Springcloud-服务注册与发现
注册服务与发现
相关概念
Eureka
两大组件
搭建单机Eureka环境
搭建集群Eureka环境
actuator完善微服务信息
服务发现
自我保护机制
Consul
概述
作用
下载与安装
使用
补充-CAP
简介
AP(Eureka)
CP(Consul)
注册服务与发现
相关概念
服务治理
什么是服务治理 Spring Cloud 封装了 Netflix 公司开发的 Eureka 模块来实现服务治理
在传统的rpc远程调用框架中,管理每个服务与服务之间依赖关系比较复杂,管理比较复杂,所以需要使用服务治理,管理服务于服务之间依赖关系,可以实现服务调用、负载均衡、容错等,实现服务发现与注册。
注册中心
什么是服务注册与发现? Eureka采用了CS的设计架构,Eureka Server 作为服务注册功能的服务器,它是服务注册中心。而系统中的其他微服务,使用 Eureka的客户端连接到 Eureka Server并维持心跳连接。这样系统的维护人员就可以通过 Eureka Server 来监控系统中各个微服务是否正常运行。 在服务注册与发现中,有一个注册中心。当服务器启动的时候,会把当前自己服务器的信息 比如 服务地址通讯地址等以别名方式注册到注册中心上。另一方(消费者|服务提供者),以该别名的方式去注册中心上获取到实际的服务通讯地址,然后再实现本地RPC调用RPC远程调用框架核心设计思想:在于注册中心,因为使用注册中心管理每个服务与服务之间的一个依赖关系(服务治理概念)。在任何rpc远程框架中,都会有一个注册中心(存放服务地址相关信息(接口地址))
Eureka
两大组件
Eureka包含两个组件:Eureka Server和Eureka Client
Eureka Server提供服务注册服务 各个微服务节点通过配置启动后,会在EurekaServer中进行注册,这样EurekaServer中的服务注册表中将会存储所有可用服务节点的信息,服务节点的信息可以在界面中直观看到。
EurekaClient通过注册中心进行访问 是一个Java客户端,用于简化Eureka Server的交互,客户端同时也具备一个内置的、使用轮询(round-robin)负载算法的负载均衡器。在应用启动后,将会向Eureka Server发送心跳(默认周期为30秒)。如果Eureka Server在多个心跳周期内没有接收到某个节点的心跳,EurekaServer将会从服务注册表中把这个服务节点移除(默认90秒)
搭建单机Eureka环境
-
搭建EurekaServer注册中心
导入依赖org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server 编写yml文件# eureka相关设置 eureka: instance: hostname: localhost # EurekaServer的实例名称 client: # 是否向eureka服务端注册 register-with-eureka: false # false表示自己端就是注册中心,我的职责就是维护服务实例,并不需要去检索服务 fetch-registry: false # 设置与Eureka Server交互的地址查询服务和注册服务都需要依赖这个地址。 service-url: defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/在启动类上添加依赖package cn.pigman.springcloud; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer; @SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaServer //声明当前模块为Eureka的服务注册中心 public class EurekaMain7001 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(EurekaMain7001.class, args); } } -
给EurekaServer工程的启动类上添加注解
package cn.pigman.springcloud; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer; @SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaServer //声明当前模块为Eureka的服务注册中心 public class EurekaMain7001 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(EurekaMain7001.class, args); } } -
将boot工程注册入EurekaServer
导入EurekaClient依赖org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client 编写yml文件eureka: client: # 是否将当前工程注册进为EurekaServer,默认为true register-with-eureka: true # 是否从EurekaServer抓取已有的注册信息,默认为true fetch-registry: true service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
在启动类上添加注解package cn.pigman.springcloud; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient; @SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaClient //将当前工程声明为eureka的客户端 public class PaymentMain8001 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain8001.class, args); } } -
测试
搭建集群Eureka环境
搭建集群EurekaServer
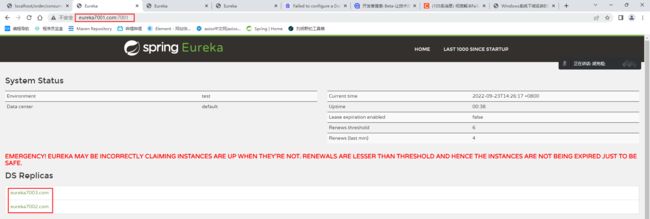
单机的EurekaServer与集群的EurekaServer集群最大的不同就在于每个注册中心的yml配置文件的不同。其主要实现原来可以概括为“互相注册,相互守望”。
-
编写yml配置文件
EurekaServer7001eureka: instance: hostname: eureka7001.com client: register-with-eureka: false fetch-registry: false #如果是搭建集群EurekaServer的话,这里的service-url必须写除了当前EurekaServer之外的其他EurekaServer的地址(hostname+端口) #多个EurekaServer之间以 , 分隔 service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/, http://eureka7003.com:7003/eureka/
EurekaServer7002eureka: instance: hostname: eureka7002.com client: register-with-eureka: false fetch-registry: false service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/, http://eureka7003.com:7003/eureka/
EurekaServer7003eureka: instance: hostname: eureka7003.com client: register-with-eureka: false fetch-registry: false service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/, http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/
-
写完配置文件后,在每个EurekaServer的启动类上添加
@EnableEurekaServer注解。package cn.pigman.springcloud; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer; @SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaServer //声明当前模块为Eureka的服务注册中心 public class EurekaMain7001 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(EurekaMain7001.class, args); } } -
将服务工程注册到三个EurekaServer中
eureka: client: # 是否将当前工程注册进为EurekaServer,默认为true register-with-eureka: true # 是否从EurekaServer抓取已有的注册信息,默认为true fetch-registry: true service-url: #defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka #多个EurekaServer之间以 , 分隔 defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka, http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka, http://eureka7003.com:7003/eureka
-
测试
搭建功能服务集群
-
创建多个服务工程
-
为每个工程编写yml文件
cloud-provider-payment8001模块server: port: 8001 spring: application: name: cloud-payment-service eureka: client: # 是否将当前工程注册进为EurekaServer,默认为true register-with-eureka: true # 是否从EurekaServer抓取已有的注册信息,默认为true fetch-registry: true service-url: #defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka, http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka, http://eureka7003.com:7003/eureka
cloud-provider-payment8002模块server: port: 8002 spring: application: name: cloud-payment-service eureka: client: # 是否将当前工程注册进为EurekaServer,默认为true register-with-eureka: true # 是否从EurekaServer抓取已有的注册信息,默认为true fetch-registry: true service-url: #defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka, http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka, http://eureka7003.com:7003/eureka
注意:
这里虽然是多个服务工程,但
spring.application.name的属性值可以相同,后期EurekaServer在调用服务的时候会通过端口号来进行区分。也就是说,EurekaServer中可以有多个同名的服务工程,调用工程的时候通过端口号来区分。 -
测试
搭建完Eureka集群环境后,想要访问集群中的某个服务,只需要通过服务名就可以访问。但在此处会有个小bug,就是如果该服务名下有多个服务工程,那么EurekaServer并不知道你想要访问的是那一个服务,就会抛出一个异常。要想解决该问题,可以通过Ribbon和Eureka整合。
给RedisTemplate对象添加 @Loadbalanced 注解赋予负载均衡功能:
package cn.pigman.springcloud.config;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@Configuration
public class ApplicationContextConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced //赋予RestTemplate对象负载均衡的能力
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
actuator完善微服务信息
修改服务名称
eureka:
instance:
instance-id: payment-8001 # 修改服务模块的名称(不能重复)
修改前
修改后
启用访问路径显示Ip地址
eureka:
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
服务发现
对于注册进EurekaServer的微服务,可以通过服务发现(DiscoveryClient)来获取该服务的信息。
使用步骤
-
在启动类上添加注解
@SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaClient @EnableDiscoveryClient //服务发现 public class PaymentMain8001{ public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain8001.class,args); } } -
注入DiscoveryClient对象
@Resource private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient; @GetMapping(value = "/payment/discovery") public Object discovery() { Listservices = discoveryClient.getServices(); for (String element : services) { System.out.println(element); } List instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE"); for (ServiceInstance element : instances) { System.out.println(element.getServiceId() + "\t" + element.getHost() + "\t" + element.getPort() + "\t" + element.getUri()); } return this.discoveryClient; }
自我保护机制
概述
保护模式主要用于一组客户端和Eureka Server之间存在网络分区场景下的保护。一旦进入保护模式,Eureka Server将会尝试保护其服务注册表中的信息,不再删除服务注册表中的数据,也就是不会注销任何微服务。
如果在EurekaServer网页上看到了这段信息,就说明开了自我保护机制。
为什么需要自我保护
为了防止一种情况:EurekaClient可以正常运行,但可能因为网络不通的原因,EurekaClient没法连接到EurekaServer。
什么是自我保护模式?
默认情况下,如果EurekaServer在一定时间内没有接收到某个微服务实例的心跳,EurekaServer将会注销该实例(默认90秒)。但是当网络分区故障发生(延时、卡顿、拥挤)时,微服务与EurekaServer之间无法正常通信,以上行为可能变得非常危险了——因为微服务本身其实是健康的,此时本不应该注销这个微服务。Eureka通过“自我保护模式”来解决这个问题——当EurekaServer节点在短时间内丢失过多客户端时(可能发生了网络分区故障),那么这个节点就会进入自我保护模式。
在自我保护模式中,Eureka Server会保护服务注册表中的信息,不再注销任何服务实例。
综上,自我保护模式是一种应对网络异常的安全保护措施。它的架构哲学是宁可同时保留所有微服务(健康的微服务和不健康的微服务都会保留)也不盲目注销任何健康的微服务。使用自我保护模式,可以让Eureka集群更加的健壮、稳定。
停止自我保护模式
默认情况下,Eureka会自动开启自我保护机制,那么要如何关闭自我保护机制呢?
-
在EurekaServer端的yml文件添加如下配置
server: #关闭自我保护机制,保证不可用服务被及时踢除,默认为true(开启) enable-self-preservation: false eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 2000
-
在EurekaClient端的yml文件添加如下配置
eureka: instance: #Eureka客户端向服务端发送心跳的时间间隔,单位为秒(默认是30秒) lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 1 #Eureka服务端在收到最后一次心跳后等待时间上限,单位为秒(默认是90秒),超时将剔除服务 lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 2
Consul
概述
Consul 是一套开源的分布式服务发现和配置管理系统,由 HashiCorp 公司用 Go 语言开发。提供了微服务系统中的服务治理、配置中心、控制总线等功能。这些功能中的每一个都可以根据需要单独使用,也可以一起使用以构建全方位的服务网格,总之Consul提供了一种完整的服务网格解决方案。
它具有很多优点。包括: 基于 raft 协议,比较简洁; 支持健康检查, 同时支持 HTTP 和 DNS 协议 支持跨数据中心的 WAN 集群 提供图形界面 跨平台,支持 Linux、Mac、Windows。
作用
-
服务发现
-
健康检测
-
KV存储
-
多数据中心
-
可视化Web界面
下载与安装
下载完成后,在命令行界面通过 consul agent -dev 命令运行。
使用
-
EurekaServer端
导入依赖org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-starter-consul-discovery 在yml文件中添加如下配置###consul服务端口号 server: port: 8003 spring: application: name: consul-provider-payment ####consul注册中心地址 cloud: consul: host: localhost port: 8500 discovery: #hostname: 127.0.0.1 service-name: ${spring.application.name}主启动类@SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient //该注解用于向使用consul或者zookeeper作为注册中心时注册服务 public class PaymentMain8003{ public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain8006.class,args); } } -
EurekaClient端
导入依赖org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-starter-consul-discovery 在yml文件中添加如下配置###consul服务端口号 server: port: 80 spring: application: name: cloud-consumer-order ####consul注册中心地址 cloud: consul: host: localhost port: 8500 discovery: #hostname: 127.0.0.1 service-name: ${spring.application.name}主启动类@SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient public class OrderConsulMain80{ public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderConsulMain80.class,args); } }
补充-CAP
简介
CAP理论关注粒度是数据,而不是整体系统设计的策略。
-
C:Consistency(强一致性)
-
A:Availability(可用性)
-
P:Partition tolerance(分区容错性)
CAP理论最多只能同时较好的满足两个。
CAP理论的核心是:一个分布式系统不可能同时很好的满足一致性,可用性和分区容错性这三个需求, 因此,根据 CAP 原理将 NoSQL 数据库分成了满足 CA 原则、满足 CP 原则和满足 AP 原则三大类:
CA - 单点集群,满足一致性,可用性的系统,通常在可扩展性上不太强大。
CP - 满足一致性,分区容忍必的系统,通常性能不是特别高。
AP - 满足可用性,分区容忍性的系统,通常可能对一致性要求低一些。
AP(Eureka)
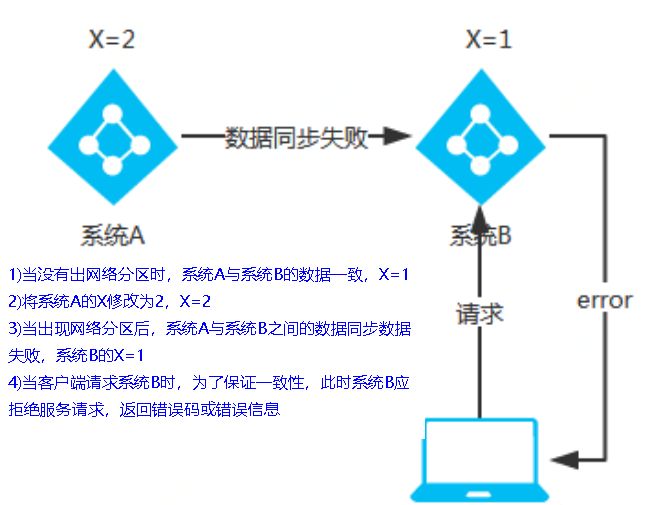
当网络分区出现后,为了保证可用性,系统B可以返回旧值,保证系统的可用性。 结论:违背了一致性C的要求,只满足可用性和分区容错,即AP
CP(Consul)
当网络分区出现后,为了保证一致性,就必须拒接请求,否则无法保证一致性 结论:违背了可用性A的要求,只满足一致性和分区容错,即CP