Java-String
任何字符串都是String类的对象,字符串是不变的,它们的值在创建后无法更改
在字符串的内部,是用一串字符char[]来存储的。因为数组一经确定长度无法更改,所以字符串一经创建就无法更改。
如果两个字符串内容相同,则他俩使用同一个内存地址,所以可以共享它们
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "123";
String s2 = "123";
String s3 = new String("123");
//s1 和 s2共享内存地址
System.out.println(s1==s2);//true
//通过new在堆中新开辟的空间,内存地址不同
System.out.println(s1==s3);//false
}
}
字符串常量池
方法区(Method Area),又称永久代(Permanent Generation),又称非堆区(Non-Heap space)方法区,又称永久代,位于非堆区。
方法区是被所有线程共享的。
所有字段和方法字节码,以及一些特殊方法如构造函数,接口代码也在此定义。
简单说,所有定义的方法的信息都保存在该区域,此区属于共享区间。
堆(heap)
一个jvm实例只存在一个堆内存,堆内存的大小是可以调节的。类加载器读取了类文件后,需要把、类、方法、常变量放到堆内存中,保存所有引用类型的真实信息,以便执行器执行。
堆 在逻辑上分为三部分(perm):
新生代(Young generation,常称为YoungGen)
刚创建的对象在新生代,新生代GC机制不一样。GC询问的频率很高。
老年代(Old Generation,常称为OldGen、 TenuringGen)
如果一个对象经过很多次(15次)GC过滤都没有被清理。则会转入老年代。老年代中,GC活动频率很低。
永久代(Permannent)
永不GC。类、方法、常量以及静态加载的,每一个字符串对象的创建都会放入永久代
构造器:
String() 初始化新创建的 String对象,使其表示空字符序列。
String(byte[] bytes) 通过使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的字节数组构造新的 String 。
String(byte[] bytes, String charsetName) 构造一个新的String由指定用指定的字节的数组解码charset 。
String(char[] value) 分配新的 String ,使其表示当前包含在字符数组参数中的字符序列。
常用方法
- char charAt(int index) 返回指定索引处的 char值。
- int compareTo(String anotherString) 按字典顺序比较两个字符串。
结果为整数则表示大于,结果为0表示等于,结果为负数表示小于。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "123";
String s2 = "123";
String s3 = "456";
String s4 = "789";
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));//0
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3));//-3
System.out.println(s4.compareTo(s3));//3
}
}
- int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) 按字典顺序比较两个字符串,忽略大小写差异。
结果为整数则表示大于,结果为0表示等于,结果为负数表示小于。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "Abc";
String s3 = "abC";
String s4 = "aBc";
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2));//0
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));//32
System.out.println(s3.compareToIgnoreCase(s4));//0
System.out.println(s3.compareTo(s4));//32
}
}
- boolean contains(CharSequence s) 当且仅当此字符串包含指定的char值序列时,才返回true。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "bc";
String s3 = "C";
String s4 = "";
String s5 = " ";
System.out.println(s1.contains(s2));//true
System.out.println(s2.contains(s1));//false
//contains()区分大小写
System.out.println(s1.contains(s3));//false
//任何字符串包含空字符串
System.out.println(s1.contains(s4));//true
//空格属于字符串
System.out.println(s1.contains(s5));//false
}
}
- boolean contentEquals(CharSequence cs)
将此字符串与指定的 CharSequence 比较。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcd";
CharSequence cs1 = "abcd";
CharSequence cs2 = "abc";
CharSequence cs3 = "";
CharSequence cs4 = "Abcd";
System.out.println(s1.contentEquals(cs1));//true
System.out.println(s1.contentEquals(cs2));//false
System.out.println(s1.contentEquals(cs3));//false
System.out.println(s1.contentEquals(cs4));//false
}
}
-
boolean contentEquals(StringBuffer sb)
将此字符串与指定的 StringBuffer 比较。 -
boolean endsWith(String suffix)
测试此字符串是否以指定的后缀结尾。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcd";
System.out.println(s1.endsWith("d"));//true
System.out.println(s1.contentEquals("c"));//false
System.out.println(s1.contentEquals(""));//false
}
}
- boolean equals(Object anObject)
将此字符串与指定的对象进行比较。(只能比较两个String 类型,如果用一个String类型的字符串和一个StringBuilder类型作比较,即使内容一样也是false)
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcd";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("abcd");
System.out.println(s1.equals(sb));//false
System.out.println(s1.contentEquals(sb));//true
}
}
-
static String format(String format, Object… args)
String类的format()方法用于创建格式化的字符串以及连接多个字符串对象。format()方法有两种重载形式:
format(String format, Object… args) 新字符串使用本地语言环境,制定字符串格式和参数生成格式化的新字符串。
format(Locale locale, String format, Object… args) 使用指定的语言环境,制定字符串格式和参数生成格式化的字符串。
参考下表:
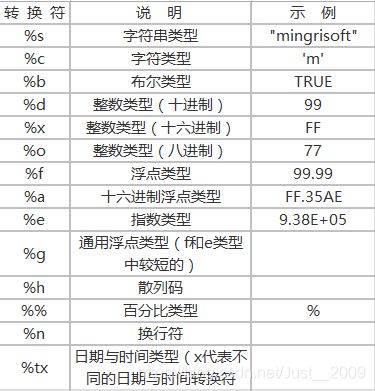
-
void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin)
将此字符串中的字符复制到目标字符数组中。
参数列表
srcBegin:字符串中起始索引位置(包含)
srcEnd:字符串中结束索引位置(不包含)
dst:目标字符数组
dstBegin:目标字符数组开始索引位置
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcd";
char [] s2 = new char[10];
s1.getChars(1,4,s2,5);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s2));//[ , , , , , b, c, d, , ]
}
}
- int hashCode()
返回此字符串的哈希码。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcd";
String s2 = "abcd";
String s3 = "abc";
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());//2987074
System.out.println(s2.hashCode());//2987074
System.out.println(s3.hashCode());//96354
}
}
- int indexOf(int ch)
返回指定字符第一次出现的字符串中的索引。
int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)
返回指定字符第一次出现的此字符串中的索引,从指定索引处开始搜索。
int indexOf(String str)
返回指定子字符串第一次出现的字符串中的索引。
int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
从指定的索引处开始,返回指定子字符串第一次出现的字符串的索引位置。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcd efgh";
String s2 = "aBc";
String s3 = "abc";
String s4 = "";
String s5 = " ";
String s6 = "abcdccf";
System.out.println(s1.indexOf(s2));//-1
System.out.println(s1.indexOf(s3));//0
System.out.println(s1.indexOf(s4));//0
System.out.println(s1.indexOf(s5));//4
System.out.println(s6.indexOf("c"));//2 返还第一次出现的字符串的索引位置
}
}
-
boolean isBlank()
如果字符串为空或仅包含 white space代码点,则返回 true ,否则 false 。 -
boolean isEmpty()
返回 true ,当且仅当, length()是 0 。 -
int lastIndexOf(int ch)
返回指定字符最后一次出现的字符串中的索引。
int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)
返回指定字符最后一次出现的字符串中的索引,从指定的索引开始向后搜索。
int lastIndexOf(String str)
返回指定子字符串最后一次出现的字符串中的索引。
int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
返回指定子字符串最后一次出现的字符串中的索引,从指定索引开始向后搜索。 -
int length()
返回此字符串的长度。 -
String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)
返回从替换所有出现的导致一个字符串 oldChar在此字符串 newChar 。
String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement)
将此字符串中与文字目标序列匹配的每个子字符串替换为指定的文字替换序列。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcd efghd";
String s2 = "xxxc";
System.out.println(s1.replace("b",s2));//axxxccd efgh
System.out.println(s1.replace("d",s2));//abcxxxc efghxxxc
System.out.println(s1.replace("",s2));//xxxcaxxxcbxxxccxxxcdxxxc xxxcexxxcfxxxcgxxxchxxxc
}
}
- String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement)
将给定替换的给定 regular expression匹配的此字符串的每个子字符串替换。
通常情况下与replace没有区别,但是在替换转移字符串时,replace会出现问题,replaceAll的参数就是regex,是正则表达式。首先会转义,所以报错。
System.out.println(x.replace("\\", "++")); //不会报错
System.out.println(x.replaceAll("\\", "++")); //报错 java.util.regex.PatternSyntaxException
System.out.println(x.replaceAll("\\\\", "++"));//不会报错
当字符串无法确定是否含有转移字符是,且无需使用转义字符,用replace()
否则使用replaceAll()
- String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement)
将给定替换的给定 regular expression匹配的此字符串的第一个子字符串替换。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcd efghd";
String s2 = "!";
System.out.println(s1.replaceFirst("d",s2));//abc! efghd
}
}
- String[] split(String regex)
将此字符串拆分依据与 regular expression匹配项 。
String[] split(String regex, int limit)
将此字符串拆分依据与 regular expression的匹配项 。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcd efghd";
String s2 = "!";
//以匹配的的字符串"d"进行拆分,移除"d",将"d"两侧的元素分别放入不同的位置。
String[] s3 = s1.split("d");
String[] s4 = s1.split("c");
//以匹配的的字符串"d"进行拆分,移除"d",将"d"两侧的元素分别放入不同的位置。同时限制数组最大长度。
String[] s5 = s1.split("d",5);
String[] s6 = s1.split("d",2);
String[] s7 = s1.split("d",1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s3));//[abc, efgh]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s4));//[ab, d efghd]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s5));//[abc, efgh, ]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s6));//[abc, efghd]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s7));//[abcd efghd]
}
}
- boolean startsWith(String prefix)
测试此字符串是否以指定的前缀开头。 - boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset)
测试从指定索引开始的此字符串的子字符串是否以指定的前缀开头。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcd efghd";
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("a"));//true
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("d"));//false
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("c"));//false
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("c",2));//true
}
}
- String strip()
返回一个字符串,其值为此字符串,并删除了所有前导和尾随 white space 。
String stripLeading()
返回一个字符串,其值为此字符串,并删除了所有前导 white space 。
String stripTrailing()
返回一个字符串,其值为此字符串,并删除所有尾随 white space 。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = " W a r ";
System.out.println(s1.strip());//"W a r" 去头尾空格
System.out.println(s1.stripLeading());//"W a r "去头空格
System.out.println(s1.stripTrailing());//" W a r"去尾空格
}
}
- String substring(int beginIndex)
返回一个字符串,该字符串是此字符串的子字符串。
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
返回一个字符串,该字符串是此字符串的子字符串。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcdefg";
System.out.println(s1.substring(1));//bcdefg
System.out.println(s1.substring(3));//defg
System.out.println(s1.substring(4,6));//ef(包括头不包括尾)
}
}
- String toLowerCase()
使用默认语言环境的规则将此 String所有字符转换为小写。
String toLowerCase(Locale locale)
使用给定 Locale的规则将此 String所有字符转换为 Locale 。
String toUpperCase()
使用默认语言环境的规则将此 String所有字符转换为大写。
String toUpperCase(Locale locale)
使用给定 Locale的规则将此 String所有字符转换为大写。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "aBcDeFg";
System.out.println(s1.toLowerCase());//abcdefg
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());//ABCDEFG
}
}
- String trim()
trim()方法实际上的行为并不是”去掉两端的空白字符“,而是”截取中间的非空白字符“。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = " aBcD eFg ";
String s2 = "aBcDeFg ";
String s3 = " aBcDeFg";
System.out.println(s1.trim());//aBcD eFg
System.out.println(s2.trim());//aBcDeFg
System.out.println(s3.trim());//aBcDeFg
}
}
27.由基本数据型态转换成String
static String valueOf(boolean b)
将传入参数的类型转化为字符串类型输出。
static String valueOf(char c)
static String valueOf(char[] data)
static String valueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count)
static String valueOf(double d)
static String valueOf(float f)
static String valueOf(int i)
static String valueOf(long l)
static String valueOf(Object obj)
StringBuffer和StringBuilder
两者皆是字符串变量 而String是字符串常量
1.运算速率:StringBuilder>StringBuffer>String
2.线程安全:StringBuilder线程不安全 StringBuffer线程安全