java~jdk1.8新特性:Stream详解
一、概念:
- Java 8 API添加了一个新的抽象称为流Stream,可以让你以一种声明的方式处理数据。
- Stream 使用一种类似用 SQL 语句从数据库查询数据的直观方式来提供一种对 Java 集合运算和表达的高阶抽象。
- Stream API可以极大提高Java程序员的生产力,让程序员写出高效率、干净、简洁的代码。
- 这种风格将要处理的元素集合看作一种流, 流在管道中传输, 并且可以在管道的节点上进行处理, 比如筛选, 排序,聚合等。
二、获取stream的方法:
当我们在用strema流时,首先要获取到集合流,从而调用java为我们提供Strema接口中的方法,关于获取stream流的方式则有以下三种:
- 集合Collection:直接 .stream();
- 集合Map:使用间接方法 entrySet、keySet、values,再 .stream();
- 数组:Arrays.stream方法、或者是Stream.of()。
三、stream中常用的方法:
- 条件过滤:filter()
- 统计个事:count()
- 截取集合中的前几个元素:limit()
- 去除集合中的前几个元素:skip()
- 合并集合:concat()
- 排序:sorted()
- 去重:distinct()
四、将stream流转换成集合的方法:
- 转List集合:stream.collect(Collectors.toList());
- 转Set集合:stream.collect(Collectors.toSet());
- 转数组:stream.toArray() \ stream.toArray(泛型)。注:推荐第二种,因为可以直接指定转换后数组的泛型
五、获取stream并发流:
- 直接获取: .parallelStream();
- 间接获取: stream.paeallel();
六、方法代码按理:
首先创建一个实体Student,并建一个List集合:
public class Student {
private String name; //姓名
private int age; //年龄
private String sex; //性别
private String classCode; //班级
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getClassCode() {
return classCode;
}
public void setClassCode(String classCode) {
this.classCode = classCode;
}
public Student(String name,int age,String sex,String classCode) {
this.name =name;
this.age =age;
this.sex =sex;
this.classCode = classCode;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", sex=" + sex + ", classCode=" + classCode + "]";
}
}
public static List<Student> getList(){
List<Student> studs = Arrays.asList(new Student("唐三藏", 34, "男·", "六年级"),
new Student("孙悟空", 503, "男", "五年级"),
new Student("猪八戒", 66, "男", "五年级"),
new Student("沙悟净", 99, "男", "五年级"),
new Student("白骨精", 18, "女", "二年级"),
new Student("女儿国国王", 46, "女", "四年级"));
return studs;
}
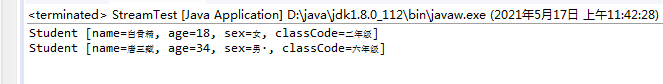
1. filter 过滤:
/** filter过滤(T -> boolean)
* 输出:年龄大于20的同学【除了白骨精】
*/
List<Student> list =getList();
List<Student> collect = list.stream().filter(student -> student.getAge() > 20).collect(Collectors.toList());
for (Student stu : collect) {
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
List<Student> list = getList();
List<Student> collect = list.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
for(Student stu : collect){
System.out.println(stu.getName());
}
3. sorted 排序
/** sorted排序
* 按年龄大小来排序
*/
List<Student> list = getList();
List<Student> collect = list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(Student :: getAge)).collect(Collectors.toList());
for(Student stu : collect){
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
/** 排完序显示前2条数据
*/
List<Student> list = getList();
List<Student> collect = list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(Student :: getAge)).limit(2).collect(Collectors.toList());
for(Student stu : collect){
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
5. map 输出一列
//只输出name的那一列并去重
List<Student> list = getList();
List<String> collect = list.stream().map(Student :: getName).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
for(String stu : collect){
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
输出结果:

6. allMatch (T -> boolean) 检测是否全部满足参数行为
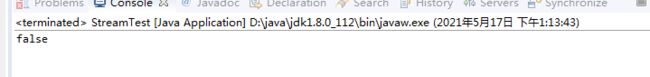
List<Student> list = getList();
boolean allMatch = list.stream().allMatch(student -> student.getAge()>100);
System.out.println(allMatch);
输出结果:
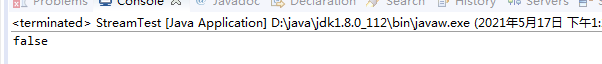
7. anyMatch (T ->boolean) : 检测是否有任意元素满足给定的条件
List<Student> list = getList();
boolean allMatch = list.stream().anyMatch(student -> student.getAge()>100);
System.out.println(allMatch);
8. noneMatch (T ->boolean) 流中是否有元素匹配给定的 T -> boolean条件
List<Student> list = getList();
boolean allMatch = list.stream().noneMatch(student -> student.getClassCode().contains("二年级"));
System.out.println(allMatch);
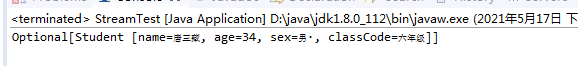
9. findFirst 找到第一个元素
List<Student> list = getList();
Optional<Student> findFirst = list.stream().findFirst();
System.out.println(findFirst.toString());
List<Student> list = getList();
Optional<Student> findFirst = list.stream().findAny();
System.out.println(findFirst.toString());
List<Student> list = getList();
long count = list.stream().count();
System.out.println(count);
12. maxBy /minBy 最大/最小值
List<Student> list = getList();
Optional<Student> max = list.stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge)));
Optional<Student> min = list.stream().collect(Collectors.minBy(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge)));
System.out.println("max:"+max);
System.out.println("min:"+min);
输出结果:

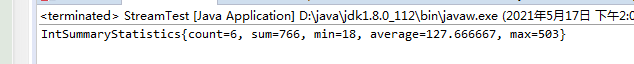
13. summarizingInt 一次性得到元素的个数、总和、最大值、最小值
List<Student> list = getList();
IntSummaryStatistics collect = list.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(Student::getAge));
System.out.println(collect);
14. joining 拼接
List<Student> list = getList();
String string = list.stream().map(Student :: getName).collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
System.out.println(string);
输出结果:

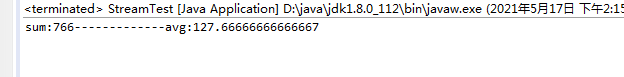
15. summingInt()/averagingInt() 求和/平均值
List<Student> list = getList();
Integer sumAge = list.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(Student ::getAge));
Double avg = list.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Student:: getAge));
System.out.println("sum:"+sumAge+"-------------avg:"+avg);
输出结果:
16. flatMap(T ->Stream) 数组转集合
List<String> flatmap = new ArrayList<>();
flatmap.add("常宣灵,常昊灵");
flatmap.add("孟婆,判官红,判官蓝");
/* 这里原集合中的数据由逗号分割,使用split进行拆分后,得到的是Stream, 字符串数组组成的流,要使用flatMap的Arrays::stream 将Stream转为Stream,然后把流相连接 */
flatmap = flatmap.stream() .map(s -> s.split(",")) .flatMap(Arrays::stream) .collect(Collectors.toList());
for (String name : flatmap) { System.out.println(name); }