leetcode 二叉树
二叉树
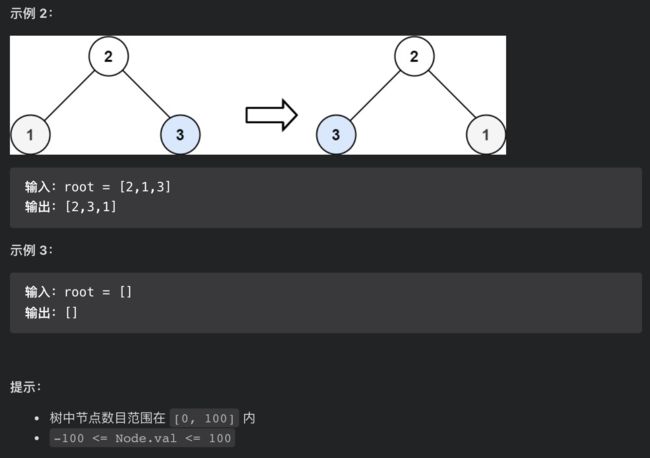
226. 翻转二叉树
思路分析
通过观察,我们发现只要把二叉树上的每一个节点的左右子节点进行交换,最后的结果就是完全翻转之后的二叉树。
这道题目比较简单,关键思路在于我们发现翻转整棵树就是交换每个节点的左右子节点,于是我们把交换左右子节点的代码放在了前序遍历的位置。
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/invert-binary-tree/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-28 3:32 PM
*/
public class _226_翻转二叉树 {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
// base case
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
/**** 前序遍历位置 ****/
// root 节点需要交换它的左右子节点
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
// 让左右子节点继续翻转它们的子节点
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
}
}
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
思路分析
题目的意思就是把二叉树的每一层节点都用 next 指针连接起来:
而且题目说了,输入是一棵「完美二叉树」,形象地说整棵二叉树是一个正三角形,除了最右侧的节点 next 指针会指向 null,其他节点的右侧一定有相邻的节点。
这道题怎么做呢?把每一层的节点穿起来,是不是只要把每个节点的左右子节点都穿起来就行了?
我们可以模仿上一道题,写出如下代码:
Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null || root.left == null) {
return root;
}
root.left.next = root.right;
connect(root.left);
connect(root.right);
return root;
}
这样其实有很大问题,再看看这张图:
节点 5 和节点 6 不属于同一个父节点,那么按照这段代码的逻辑,它俩就没办法被穿起来,这是不符合题意的。
回想刚才说的,二叉树的问题难点在于,如何把题目的要求细化成每个节点需要做的事情,但是如果只依赖一个节点的话,肯定是没办法连接「跨父节点」的两个相邻节点的。
那么,我们的做法就是增加函数参数,一个节点做不到,我们就给他安排两个节点,「将每一层二叉树节点连接起来」可以细化成「将每两个相邻节点都连接起来」。
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-28 7:52 PM
*/
public class _116_填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 {
// 主函数
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
connectTwoNode(root.left, root.right);
return root;
}
// 辅助函数
public void connectTwoNode(Node node1, Node node2) {
if (node1 == null || node2 == null) {
return;
}
/**** 前序遍历位置 ****/
// 将传入的两个节点连接
node1.next = node2;
// 连接相同父节点的两个子节点
connectTwoNode(node1.left, node1.right);
connectTwoNode(node2.left, node2.right);
// 连接跨越父节点的两个子节点
connectTwoNode(node1.right, node2.left);
}
}
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
}
114. 二叉树展开为链表
思路分析
我们尝试给出这个函数的定义:
给 flatten 函数输入一个节点 root,那么以 root 为根的二叉树就会被拉平为一条链表。
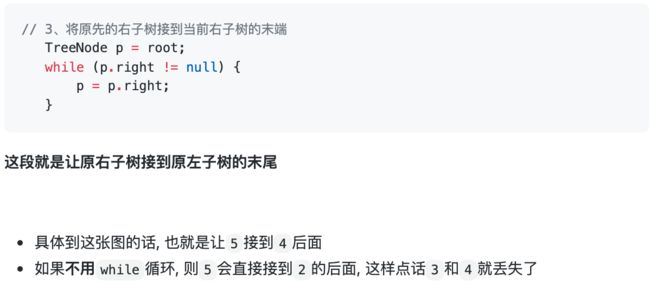
我们再梳理一下,如何按题目要求把一棵树拉平成一条链表?很简单,以下流程:
1、将 root 的左子树和右子树拉平。
2、将 root 的右子树接到左子树下方,然后将整个左子树作为右子树。
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/
* 核心思路都是将左节点放到右节点; 旧的右节点,再挂载到当前右节点最下面
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-28 8:15 PM
*/
public class _114_二叉树展开为链表 {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
flatten(root.left);
flatten(root.right);
/**** 后序遍历位置 ****/
// 1、左右子树已经被拉平成一条链表
TreeNode left = root.left;
TreeNode right = root.right;
// 2、将左子树作为右子树
root.left = null;
root.right = left;
// 3、将原先的右子树接到当前右子树的末端
TreeNode p = root;
while (p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
}
p.right = right;
}
}
654. 最大二叉树
思路分析
先明确根节点做什么?对于构造二叉树的问题,根节点要做的就是把想办法把自己构造出来。
我们肯定要遍历数组把找到最大值maxVal,把根节点root做出来,然后对maxVal左边的数组和右边的数组进行递归调用,作为root的左右子树。
按照题目给出的例子,输入的数组为[3,2,1,6,0,5],对于整棵树的根节点来说,其实在做这件事:
TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree([3,2,1,6,0,5]) {
// 找到数组中的最大值
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(6);
// 递归调用构造左右子树
root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree([3,2,1]);
root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree([0,5]);
return root;
}
再详细一点,就是如下伪码:
TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
if (nums is empty) return null;
// 找到数组中的最大值
int maxVal = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > maxVal) {
maxVal = nums[i];
index = i;
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(maxVal);
// 递归调用构造左右子树
root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums[0..index-1]);
root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums[index+1..nums.length-1]);
return root;
}
看懂了吗?对于每个根节点,只需要找到当前nums中的最大值和对应的索引,然后递归调用左右数组构造左右子树即可。
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-binary-tree/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-29 9:45 PM
*/
public class _654_最大二叉树 {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
return build(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) {
// base case
if (lo > hi) {
return null;
}
// 找到数组中的最大值和对应的索引
int index = -1, maxVal = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
if (maxVal < nums[i]) {
index = i;
maxVal = nums[i];
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(maxVal);
// 递归调用构造左右子树
root.left = build(nums, lo, index - 1);
root.right = build(nums, index + 1, hi);
return root;
}
}
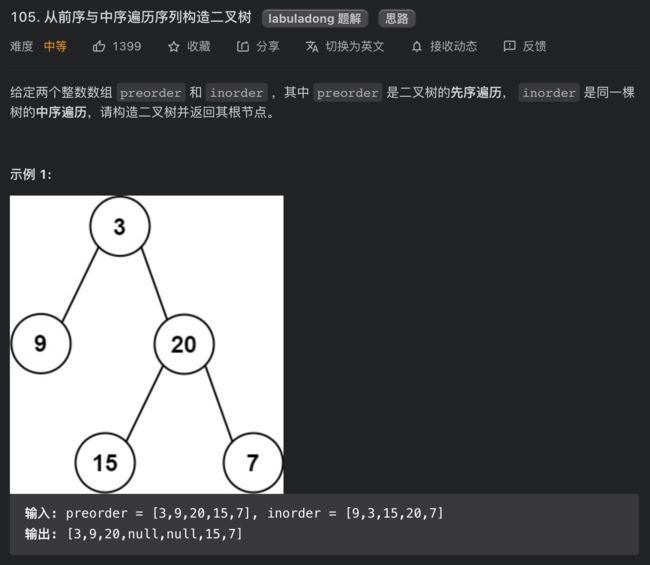
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
思路分析
类似上一题,我们肯定要想办法确定根节点的值,把根节点做出来,然后递归构造左右子树即可。
我们先来回顾一下,前序遍历和中序遍历的结果有什么特点?
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
// 前序遍历
preorder.add(root.val);
traverse(root.left);
traverse(root.right);
}
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root.left);
// 中序遍历
inorder.add(root.val);
traverse(root.right);
}
找到根节点是很简单的,前序遍历的第一个值preorder[0]就是根节点的值,关键在于如何通过根节点的值,将preorder和postorder数组划分成两半,构造根节点的左右子树?
换句话说,对于以下代码中的?部分应该填入什么:
/* 主函数 */
TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return build(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1,
inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
/*
若前序遍历数组为 preorder[preStart..preEnd],
后续遍历数组为 postorder[postStart..postEnd],
构造二叉树,返回该二叉树的根节点
*/
TreeNode build(int[] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd,
int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd) {
// root 节点对应的值就是前序遍历数组的第一个元素
int rootVal = preorder[preStart];
// rootVal 在中序遍历数组中的索引
int index = 0;
for (int i = inStart; i <= inEnd; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// 递归构造左右子树
root.left = build(preorder, ?, ?,
inorder, ?, ?);
root.right = build(preorder, ?, ?,
inorder, ?, ?);
return root;
}
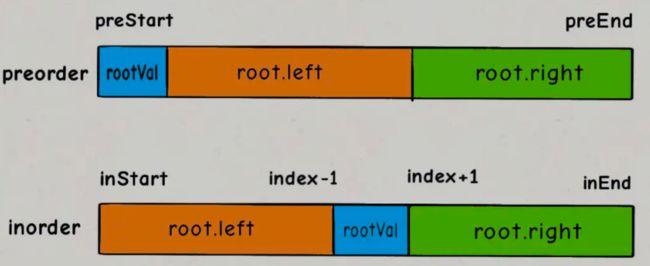
对于代码中的rootVal和index变量,就是下图这种情况:
现在我们来看图做填空题,下面这几个问号处应该填什么:
root.left = build(preorder, ?, ?,
inorder, ?, ?);
root.right = build(preorder, ?, ?,
inorder, ?, ?);
对于左右子树对应的inorder数组的起始索引和终止索引比较容易确定:
root.left = build(preorder, ?, ?,
inorder, inStart, index - 1);
root.right = build(preorder, ?, ?,
inorder, index + 1, inEnd);
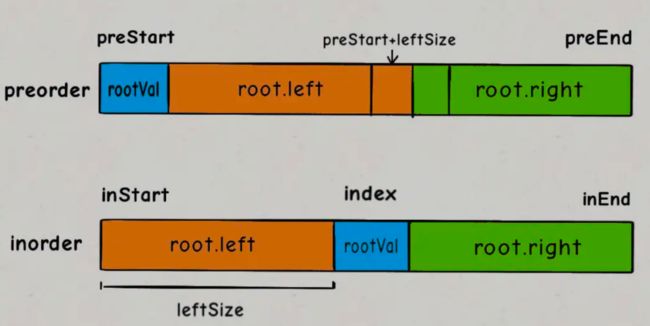
对于preorder数组呢?如何确定左右数组对应的起始索引和终止索引?
这个可以通过左子树的节点数推导出来,假设左子树的节点数为leftSize,那么preorder数组上的索引情况是这样的:
看着这个图就可以把preorder对应的索引写进去了:
int leftSize = index - inStart;
root.left = build(preorder, preStart + 1, preStart + leftSize,
inorder, inStart, index - 1);
root.right = build(preorder, preStart + leftSize + 1, preEnd,
inorder, index + 1, inEnd);
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-29 10:07 PM
*/
public class _105_从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return build(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
/**
* 若前序遍历数组为 preorder[preStart..preEnd],
* 后续遍历数组为 postorder[postStart..postEnd],
* 构造二叉树,返回该二叉树的根节点
*/
public TreeNode build(int[] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd, int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd) {
if (preStart > preEnd) {
return null;
}
// root 节点对应的值就是前序遍历数组的第一个元素
int rootVal = preorder[preStart];
// rootVal 在中序遍历数组中的索引
int index = 0;
for (int i = inStart; i <= inEnd; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// 左子树的节点个数
int leftSize = index - inStart;
// 递归构造左右子树
root.left = build(preorder, preStart + 1, preStart + leftSize, inorder, inStart, index - 1);
root.right = build(preorder, preStart + leftSize + 1, preEnd, inorder, index + 1, inEnd);
return root;
}
}
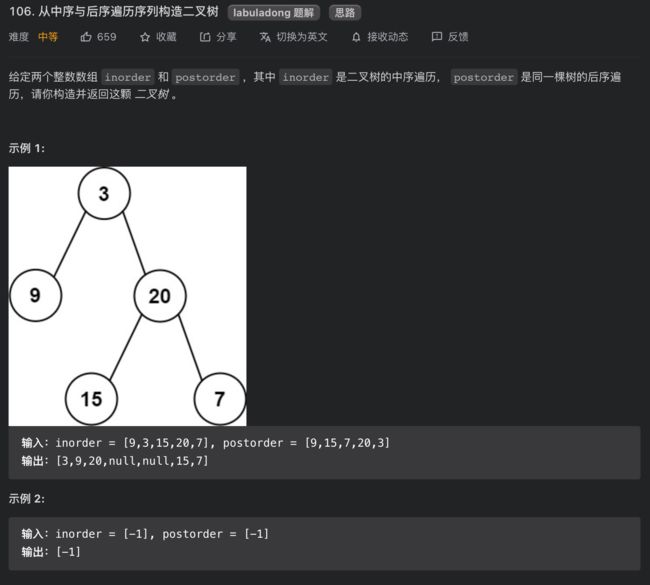
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
思路分析
类似的,看下后序和中序遍历的特点:
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root.left);
traverse(root.right);
// 前序遍历
postorder.add(root.val);
}
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root.left);
// 中序遍历
inorder.add(root.val);
traverse(root.right);
}
这样的遍历顺序差异,导致了preorder和inorder数组中的元素分布有如下特点:
这道题和上一题的关键区别是,后序遍历和前序遍历相反,根节点对应的值为postorder的最后一个元素。
整体的算法框架和上一题非常类似,我们依然写一个辅助函数build:
TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
return build(inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1,
postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1);
}
TreeNode build(int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd,
int[] postorder, int postStart, int postEnd) {
// root 节点对应的值就是后序遍历数组的最后一个元素
int rootVal = postorder[postEnd];
// rootVal 在中序遍历数组中的索引
int index = 0;
for (int i = inStart; i <= inEnd; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// 递归构造左右子树
root.left = build(preorder, ?, ?,
inorder, ?, ?);
root.right = build(preorder, ?, ?,
inorder, ?, ?);
return root;
}
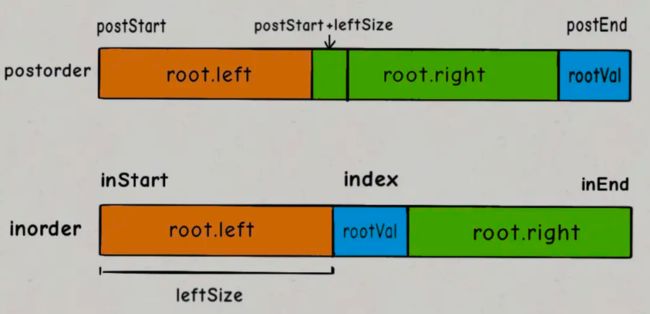
现在postoder和inorder对应的状态如下:
我们可以按照上图将问号处的索引正确填入:
int leftSize = index - inStart;
root.left = build(inorder, inStart, index - 1,
postorder, postStart, postStart + leftSize - 1);
root.right = build(inorder, index + 1, inEnd,
postorder, postStart + leftSize, postEnd - 1);
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-29 10:26 PM
*/
public class _106_从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
return build(inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1, postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postStart, int postEnd) {
if (inStart > inEnd) {
return null;
}
// root 节点对应的值就是后序遍历数组的最后一个元素
int rootVal = postorder[postEnd];
int index = 0;
for (int i = inStart; i <= inEnd; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
// 左子树的节点个数
int leftSize = index - inStart;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// 递归构造左右子树
root.left = build(inorder, inStart, index - 1, postorder, postStart, postStart + leftSize - 1);
root.right = build(inorder, index + 1, inEnd, postorder, postStart + leftSize, postEnd - 1);
return root;
}
}
652. 寻找重复的子树
思路分析
输入是一棵二叉树的根节点root,返回的是一个列表,里面装着若干个二叉树节点,这些节点对应的子树在原二叉树中是存在重复的。
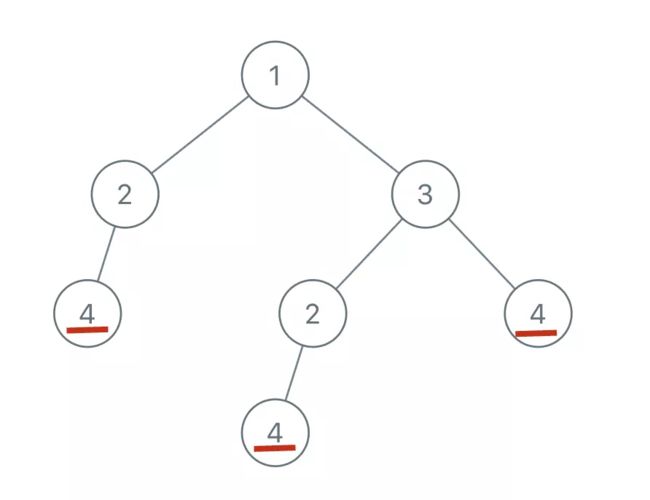
说起来比较绕,举例来说,比如输入如下的二叉树:
首先,节点 4 本身可以作为一棵子树,且二叉树中有多个节点 4:
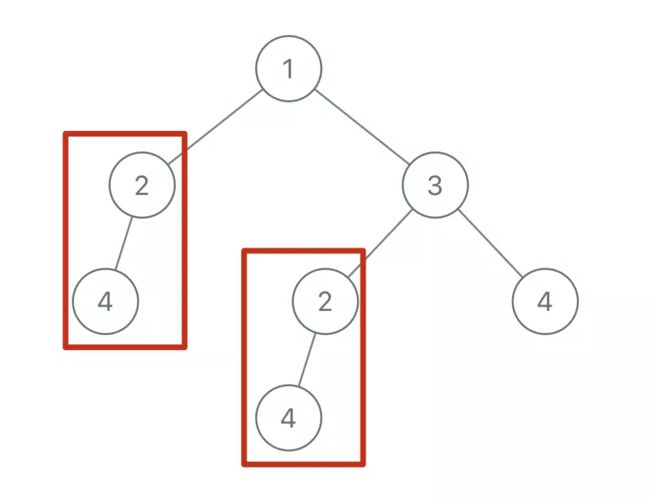
类似的,还存在两棵以 2 为根的重复子树:
那么,我们返回的List中就应该有两个TreeNode,值分别为 4 和 2(具体是哪个节点都无所谓)。
这题咋做呢?还是老套路,先思考,对于某一个节点,它应该做什么。
比如说,你站在图中这个节点 2 上:
如果你想知道以自己为根的子树是不是重复的,是否应该被加入结果列表中,你需要知道什么信息?
你需要知道以下两点:
1、以我为根的这棵二叉树(子树)长啥样?
2、以其他节点为根的子树都长啥样?
这就叫知己知彼嘛,我得知道自己长啥样,还得知道别人长啥样,然后才能知道有没有人跟我重复,对不对?
好,那我们一个一个来解决,先来思考,我如何才能知道以自己为根的二叉树长啥样?
其实看到这个问题,就可以判断本题要使用「后序遍历」框架来解决:
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root.left);
traverse(root.right);
/* 解法代码的位置 */
}
为什么?很简单呀,我要知道以自己为根的子树长啥样,是不是得先知道我的左右子树长啥样,再加上自己,就构成了整棵子树的样子?
如果你还绕不过来,我再来举个非常简单的例子:计算一棵二叉树有多少个节点。这个代码应该会写吧:
int count(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
// 先算出左右子树有多少节点
int left = count(root.left);
int right = count(root.right);
/* 后序遍历代码位置 */
// 加上自己,就是整棵二叉树的节点数
int res = left + right + 1;
return res;
}
这不就是标准的后序遍历框架嘛,和我们本题在思路上没啥区别对吧。
现在,明确了要用后序遍历,那应该怎么描述一棵二叉树的模样呢?二叉树的前序/中序/后序遍历结果可以描述二叉树的结构。
所以,我们可以通过拼接字符串的方式把二叉树序列化,看下代码:
String traverse(TreeNode root) {
// 对于空节点,可以用一个特殊字符表示
if (root == null) {
return "#";
}
// 将左右子树序列化成字符串
String left = traverse(root.left);
String right = traverse(root.right);
/* 后序遍历代码位置 */
// 左右子树加上自己,就是以自己为根的二叉树序列化结果
String subTree = left + "," + right + "," + root.val;
return subTree;
}
我们用非数字的特殊符#表示空指针,并且用字符,分隔每个二叉树节点值,这属于序列化二叉树的套路了,不多说。
注意我们subTree是按照左子树、右子树、根节点这样的顺序拼接字符串,也就是后序遍历顺序。你完全可以按照前序或者中序的顺序拼接字符串,因为这里只是为了描述一棵二叉树的样子,什么顺序不重要。
这样,我们第一个问题就解决了,对于每个节点,递归函数中的subTree变量就可以描述以该节点为根的二叉树。
现在我们解决第二个问题,我知道了自己长啥样,怎么知道别人长啥样?这样我才能知道有没有其他子树跟我重复对吧。
这很简单呀,我们借助一个外部数据结构,让每个节点把自己子树的序列化结果存进去,这样,对于每个节点,不就可以知道有没有其他节点的子树和自己重复了么?
初步思路可以使用HashSet记录子树,代码如下:
// 记录所有子树
HashSet<String> memo = new HashSet<>();
// 记录重复的子树根节点
LinkedList<TreeNode> res = new LinkedList<>();
String traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return "#";
}
String left = traverse(root.left);
String right = traverse(root.right);
String subTree = left + "," + right+ "," + root.val;
if (memo.contains(subTree)) {
// 有人和我重复,把自己加入结果列表
res.add(root);
} else {
// 暂时没人跟我重复,把自己加入集合
memo.add(subTree);
}
return subTree;
}
但是呢,这有个问题,如果出现多棵重复的子树,结果集res中必然出现重复,而题目要求不希望出现重复。
为了解决这个问题,可以把HashSet升级成HashMap,额外记录每棵子树的出现次数:
// 记录所有子树以及出现的次数
HashMap<String, Integer> memo = new HashMap<>();
// 记录重复的子树根节点
LinkedList<TreeNode> res = new LinkedList<>();
/* 主函数 */
List<TreeNode> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root);
return res;
}
/* 辅助函数 */
String traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return "#";
}
String left = traverse(root.left);
String right = traverse(root.right);
String subTree = left + "," + right+ "," + root.val;
int freq = memo.getOrDefault(subTree, 0);
// 多次重复也只会被加入结果集一次
if (freq == 1) {
res.add(root);
}
// 给子树对应的出现次数加一
memo.put(subTree, freq + 1);
return subTree;
}
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-duplicate-subtrees/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-29 11:00 PM
*/
public class _652_寻找重复的子树 {
// 记录所有子树以及出现的次数
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// 记录重复的子树根节点
LinkedList<TreeNode> res = new LinkedList<>();
public List<TreeNode> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root);
return res;
}
/* 辅助函数 */
public String traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return "#";
}
String left = traverse(root.left);
String right = traverse(root.right);
String subTree = left + "," + right + "," + root.val;
int freq = map.getOrDefault(subTree, 0);
// 多次重复也只会被加入结果集一次
if (freq == 1) {
res.add(root);
}
// 给子树对应的出现次数加一
map.put(subTree, freq + 1);
return subTree;
}
}
1373. 二叉搜索子树的最大键值和
思路分析
traverse(root)返回一个大小为 4 的 int 数组,我们暂且称它为res,其中:
res[0]记录以root为根的二叉树是否是 BST,若为 1 则说明是 BST,若为 0 则说明不是 BST;
res[1]记录以root为根的二叉树所有节点中的最小值;
res[2]记录以root为根的二叉树所有节点中的最大值;
res[3]记录以root为根的二叉树所有节点值之和。
其实这就是把之前分析中说到的几个值放到了res数组中,最重要的是,我们要试图通过left和right正确推导出res数组。
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-sum-bst-in-binary-tree/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-30 11:13 AM
*/
public class _1373_二叉搜索子树的最大键值和 {
// 全局变量,记录最终结果
int maxSum = 0;
public int maxSumBST(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root);
return maxSum;
}
public int[] traverse(TreeNode root) {
// base case
if (root == null) {
return new int[]{1, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MIN_VALUE, 0};
}
// 递归计算左右子树
int[] left = traverse(root.left);
int[] right = traverse(root.right);
/******* 后序遍历位置 *******/
int[] res = new int[4];
// 这个 if 在判断以 root 为根的二叉树是不是 BST
if (left[0] == 1 && right[0] == 1 && root.val > left[2] && root.val < right[1]) {
// 以 root 为根的二叉树是 BST
res[0] = 1;
// 计算以 root 为根的这棵 BST 的最小值
res[1] = Math.min(left[1], root.val);
// 计算以 root 为根的这棵 BST 的最大值
res[2] = Math.max(right[2], root.val);
// 计算以 root 为根的这棵 BST 所有节点之和
res[3] = left[3] + right[3] + root.val;
// 更新全局变量
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, res[3]);
} else {
// 以 root 为根的二叉树不是 BST
res[0] = 0;
// 其他的值都没必要计算了,因为用不到
}
return res;
}
}
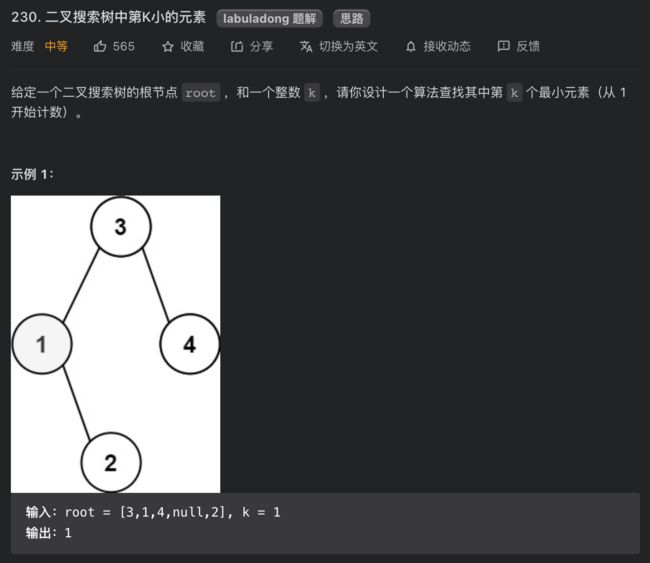
230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
思路分析
这个需求很常见吧,一个直接的思路就是升序排序,然后找第k个元素呗。BST 的中序遍历其实就是升序排序的结果,找第k个元素肯定不是什么难事。
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-30 11:46 AM
*/
public class _230_二叉搜索树中第K小的元素 {
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
// 利用 BST 的中序遍历特性
traverse(root, k);
return res;
}
// 记录结果
int res = 0;
// 记录当前元素的排名
int rank = 0;
public void traverse(TreeNode root, int k) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
traverse(root.left, k);
/* 中序遍历代码位置 */
rank++;
if (k == rank) {
// 找到第 k 小的元素
res = root.val;
return;
}
traverse(root.right, k);
}
}
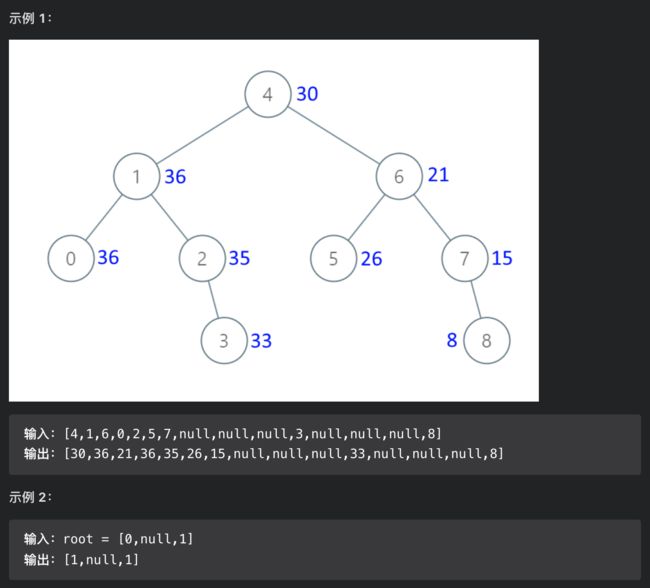
538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
思路分析
题目应该不难理解,比如图中的节点 5,转化成累加树的话,比 5 大的节点有 6,7,8,加上 5 本身,所以累加树上这个节点的值应该是 5+6+7+8=26。
BST 的中序遍历代码可以升序打印节点的值:
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
traverse(root.left);
// 中序遍历代码位置
print(root.val);
traverse(root.right);
}
那如果我想降序打印节点的值怎么办?
很简单,只要把递归顺序改一下就行了:
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
// 先递归遍历右子树
traverse(root.right);
// 中序遍历代码位置
print(root.val);
// 后递归遍历左子树
traverse(root.left);
}
这段代码可以从大到小降序打印 BST 节点的值,如果维护一个外部累加变量sum,然后把sum赋值给 BST 中的每一个节点,不就将 BST 转化成累加树了吗?
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-bst-to-greater-tree/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-30 12:25 PM
*/
public class _538_把二叉搜索树转换为累加树 {
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root);
return root;
}
// 记录累加和
int sum = 0;
public void traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
traverse(root.right);
// 维护累加和
sum += root.val;
// 将 BST 转化成累加树
root.val = sum;
traverse(root.left);
}
}
700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
思路分析
如果是在二叉树中寻找元素,可以这样写代码:
boolean isInBST(TreeNode root, int target) {
if (root == null) return false;
if (root.val == target) return true;
// 当前节点没找到就递归地去左右子树寻找
return isInBST(root.left, target)
|| isInBST(root.right, target);
}
这样写完全正确,但这段代码相当于穷举了所有节点,适用于所有普通二叉树。那么应该如何充分利用信息,把 BST 这个「左小右大」的特性用上?
很简单,其实不需要递归地搜索两边,类似二分查找思想,根据target和root.val的大小比较,就能排除一边。我们把上面的思路稍稍改动:
boolean isInBST(TreeNode root, int target) {
if (root == null) return false;
if (root.val == target)
return true;
if (root.val < target)
return isInBST(root.right, target);
if (root.val > target)
return isInBST(root.left, target);
// root 该做的事做完了,顺带把框架也完成了,妙
}
于是,我们对原始框架进行改造,抽象出一套针对 BST 的遍历框架:
void BST(TreeNode root, int target) {
if (root.val == target)
// 找到目标,做点什么
if (root.val < target)
BST(root.right, target);
if (root.val > target)
BST(root.left, target);
}
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-in-a-binary-search-tree/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-30 4:11 PM
*/
public class _700_二叉搜索树中的搜索 {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
// 去左子树搜索
if (root.val > val) {
return searchBST(root.left, val);
}
// 去右子树搜索
if (root.val < val) {
return searchBST(root.right, val);
}
return root;
}
}
701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
思路分析
对数据结构的操作无非遍历 + 访问,遍历就是「找」,访问就是「改」。具体到这个问题,插入一个数,就是先找到插入位置,然后进行插入操作。
上一个问题,我们总结了 BST 中的遍历框架,就是「找」的问题。直接套框架,加上「改」的操作即可。一旦涉及「改」,函数就要返回TreeNode类型,并且对递归调用的返回值进行接收。
TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
// 找到空位置插入新节点
if (root == null) return new TreeNode(val);
// if (root.val == val)
// BST 中一般不会插入已存在元素
if (root.val < val)
root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val);
if (root.val > val)
root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val);
return root;
}
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/insert-into-a-binary-search-tree/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-30 4:07 PM
*/
public class _701_二叉搜索树中的插入操作 {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
// 找到空位置插入新节点
if (root == null) {
return new TreeNode(val);
}
if (root.val > val) {
root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val);
}
if (root.val < val) {
root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val);
}
return root;
}
}
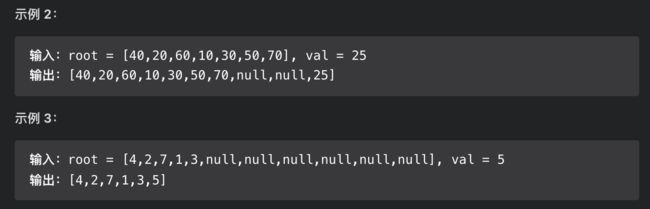
450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
思路分析
这个问题稍微复杂,跟插入操作类似,先「找」再「改」,先把框架写出来再说:
TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root.val == key) {
// 找到啦,进行删除
} else if (root.val > key) {
// 去左子树找
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
} else if (root.val < key) {
// 去右子树找
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
}
return root;
}
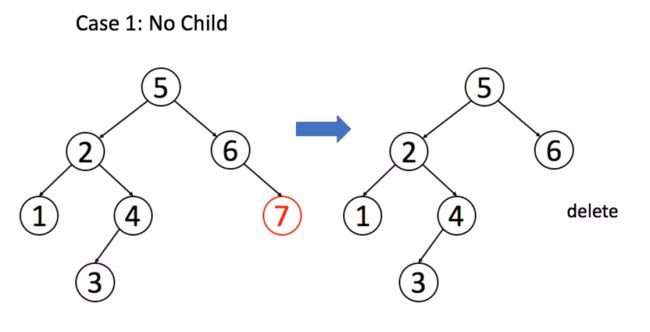
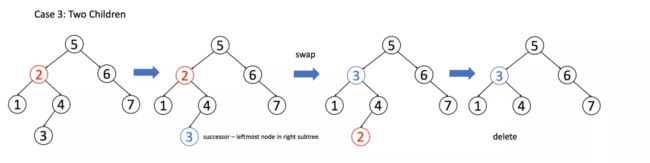
找到目标节点了,比方说是节点A,如何删除这个节点,这是难点。因为删除节点的同时不能破坏 BST 的性质。有三种情况,用图片来说明。
情况 1:
A恰好是末端节点,两个子节点都为空,那么它可以当场去世了。
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return null;
情况 2:
A只有一个非空子节点,那么它要让这个孩子接替自己的位置。
// 排除了情况 1 之后
if (root.left == null) return root.right;
if (root.right == null) return root.left;
情况 3:
A有两个子节点,麻烦了,为了不破坏 BST 的性质,A必须找到左子树中最大的那个节点,或者右子树中最小的那个节点来接替自己。我们以第二种方式讲解。
if (root.left != null && root.right != null) {
// 找到右子树的最小节点
TreeNode minNode = getMin(root.right);
// 把 root 改成 minNode
root.val = minNode.val;
// 转而去删除 minNode
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minNode.val);
}
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-30 12:39 PM
*/
public class _450_删除二叉搜索树中的节点 {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.val == key) {
// 这两个 if 把情况 1 和 2 都正确处理了
if (root.left == null) {
return root.right;
}
if (root.right == null) {
return root.left;
}
// 处理情况 3
// 找到右子树的最小值
TreeNode minNode = getMin(root.right);
root.val = minNode.val;
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minNode.val);
} else if (root.val > key) {
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
} else if (root.val < key) {
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
}
return root;
}
public TreeNode getMin(TreeNode node) {
// BST 最左边的就是最小的
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
}
98. 验证二叉搜索树
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-30 4:18 PM
*/
public class _98_验证二叉搜索树 {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return isValidBST(root, null, null);
}
/* 限定以 root 为根的子树节点必须满足 max.val > root.val > min.val */
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root, TreeNode min, TreeNode max) {
// base case
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
// 若 root.val 不符合 max 和 min 的限制,说明不是合法 BST
if (min != null && root.val <= min.val) {
return false;
}
if (max != null && root.val >= max.val) {
return false;
}
// 限定左子树的最大值是 root.val,右子树的最小值是 root.val
return isValidBST(root.left, min, root) && isValidBST(root.right, root, max);
}
}
96. 不同的二叉搜索树
思路分析
递归解法
比如说输入n = 3,算法返回 5,因为共有如下 5 种不同的 BST 结构存储{1,2,3}:
二叉树算法的关键就在于明确根节点需要做什么,其实 BST 作为一种特殊的二叉树,核心思路也是一样的。
举个例子,比如给算法输入n = 5,也就是说用{1,2,3,4,5}这些数字去构造 BST。
首先,这棵 BST 的根节点总共有几种情况?
显然有 5 种情况对吧,因为每个数字都可以作为根节点。
比如说我们固定3作为根节点,这个前提下能有几种不同的 BST 呢?
根据 BST 的特性,根节点的左子树都比根节点的值小,右子树的值都比根节点的值大。
所以如果固定3作为根节点,左子树节点就是{1,2}的组合,右子树就是{4,5}的组合。
左子树的组合数和右子树的组合数乘积就是3作为根节点时的 BST 个数。
我们这是说了3为根节点这一种特殊情况,其实其他的节点也是一样的。
动态规划解法
代码实现
递归解法
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-31 7:23 PM
*/
public class _96_不同的二叉搜索树 {
// 备忘录
int[][] memo;
public int numTrees(int n) {
// 备忘录的值初始化为 0
memo = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
// 计算闭区间 [1, n] 组成的 BST 个数
return count(1, n);
}
/**
* 计算闭区间 [lo, hi] 组成的 BST 个数
*/
public int count(int lo, int hi) {
// base case
if (lo > hi) { //虽然是个空区间,对应空节点null,但也算是一种情况
return 1;
}
// 查看备忘录
if (memo[lo][hi] != 0) {
return memo[lo][hi];
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
// i 的值作为根节点 root
int left = count(lo, i - 1);
int right = count(i + 1, hi);
// 左右子树的组合数乘积是 BST 的总数
res += left * right;
}
// 将结果存入备忘录
memo[lo][hi] = res;
return res;
}
}
动态规划解法
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-31 7:23 PM
*/
public class _96_不同的二叉搜索树_动态规划 {
public int numTrees(int n) {
// dp[i] 表示i个元素的二叉搜素树有多少种
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int num = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) { // 以 j 为根节点
num += dp[j - 1] * dp[i - j];
}
dp[i] = num;
}
return dp[n];
}
}
95. 不同的二叉搜索树 II
思路分析
比如说输入n = 3,算法返回一个列表,列表中存储着如下五棵 BST 的根节点:
明白了上道题构造合法 BST 的方法,这道题的思路也是一样的:
1、穷举root节点的所有可能。
2、递归构造出左右子树的所有合法 BST。
3、给root节点穷举所有左右子树的组合。
代码实现
/**
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees-ii/
*
* @author xiexu
* @create 2022-01-31 8:28 PM
*/
public class _95_不同的二叉搜索树_II {
public List<TreeNode> generateTrees(int n) {
if (n == 0) return new LinkedList<>();
// 构造闭区间 [1, n] 组成的 BST
return build(1, n);
}
/**
* 构造闭区间 [lo, hi] 组成的 BST
*/
public List<TreeNode> build(int lo, int hi) {
LinkedList<TreeNode> res = new LinkedList<>();
// base case
if (lo > hi) {
res.add(null);
return res;
}
// 1、穷举 root 节点的所有可能
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
// 2、递归构造出左右子树的所有合法 BST
List<TreeNode> leftTree = build(lo, i - 1);
List<TreeNode> rightTree = build(i + 1, hi);
// 3、给 root 节点穷举所有左右子树的组合
for (TreeNode left : leftTree) {
for (TreeNode right : rightTree) {
// i 作为根节点 root 的值
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(i);
root.left = left;
root.right = right;
res.add(root);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}