把我们的html页面放在类路径下的templates下,thymeleaf就可以帮我们自动渲染了。
- 使用thymeleaf什么都不需要配置,只需要将他放在指定的文件夹下即可!
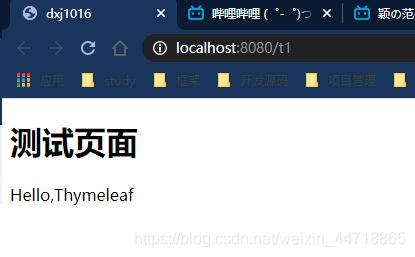
3.4、测试
1、编写一个TestController
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/t1")
public String test1(){
//classpath:/templates/test.html
return "test";
}
}
2、编写一个测试页面 test.html 放在 templates 目录下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>测试页面</h1>
</body>
</html>
3.5、练习 :我们需要查出一些数据,在页面中展示
1、修改测试请求,增加数据传输;
@RequestMapping("/t1")
public String test1(Model model){
//存入数据
model.addAttribute("msg","Hello,Thymeleaf");
//classpath:/templates/test.html
return "test";
}
2、我们要使用thymeleaf,需要在html文件中导入命名空间的约束,方便提示。我们可以去官方文档的#3中看一下命名空间拿来过来:
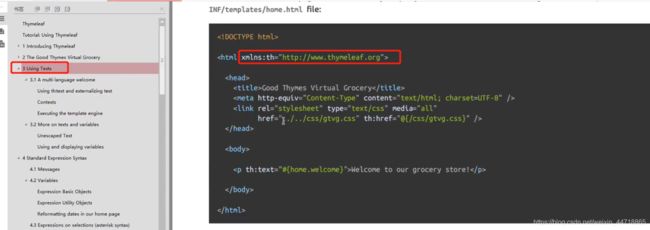
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
3、我们去编写下前端页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>dxj1016</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>测试页面</h1>
<!-- 所有的html元素都可以被thymeleaf替换接管:th:元素名 -->
<!--th:text就是将div中的内容设置为它指定的值,和之前学习的Vue一样-->
<div th:text="${msg}"></div>
</body>
</html>
3.6、Thymeleaf的使用语法
Thymeleaf 官网
1、我们可以使用任意的 th:attr 来替换Html中原生属性的值!

2、我们能写哪些表达式呢?
Simple expressions:(表达式语法)
Variable Expressions: ${...}:获取变量值;OGNL;
1)、获取对象的属性、调用方法
2)、使用内置的基本对象:#18
#ctx : the context object.
#vars: the context variables.
#locale : the context locale.
#request : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletRequest object.
#response : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletResponse object.
#session : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpSession object.
#servletContext : (only in Web Contexts) the ServletContext object.
3)、内置的一些工具对象:
#execInfo : information about the template being processed.
#uris : methods for escaping parts of URLs/URIs
#conversions : methods for executing the configured conversion service (if any).
#dates : methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc.
#calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects.
#numbers : methods for formatting numeric objects.
#strings : methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc.
#objects : methods for objects in general.
#bools : methods for boolean evaluation.
#arrays : methods for arrays.
#lists : methods for lists.
#sets : methods for sets.
#maps : methods for maps.
#aggregates : methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections.
==================================================================================
Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}:选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样;
Message Expressions: #{...}:获取国际化内容
Link URL Expressions: @{...}:定义URL;
Fragment Expressions: ~{...}:片段引用表达式
Literals(字面量)
Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,…
Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,…
Boolean literals: true , false
Null literal: null
Literal tokens: one , sometext , main ,…
Text operations:(文本操作)
String concatenation: +
Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}|
Arithmetic operations:(数学运算)
Binary operators: + , - , * , / , %
Minus sign (unary operator): -
Boolean operations:(布尔运算)
Binary operators: and , or
Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not
Comparisons and equality:(比较运算)
Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne )
Conditional operators:条件运算(三元运算符)
If-then: (if) ? (then)
If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
Special tokens:
No-Operation: _
3.7、练习测试:
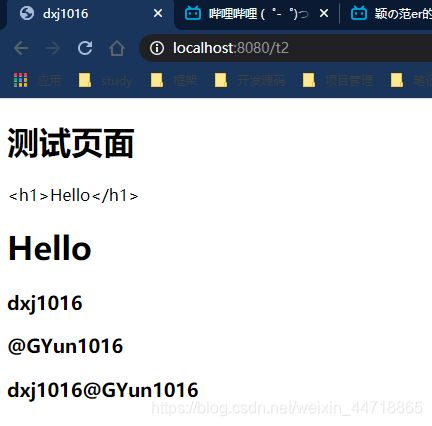
1、 我们编写一个Controller,放一些数据
@RequestMapping("/t2")
public String test2(Map<String,Object> map){
//存入数据
map.put("msg","Hello
");
map.put("users", Arrays.asList("dxj1016","@GYun1016"));
//classpath:/templates/test.html
return "test";
}
2、测试页面取出数据
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>dxj1016</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>测试页面</h1>
<!-- 所有的html元素都可以被thymeleaf替换接管:th:元素名 -->
<!--th:text就是将div中的内容设置为它指定的值,和之前学习的Vue一样-->
<div th:text="${msg}"></div>
<!--不转义-->
<div th:utext="${msg}"></div>
<!--遍历数据-->
<!--th:each每次遍历都会生成当前这个标签:官网#9-->
<h3 th:each="user :${users}" th:text="${user}"></h3>
<h3>
<!--行内写法:官网#12-->
<span th:each="user:${users}">[[${user}]]</span>
</h3>
</body>
</html>
4、MVC自动配置原理
官方文档
官方文档解析:
Spring MVC Auto-configuration
// Spring Boot为Spring MVC提供了自动配置,它可以很好地与大多数应用程序一起工作。
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications.
// 自动配置在Spring默认设置的基础上添加了以下功能:
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s defaults:
// 包含视图解析器
Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans.
// 支持静态资源文件夹的路径,以及webjars
Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars
// 自动注册了Converter:
// 转换器,这就是我们网页提交数据到后台自动封装成为对象的东西,比如把"1"字符串自动转换为int类型
// Formatter:【格式化器,比如页面给我们了一个2019-8-10,它会给我们自动格式化为Date对象】
Automatic registration of Converter, GenericConverter, and Formatter beans.
// HttpMessageConverters
// SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的的,比如我们要把一个User对象转换为JSON字符串,可以去看官网文档解释;
Support for HttpMessageConverters (covered later in this document).
// 定义错误代码生成规则的
Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver (covered later in this document).
// 首页定制
Static index.html support.
// 图标定制
Custom Favicon support (covered later in this document).
// 初始化数据绑定器:帮我们把请求数据绑定到JavaBean中!
Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean (covered later in this document).
/*
如果您希望保留Spring Boot MVC功能,并且希望添加其他MVC配置(拦截器、格式化程序、视图控制器和其他功能),则可以添加自己
的@configuration类,类型为webmvcconfiguer,但不添加@EnableWebMvc。如果希望提供
RequestMappingHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerAdapter或ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver的自定义
实例,则可以声明WebMVCregistrationAdapter实例来提供此类组件。
*/
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features and you want to add additional MVC configuration
(interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own
@Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide
custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance to provide such components.
// 如果您想完全控制Spring MVC,可以添加自己的@Configuration,并用@EnableWebMvc进行注释。
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
4.1、ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 内容协商视图解析器
- 自动配置了ViewResolver,就是我们之前学习的SpringMVC的视图解析器;
- 即根据方法的返回值取得视图对象(View),然后由视图对象决定如何渲染(转发,重定向)。
- 我们去看看这里的源码:我们找到 WebMvcAutoConfiguration , 然后搜索ContentNegotiatingViewResolver。找到如下方法!

- ContentNegotiatingViewResolver使用所有其他视图解析器来定位视图,因此它应该具有较高的优先级
- 我们可以点进ContentNegotiatingViewResolver类看看!找到对应的解析视图的代码;

- @Nullable // 注解说明:@Nullable 即参数可为null;
- getCandidateViews是获取候选的视图对象,点进去这个类中看看
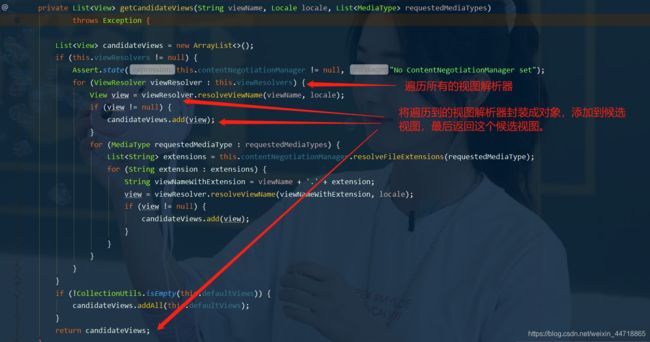
- 我们继续点进去看,他是怎么获得候选的视图的呢?
getCandidateViews中看到他是把所有的视图解析器拿来,进行while循环,挨个解析!
Iterator var5 = this.viewResolvers.iterator();
- 所以得出结论:ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 这个视图解析器就是用来组合所有的视图解析器的
- 我们再去研究下他的组合逻辑,看到有个属性viewResolvers,看看它是在哪里进行赋值的!
protected void initServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 这里它是从beanFactory工具中获取容器中的所有视图解析器
// ViewRescolver.class 把所有的视图解析器来组合的
Collection<ViewResolver> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(this.obtainApplicationContext(), ViewResolver.class).values();
ViewResolver viewResolver;
if (this.viewResolvers == null) {
this.viewResolvers = new ArrayList(matchingBeans.size());
}
// ...............
}
- 既然它是在容器中去找视图解析器,我们是否可以猜想,我们就可以去实现一个视图解析器了呢?
- 我们可以自己给容器中去添加一个视图解析器;这个类就会帮我们自动的将它组合进来;我们去实现一下
package com.spring.config;
//dispatchservlet类中的doDispatch方法,点击进去给doDispatch方法打个断点,然后debug看看
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
// ViewResolver实现了视图解析器接口的类,我们就可以把他看做视图解析器
@Bean //放到bean中
public ViewResolver myViewResolver(){
return new MyViewResolver();
}
//我们写一个静态内部类,视图解析器就需要实现ViewResolver接口
// 自定义一个自己的视图解析器MyViewResolver
public static class MyViewResolver implements ViewResolver{
@Override
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
return null;
}
}
}
- 怎么看我们自己写的视图解析器有没有起作用呢?双击shift搜索DispatcherServlet找到doServlet方法中调用doDispatch方法,点击doDispatch方法进去给doDispatch方法加个断点进行调试一下,因为所有的请求都会走到这个方法中
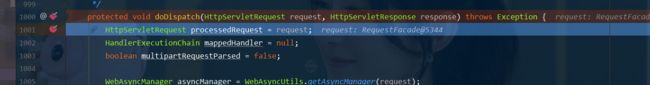
- 我们启动我们的项目,然后随便访问一个页面,看一下Debug信息;找到this,找到视图解析器,我们看到我们自己定义的就在这里了;
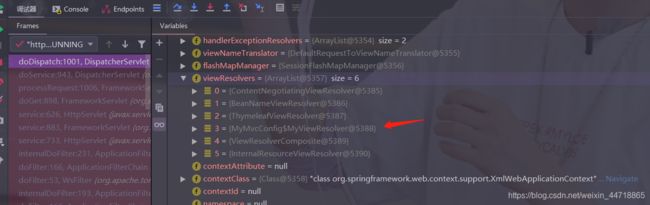
- 如果,你想diy(自定义)一些定制化的功能,只要写这个组件,然后将他交给springboot,springboot就会帮我们自动装配!
4.2、转换器和格式化器
- 在WebMvcAutoConfiguration类中搜索FormattingConversionService找到格式化转换器:
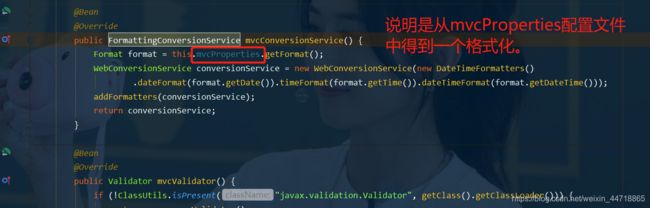
- 进去getFormat看看
- 继续进去format看看

- 继续进去Format这个类中看看
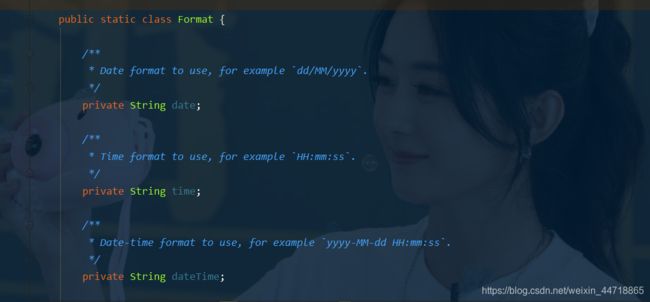
- 可以看到在我们的Properties文件中,我们可以进行自动配置它!
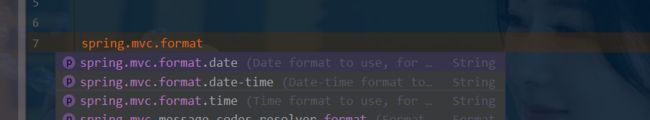
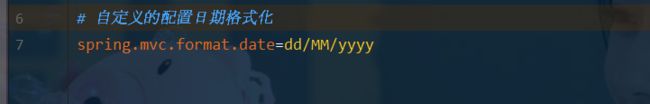
- 如果配置了自己的格式化方式,就会注册到Bean中生效,我们可以在配置文件中配置日期格式化的规则:
4.3、修改SpringBoot的默认配置
- 这么多的自动配置,原理都是一样的,通过这个WebMVC的自动配置原理分析,我们要学会一种学习方式,通过源码探究,得出结论;这个结论一定是属于自己的,而且一通百通。
- SpringBoot的底层,大量用到了这些设计细节思想,所以,没事需要多阅读源码!得出结论
- SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(如果用户自己配置@bean),如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有就用自动配置的;
- 如果有些组件可以存在多个,比如我们的视图解析器,就将用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来!
扩展使用SpringMVC 官方文档如下:
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features and you want to add additional MVC configuration (interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance to provide such components.
- 我们要做的就是编写一个@Configuration注解类,并且类型要为WebMvcConfigurer,还不能标注@EnableWebMvc注解;我们去自己写一个;我们新建一个包叫config,写一个类MyMvcConfig;
//应为类型要求为WebMvcConfigurer,所以我们实现其接口
//可以使用自定义类扩展MVC的功能
//如果我们要扩展springmvc,官方建议我们这样做。
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//视图跳转
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// 浏览器发送/test , 就会跳转到test页面;
registry.addViewController("/test").setViewName("test");
}
}
- 我们去浏览器访问一下:
- 确实也跳转过来了!所以说,我们要扩展SpringMVC,官方就推荐我们这么去使用,既保SpringBoot留所有的自动配置,也能用我们扩展的配置!
- @EnableWebMvc这个注解导入了一个类:DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration:从容器中获取所有的webmvc。
我们可以去分析一下原理:
1、WebMvcAutoConfiguration 是 SpringMVC的自动配置类,里面有一个类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter
2、这个类上有一个注解,在做其他自动配置时会导入:@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
3、我们点进EnableWebMvcConfiguration这个类看一下,它继承了一个父类:DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration
这个父类中有这样一段代码:
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
// 从容器中获取所有的webmvcConfigurer
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
}
}
4、我们可以在这个类中去寻找一个我们刚才设置的viewController当做参考,发现它调用了一个
protected void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.addViewControllers(registry);
}
5、我们点进去看一下
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
Iterator var2 = this.delegates.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
// 将所有的WebMvcConfigurer相关配置来一起调用!包括我们自己配置的和Spring给我们配置的
WebMvcConfigurer delegate = (WebMvcConfigurer)var2.next();
delegate.addViewControllers(registry);
}
}
所以得出结论:所有的WebMvcConfiguration都会被作用,不止Spring自己的配置类,我们自己的配置类当然也会被调用;
4.4、全面接管SpringMVC
官方文档:
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC
you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
- 全面接管即:SpringBoot对SpringMVC的自动配置不需要了,所有都是我们自己去配置!
- 只需在我们的配置类中要加一个@EnableWebMvc。
- 我们看下如果我们全面接管了SpringMVC了,我们之前SpringBoot给我们配置的静态资源映射一定会无效,我们可以去测试一下;
配置类:
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//视图跳转
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// 浏览器发送/test , 就会跳转到test页面;
registry.addViewController("/test").setViewName("test");
}
test.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>dxj1016</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>测试页面</h1>
</body>
</html>
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>dxj1016</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>首页</h1>
</body>
</html>
思考问题?为什么加了一个注解,自动配置就失效了!我们看下源码:
1、这里发现它是导入了一个类,我们可以继续进去看
@Import({DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class})
public @interface EnableWebMvc {
}
2、它继承了一个父类 WebMvcConfigurationSupport
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
// ......
}
3、我们来回顾一下Webmvc自动配置类
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
// 这个注解的意思就是:容器中没有这个组件的时候,这个自动配置类才生效
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
}
总结一句话:@EnableWebMvc将WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件导入进来了;而导入的WebMvcConfigurationSupport只是SpringMVC最基本的功能!在SpringBoot中会有非常多的扩展配置,只要看见了这个,我们就应该多留心注意.