《视觉 SLAM 十四讲》V2 第 12 讲 建图
文章目录
-
- 12.2 单目稠密 重建
-
- 12.2.2 极线搜索 && 块匹配
- 12.2.3 高斯分布的深度滤波器
- 12.3 单目稠密重建 【Code】
-
- 待改进
- 12.3.4 图像间的变换
- 12.4 RGB-D 稠密建图
-
- 12.4.1 点云地图 【Code】
-
-
-
- 查询OpenCV版本 opencv_version
-
-
- 12.4.2 从点云 重建 网格 【Code】
-
-
-
- 查看PCL 版本 aptitude show libpcl-dev
-
-
- 12.4.3 八叉树地图(Octomap) 【灵活压缩、随时更新】
- 12.4.4 八叉树地图 【建模大场景】 【Code】
- 习题
-
- √ 题1
- √ 题2
- 题3
- 题4
- 题5
- 题6
单目SLAM 稠密 深度估计
单目 稠密 重建
RGB-D 重建 的地图形式
估计 相机运动轨迹 + 特征点空间位置
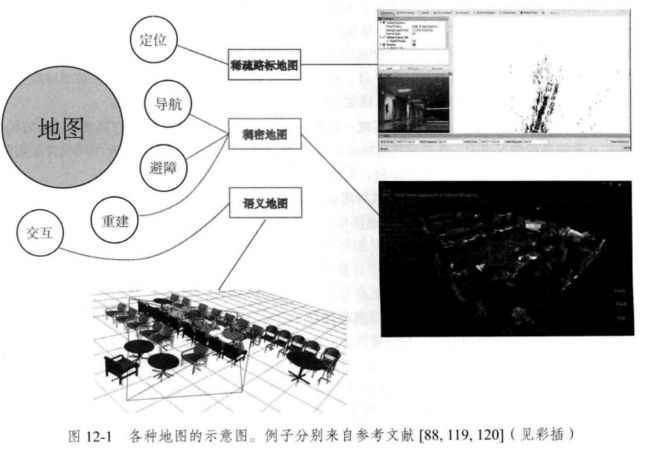
机器人SLAM:定位、导航、避障和交互
SLAM: 同时定位 与 建图
经典 SLAM 地图(路标点的集合)
视觉里程计、BA: 建模了路标点的位置
扫地机: 全局定位,导航,路径规划
增强现实设备: 将虚拟物叠加在现实物体之中, 处理虚拟物体与真实物体之间的遮挡关系。
定位(空间位姿信息): 把地图保存下来,这样只需对地图进行一次建模, 而不是每次启动机器人都重新做一次完整的SLAM
导航、避障:需要 稠密地图。哪些地方可通过
重建 三维视频通话、网上购物 纹理稠密
交互 语义地图
稀疏路标地图 只建模感兴趣部分 定位
稠密地图 建模 所有看到过的部分 导航避障
视觉SLAM 如何建 稠密地图
12.2 单目稠密 重建
获取像素点间距离的方法:
1、单目相机 三角化 计算像素之间的距离
2、双目相机, 利用左右目的视差 计算像素的距离
3、RGB-D相机 直接 获取 像素距离。
立体视觉(Stereo Vision)
移动单目相机 (移动视角的立体视觉(Moving View Stereo,MVS))
使用单目和双目 获取深度 费力不讨好。 计算量巨大、不可靠
场景: 室外,大场景
RGB-D: 量程、应用范围、光照限制。
极线搜索 块匹配
深度滤波技术 :多次使用 三角测量法 让深度估计收敛。
12.2.2 极线搜索 && 块匹配
单个像素的亮度 没有区分性 ——> 比较 像素块。
计算两个小块之间的差异:
不断 对不同图像 进行极线 搜索时, 估计的深度分布将如何变化。
12.2.3 高斯分布的深度滤波器
均匀-高斯混合分布的滤波器
12.3 单目稠密重建 【Code】
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make
./dense_mapping /home/xixi/Downloads/slambook2-master/ch12/semi_dense_mono/dataset/test_data
#include CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(dense_monocular)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Debug")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++17 -march=native -O3")
############### dependencies ######################
# Eigen
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
# OpenCV
find_package(OpenCV 4.8.0 REQUIRED)
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# Sophus
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories(${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS})
set(THIRD_PARTY_LIBS
${OpenCV_LIBS}
${Sophus_LIBRARIES})
add_executable(dense_mapping dense_mapping.cpp)
target_link_libraries(dense_mapping ${THIRD_PARTY_LIBS})
待改进
12.3.2 像素梯度
块匹配的正确与否 依赖于 图像块是否具有区分度。
立体视觉的重建质量 依赖 环境纹理。

——————————
12.3.3 逆深度(深度的倒数), 认为符合高斯分布。
12.3.4 图像间的变换
GPU 并行化 提高效率
极线搜索
其它改进:
1、给深度估计 加上 空间正则项
2、考虑错误匹配的情形: 均匀-高斯混合分布下的深度滤波器(显式地将内点与外点进行区别并进行概率建模)
————————
12.4 RGB-D 稠密建图
深度数据与纹理无关
根据估算的相机位姿,将RGB-D数据转化为点云,然后进行拼接。
12.4.1 点云地图 【Code】
点云: 一组离散的点表示的地图。
外点去除滤波器 体素网格的降采样滤波器(Voxel grid filter)
安装点云库
sudo apt-get install libpcl-dev pcl-tools

与第5讲的变化:
1、生成每帧点云时,去掉深度值无效的点。Kinect 的量程限制
2、利用统计滤波器去除孤立点。计算附近N个点距离的平均值,去除距离均值过大的点。
3、体素网格滤波器进行降采样。
要在CMakeLists.txt文件里加这一句,使得 支持C++14标准。 可能是最新版本的PCL 要求支持C++14标准。
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
查询OpenCV版本 opencv_version
所有.cpp中的文件路径都要改成..多回一级

pointcloud_mapping.cpp
#include CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -O2")
# opencv
find_package(OpenCV 4.8.0 REQUIRED) ## 改成 当前系统的OpenCV版本
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# eigen
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3/")
# pcl
find_package(PCL 1.10.0 REQUIRED) #
include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS})
# octomap
find_package(octomap REQUIRED)
include_directories(${OCTOMAP_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_executable(pointcloud_mapping pointcloud_mapping.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pointcloud_mapping ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
add_executable(octomap_mapping octomap_mapping.cpp)
target_link_libraries(octomap_mapping ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${PCL_LIBRARIES} ${OCTOMAP_LIBRARIES})
add_executable(surfel_mapping surfel_mapping.cpp)
target_link_libraries(surfel_mapping ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
mkdir build && cd build ## 需要将.cpp中数据的路径 多加一个.
cmake ..
make
./pointcloud_mapping
pcl_viewer map.pcd
12.4.2 从点云 重建 网格 【Code】
./surfel_mapping map.pcd
点云转换成 网格地图(栅格地图)。
surfel_mapping.cpp
//
// Created by gaoxiang on 19-4-25.
//
#include 重建算法: Moving Least Square 、 Greedy Projection
查看PCL 版本 aptitude show libpcl-dev
aptitude show libpcl-dev
可参考链接
12.4.3 八叉树地图(Octomap) 【灵活压缩、随时更新】
点云地图 不足:
1、占内存,提供了很多不必要的细节
2、无法处理运动物体。 只有 “添加点”,点消失时 不会 被移除。
八叉树 比 点云 节省大量的存储空间
- 当某个方块的所有子结点都被占据或都不被占据时,就没必要展开。
12.4.4 八叉树地图 【建模大场景】 【Code】
安装 octomap库
sudo apt-get install liboctomap-dev octovis
./octomap_mapping
octovis octomap.bt
动图截取:
byzanz-record -x 72 -y 64 -w 1848 -h 893 -d 10 --delay=5 -c /home/xixi/myGIF/test.gif
#include ——————————
12.5 TSDF 地图 和 Fusion系列
TSDF(Truncated Signed Distance Function,截断符号距离函数)
实时三维重建: 重建准确地图
定位算法 可以满足实时性需求,地图加工可在关键帧处进行处理,无需实时。
SLAM 轻量级、小型化
实时三维重建 大规模、大型动态场景。
——————————
12.6 小结
度量地图
RGB-D 构建稠密地图 更容易、更稳定一些
习题
√ 题1
#*********************************解题1开始
设某个像素点的深度 d d d 服从高斯分布 P ( d ) = N ( μ , σ 2 ) P(d) = N(\mu, σ^2) P(d)=N(μ,σ2)
增加新数据后,重新观测到的深度分布符合高斯分布 P ( d o b s ) = N ( μ o b s , σ o b s 2 ) P(d_{obs}) = N(\mu_{obs}, σ_{obs}^2) P(dobs)=N(μobs,σobs2)
信息融合后的深度为这两个高斯分布的乘积,即
P ( d f u s e ) = N ( μ , σ 2 ) ⋅ N ( μ o b s , σ o b s 2 ) = 1 2 π σ e x p ( − 1 2 ( x − μ ) 2 σ 2 ) ⋅ 1 2 π σ o b s e x p ( − 1 2 ( x − μ o b s ) 2 σ o b s 2 ) = 1 2 π σ σ o b s e x p ( − 1 2 ( x − μ ) 2 σ 2 − 1 2 ( x − μ o b s ) 2 σ o b s 2 ) = 1 2 π σ σ o b s e x p ( − 1 2 σ o b s 2 ⋅ ( x − μ ) 2 + σ 2 ⋅ ( x − μ o b s ) 2 σ 2 σ o b s 2 ) = 1 2 π σ σ o b s e x p ( − 1 2 ( σ o b s 2 + σ 2 ) ⋅ x 2 − 2 ( σ o b s 2 μ + σ 2 μ o b s ) ⋅ x + σ o b s 2 μ 2 + σ 2 μ o b s 2 σ 2 σ o b s 2 ) = 1 2 π σ σ o b s e x p ( − 1 2 x 2 − 2 σ o b s 2 μ + σ 2 μ o b s σ o b s 2 + σ 2 ⋅ x + σ o b s 2 μ 2 + σ 2 μ o b s 2 σ o b s 2 + σ 2 σ 2 σ o b s 2 σ o b s 2 + σ 2 ) = 1 2 π σ σ o b s e x p ( − 1 2 ( x − σ o b s 2 μ + σ 2 μ o b s σ o b s 2 + σ 2 ) 2 σ 2 σ o b s 2 σ o b s 2 + σ 2 ) ⋅ e x p ( − 1 2 σ o b s 2 μ 2 + σ 2 μ o b s 2 σ o b s 2 + σ 2 − ( σ o b s 2 μ + σ 2 μ o b s σ o b s 2 + σ 2 ) 2 σ 2 σ o b s 2 σ o b s 2 + σ 2 ) = 1 2 π σ σ o b s σ o b s 2 + σ 2 e x p ( − 1 2 ( x − σ o b s 2 μ + σ 2 μ o b s σ o b s 2 + σ 2 ) 2 σ 2 σ o b s 2 σ o b s 2 + σ 2 ) ⋅ e x p ( − 1 2 σ o b s 2 μ 2 + σ 2 μ o b s 2 σ o b s 2 + σ 2 − ( σ o b s 2 μ + σ 2 μ o b s σ o b s 2 + σ 2 ) 2 σ 2 σ o b s 2 σ o b s 2 + σ 2 ) 2 π σ o b s 2 + σ 2 \begin{align*}P(d_{fuse}) &= N(\mu, σ^2) ·N(\mu_{obs}, σ_{obs}^2) \\ & = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}\sigma}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(x-\mu)^2}{\sigma^2}) · \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}\sigma_{obs}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(x-\mu_{obs})^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2}) \\ &= \frac{1}{2\pi\sigma\sigma_{obs}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(x-\mu)^2}{\sigma^2}-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(x-\mu_{obs})^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2})\\ &= \frac{1}{2\pi\sigma\sigma_{obs}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2·(x-\mu)^2+\sigma^2·(x-\mu_{obs})^2}{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2})\\ &= \frac{1}{2\pi\sigma\sigma_{obs}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2)·x^2-2(\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs})·x+\sigma_{obs}^2\mu^2+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}^2}{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2})\\ &= \frac{1}{2\pi\sigma\sigma_{obs}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{x^2-2\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}·x+\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu^2+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}}{\frac{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}})\\ &= \frac{1}{2\pi\sigma\sigma_{obs}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(x-\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2})^2}{\frac{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}})·exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu^2+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}-(\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2})^2}{\frac{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}})\\ &= \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}\frac{\sigma\sigma_{obs}}{\sqrt{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(x-\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2})^2}{\frac{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}})·\frac{exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu^2+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}-(\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2})^2}{\frac{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}})}{\sqrt{2\pi}\sqrt{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}}\\ \end{align*} P(dfuse)=N(μ,σ2)⋅N(μobs,σobs2)=2πσ1exp(−21σ2(x−μ)2)⋅2πσobs1exp(−21σobs2(x−μobs)2)=2πσσobs1exp(−21σ2(x−μ)2−21σobs2(x−μobs)2)=2πσσobs1exp(−21σ2σobs2σobs2⋅(x−μ)2+σ2⋅(x−μobs)2)=2πσσobs1exp(−21σ2σobs2(σobs2+σ2)⋅x2−2(σobs2μ+σ2μobs)⋅x+σobs2μ2+σ2μobs2)=2πσσobs1exp(−21σobs2+σ2σ2σobs2x2−2σobs2+σ2σobs2μ+σ2μobs⋅x+σobs2+σ2σobs2μ2+σ2μobs2)=2πσσobs1exp(−21σobs2+σ2σ2σobs2(x−σobs2+σ2σobs2μ+σ2μobs)2)⋅exp(−21σobs2+σ2σ2σobs2σobs2+σ2σobs2μ2+σ2μobs2−(σobs2+σ2σobs2μ+σ2μobs)2)=2πσobs2+σ2σσobs1exp(−21σobs2+σ2σ2σobs2(x−σobs2+σ2σobs2μ+σ2μobs)2)⋅2πσobs2+σ2exp(−21σobs2+σ2σ2σobs2σobs2+σ2σobs2μ2+σ2μobs2−(σobs2+σ2σobs2μ+σ2μobs)2)
显然,前面部分符合高斯分布 N ( μ f u s e , σ f u s e 2 ) N(\mu_{fuse}, σ_{fuse}^2) N(μfuse,σfuse2),其中
μ f u s e = σ o b s 2 μ + σ 2 μ o b s σ o b s 2 + σ 2 , , , σ f u s e 2 = σ 2 σ o b s 2 σ o b s 2 + σ 2 \mu_{fuse} = \frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}, ,, σ_{fuse}^2=\frac{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2} μfuse=σobs2+σ2σobs2μ+σ2μobs,,,σfuse2=σobs2+σ2σ2σobs2
后面部分为 常数,不影响其高斯分布类型
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 绘制高斯分布曲线
x = np.linspace(-4, 4, 100)
y = gaussian.pdf(x)
plt.plot(x, 0.2*y, 'orange')
plt.plot(x, y, 'r')
plt.plot(x, 2*y, 'b')
plt.xlabel('Value')
plt.ylabel('Density')
plt.title('Gaussian Distribution')
plt.show()
正态分布的数学期望值或期望值 μ μ μ 等于位置参数,决定了分布的位置;其方差 σ 2 \sigma ^{2} σ2 等于尺度参数,决定了分布的幅度。

#*********************************解题1结束
√ 题2
半稠密深度估计,先把梯度明显的地方筛选出来。


数据集下载链接: https://rpg.ifi.uzh.ch/datasets/remode_test_data.zip
#*********************************解题2开始
建 空白文件
touch CMakeLists.txt
touch semi_dense_mapping.cpp
复制相应的代码
报错:
/home/xixi/Downloads/slambook2-master/ch12/dense_mono/dense_mapping.cpp:12:15: error: ‘Sophus::SE3d’ has not been declared
12 | using Sophus::SE3d;
解决办法链接
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make
./semi_dense_mapping /home/xixi/Downloads/slambook2-master/ch12/semi_dense_mono/dataset/test_data
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(semi_dense_monocular)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -march=native -O3")
############### dependencies ######################
# Eigen
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
# OpenCV
find_package(OpenCV 4 REQUIRED) ## OpenCV是4.8.0 .cpp文件需要修改
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# Sophus
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories(${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS})
set(THIRD_PARTY_LIBS
${OpenCV_LIBS}
${Sophus_LIBRARIES})
add_executable(semi_dense_mapping semi_dense_mapping.cpp)
target_link_libraries(semi_dense_mapping ${THIRD_PARTY_LIBS})
semi_dense_mapping.cpp
#include #*********************************解题2结束
题3
3、单目稠密重建从正深度 改成 逆深度,并添加仿射变换。
仿射变换用于 块匹配前,进一步考虑了相机发生运动的情形(当前帧和参考帧之间发行运动了),以期可以取得更好的 匹配效果。
实际的深度分布: 尾部稍长,负数区域为0 逆深度


ORB_SLAM2
题4
4、论证如何在八叉树中进行导航和路径规划
navigation based on octomap
导航:如何从地图中A点到B点。
- 如何在地图中地位自己(localization)
- 如何从 A 到 B 规划一条路径(planning), path planning 有global和local之分,同时都需要。global path planning有dijkstra,A* ,D*等算法。local path planning 有自适应动态窗法等。
Autonomous Navigation in Unknown Environments with Sparse Bayesian Kernel-based Occupancy Mapping
OctoMap:An Efficient Probabilistic 3D Mapping Framework Based on Octrees
找到了别的树
FAST-LIO2: Fast Direct LiDAR-inertial Odometry
题5
5、TSDF是如何进行位姿估计和更新的。
论文链接: KinectFusion: Real-Time Dense Surface Mapping and Tracking


题6
6、均匀-高斯混合滤波器的原理与实现
待做:
- 用数据集 跑源码
在12.2.3 节讨论了。P311
SVO源码链接
PDF链接:https://rpg.ifi.uzh.ch/docs/ICRA14_Forster.pdf
SVO 全称 Semi-direct monocular Visual Odometry(半直接视觉里程计)
点云 深度 概率模型是 高斯+均匀分布
瑞士苏黎世大学 机器人与感知小组http://rpg.ifi.uzh.ch。



https://github.com/uzh-rpg/rpg_svo/blob/master/svo/src/depth_filter.cpp
其它:
SVO的深度滤波器使用的概率模型是《Video-based, Real-Time Multi View Stereo》中的深度概率模型,不同的是SVO中的使用的逆深度估计。
Video-based, Real-Time Multi View Stereo》pdf链接