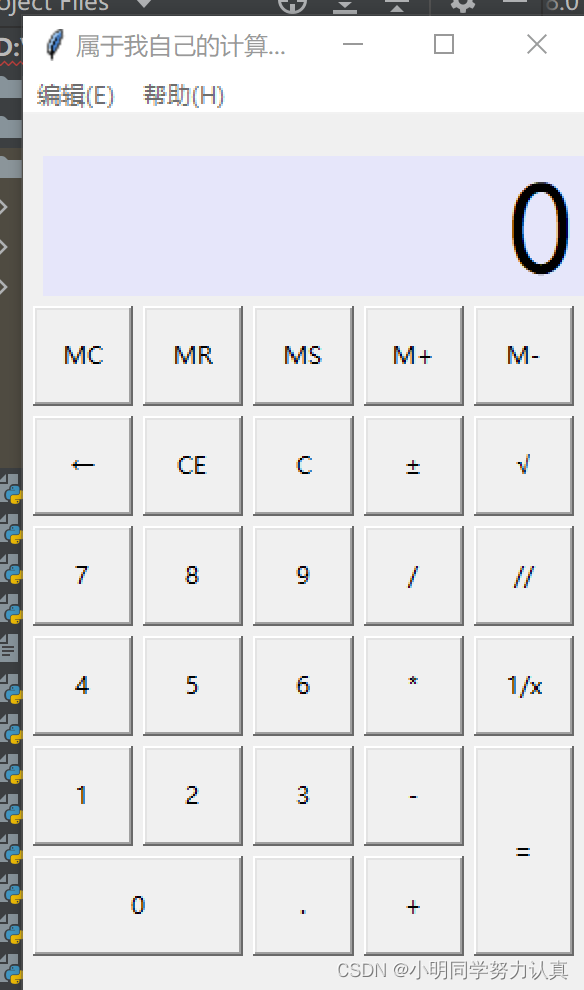
做一个简易计算器 Python
做一个简易的计算器,实现功能加减乘除
菜单栏实现复制粘贴帮助等功能
使用Pycharm运行
import tkinter
import math
import tkinter.messagebox
class Calculator:
# 界面布局方法
def __init__(self):
# 创建主界面,并且保存到成员属性中
self.root = tkinter.Tk()
self.root.minsize(280, 450)
self.root.maxsize(280, 470)
self.root.title('属于我自己的计算器3.0')
# 设置显式面板的变量
self.result = tkinter.StringVar()
self.result.set(0)
# 设置一个全局变量
self.lists = []
# 添加一个用于判断是否按下运算符号的标志
self.ispresssign = False
# 界面布局
self.menus()
self.layout()
self.root.mainloop()
# 计算器菜单界面摆放
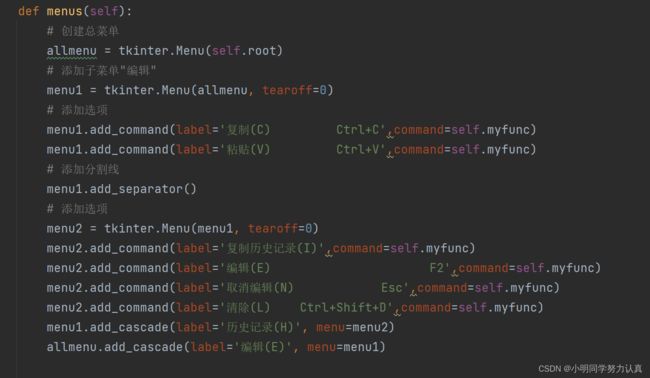
def menus(self):
# 创建总菜单
allmenu = tkinter.Menu(self.root)
# 添加子菜单"编辑"
menu1 = tkinter.Menu(allmenu, tearoff=0)
# 添加选项
menu1.add_command(label='复制(C) Ctrl+C',command=self.myfunc)
menu1.add_command(label='粘贴(V) Ctrl+V',command=self.myfunc)
# 添加分割线
menu1.add_separator()
# 添加选项
menu2 = tkinter.Menu(menu1, tearoff=0)
menu2.add_command(label='复制历史记录(I)',command=self.myfunc)
menu2.add_command(label='编辑(E) F2',command=self.myfunc)
menu2.add_command(label='取消编辑(N) Esc',command=self.myfunc)
menu2.add_command(label='清除(L) Ctrl+Shift+D',command=self.myfunc)
menu1.add_cascade(label='历史记录(H)', menu=menu2)
allmenu.add_cascade(label='编辑(E)', menu=menu1)
# 添加子菜单"帮助"
helpmenu = tkinter.Menu(allmenu, tearoff=0)
# 添加选项卡
helpmenu.add_command(label='查看帮助(V) F1',command=self.myfunc)
# 添加分割线
helpmenu.add_separator()
# 添加选项卡
helpmenu.add_command(label='关于计算器(A)',command=self.myfunc)
allmenu.add_cascade(label='帮助(H)',menu=helpmenu)
#读取文件中的配置
self.root.config(menu=allmenu)
# 计算器主界面摆放
def layout(self):
result = tkinter.StringVar()
result.set(0)
show_label = tkinter.Label(self.root, bd=3, bg='lavender', font=('楷体', 50),anchor='e', textvariable=self.result)
show_label.place(x=10, y=20, width=270, height=70)
button_mc = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='MC', command=self.wait)
button_mc.place(x=5, y=95, width=50, height=50)
button_mr = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='MR', command=self.wait)
button_mr.place(x=60, y=95, width=50, height=50)
button_ms = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='MS', command=self.wait)
button_ms.place(x=115, y=95, width=50, height=50)
button_mjia = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='M+', command=self.wait)
button_mjia.place(x=170, y=95, width=50, height=50)
button_mjian = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='M-', command=self.wait)
button_mjian.place(x=225, y=95, width=50, height=50)
button_zuo = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='←', command=self.dele_one)
button_zuo.place(x=5, y=150, width=50, height=50)
button_ce = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='CE', command=lambda: self.result.set(0))
button_ce.place(x=60, y=150, width=50, height=50)
button_c = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='C', command=self.sweeppress)
button_c.place(x=115, y=150, width=50, height=50)
button_zf = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='±', command=self.zf)
button_zf.place(x=170, y=150, width=50, height=50)
button_kpf = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='√', command=self.kpf)
button_kpf.place(x=225, y=150, width=50, height=50)
button_7 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='7', command=lambda: self.pressnum('7'))
button_7.place(x=5, y=205, width=50, height=50)
button_8 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='8', command=lambda: self.pressnum('8'))
button_8.place(x=60, y=205, width=50, height=50)
button_9 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='9', command=lambda: self.pressnum('9'))
button_9.place(x=115, y=205, width=50, height=50)
button_division = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='/', command=lambda: self.pressnum('/'))
button_division.place(x=170, y=205, width=50, height=50)
button_remainder = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='//', command=lambda: self.pressnum('//'))
button_remainder.place(x=225, y=205, width=50, height=50)
button_4 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='4', command=lambda: self.pressnum('4'))
button_4.place(x=5, y=260, width=50, height=50)
button_5 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='5', command=lambda: self.pressnum('5'))
button_5.place(x=60, y=260, width=50, height=50)
button_6 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='6', command=lambda: self.pressnum('6'))
button_6.place(x=115, y=260, width=50, height=50)
button_multiplication = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='*', command=lambda: self.pressnum('*'))
button_multiplication.place(x=170, y=260, width=50, height=50)
button_reciprocal = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='1/x', command=self.ds)
button_reciprocal.place(x=225, y=260, width=50, height=50)
button_1 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='1', command=lambda: self.pressnum('1'))
button_1.place(x=5, y=315, width=50, height=50)
button_2 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='2', command=lambda: self.pressnum('2'))
button_2.place(x=60, y=315, width=50, height=50)
button_3 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='3', command=lambda: self.pressnum('3'))
button_3.place(x=115, y=315, width=50, height=50)
button_subtraction = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='-', command=lambda: self.pressnum('-'))
button_subtraction.place(x=170, y=315, width=50, height=50)
button_equal = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='=', command=lambda: self.pressequal())
button_equal.place(x=225, y=315, width=50, height=105)
button_0 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='0', command=lambda: self.pressnum('0'))
button_0.place(x=5, y=370, width=105, height=50)
button_point = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='.', command=lambda: self.pressnum('.'))
button_point.place(x=115, y=370, width=50, height=50)
button_plus = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='+', command=lambda: self.pressnum('+'))
button_plus.place(x=170, y=370, width=50, height=50)
# 计算器菜单功能
def myfunc(self):
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('','菜单只是装饰')
# 数字方法
def pressnum(self, num):
# 判断是否按下了运算符号
if self.ispresssign == False:
pass
else:
self.result.set(0)
# 重置运算符号的状态
self.ispresssign = False
if num == '.':
num = '0.'
# 获取面板中的原有数字
oldnum = self.result.get()
# 判断界面数字是否为0
if oldnum == '0':
self.result.set(num)
else:
# 连接上新按下的数字
newnum = oldnum + num
# 将按下的数字写到面板中
self.result.set(newnum)
# 运算函数
def presscalculate(self, sign):
# 获取界面数字
num = self.result.get()
self.lists.append(num)
# 保存按下的操作符号
self.lists.append(sign)
# 设置运算符号为按下状态
self.ispresssign = True
# 获取运算结果
def pressequal(self):
# 获取当前界面上的数字
curnum = self.result.get()
# 将当前界面的数字存入列表
self.lists.append(curnum)
# 将列表转化为字符串
calculatestr = ''.join(self.lists)
# 使用eval执行字符串中的运算即可
endnum = eval(calculatestr)
# 将运算结果显示在界面中
self.result.set(str(endnum)[:10])
if self.lists != 0:
self.ispresssign = True
# 清空运算列表
self.lists.clear()
# 暂未开发说明
def wait(self):
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('', '此功能不会')
# ←按键功能
def dele_one(self):
if self.result.get() == '' or self.result.get() == '0':
self.result.set('0')
return
else:
num = len(self.result.get())
if num > 1:
strnum = self.result.get()
strnum = strnum[0:num - 1]
self.result.set(strnum)
else:
self.result.set('0')
# ±按键功能
def zf(self):
strnum = self.result.get()
if strnum[0] == '-':
self.result.set(strnum[1:])
elif strnum[0] != '-' and strnum != '0':
self.result.set('-' + strnum)
# 1/x按键功能
def ds(self):
dsnum = 1 / int(self.result.get())
self.result.set(str(dsnum)[:10])
if self.lists != 0:
self.ispresssign = True
# 清空运算列表
self.lists.clear()
# C按键功能
def sweeppress(self):
self.lists.clear()
self.result.set(0)
# √按键功能
def kpf(self):
strnum = float(self.result.get())
endnum = math.sqrt(strnum)
if str(endnum)[-1] == '0':
self.result.set(str(endnum)[:-2])
else:
self.result.set(str(endnum)[:10])
if self.lists != 0:
self.ispresssign = True
# 清空运算列表
self.lists.clear()
if __name__ == '__main__':
myCalculator = Calculator()