iOS之深入解析alloc、init与new的底层原理
底层探索
一、对于 iOS 的底层原理探索,查找到函数所在的源码库,一般有以下方法实现:
① 符号断点
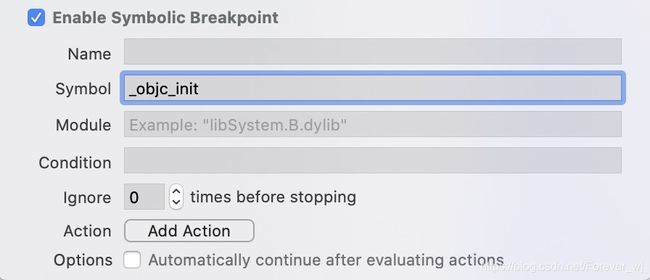
- 在哪里新建符号断点:选择 Symbolic Breakpoint :
- 怎么添加符号断点:在Symbol中加入 alloc、objc_alloc、_objc_rootAlloc 等:
- 继续追踪方法底层原理,可以继续使用以上符号断点方法添加对应的方法名即可;
- 直到最后追踪到系统底层库为止,例如: alloc 的源码最后追踪到位于 libobjc.A.dylib 库。
② LLDB调试
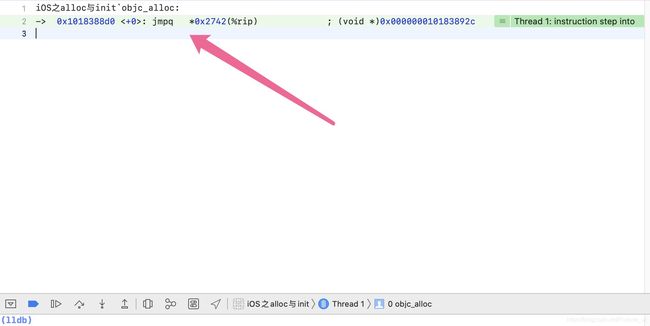
- 在需要探索的内部方法或者实现的地方,打上断点;
- 运行代码,执行到断点地方,然后按住 control 键,即出现以下调试断点:
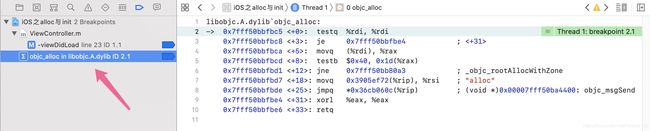
- 点击上图中的第四个step into之后,即可看见相应实现方法,如:alloc 如下:
- 再添加一个 objc_alloc 符号断点,便可显示 objc_alloc 所在的源码库 libobjc.A.dylib 。
③ 汇编分析
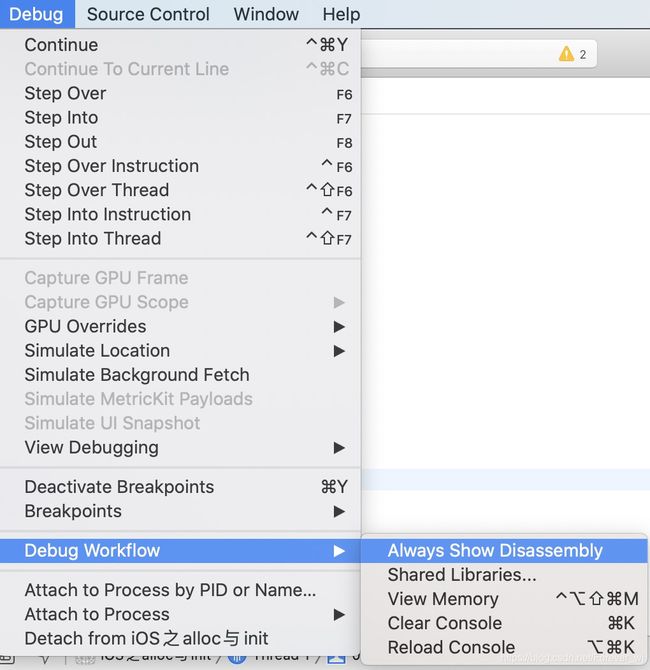
- xcode 工具栏选择 Xcode -> Debug WorkFlow -> Always Show Disassembly ,该选项表示始终显示反汇编 ,即汇编分析:
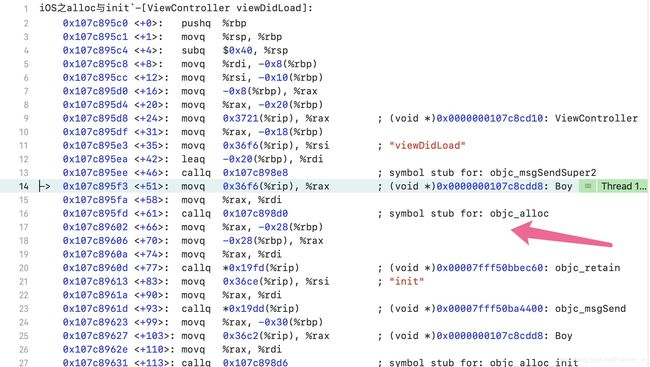
- 按照“符号断点”的运行代码,执行到断点地方,然后按住 control 键,即出现以下调试断点方法,即可进入 callq ,对应 objc_alloc:
- 最后,也可以看到 alloc 对应的源码库为 libobjc.A.dylib 库。
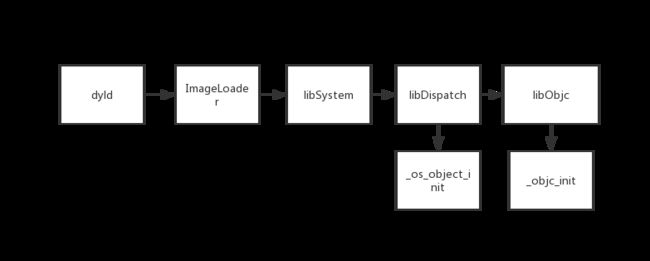
二、作为 iOS 开发者,最需要关注的应该就是从应用启动到应用被 kill 掉这一整个生命周期的内容。不妨从最熟悉的 main 函数开始,一般来说,在 main.m 文件中打一个断点,左侧的调用堆栈视图应该如下图所示:
- 需要关闭 Xcode 左侧 Debug 区域最下面的 show only stack frames with debug symbols and between libraries
- 增加一个 _objc_init 的符号断点
五、Apple 开源库源码
- Apple 所有开源源码汇总地址,根据相应的版本查找对应的源码,以 Mac 10.15 为例: macOS --> 10.15 --> 选择10.15 --> 搜索 objc;
- Apple 比较直接的源码下载地址,直接搜索想要下载的源码名称即可,例如objc:直接搜索 objc --> objc4/ --> 选择相应的 objc 的版本。
内存对齐
一、内存对齐概念
① 什么是内存对齐?
- 内存对齐是一种在计算机内存中 排列数据 (表现为变量的地址)、 访问数据 (表现为CPU读取数据)的一种方式。
- 内存对齐包含了两种相互独立又相互关联的部分: 基本数据对齐和结构体数据对齐 。
② 为什么要进行内存对齐?
- 平台原因(移植原因):不是所有的硬件平台都能访问任意地址上的任意数据的;某些硬件平台只能在某些地址处取某些特定类型的数据,否则抛出硬件异常。
- 性能原因:数据结构(尤其是栈)应该尽可能地在 自然边界上对齐 。原因在于,为了访问未对齐的内存,处理器需要作两次内存访问;而对齐的内存访问仅需要 一次访问 。
③ 内存对齐原则
在 iOS 中,对象的属性需要进行内存对齐,而对象本身也需要进行内存对齐。内存对齐有三原则:
- 数据成员对齐原则 :结构( struct )(或联合( union ))的数据成员,第一个数据成员放在 offset 为 0 的地方,以后每个数据成员存储的起始位置要从该成员大小或者成员的子成员大小。
- 结构体作为成员 :如果一个结构里有某些结构体成员,则结构体成员要从其内部最大元素大小的整数倍地址开始存储。(如:struct a⾥存有struct b,b⾥有char、int 、double等元素,那b应该从8的整数倍开始存储)
- 收尾工作:结构体的总大小,也就是 sizeof 的结果,必须是其 内部最大成员的整数倍 ,不足的要补⻬。
简而言之:
- 前面的地址必须是后面的地址正数倍,不是就补齐;
- 结构体里面的嵌套结构体大小要以该嵌套结构体最大元素大小的整数倍;
- 整个 Struct 的地址必须是最大字节的整数倍。
注意:
- 在字节对齐算法中,对齐的主要是对象,而对象的本质则是一个 struct objc_object 的结构体;
- 结构体在内存中是 连续存放 的,所以可以利用这点对结构体进行强转;
- 苹果早期是8字节对齐,现在是 16字节对齐 。
二、对象申请内存和系统开辟内存
在Xocde中打印以下两个函数:
Boy *boy = [Boy alloc];
NSLog(@"%lu - %lu - %lu", sizeof(boy), class_getInstanceSize([Boy class]), malloc_size((__bridge const void *)(boy)));
- 可以发现对象自己申请的内存大小与系统实际给开辟的大小时不一样的,这里对象申请的内存大小是 40 个字节,而系统开辟的是 48 个字节。
- 40 个字节不难理解,是因为当前对象有 4 个属性,有三个属性为 8 个字节,有一个属性为 4个字节,再加上 isa 的 8 个字节,就是 32 + 4 = 36 个字节,然后根据内存对齐原则,36 不能被 8 整除,36 往后移动刚好到了 40 就是 8 的倍数,所以内存大小为 40。
- class_getInstanceSize 和 malloc_size 对同一个对象返回的结果不一样的,原因是 malloc_size 是直接返回的 calloc 之后的指针的大小。
size_t instanceSize(size_t extraBytes) {
size_t size = alignedInstanceSize() + extraBytes;
// CF requires all objects be at least 16 bytes.
if (size < 16) size = 16;
return size;
}
- 通过instanceSize计算的内存大小,向内存中申请大小为 size 的内存,并赋值给 obj ,因此 obj 是指向内存地址的指针;在未执行 calloc 时,po obj 为 nil,执行后,再 po obj ,返回一个16进制的地址。
obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
- 而 class_getInstanceSize 内部实现是:也就是说 class_getInstanceSize 会输出 8 个字节,malloc_size 会输出 16 个字节,当然前提是该对象没有任何属性。
size_t class_getInstanceSize(Class cls) {
if (!cls) return 0;
return cls->alignedInstanceSize();
}
三、不同数据类型占据的内存大小(字节)
| C | OC | 32位 | 64位 |
|---|---|---|---|
| bool | BOOL(64位) | 1 | 1 |
| signed char | (_signed char)int8_t、BOOL(32位) | 1 | 1 |
| unsigned char | Boolean | 1 | 1 |
| short | int16_t | 2 | 2 |
| unsigned short | unichar | 2 | 2 |
| int、int32_t | NSInteger(32位)、boolean_t(32位) | 4 | 4 |
| unsigned int | NSUInteger(32位)、boolean_t(64位) | 4 | 4 |
| long | NSInteger(64位) | 4 | 8 |
| unsigned long | NSUInteger(64位) | 4 | 8 |
| long long | int64_t | 8 | 8 |
| float | CGFloat(32位) | 4 | 4 |
| double | CGFloat(64位) | 8 | 8 |
alloc、init与new的底层原理
一、实例初始化
运用Objective-C语言进行开发的时候,我们都知道可以通过 [XXX alloc]、[[XXX alloc] init]、[XXX new]的形式进行对象实例的创建,那么不禁会疑惑alloc、init、new它们各自都做了什么呢?同样的都是进行实例创建,它们之间有什么内在的关联呢?它们之间又有着什么样的区别呢?
- 我们不妨先出使用alloc、init、new分别初始化对象,具体实现和并打印对象结果、指针地址、内存地址如下:
Boy *boy1 = [Boy alloc];
Boy *boy2 = [boy1 init];
Boy *boy3 = [[Boy alloc] init];
Boy *boy4 = [Boy new];
NSLog(@"%@ %p %p",boy1, boy1, &boy1);
NSLog(@"%@ %p %p",boy2, boy2, &boy2);
NSLog(@"%@ %p %p",boy3, boy3, &boy3);
NSLog(@"%@ %p %p",boy4, boy4, &boy4);
打印结果
2020-09-02 00:32:43.295969+0800 iOS之alloc与init[1284:37780] <Boy: 0x6000008c03d0> 0x6000008c03d0 0x7ffee75284d8
2020-09-02 00:32:43.296121+0800 iOS之alloc与init[1284:37780] <Boy: 0x6000008c03d0> 0x6000008c03d0 0x7ffee75284d0
2020-09-02 00:32:43.296282+0800 iOS之alloc与init[1284:37780] <Boy: 0x6000008c03a0> 0x6000008c03a0 0x7ffee75284c8
2020-09-02 00:32:43.296370+0800 iOS之alloc与init[1284:37780] <Boy: 0x6000008c03c0> 0x6000008c03c0 0x7ffee75284c0
- 通过以上可以看出:boy1与boy2是同一个对象,而与boy3、boy4则是不同的对象。虽然boy1与boy2是同一个对象,并且指针地址相同,指向的是同一个内存空间,但是它们的内存地址却又不一样,那么alloc、init、new到底做了什么呢?其实,当alloc执行返回的时候,x0寄存器就会存储一个指针,指向申请的内存空间,并且可以看到内存地址相差8个字节。
二、如何查找alloc实现?
- 在alloc初始化的地方,打上断点,如下:
- 运行代码,执行到断点地方,然后按住 control键,即出现以下调试断点:

- 按住control,然后点击第四个图标调试,就可以进入到 objc_alloc 中;
- symbolic Beakpoint 添加符号断点 objc_alloc 可以发现在 libobjc.A.dylib ;
- 也可以先把断点打在alloc的地方,运行,断点断住之后再下一个alloc的符号断点,会发现有很多的类实现了alloc方法,先不用管直接过掉断点,就会进入汇编的代码之中;
- 可以通过 Xcode -> Debug 进入汇编分析:
X0 X1..其中x0-x7八个寄存器是用来保存参数的
objc_msgSend会有两个默认参数,这也就意味着x0保存的是self,也就是isa指针,x1保存的是_cmd
register read x0 (register指令能够获取和修改各个寄存器的信息。)
po 0x4567899. “po”命令是“print object”(打印对象)的简写
三、底层实现源码分析
既然是深入底层,那么肯定需要知道底层代码是做了什么事情,苹果是开源了这部分的代码,可以在Source Browser下载。下载下来的源码直接编译是通不过的,需要自己修改下配置,具体请参考objc_debug。
① alloc
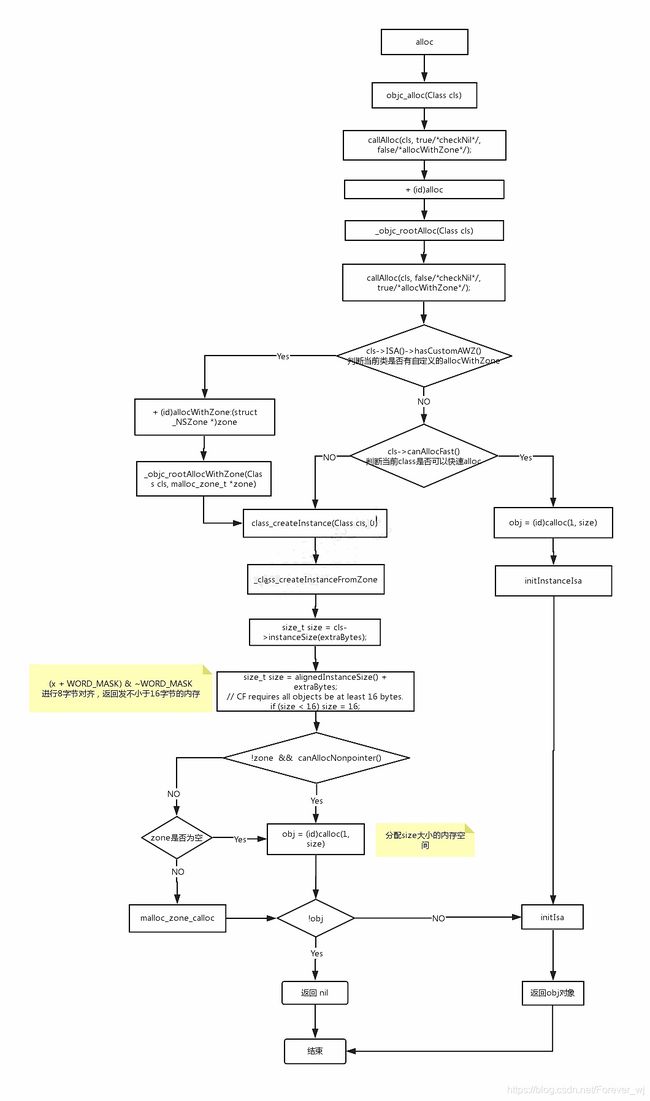
- 进入到 alloc 的源码里面,我们发现 alloc 调用了 _objc_rootAlloc 方法,而_objc_rootAlloc调用了 callAlloc 方法。
+ (id)alloc {
return _objc_rootAlloc(self);
}
id _objc_rootAlloc(Class cls) {
return callAlloc(cls, false/*checkNil*/, true/*allocWithZone*/);
}
static ALWAYS_INLINE id
callAlloc(Class cls, bool checkNil, bool allocWithZone=false) {
#if __OBJC2__
// checkNil 为false,!cls 也为false ,所以slowpath 为 false,假值判断不会走到if里面,即不会返回nil
if (slowpath(checkNil && !cls)) return nil;
// 判断一个类是否有自定义的 +allocWithZone 实现,没有则走到if里面的实现
if (fastpath(!cls->ISA()->hasCustomAWZ())) {
return _objc_rootAllocWithZone(cls, nil);
}
#endif
// No shortcuts available.
if (allocWithZone) {
return ((id(*)(id, SEL, struct _NSZone *))objc_msgSend)(cls, @selector(allocWithZone:), nil);
}
return ((id(*)(id, SEL))objc_msgSend)(cls, @selector(alloc));
}
- 在callAlloc方法里面可以看到if的判断条件,那么 fastpath(!cls->ISA()->hasCustomAWZ()) 都做了什么呢?fastpath又是什么呢?fastpath的定义如下:
#define fastpath(x) (__builtin_expect(bool(x), 1))
#define slowpath(x) (__builtin_expect(bool(x), 0))
- 要搞清楚fastpath是什么,就要知道 __builtin_expect 是什么。其实,这个指令是 gcc 引入的,作用是允许程序员将最有可能执行的分支告诉编译器。这个指令的写法为: __builtin_expect(EXP, N) 。
- 目的:编译器可以对代码进行优化,以 减少指令跳转带来的性能下降 ,即性能优化;
- 作用:允许程序员 将最有可能执行的分支告诉编译器 ;
- 指令的写法为: __builtin_expect(EXP, N) ,表示 EXP==N的概率很大;
- fastpath定义中__builtin_expect((x),1)表示 x 的值为真的可能性更大;即执行 if 里面语句的机会更大;
- slowpath定义中的 __builtin_expect((x),0) 表示 x 的值为假的可能性更大,即执行 else 里面语句的机会更大;
- !cls->ISA()->hasCustomAWZ() 做了什么呢?很明显是调用了 hasCustomAWZ 这样一个方法:
bool hasDefaultAWZ( ) {
return data()->flags & RW_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ;
}
#define RW_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ (1<<16)
- RW_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ 这个是用来标示当前的 class 或者是 superclass 是否有默认的 alloc/allocWithZone: 。值得注意的是,这个值会存储在 metaclass 中。
- hasDefaultAWZ( ) 方法是用来判断当前 class 是否有 重写allocWithZone 。如果 cls->ISA()->hasCustomAWZ() 返回YES,意味着当前的 class 有重写 allocWithZone方法 ,那么就直接对 class 进行 allocWithZone,申请内存空间 。
if (allocWithZone) return [cls allocWithZone:nil];
+ (id)allocWithZone:(struct _NSZone *)zone {
return _objc_rootAllocWithZone(self, (malloc_zone_t *)zone);
}
- allocWithZone 内部调用了 _objc_rootAllocWithZone 方法,接下来分析下_objc_rootAllocWithZone方法
id
_objc_rootAllocWithZone(Class cls, malloc_zone_t *zone)
{
id obj;
#if __OBJC2__
// allocWithZone under __OBJC2__ ignores the zone parameter
(void)zone;
obj = class_createInstance(cls, 0);//创建对象
#else
if (!zone) {
obj = class_createInstance(cls, 0);
}
else {
obj = class_createInstanceFromZone(cls, 0, zone);
}
#endif
if (slowpath(!obj)) obj = callBadAllocHandler(cls);
return obj;
}
- 不难发现直接调用了 class_createInstance 方法来创建对象,而 _class_createInstanceFromZone 是 alloc 源码的核心操作,实现主要分为三部分:
- cls->instanceSize :计算需要开辟的内存空间大小
- calloc :申请内存,返回地址指针;
- obj->initInstanceIsa :将 类 与 isa 关联。
id class_createInstance(Class cls, size_t extraBytes) {
return _class_createInstanceFromZone(cls, extraBytes, nil);
}
tatic __attribute__((always_inline))
id
_class_createInstanceFromZone(Class cls, size_t extraBytes, void *zone,
bool cxxConstruct = true,
size_t *outAllocatedSize = nil)
{
if (!cls) return nil;
assert(cls->isRealized());
// Read class's info bits all at once for performance
//读取class的信息
bool hasCxxCtor = cls->hasCxxCtor();
bool hasCxxDtor = cls->hasCxxDtor();
bool fast = cls->canAllocNonpointer();
size_t size = cls->instanceSize(extraBytes);
if (outAllocatedSize) *outAllocatedSize = size;
id obj;
if (!zone && fast) {
obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
if (!obj) return nil;
obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, hasCxxDtor);
}
else {
if (zone) {
obj = (id)malloc_zone_calloc ((malloc_zone_t *)zone, 1, size);
} else {
obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
}
if (!obj) return nil;
// Use raw pointer isa on the assumption that they might be
// doing something weird with the zone or RR.
obj->initIsa(cls);
}
if (cxxConstruct && hasCxxCtor) {
obj = _objc_constructOrFree(obj, cls);
}
return obj;
}
- 创建对象就要为对象开辟内存空间,这里会不会就是为对象开辟了空间呢?我们发现方法里面调用了 instanceSize方法 ,这个是不是就是开辟内存空间的方法呢?
size_t instanceSize(size_t extraBytes) const {
// 编译器快速计算内存大小
if (fastpath(cache.hasFastInstanceSize(extraBytes))) {
return cache.fastInstanceSize(extraBytes);
}
// 计算类中所有属性的大小 + 额外的字节数0
size_t size = alignedInstanceSize() + extraBytes;
// CF requires all objects be at least 16 bytes.
// 如果size 小于 16,最小取16
if (size < 16) size = 16;
return size;
}
uint32_t alignedInstanceSize() {
return word_align(unalignedInstanceSize());
}
// May be unaligned depending on class's ivars.
// 读取当前的类的属性数据大小
uint32_t unalignedInstanceSize() {
assert(isRealized());
return data()->ro->instanceSize;
}
// 进行内存对齐
// WORD_MASK == 7
static inline uint32_t word_align(uint32_t x) {
return (x + WORD_MASK) & ~WORD_MASK;
}
- 不难看出,instanceSize 方法计算出了对象所需内存的大小,而且必须是大于或等于 16 字节,然后调用 calloc 函数为对象分配内存空间。通过 obj = (id)calloc(1, size) 创建 obj 对象传递了一个 size ,就是 obj 的内存大小对,对于 alloc 申请内存,任何集成 NSObject 对象创建之后默认的内存大小为 16 个字节;
- 那 initInstanceIsa 方法又是干什么的呢?其实这个方法就是初始化isa指针。
- 上面分析了 hasDefaultAWZ( ) 方法返回 Yes 的情况,那如果 hasDefaultAWZ( )方法返回NO呢?以下是 hasDefaultAWZ( ) 返回 NO 的情况,有去判断当前的 class 是否支持快速 alloc。如果可以,直接调用calloc函数,并且申请一块 bits.fastInstanceSize() 大小的内存空间,然后初始化 isa 指针,否则直接调用 class_createInstance 方法。
if (fastpath(cls->canAllocFast())) {
// No ctors, raw isa, etc. Go straight to the metal.
bool dtor = cls->hasCxxDtor();
id obj = (id)calloc(1, cls->bits.fastInstanceSize());
if (slowpath(!obj)) return callBadAllocHandler(cls);
obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, dtor);
return obj;
}
else {
// Has ctor or raw isa or something. Use the slower path.
id obj = class_createInstance(cls, 0);
if (slowpath(!obj)) return callBadAllocHandler(cls);
return obj;
}
- fastInstanceSize 会执行到 align16
size_t fastInstanceSize(size_t extra) const
{
ASSERT(hasFastInstanceSize(extra));
//Gcc的内建函数 __builtin_constant_p 用于判断一个值是否为编译时常数,如果参数EXP 的值是常数,函数返回 1,否则返回 0
if (__builtin_constant_p(extra) && extra == 0) {
return _flags & FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_MASK16;
} else {
size_t size = _flags & FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_MASK;
// remove the FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_DELTA16 that was added
// by setFastInstanceSize
//删除由setFastInstanceSize添加的FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_DELTA16 8个字节
return align16(size + extra - FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_DELTA16);
}
}
- 然后 align16 是 16 字节对齐算法:
// 16字节对齐算法
static inline size_t align16(size_t x) {
return (x + size_t(15)) & ~size_t(15);
}
- 总结:alloc 创建了一个对象并且申请了一块不少于 16 字节的内存空间,并初始化 isa 指针。
② init
既然 alloc 创建了对象,那还要 init 干嘛呢?init 又做了什么呢?
- init 源码如下:
- (id)init {
return _objc_rootInit(self);
}
id _objc_rootInit(id obj) {
// In practice, it will be hard to rely on this function.
// Many classes do not properly chain -init calls.
return obj;
}
- 不难看出,init 并没有做什么,只是把当前的对象返回了。既然什么都没做那我们还需要调用 init 吗?答案是肯定的,其实 init 就是一个工厂模式,方便开发者自行重写定义,即交给子类可以自定义去重写。
③ new
- new 底层源码:
+ (id)new {
return [callAlloc(self, false/*checkNil*/) init];
}
- new 调用的是 callAlloc 方法和 init,那么可以理解为new实际上就是 alloc+init 的综合体。
总结
- alloc 创建了对象并且申请了一块不少于 16 字节的内存空间,并初始化了 isa 指针;
- 相比于 alloc 来说, init 内部实现十分简单,先来到的是 _objc_rootInit ,然后就直接返回 obj 了。其实这里是一种抽象工厂设计模式的体现,对于 NSObject 自带的 init 方法来说,其实啥也没干,但是如果你继承于 NSObject 的话,然后就可以去重写 initWithXXX 之类的初始化方法来做一些初始化操作;
- new 其实是 alloc+init 的一个综合使用。