spring cloud config 读不到文件 不报错_Spring Cloud 系列之 Config 配置中心(一)
服务配置现状
配置文件是我们再熟悉不过的,在微服务系统中,每个微服务不仅仅只有代码,还需要连接其他资源,例如数据库的配置或功能性的开关 MySQL、Redis 、Security 等相关的配置。除了项目运行的基础配置之外,还有一些配置是与我们业务有关系的,比如说七牛存储、短信和邮件相关,或者一些业务上的开关。
但是随着微服务系统的不断迭代,整个微服务系统可能会成为一个网状结构,这个时候就要考虑整个微服务系统的扩展性、伸缩性、耦合性等等。其中一个很重要的环节就是配置管理的问题。
常规配置管理解决方案缺点
- 硬编码(需要修改代码、繁琐、风险大)
- properties 或者 yml(集群环境下需要替换和重启)
- xml(重新打包和重启)
为什么使用 Spring Cloud Config
由于常规配置管理有很大的缺点,所以采用 Spring Cloud Config 集中式的配置中心来管理每个服务的配置信息。
Spring Cloud Config 在微服务分布式系统中,采用 Server 服务端和 Client 客户端的方式来提供可扩展的配置服务。服务端提供配置文件的存储,以接口的形式将配置文件的内容提供出去;客户端通过接口获取数据、并依据此数据初始化自己的应用。
配置中心负责管理所有服务的各种环境配置文件。
配置中心默认采用 Git 的方式存储配置文件,因此我们可以很容易的部署和修改,有助于环境配置进行版本管理。
Spring Cloud Config 解决了什么问题
Spring Cloud Config 解决了微服务配置的中心化、版本控制、平台独立、语言独立等问题。其特性如下:
- 提供服务端和客户端支持(Spring Cloud Config Server 和 Spring Cloud Config Client)
- 集中式管理分布式环境下的应用部署
- 属性值的加密和解密(对称加密和非对称加密)
- 基于 Spring 环境,无缝与 Spring 应用集成
- 可用于任何语言开发的程序
- 默认实现基于 Git ,可以进行版本管理
接下来,我们主要从以下几块来讲一下 Config 的使用。
- 基础版的配置中心(不集成 Eureka)
- 集成 Eureka 版的高可用配置中心
- 基于 Actuator 实现配置的自动刷新
- 配置中心属性值的加密和解密(对称加密和非对称加密)
- 基于 Spring Cloud Bus 实现配置的自动刷新
- 配置中心用户安全认证
环境准备
项目
config-demo 聚合工程。SpringBoot 2.2.4.RELEASE、Spring Cloud Hoxton.SR1。
eureka-server:注册中心(用于集成 Eureka 版的配置中心)eureka-server02:注册中心(用于集成 Eureka 版的配置中心)order-service:订单服务(用于集成 Eureka 版的配置中心)
仓库
config-repo 仓库。
Repository name:仓库名称Description(可选):仓库描述介绍Public,Private:仓库权限(公开共享,私有或指定合作者)Initialize this repository with a README:添加一个 README.mdAdd .gitignore:不需要进行版本管理的文件类型,生成对应文件.gitignoreAdd a license:证书类型,生成对应文件LICENSE
配置文件
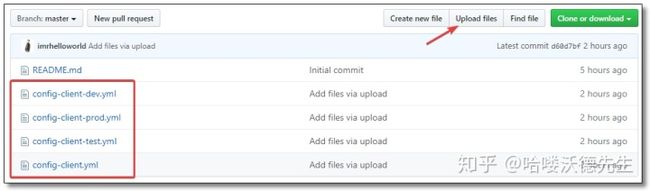
不同环境的配置文件,上传至 config-repo 仓库。
配置文件的名称不是乱起的,例如config-client-dev.yml和config-client-prod.yml这两个文件是同一个项目的不同环境,项目名称为config-client, 一个对应开发环境,一个对应正式环境。test表示测试环境。
config-client.yml
server:
port: 7777 # 端口
spring:
application:
name: config-client # 应用名称
# 自定义配置
name: config-client-defaultconfig-client-dev.yml
server:
port: 7778 # 端口
spring:
application:
name: config-client # 应用名称
# 自定义配置
name: config-client-devconfig-client-test.yml
server:
port: 7779 # 端口
spring:
application:
name: config-client # 应用名称
# 自定义配置
name: config-client-testconfig-client-prod.yml
server:
port: 7780 # 端口
spring:
application:
name: config-client # 应用名称
# 自定义配置
name: config-client-prod入门案例
入门案例讲解:基础版的配置中心(不集成 Eureka)
官方文档:https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/spring-cloud-config/2.2.2.RELEASE/reference/html/
创建服务端
https://www.zhihu.com/video/1243099097307230208在 config-demo 父工程下创建子项目 config-server。
添加依赖
添加 spring-cloud-config-server 依赖,完整 pom.xml 文件如下:
4.0.0
com.example
config-server
1.0-SNAPSHOT
com.example
config-demo
1.0-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-config-server
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.junit.vintage
junit-vintage-engine
配置文件
server:
port: 8888 # 端口
spring:
application:
name: config-server # 应用名称
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/imrhelloworld/config-repo # 配置文件所在仓库地址
#username: # Github 等产品的登录账号
#password: # Github 等产品的登录密码
#default-label: master # 配置文件分支
#search-paths: # 配置文件所在根目录启动类
启动类添加 @EnableConfigServer 注解。
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;
// 配置中心服务端注解
@EnableConfigServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args);
}
}访问规则
Spring Cloud Config 有一套访问规则,我们通过这套规则在浏览器上直接访问即可。
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{application}-{profile}.properties
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties{application}:应用名称(目标服务名称){profile}:获取指定环境配置,项目有开发环境、测试环境、生产环境,对应到配置文件就是以 application-{profile}.yml 加以区分,例如 application-dev.yml、application-test.yml、application-prod.yml。默认值为 default。{label}:表示 git 分支,默认是 master 分支,如果项目是以分支做区分也是可以的,那就可以通过不同的 label 来控制访问不同的配置文件。
测试
http://localhost:8888/config-client/default
http://localhost:8888/config-client/dev/master
http://localhost:8888/config-client-test.yml
http://localhost:8888/master/config-client-prod.yml
访问以上地址,如果可以正常返回数据,说明配置中心服务端一切正常。
创建客户端
https://www.zhihu.com/video/1243099218782777344在 config-demo 父工程下创建子项目 config-client。
添加依赖
添加 spring-cloud-starter-config 依赖,完整 pom.xml 文件如下:
4.0.0
com.example
config-client
1.0-SNAPSHOT
com.example
config-demo
1.0-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-config
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.junit.vintage
junit-vintage-engine
配置文件
客户端配置文件名称必须叫 bootstrap.yml
spring:
cloud:
config:
name: config-client # 配置文件名称,对应 git 仓库中配置文件前半部分
uri: http://localhost:8888 # config-server 服务端地址
label: master # git 分支
profile: default # 指定环境控制层
添加一个 RestController 用于测试获取配置文件信息。
package com.example.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class ConfigController {
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
@GetMapping("/name")
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}启动类
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConfigClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigClientApplication.class, args);
}
}测试
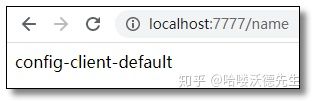
访问:http://localhost:7777/name 结果如下:
修改配置文件为 dev 环境:
spring:
cloud:
config:
name: config-client # 应用名称,对应 git 仓库中配置文件前半部分
uri: http://localhost:8888 # config-server 服务端地址
label: master # git 分支
profile: dev # 指定环境访问:http://localhost:7778/name 结果如下:
Spring Cloud Config 高可用
以上讲了 Spring Cloud Config 最基础的用法,如果我们的项目中使用了 Eureka 作为服务注册发现中心,那么 Spring Cloud Config 也应该注册到 Eureka,方便其他服务使用,并且可以注册多个配置中心服务端,实现高可用。
接下来就集成 Spring Cloud Config 到 Eureka。关于 Eureka 的相关知识大家可翻阅我的历史文章进行学习。
添加配置文件
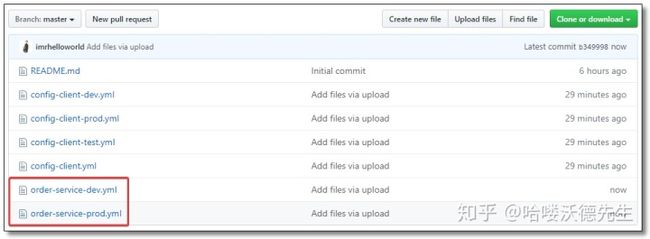
在 Github 仓库中增加配置文件。
order-service-dev.yml
server:
port: 9090 # 端口
spring:
application:
name: order-service # 应用名称
# 配置 Eureka Server 注册中心
eureka:
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true # 是否使用 ip 地址注册
instance-id: ${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${server.port} # ip:port
client:
service-url: # 设置服务注册中心地址
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/,http://localhost:8762/eureka/
# 自定义配置
name: order-service-devorder-service-prod.yml
server:
port: 9091 # 端口
spring:
application:
name: order-service # 应用名称
# 配置 Eureka Server 注册中心
eureka:
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true # 是否使用 ip 地址注册
instance-id: ${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${server.port} # ip:port
client:
service-url: # 设置服务注册中心地址
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/,http://localhost:8762/eureka/
# 自定义配置
name: order-service-prod整合注册中心
案例已经给大家准备好了,无需创建注册中心直接使用即可,为了清楚,把依赖和配置信息给大家贴出来。
依赖
eureka-server 和 eureka-server02 核心依赖部分一致。
4.0.0
com.example
eureka-server
1.0-SNAPSHOT
com.example
config-demo
1.0-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.junit.vintage
junit-vintage-engine
配置文件
eureka-server 的 application.yml
server:
port: 8761 # 端口
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server # 应用名称(集群下相同)
# 配置 Eureka Server 注册中心
eureka:
instance:
hostname: eureka01 # 主机名,不配置的时候将根据操作系统的主机名来获取
prefer-ip-address: true # 是否使用 ip 地址注册
instance-id: ${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${server.port} # ip:port
client:
# 设置服务注册中心地址,指向另一个注册中心
service-url: # 注册中心对外暴露的注册地址
defaultZone: http://localhost:8762/eureka/eureka-server02 的 application.yml
server:
port: 8762 # 端口
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server # 应用名称(集群下相同)
# 配置 Eureka Server 注册中心
eureka:
instance:
hostname: eureka02 # 主机名,不配置的时候将根据操作系统的主机名来获取
prefer-ip-address: true # 是否使用 ip 地址注册
instance-id: ${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${server.port} # ip:port
client:
# 设置服务注册中心地址,指向另一个注册中心
service-url: # 注册中心对外暴露的注册地址
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/启动类
eureka-server 和 eureka-server02 启动类核心代码一致。
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@SpringBootApplication
// 开启 EurekaServer 注解
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class, args);
}
}Spring Cloud Config 服务端
服务端和基础版的配置中心相比多了 Eureka 的配置,其他地方都是一样的。
config-server 服务端构建完成以后再复刻一个 config-server02 实现高可用。
依赖
config-server 和 config-server02 核心依赖部分一致。注意是 spring-cloud-config-server 依赖。
4.0.0
com.example
config-server
1.0-SNAPSHOT
com.example
config-demo
1.0-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-config-server
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.junit.vintage
junit-vintage-engine
配置文件
config-server 的 application.yml
server:
port: 8888 # 端口
spring:
application:
name: config-server # 应用名称
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/imrhelloworld/config-repo # 配置文件所在仓库地址
#username: # Github 等产品的登录账号
#password: # Github 等产品的登录密码
#default-label: master # 配置文件分支
#search-paths: # 配置文件所在根目录
# 配置 Eureka Server 注册中心
eureka:
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true # 是否使用 ip 地址注册
instance-id: ${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${server.port} # ip:port
client:
service-url: # 设置服务注册中心地址
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/,http://localhost:8762/eureka/config-server02 的 application.yml
server:
port: 8889 # 端口
spring:
application:
name: config-server # 应用名称
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/imrhelloworld/config-repo # 配置文件所在仓库地址
#username: # Github 等产品的登录账号
#password: # Github 等产品的登录密码
#default-label: master # 配置文件分支
#search-paths: # 配置文件所在根目录
# 配置 Eureka Server 注册中心
eureka:
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true # 是否使用 ip 地址注册
instance-id: ${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${server.port} # ip:port
client:
service-url: # 设置服务注册中心地址
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/,http://localhost:8762/eureka/启动类
config-server 和 config-server02 启动类核心代码一致。
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;
// 开启 EurekaClient 注解,当前版本如果配置了 Eureka 注册中心,默认会开启该注解
//@EnableEurekaClient
// 配置中心服务端注解
@EnableConfigServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args);
}
}Spring Cloud Config 客户端
客户端加入 Eureka 以后,就不用直接和配置中心服务端打交道了,而是通过 Eureka 来访问。
依赖
order-service 的 pom.xml。注意是 spring-cloud-starter-config 依赖。
4.0.0
com.example
order-service
1.0-SNAPSHOT
com.example
config-demo
1.0-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-config
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.junit.vintage
junit-vintage-engine
配置文件
order-service 的 bootstrap.yml
spring:
cloud:
config:
name: order-service # 配置文件名称,对应 git 仓库中配置文件前半部分
label: master # git 分支
profile: dev # 指定环境
discovery:
enabled: true # 开启
service-id: config-server # 指定配置中心服务端的 service-id控制层
添加一个 RestController 用于测试获取配置文件信息。
package com.example.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class ConfigController {
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
@GetMapping("/name")
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}启动类
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
// 开启 EurekaClient 注解,当前版本如果配置了 Eureka 注册中心,默认会开启该注解
//@EnableEurekaClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}测试
启动注册中心 eureka-server 和 eureka-server02。
启动配置中心服务端 config-server。
启动配置中心客户端 order-service。
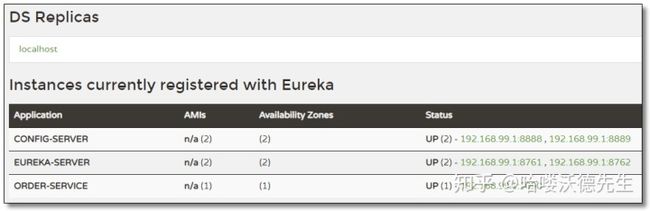
当前环境在 Eureka UI 界面中如下:
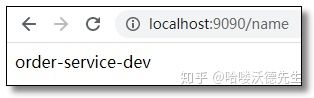
访问:http://localhost:9090/name 结果如下:
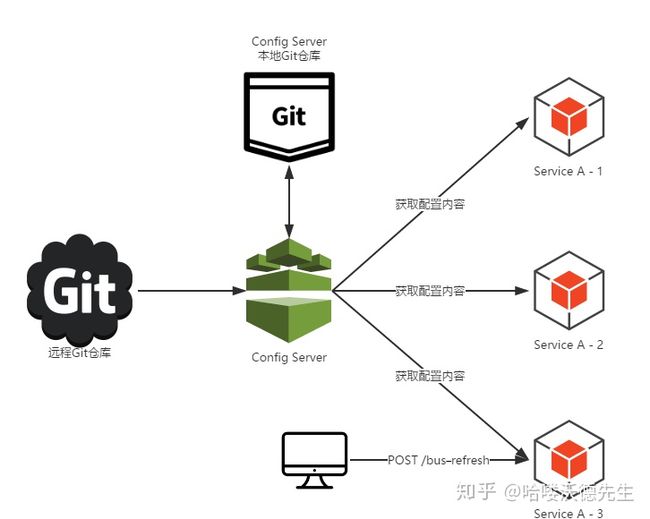
配置中心工作原理
开发人员将配置文件存储至 Git 远程仓库,或后期对 Git 远程仓库的文件进行修改。如果远程仓库发生了版本改变,Config Server 会将 Git 远程仓库中的文件同步至本地仓库中。大家仔细观察 Config Server 的控制台可以看到类似如下信息。
[nio-8888-exec-1] o.s.c.c.s.e.NativeEnvironmentRepository : Adding property source: file:/C:/Users/MRHELL~1/AppData/Local/Temp/config-repo-17506367621853740906/order-service-dev.yml根据控制台信息打开对应的本地目录,会发现 Git 远程仓库中的文件已同步至本地仓库中。
为什么要这么做呢?因为我们要考虑网络波动的情况下,无法访问远程仓库的问题。
下一篇我们讲解 Config 如何实现配置中心自动刷新,记得关注噢~
大家可以通过 分类 查看更多关于 Spring Cloud 的文章。
本文采用 知识共享「署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际」许可协议。
您的点赞和转发是对我最大的支持。
扫码关注 哈喽沃德先生「文档 + 视频」每篇文章都配有专门视频讲解,学习更轻松噢 ~