力扣总结记录
一、动态规划
1.连续数列 / 最大子序和
给定一个整数数组,找出总和最大的连续数列,并返回总和。
int Func(Vector& nums)
{
if(nums.empty()) return 0;
int pre = 0;//f(i) = max(f(i)+x,x)
int ans = nums[0];
for(auto x:nums)
{
pre = max(pre+x,x);
ans = max(pre,ans);
}
return ans;
} 2.买卖股票的最佳时机 II
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
int dp[n][2];
dp[0][0] = 0;
dp[0][1] = -prices[0];//第0天持有一支股票的时候,肯定是买入,所以是负的
for(int i=1;i 3.零钱兑换
给你一个整数数组 coins ,表示不同面额的硬币;以及一个整数 amount ,表示总金额。
计算并返回可以凑成总金额所需的 最少的硬币个数 。如果没有任何一种硬币组合能组成总金额,返回 -1 。你可以认为每种硬币的数量是无限的。
int coinChange(vector& coins, int amount) {
int MAX = amount+1;//凑成amount多需要amount个1元的硬币
vector dp(MAX,MAX);//dp[i]表示凑成i元时所需要的最小硬币个数
dp[0] = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=amount;++i)
{
for(int j = 0;j=coins[j])
{
dp[i] = min(dp[i],dp[i-coins[j]]+1);
}
}
}
return dp[amount]>amount?-1:dp[amount];
} 4. 最长公共子序列
给定两个字符串 text1 和 text2,返回这两个字符串的最长 公共子序列 的长度。如果不存在 公共子序列 ,返回 0 。
一个字符串的 子序列 是指这样一个新的字符串:它是由原字符串在不改变字符的相对顺序的情况下删除某些字符(也可以不删除任何字符)后组成的新字符串。
例如,"ace" 是 "abcde" 的子序列,但 "aec" 不是 "abcde" 的子序列。
两个字符串的 公共子序列 是这两个字符串所共同拥有的子序列。
class Solution {
public:
int longestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) {
int m = text1.length();
int n = text2.length();
if(m == 0 || n == 0) return 0;
vector> dp(m+1,vector(n+1));
for(int i = 1;i<=m;++i)
{
char c1 = text1[i-1];
for(int j = 1;j<=n;++j)
{
char c2 = text2[j-1];
if(c1 == c2)
{
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
}
else
{
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j-1],dp[i-1][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
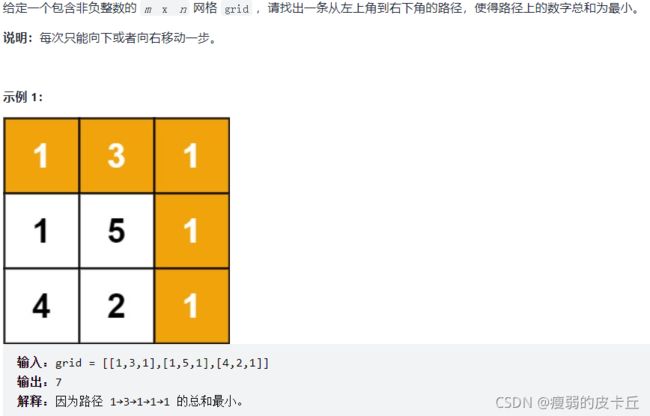
}; 5.最小路径和
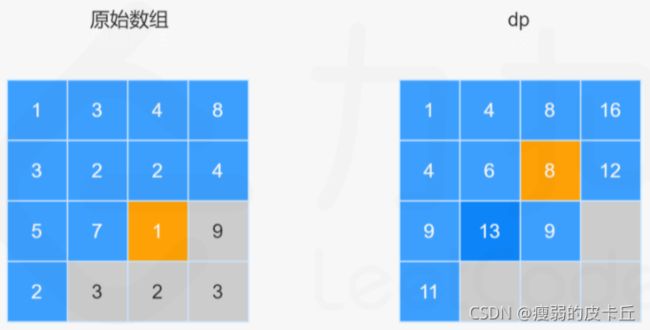
int minPathSum(vector>& grid) {
if(grid.empty() || grid[0].empty()) return 0;
int rows = grid.size();
int columns = grid[0].size();
vector> dp(rows,vector(columns,0));
dp[0][0] = grid[0][0];
for(int i = 1;i 6.最长递增子序列
输入:nums = [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18] 输出:4 解释:最长递增子序列是 [2,3,7,101],因此长度为 4 。
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLIS(vector& nums) {
int n = (int)nums.size();
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
vector dp(n, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
dp[i] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
if (nums[j] < nums[i]) {
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
}
return *max_element(dp.begin(), dp.end());
}
}; 7.丑数
我们把只包含质因子 2、3 和 5 的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。求按从小到大的顺序的第 n 个丑数。
某个丑数是通过其他丑数*2 *3 或*5得到的。
class Solution {
public:
int nthUglyNumber(int n) {
vector dp(n+1);
dp[1] = 1;
int p2 = 1;
int p3 = 1;
int p5 = 1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;++i)
{
dp[i] = min(min(dp[p2]*2,dp[p3]*3),dp[p5]*5);
if(dp[i] == dp[p2]*2)
{
p2++;
}
if(dp[i] == dp[p3]*3)
{
p3++;
}
if(dp[i] == dp[p5]*5)
{
p5++;
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}; 8.不同路径
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
if(m<0 || n<0) return 0;
vector> dp(m,vector(n,0));
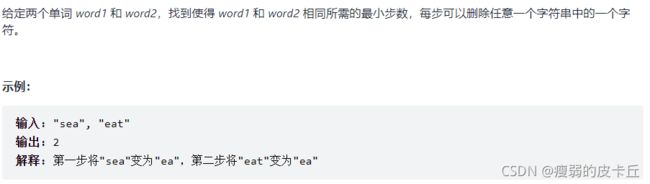
for(int i=0;i 9.两个字符串的删除操作
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
if(word1.empty() || word2.empty()) return 0;
int m = word1.size();
int n = word2.size();
vector> dp(m+1,vector(n+1));
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i)
{
for(int j = 1;j<=n;++j)
{
if(word1[i-1] == word2[j-1])
{
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
}
else
{
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
return m+n-2*dp[m][n];
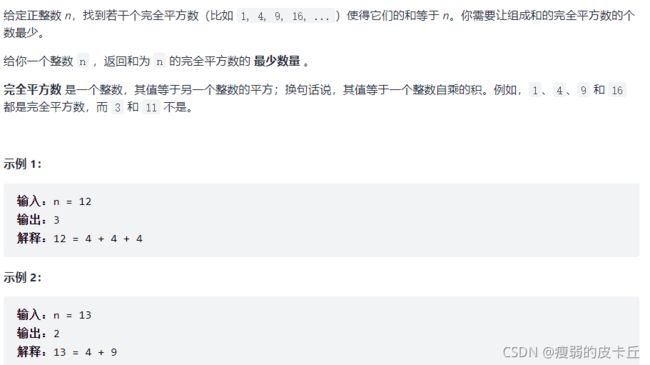
} 10.完全平方数
class Solution {
public:
int numSquares(int n) {
vector dp(n+1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
int ans = INT_MAX;
for(int j=1;j*j<=i;++j)
{
ans = min(ans,dp[i-j*j]+1);
}
dp[i] = ans;//加1代表j当前是一个完全平方数,应该算上j
}
return dp[n];
}
}; 11.回文子串
动态规划 dp[j]表示从 j位置 到当前遍历到的字符 位置i 是否为回文字符串。
class Solution {
public:
int countSubstrings(string s) {
vector dp(s.length());
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i 12.不同的二叉搜索树
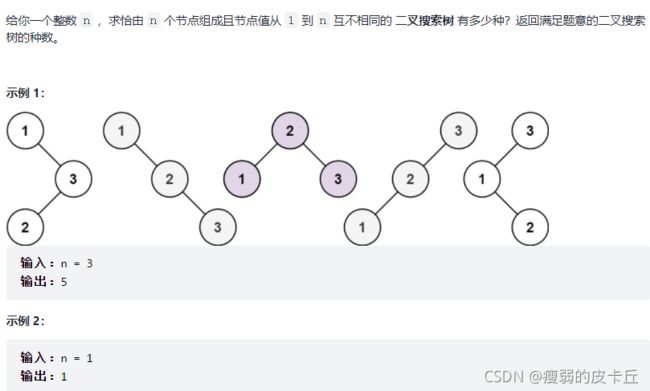
class Solution {
public:
int numTrees(int n) {
vector dp(n+1,0);
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;++i)//i代表当前序列的长度
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;++j)//j代表当前树的根结点
{
dp[i]+=dp[j-1]*dp[i-j];
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}; 13.最长重复子数组
class Solution {
public:
int findLength(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {
int m = nums1.size();
int n = nums2.size();
if(m == 0||n==0) return 0;
vector> dp(m+1,vector(n+1,0));
int ans = INT_MIN;
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;++j)
{
if(nums1[i-1] == nums2[j-1])
{
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
}
if(dp[i][j] > ans) ans = dp[i][j];
}
}
return ans;
}
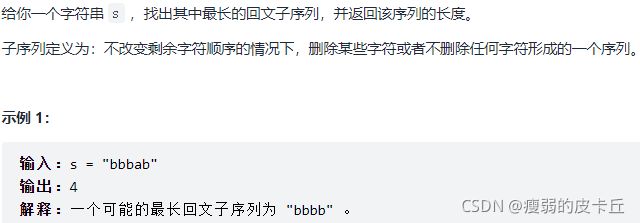
}; 14.最长回文子序列
class Solution {
public:
int longestPalindromeSubseq(string s) {
if(s.empty()) return 0;
vector> dp(s.size(),vector(s.size()));
/*dp[i][j]代表字符串s i到j中的最长回文子串*/
for(int i = s.size()-1;i>=0;--i)
{
dp[i][i] = 1;
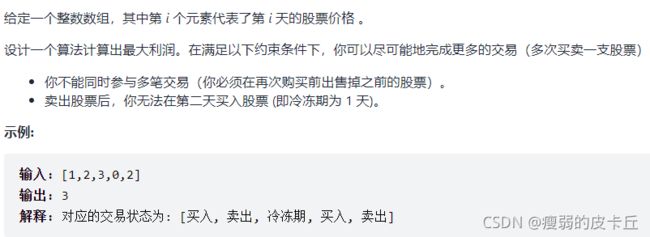
for(int j=i+1;j 15.最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector& prices) {
if (prices.empty()) {
return 0;
}
int n = prices.size();
// f[i][0]: 手上持有股票的最大收益
// f[i][1]: 手上不持有股票,并且处于冷冻期中的累计最大收益
// f[i][2]: 手上不持有股票,并且不在冷冻期中的累计最大收益
vector> f(n, vector(3));
f[0][0] = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
f[i][0] = max(f[i - 1][0], f[i - 1][2] - prices[i]);
f[i][1] = f[i - 1][0] + prices[i];
f[i][2] = max(f[i - 1][1], f[i - 1][2]);
}
return max(f[n - 1][1], f[n - 1][2]);
}
};
16.编辑距离
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
int m = word1.size();
int n = word2.size();
vector> dp(m+1,vector(n+1));
for(int i=0;i<=m;++i)
{
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for(int i=0;i<=n;++i)
{
dp[0][i] = i;
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;++j)
{
if(word1[i-1] == word2[j-1])
{
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1];
}
else{
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j-1],min(dp[i][j-1],dp[i-1][j]))+1;
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}; 17.不同路径2
class Solution {
public:
int uniquePathsWithObstacles(vector>& obstacleGrid) {
if(obstacleGrid.empty()) return 0;
int m = obstacleGrid.size();
int n = obstacleGrid[0].size();
vector> dp(m,vector(n));
for(int i=0;i 18. 机器人的运动范围
class Solution {
public:
int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {
if(k<=0) return 1;
vector> dp(m,vector(n,0));
int ans = 1;
dp[0][0] = 1;
for(int i=0;ik) continue;
if(i!=0) dp[i][j] |= dp[i-1][j];
if(j!=0) dp[i][j] |= dp[i][j-1];
ans+=dp[i][j];
}
}
return ans;
}
int get(int x,int y)
{
int ans = 0;
while(x>0)
{
ans += x%10;
x/=10;
}
while(y>0)
{
ans+=y%10;
y/=10;
}
return ans;
}
}; 19.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector& prices, int fee) {
int n = prices.size();
vector> dp(n,vector(2));
dp[0][0] = 0;
dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
for(int i=1;i 二、贪心算法
1.最长连续递增序列
给定一个未经排序的整数数组,找到最长且 连续递增的子序列,并返回该序列的长度。
class Solution {
public:
int findLengthOfLCIS(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return 0;
int ans = 0;
int start = 0;
for(int i=0;i0 && nums[i]<=nums[i-1])
{
start = i;
}
ans = max(ans,i-start+1);
}
return ans;
}
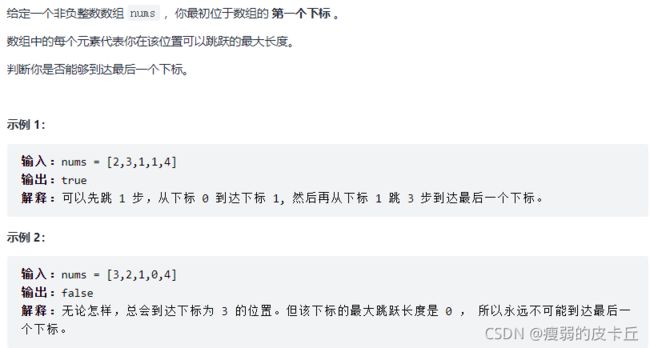
}; 2.跳跃游戏
class Solution {
public:
bool canJump(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return false;
int n = nums.size();
int maxlength = 0;
for(int i=0;i=n-1)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
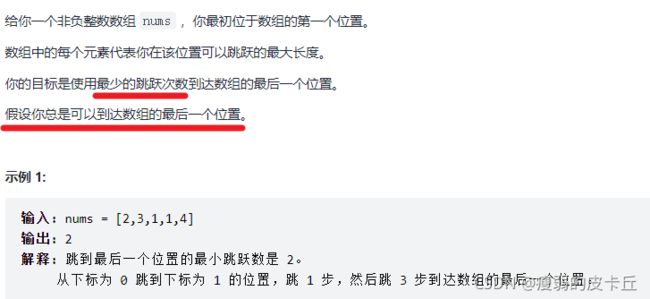
}; 3.跳跃游戏2
class Solution {
public:
int jump(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return 0;
int ans = 0;//跳跃次数
int maxlen = 0;//目前能跳跃的最远位置
int right = 0;//上次跳跃可达范围的右边界
for(int i=0;i 4.加油站
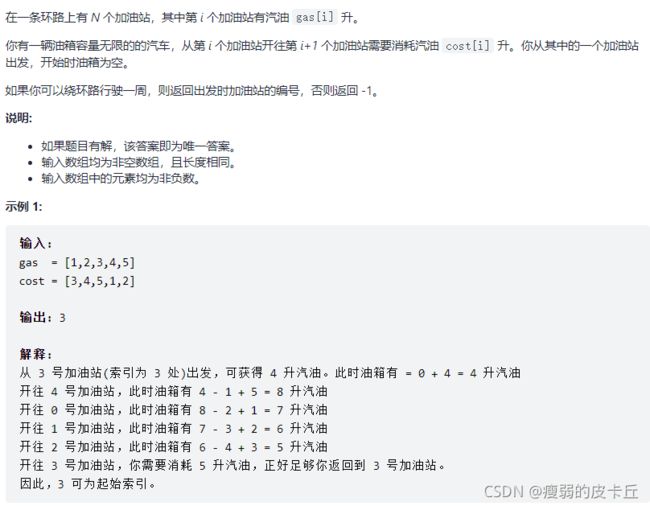
class Solution {
public:
int canCompleteCircuit(vector& gas, vector& cost) {
int start = 0;
int curcost = 0;//以当前start出发,走到当前站点还剩余的油量
int sumcost = 0;//走完一圈后,总共剩余的油量
for(int i=0;i=0?start:-1;
}
}; 三、BFS
1.路径总和
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum ,判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(root == nullptr) return false;
queue q;
queue p;
q.push(root);
p.push(root->val);
while(!q.empty())
{
root = q.front();
int temp = p.front();
q.pop();
p.pop();
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr)
{
if(temp == targetSum)
{
return true;
}
continue;
}
if(root->left != nullptr)
{
q.push(root->left);
p.push(root->left->val+temp);
}
if(root->right != nullptr)
{
q.push(root->right);
p.push(root->right->val+temp);
}
}
return false;
} 2.二叉树的所有路径
vector binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return {};
queue q;
queue p;
q.push(root);
p.push(to_string(root->val));
vector paths;
while(!q.empty())
{
root = q.front();
string path = p.front();
q.pop();
p.pop();
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr)
{
paths.push_back(path);
continue;
}
if(root->left != nullptr)
{
q.push(root->left);
p.push(path+"->"+to_string(root->left->val));
}
if(root->right != nullptr)
{
q.push(root->right);
p.push(path+"->"+to_string(root->right->val));
}
}
return paths;
} 3. N叉树的前序遍历
vector postorder(Node* root)
{
if(root == nullptr) return {};
stack s;
vector v;
s.push(root);
while(!s.empty())
{
root = s.top();
s.pop();
v.push_back(root->val);
if(!root->children.empty())
{
for(int i=root->children.size()-1;i>=0;--i)
{
s.push(root->children[i]);
}
}
}
return v;
} 4.N叉树的后序遍历
vector postorder(Node* root)
{
if(root == nullptr) return{};
stack s;
vector v;
s.push(root);
while(!s.empty())
{
root = s.top();
s.pop();
v.push_back(root->val);
if(!root->children.empty())
{
for(int i=0;ichildren.size();++i)
{
s.push(root->children[i]);
}
}
}
reverse(v.begin(),v.end());
return v;
} 5.N叉树的最大深度
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
queue q;
q.push(root);
int ans = 0;
while(!q.empty())
{
int num = q.size();
while(num--)
{
root = q.front();
q.pop();
if(root->children.size()>0)
{
for(int i = 0;ichildren.size();++i)
{
q.push(root->children[i]);
}
}
}
ans++;
}
return ans;
} 6.二叉树的最大深度
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
queue q;
q.push(root);
int ans =0;
while(!q.empty())
{
int num = q.size();
while(num--)
{
root = q.front();
q.pop();
if(root->left) q.push(root->left);
if(root->right) q.push(root->right);
}
ans++;
}
return ans;
} 7.二叉树的最小深度
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
queue> que;
que.push({root,1});
while(!que.empty())
{
root = que.front().first;
int depth = que.front().second;
que.pop();
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr)
{
return depth;
}
if(root->left!=nullptr)
{
que.push({root->left,depth+1});
}
if(root->right!=nullptr)
{
que.push({root->right,depth+1});
}
}
return 0;
} 8.二叉树的层次遍历
vector> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return{};
queue q;
q.push(root);
vector> ret;
while(!q.empty())
{
int currsize = q.size();
ret.push_back(vector());
for(int i=0;ival);
if(node->left) q.push(node->left);
if(node->right) q.push(node->right);
}
}
return ret;
} 9.N叉树的层次遍历
vector> levelOrder(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return {};
vector> ans;
queue q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
ans.push_back(vector());
while(size--)
{
root = q.front();
q.pop();
ans.back().push_back(root->val);
if(!root->children.empty())
{
for(int i=0;ichildren.size();++i)
{
q.push(root->children[i]);
}
}
}
}
return ans;
} 四、DFS(递归)
1.相同的树
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(p == nullptr) return q == nullptr;
if(q == nullptr) return p == nullptr;
if(p->val != q->val) return false;
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left)&&isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}2.路径总和
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum ,判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(root == nullptr) return false;
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr)
{
return root->val == targetSum;
}
return hasPathSum(root->left,targetSum-root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right,targetSum-root->val);3.N叉树的前序遍历
vector preorder(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return {};
vector v;
func(root,v);
return v;
}
void func(Node* root,vector v)
{
if(root == nullptr) return nullptr;
v.push_back(root->val);
for(int i=0;ichildren.size();++i)
{
func(root->children[i],v);
}
} 4.N叉树的后序遍历
vector postorder(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return {};
vector v;
Func(root,v);
return v;
}
void Func(Node* root,vector& v)
{
if(root == nullptr) return ;
for(int i=0;ichildren.size();++i)
{
Func(root->children[i],v);
}
v.push_back(root->val);
} 5.N叉树的最大深度
int Func(Node* root)
{
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;ichildren.size();++i)
{
ans = max(Func(root->children[i]),ans);
}
return ans+1;
} 6.二叉树的最大深度
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
return std::max(maxDepth(root->left),maxDepth(root->right))+1;
}7.二叉树的最小深度
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) return 1;
int min_dep = INT_MAX;
if(root->left)
{
min_dep = min(minDepth(root->left),min_dep);
}
if(root->right)
{
min_dep = min(minDepth(root->right),min_dep);
}
return min_dep+1;
}8.二叉搜索树的第K大节点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
if(root == nullptr || k ==0 ) return 0;
int ans;
int count = 0;
Func(root,k,ans,count);
return ans;
}
void Func(TreeNode* root,int k,int &ans,int &count)
{
if(root == nullptr) return ;
Func(root->right,k,ans,count);
if(++count == k)
{
ans = root->val;
}
Func(root->left,k,ans,count);
}
};9.二叉搜索树的第K小节点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
if(root == nullptr || k ==0 ) return 0;
int ans;
int count = 0;
Func(root,k,ans,count);
return ans;
}
void Func(TreeNode* root,int k,int &ans,int &count)
{
if(root == nullptr) return ;
Func(root->left,k,ans,count);
if(++count == k)
{
ans = root->val;
}
Func(root->right,k,ans,count);
}
};10.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == nullptr || p == nullptr || q == nullptr) return nullptr;
if(root->val > p->val && root->val > q->val)
{
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
}
else if(root->val < p->val && root->val < q->val)
{
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
}
else{
return root;
}
}
/*
//如果是一般的二叉树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == NULL)
return NULL;
//如果根节点就是p或者q,返回根节点
if(root == p || root == q)
return root;
//分别去左右子树里面找
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left && right)//p,q各在一边,说明当前的根就是最近共同祖先
return root;
else if(left)//说明p,q都在左子树
return left;
else if(right)//说明p,q都在右子树
return right;
else
return NULL;
}
};*/
};11.平衡二叉树
class Solution {
public:
int height(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
} else {
return max(height(root->left), height(root->right)) + 1;
}
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return true;
} else {
return abs(height(root->left) - height(root->right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right);
}
}
};12.树的子结构
输入两棵二叉树A和B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
B是A的子结构, 即 A中有出现和B相同的结构和节点值。
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubStructure(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) {
if(A == nullptr || B == nullptr) return false;
//先判断当前B是不是A的子结构,如果不是分别到A的左子树和右子树中去寻找。
return Func(A,B) || isSubStructure(A->left,B) || isSubStructure(A->right,B);
}
bool Func(TreeNode* A,TreeNode* B)
{
if(B == nullptr) return true;
if(A == nullptr) return false;
if(A->val != B->val) return false;
return Func(A->left,B->left) && Func(A->right,B->right);
}
};13.二叉搜索树与双向链表
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的循环双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的节点,只能调整树中节点指针的指向。
class Solution {
public:
Node* head;
Node* pre;
void Func(Node* root)
{
if(root == nullptr) return;
Func(root->left);
if(pre != nullptr)//前继节点为空则说明此时root为转换为单链表后的第一个节点,所以root的cur为nullptr
{
pre->right = root;
}
else
{
head = root;
}
root->left = pre;
pre = root;
Func(root->right);
}
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return nullptr;
Func(root);
head->left = pre;
pre->right = head;
return head;
}
};14.根据前序和中序遍历构建二叉树
TreeNode* buildTree(vector& preorder, vector& inorder) {
if(preorder.empty() || inorder.empty()) return nullptr;
return Func(preorder,0,preorder.size()-1,inorder,0,inorder.size()-1);
}
TreeNode* Func(vector& preorder,int l1,int r1,vector& inorder,int l2,int r2)
{
if(r1 < l1) return nullptr;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[l1]);
int mid = l2;
while(inorder[mid] != preorder[l1])
{
mid++;
}
root->left = Func(preorder,l1+1,l1+mid-l2,inorder,l2,mid-1);
root->right = Func(preorder,l1+mid-l2+1,r1,inorder,mid+1,r2);
return root;
} 15.根据中序和后续遍历构建二叉树
TreeNode* buildTree(vector& inorder, vector& postorder) {
if(inorder.empty() || postorder.empty()) return nullptr;
return Func(inorder,0,inorder.size()-1,postorder,0,postorder.size()-1);
}
TreeNode* Func(vector& inorder,int l1,int r1,vector& postorder,int l2,int r2)
{
if(r1 < l1) return nullptr;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(postorder[r2]);
int mid = l1;
while(inorder[mid] != postorder[r2])
{
mid++;
}//此时mid为中序遍历中的根结点的位置
root->left = Func(inorder,l1,mid-1,postorder,l2,l2+mid-l1-1);
root->right = Func(inorder,mid+1,r1,postorder,l2+mid-l1,r2-1);
//mid-l1为根结点左孩子结点个数
return root;
} 16.全排列
vector> permute(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return {};
vector> ans;
Func(nums,ans,0,nums.size());
return ans;
}
void Func(vector& nums,vector>& ans,int left,int right)
{
if(left == right)
{
ans.push_back(nums);
return ;
}
for(int i=left;i 五、双指针法
slow 一般代表要被替换的位置。
fast一般代表要替换的位置。
1.删除有序数组中的重复项
int removeDuplicates(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return 0;
int slow = 1;
int fast = 1;
//第0项肯定不用删除,所以从1开始
while(fast 2.移除元素
给你一个数组 nums 和一个值 val,你需要 原地 移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,并返回移除后数组的新长度。
int removeElement(vector& nums, int val) {
if(nums.empty() return 0;
int slow = 0;
int fast = 0;
for(;fast 3.判断子序列
字符串的一个子序列是原始字符串删除一些(也可以不删除)字符而不改变剩余字符相对位置形成的新字符串。(例如,"ace"是"abcde"的一个子序列,而"aec"不是)。
bool isSubsequence(string s, string t) {
if(s.empty() || t.empty()) return false;
int slow = 0;
int fast = 0;
while(slow4.调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
vector exchange(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return {};
int slow = 0;
int fast = nums.size()-1;
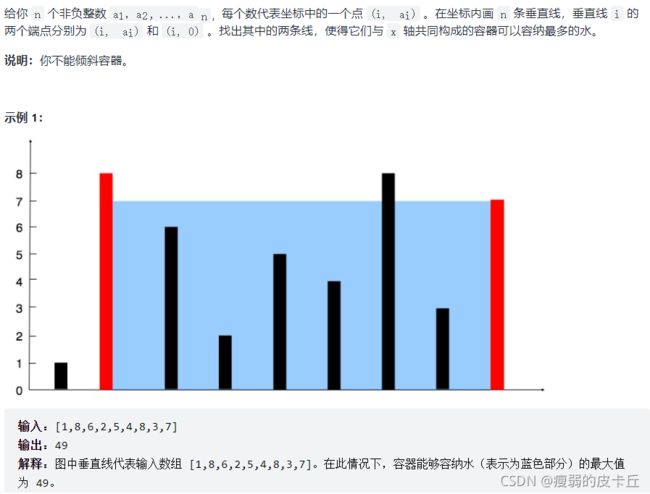
while(slow 5.盛最多水的容器
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector& height) {
if(height.empty()) return 0;
int left = 0;
int right = height.size()-1;
int ans = 0;
while(left 6.有序数组的平方
class Solution {
public:
vector sortedSquares(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return {};
vector ans(nums.size(),0);
int k = nums.size()-1;
for(int i=0,j=nums.size()-1;i<=j;)
{
if(nums[i]*nums[i] > nums[j]*nums[j])
{
ans[k--] = nums[i]*nums[i];
i++;
}
else
{
ans[k--] = nums[j]*nums[j];
j--;
}
}
return ans;
}
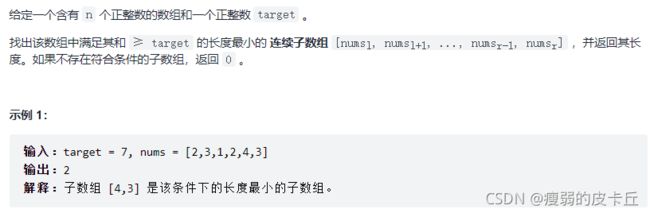
}; 7.长度最小的子数组
class Solution {
public:
int minSubArrayLen(int target, vector& nums) {
int left = 0;//左指针
int sublen = 0;//子数组的长度
int subsum = 0;//子数组的和
int ans = INT_MAX;//
for(int right=0;right= target)
{
sublen = right-left+1;
ans = min(ans,sublen);
subsum -= nums[left++];
}
}
return ans == INT_MAX?0:ans;
}
}; 六、其他
1.两数之和
/*给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出
和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。*/
vector twoSum(vector& nums, int target) {
if(nums.empty()) return {};
unordered_map m;//利用哈希
for(int i=0;isecond};
}
m[nums[i]] = i;
}
return {};
} 2.回文数
判断一个数是否为回文数,将这个数的后一半反转,与前半段作比较。
/*给你一个整数 x ,如果 x 是一个回文整数,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(int x) {
if(x<0 || (x%10) == 0 && x!=0) return false;//负数或者个位为0的数不考虑
int rever = 0;
while(x>rever)
{
rever = rever*10+x%10;
x = x/10;
}
return x == rever || x == rever/10;//整数10是为了判断当这个数的长度为奇数时
}
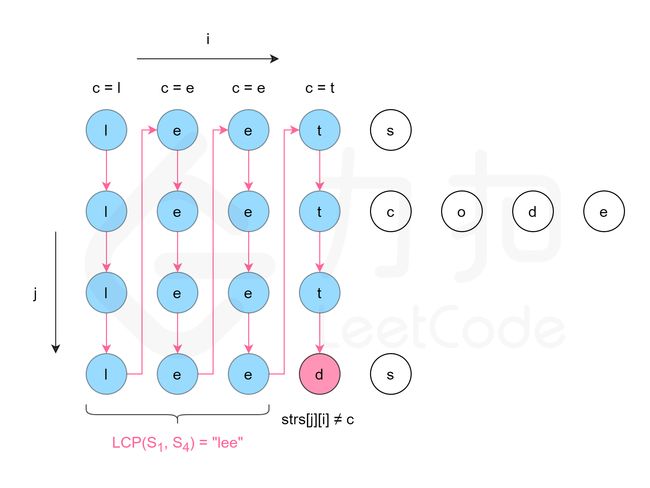
};3.最长公共前缀
纵向扫描时,从前往后遍历所有字符串的每一列,比较相同列上的字符是否相同,如果相同则继续对下一列进行比较,如果不相同则当前列不再属于公共前缀,当前列之前的部分为最长公共前缀。
string longestCommonPrefix(vector& strs)
{
if(strs.empty()) reutrn "";
for(int i=0;i 4.字符串相加(大数相加)
string addStrings(string num1, string num2) {
if(num1.empty()) return num2;
if(num2.empty()) return num1;
int i = num1.length()-1;
int j = num2.length()-1;
int res = 0;//进位
string ans = "";//答案
while(i>=0 || j>=0 || res !=0)
{
int a = i>=0?num1[i]-'0':0;
int b = j>=0?num2[j]-'0':0;
int x = a+b+res;
ans.push_back(x%10+'0');
res = x/10;
i--;
j--;
}
reverse(ans.begin(),ans.end());
return ans;
}5.字符串轮转
给定两个字符串s1和s2,请编写代码检查s2是否为s1旋转而成(比如,waterbottle是erbottlewat旋转后的字符串)。
bool isFlipedString(string s1, string s2) {
return s1.length() == s2.length() && (s1+s1).find(s2)!=-1;6.移除未排序链表中的重复节点,保留最开始出现的节点。
ListNode* removeDuplicateNodes(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
unorderer_set s;
s.insert(head->val);
ListNode* p = head;
while(p->next != nullptr)
{
ListNode* cur = p->next;
if(!s.count(cur->val)))//没找到
{
s.insert(cur->val);
p = p->next;
}
else
{
p->next = p->next->next;
}
}
p->next = nullptr;
return head;
} 7.链表相交
Node*Func(Node* headA,Node* headB)
{
if(headA == nullptr || headB == nullptr) return nullptr;
Node* p = headA;
Node* q = headB;
while(p!=q)
{
p = p == nullptr?headB:p->next;
q = q == nullptr?headA:q->next;
}
return p;
}8.最小高度树(二分法)
给定一个有序整数数组,元素各不相同且按升序排列,编写一个算法,创建一棵高度最小的二叉搜索树。
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empyt()) return nullptr;
return Func(nums,0,nums.size()-1);
}
TreeNode* Func(vector& nums,int left,int right)
{
if(left > right) return nullptr;
int mid = (right-left+1)/2+left;
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
node->left(nums,left,mid-1);
node->right(nums.mid+1,right);
return node;
} 9.最大升序子数组和
给你一个正整数组成的数组 nums ,返回 nums 中一个 升序 子数组的最大可能元素和。
子数组是数组中的一个连续数字序列。
int Func(vector& nums)
{
if(nums.empty()) return 0;
int fi = 0;
int ans = nums[0];
for(int i =0;inums[i-1])
{
fi = fi+nums[i];
}
else
{
fi = nums[i];
}
ans = max(ans,fi);
}
return ans;
} 10.买卖股票的最佳时机
int Func(vector& nums)
{
if(nums.size() < 2) return 0;
int min = nums[0];
int ans = nums[1] - min;
for(int i = 1;i0?max:0;
} 10.无重复字符的最长子串(滑动窗口+hash)
给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
if(s.empty()) return 0;
unordered_set m;
int left = 0;
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i m;//保存某个字符上一次出现的下标
int start = 0;//滑动窗口的开端
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i 11.求集合的所有子集
class Solution {
public:
vector> ans;
vector temp;
vector> subsets(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return {};
dfs(nums,0);
return ans;
}
void dfs(vector& nums,int index)
{
if(index == nums.size())
{
ans.push_back(temp);
return ;
}
temp.push_back(nums[index]);
dfs(nums,index+1);
temp.pop_back();
dfs(nums,index+1);
}
};
/*class Solution {
public:
vector> ans;
vector> subsets(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return {};
int n = nums.size();
vector arrs(n,0);
Func(nums,arrs,0,n);
return ans;
}
void Func(vector&arr,vector&brr,int left,int right)
{
if(left >= right)//说明此时已经得到了一个子集
{
vector temp;
for(int i=0;i 12.复杂链表的复制
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(head == nullptr) return head;
if(head->next == nullptr && head->random == nullptr)
{
Node* node = new Node(head->val);
return node;
}
Node* p = head;
while(p!=nullptr)
{
Node* node = new Node(p->val);
node->next = p->next;
node->random = nullptr;
p->next = node;
p=node->next;
}
p = head;
while(p!=nullptr)
{
if(p->random!=nullptr)
{
p->next->random = p->random->next;
}
p=p->next->next;
}
p = head;
Node* phead = p->next;
Node* pnode = phead;
p->next = pnode->next;
p = p->next;
while(p!=nullptr)
{
pnode->next = p->next;
pnode = pnode->next;
p->next = pnode->next;
p=p->next;
}
return phead;
}13.数组中只出现一次的数字
一个整型数组 nums 里除两个数字之外,其他数字都出现了两次。请写程序找出这两个只出现一次的数字。
vector singleNumbers(vector& nums)
{
if(nums.empty()) return {};
int ans = 0;
//1.先把所有数都异或
for(auto& x:nums)
{
ans^=x;
}
//2.寻找异或结果中为1的那位
int n = 1;
while((ans&n) == 0)
{
n<<=1;
}
//3.以找到的那一位为界限,来计算
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
for(auto& x:nums)
{
if(x&n)
{
a^=x;
}
else
{
b^=x;
}
}
return {a,b};
} 14.数组中只出现一次的数字 II
在一个数组 nums 中除一个数字只出现一次之外,其他数字都出现了三次。请找出那个只出现一次的数字。
int singleNumber(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return -1;
vector res(32);
//1.统计每一bit上1出现的次数
for(auto& x:nums)
{
for(int i = 0;i<32;++i)
{
int bit = x&(1< 15.剪绳子
给你一根长度为 n 的绳子,请把绳子剪成整数长度的 m 段,每段绳子的长度记为。请问 m段绳子可能的最大乘积是多少?例如,当绳子的长度是8时,我们把它剪成长度分别为2、3、3的三段,此时得到的最大乘积是18。
int cuttingRope(int n) {
if(n == 2) return 1;
if(n == 3) return 2;
if(n == 4) return 4;
//贪心:当n>=5时,尽可能多的剪长度为3的绳子;当剩下的绳子长度为4时,剪成两段长度为2的绳子
int times = n/3;
if(n-(times*3) == 1) times-=1;//说明剩下绳子的长度为4,回退一个3
int times2 = (n-times*3)/2; 此时将绳子剪成长度为2的两段
return pow(3,times)*pow(2,times2);
}16.把数组排成最小的数
输入一个非负整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出的所有数字中最小的一个。
class Solution {
public:
string minNumber(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return {};
vector strs;
for(auto& num:nums)
{
strs.push_back(to_string(num));
}
sort(strs.begin(),strs.end(),compare);
string ans;
for(auto& x:strs)
{
ans+=x;
}
return ans;
}
static bool compare(string &a,string& b)
{
return a+b 17.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == nullptr || p == nullptr || q == nullptr) return nullptr;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while(1)
{
if(p->valval && q->val < cur->val)
{
cur = cur->left;
}
else if(p->val > cur->val && q->val > cur->val)
{
cur = cur->right;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
return cur;
} 18.合并两个有序列表
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
if(l1 == nullptr) return l2;
else if(l2 == nullptr) return l1;
ListNode* head = new ListNode();
ListNode* node = head;
while(l1 != nullptr && l2 != nullptr)
{
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
head->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
head->next = l2;
l2=l2->next;
}
head = head->next;
}
head->next = l1 == nullptr?l2:l1;
return node->next;
/*ListNode* head = nullptr;
if(l1->val val)
{
head = l1;
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next,l2);
}
else{
head = l2;
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1,l2->next);
}
return head;
*/
} 19.旋转链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 k 个位置。
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[4,5,1,2,3]
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr || k == 0)
{
return head;
}
int length = 1;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur->next != nullptr)
{
cur = cur->next;
length++;
}
int num = length - k%length;
if( num == length)
{
return head;
}
cur->next = head;
while(num--)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
ListNode* ans = cur->next;
cur->next = nullptr;
return ans;
}20.字符串相乘
string multiply(string num1, string num2) {
if(num1.empty() || num2.empty()) return "0";
if(num1 == "0"||num2 == "0")
{
return "0";
}
vector res(num1.size()+num2.size());//
for(int i=num1.size()-1;i>=0;--i)
{
for(int j = num2.size()-1;j>=0;--j)
{
int temp = (num1[i]-'0')*(num2[j]-'0')+res[i+j+1];
res[i+j+1] = temp%10;
res[i+j] += temp/10;
}
}
int start = 0;
while(res[start] == 0 && start 21.螺旋矩阵
给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
vector spiralOrder(vector>& matrix) {
if(matrix.empty() || matrix[0].empty()) return {};
vector ans;
int m = matrix.size();
int n = matrix[0].size();
int up = 0;
int down = m-1;
int left = 0;
int right = n-1;
while(true)
{
for(int i=left;i<=right;++i)
{
ans.push_back(matrix[up][i]);
}
if(++up > down) break;
for(int i = up;i<=down;++i)
{
ans.push_back(matrix[i][right]);
}
if(--right < left) break;
for(int i = right;i>=left;--i)
{
ans.push_back(matrix[down][i]);
}
if(--down < up) break;
for(int i = down;i>=up;--i)
{
ans.push_back(matrix[i][left]);
}
if(++left > right) break;
}
return ans;
} 22.合并K 个升序链表
方法一、
利用小根堆(优先级队列),堆的大小为K,先把K个链表的头结点放入堆,然后每次选取一个最小节点后,进行pop()操作,然后判断当前被pop出的节点有无next,有的话进行push(cur->next)操作,依次循环,直至队列为空。
方法二、
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode *a, ListNode *b) {
if ((!a) || (!b)) return a ? a : b;
ListNode head, *tail = &head, *aPtr = a, *bPtr = b;
while (aPtr && bPtr) {
if (aPtr->val < bPtr->val) {
tail->next = aPtr; aPtr = aPtr->next;
} else {
tail->next = bPtr; bPtr = bPtr->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = (aPtr ? aPtr : bPtr);
return head.next;
}
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector& lists) {
ListNode *ans = nullptr;
for (size_t i = 0; i < lists.size(); ++i) {
ans = mergeTwoLists(ans, lists[i]);
}
return ans;
}
}; 23.合并排序的数组
void merge(vector& A, int m, vector& B, int n) {
int pa = m - 1;
int pb = n - 1;
int tail = m+n-1;
int cur;
while(pa>=0 || pb>=0)
{
if(pa == -1)
{
cur = B[pb--];
}
else if(pb == -1)
{
cur = A[pa--];
}
else if(A[pa] > B[pb])
{
cur = A[pa--];
}
else{
cur = B[pb--];
}
A[tail--] = cur;
}
} 24.奇偶链表
给定一个单链表,把所有的奇数节点和偶数节点分别排在一起。请注意,这里的奇数节点和偶数节点指的是节点编号的奇偶性,而不是节点的值的奇偶性。
如果链表为空,则直接返回链表。
对于原始链表,每个节点都是奇数节点或偶数节点。头节点是奇数节点,头节点的后一个节点是偶数节点,相邻节点的奇偶性不同。因此可以将奇数节点和偶数节点分离成奇数链表和偶数链表,然后将偶数链表连接在奇数链表之后,合并后的链表即为结果链表。
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* evenHead = head->next;
ListNode* odd = head;//奇数链表的表头
ListNode* even = head->next;//偶数链表的表头
while(even != nullptr && even->next != nullptr)
{
odd->next = even->next;
odd = odd->next;
even->next = odd->next;
even = even->next;
}
odd->next = evenHead;
return head;
}25.整数转换
整数转换。编写一个函数,确定需要改变几个位才能将整数A转成整数B。
输入:A = 29 (或者0b11101), B = 15(或者0b01111) 输出:2
int convertInteger(int A, int B) {
int res = A^B;
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i<32;++i)
{
if(res & (1<26.求平方根
int mySqrt(int x) {
int left = 0;
int right = x;
while(left <= right)
{
int m = (left+right)/2;
if((long)m*m>x)
{
right = m-1;
}
else{
left = m+1;
}
}
return right;
}27.回文链表
使用快慢指针,慢指针向前走的过程中就把链表的前半部分逆置,然后判断前半部分和后半部分是否相等。
使用vector,然后判断vec[i] 和 vec[j],i=0,j=vec.size()-1;i
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr) return false;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* s = nullptr;
while(fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
ListNode* temp = slow->next;
slow->next = s;
s=slow;
slow = temp;
}
if(fast != nullptr) slow = slow->next;
while(s != nullptr)
{
if(s->val != slow->val) return false;
s = s->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return true;
}28.约瑟夫环
int lastRemaining(int n, int m) {
int p = 0;
for(int i= 2;i<=n;++i)
{
p=(p+m)%i;
}
return p;
}29.有序链表转换为二叉搜索树
TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr) return nullptr;
if(head->next == nullptr) return new TreeNode(head->val);
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
while(fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr)
{
pre = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
pre->next = nullptr;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(slow->val);
root->left = sortedListToBST(head);
root->right = sortedListToBST(slow->next);
return root;
}30.二叉树的插入操作
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if(root == nullptr) return new TreeNode(val);
TreeNode* cur = root;
while(cur != nullptr)
{
if(val < cur->val)
{
if(cur->left == nullptr)
{
cur->left = new TreeNode(val);
break;
}
else
{
cur = cur->left;
}
}
else{
if(cur->right == nullptr)
{
cur->right = new TreeNode(val);
break;
}
else{
cur = cur->right;
}
}
}
return root;
}31.分割链表
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* small = new ListNode(0);//比x小的链表的头
ListNode* large = new ListNode(0);//比x大的链表的头
ListNode* p = small;
ListNode* q = large;
while(head!=nullptr)
{
if(head->val < x)
{
p->next = head;
p = p->next;
}
else
{
q->next = head;
q = q->next;
}
head = head->next;
}
q->next = nullptr;
p->next = large->next;
return small->next;
}32.包含Min函数的栈
class MinStack {
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
stack m_data;
stack m_min;
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
m_data.push(x);
if(m_min.empty() || m_min.top()>x)
{
m_min.push(x);
}
else
{
m_min.push(m_min.top());
}
}
void pop() {
if(m_data.empty() || m_min.empty()) return ;
m_data.pop();
m_min.pop();
}
int top() {
return m_data.top();
}
int min() {
return m_min.top();
}
}; class MinStack {
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
stack m_data;
int m_min = INT_MAX;
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
m_data.push(m_min);//加入上一个最小值
if(x 33.用两个栈实现队列
class CQueue {
public:
stack s1;
stack s2;
CQueue() {
}
void appendTail(int value) {
s1.push(value);
}
int deleteHead() {
if(s2.empty())
{
while(!s1.empty())
{
s2.push(s1.top());
s1.pop();
}
}
if(s2.empty())
{
return -1;
}
else
{
int t = s2.top();
s2.pop();
return t;
}
}
}; 34.用两个队列实现栈
class MyStack {
//只能尾插头删
public:
queue q1;
queue q2;
MyStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
q2.push(x);
while(!q1.empty())
{
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
swap(q1,q2);
}
int pop() {
int t = q1.front();
q1.pop();
return t;
}
int top() {
return q1.front();
}
bool empty() {
return q1.empty();
}
}; class MyStack {
public:
queue q;
MyStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
int n = q.size();
q.push(x);
while(n--)
{
q.push(q.front());
q.pop();
}
}
int pop() {
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
return t;
}
int top() {
return q.front();
}
bool empty() {
return q.empty();
}
}; 35.最长连续序列
给定一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,找出数字连续的最长序列(不要求序列元素在原数组中连续)的长度。请你设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。
输入:nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2] 输出:4 解释:最长数字连续序列是[1, 2, 3, 4]。它的长度为 4。
class Solution {
public:
int longestConsecutive(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return 0;
unordered_set s;
for(auto& x:nums)
{
s.insert(x);//去重
}
int ans = 0;
for(auto& x: s)
{
if(!s.count(x-1))
{
int cur = x;
int len = 1;
while(s.count(cur+1))
{
cur+=1;
len++;
}
ans = max(ans,len);
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 36.重排链表
// 找中点+反转后半部分+合并前后两部分
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null || head.next.next==null)return;
// 1. 找中点,让slow指向中点,或左中点位置
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast!=null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// 2. 断开中点,反转后半部分
ListNode head2 = null, next = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
slow = next;
while(slow != null) {
next = slow.next;
slow.next = head2;
head2 = slow;
slow = next;
}
// 3. 合并链表head和head2
ListNode curr = head;
ListNode curr2 = head2;
while(curr != null && curr2!=null) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = curr2;
curr2 = curr2.next;
curr.next.next = next;
curr = next;
}
}37.翻转字符串里的单词
38.组合总和
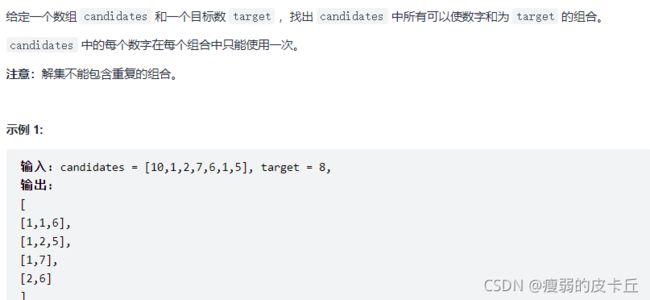
给定一个无重复元素的正整数数组 candidates 和一个正整数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为目标数 target 的唯一组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
class Solution {
public:
vector> ans;
vector temp;
vector> combinationSum(vector& candidates, int target) {
sort(candidates.begin(),candidates.end());
dfs(candidates,target,0,0);
return ans;
}
void dfs(vector& candidates,int target,int sum,int index)
{
if(sum == target)
{
ans.push_back(temp);
return;
}
for(int i=index;i target) break;//剪枝,如果已经知道下一层的sum会大于target,就没有必要进入下一层递归了。
sum+=candidates[i];
temp.push_back(candidates[i]);
dfs(candidates,target,sum,i);
sum-=candidates[i];
temp.pop_back();
}
}
}; 组合总和2
class Solution {
public:
vector> ans;
vector temp;
vector> combinationSum2(vector& candidates, int target) {
sort(candidates.begin(),candidates.end());
dfs(candidates,target,0);
return ans;
}
void dfs(vector& candidates,int target,int index)
{
if(target==0)
{
ans.push_back(temp);
return;
}
for(int i=index;itarget) break;//剪枝,如果已经知道下一层的sum会大于target,就没有必要进入下一层递归了。
if(i>index&&candidates[i]==candidates[i-1]){
continue;
}
temp.push_back(candidates[i]);
dfs(candidates,target-candidates[i],i+1);
temp.pop_back();
}
}
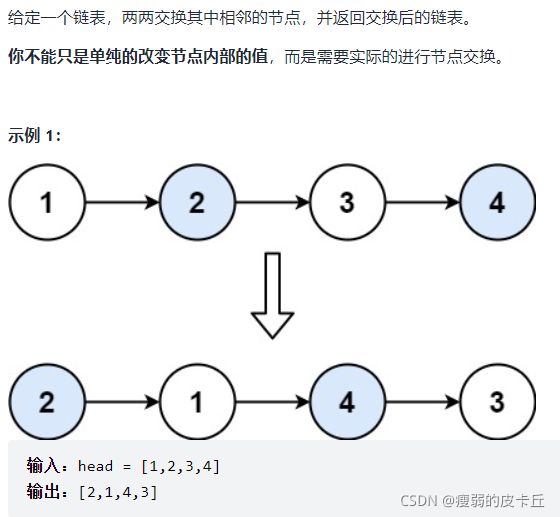
}; 39.两两交换链表中的节点
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* newhead = new ListNode(0);//因为最后链表的头结点发生了改变,所以我们新开辟一个节点来表示头结点。
newhead->next = head;
ListNode* temp = newhead;
while(temp->next!=nullptr && temp->next->next != nullptr)
{
ListNode* node1 = temp->next;//1
ListNode* node2 = node1->next;//2
temp->next = node2;
node1->next = node2->next;
node2->next= node1;
temp = node1;
}
return newhead->next;
}
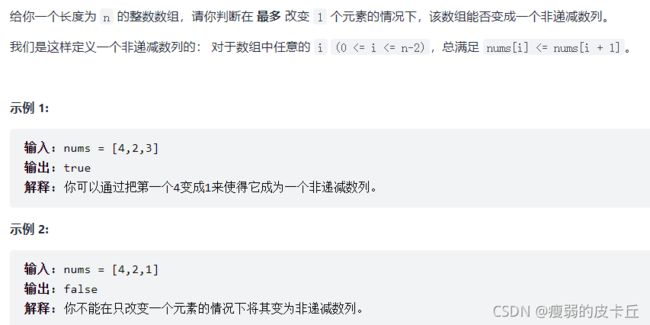
};40.非递减数列
class Solution {
public:
bool checkPossibility(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return false;
int count = 0;
for(int i=0;i nums[i+1])/*在遍历中统计nums[i]>nums[i+1]的次数,若超过1次则返回false*/
{
count++;
if(count>1) return false;
if(i>0 && nums[i+1] < nums[i-1])
{
nums[i+1] = nums[i];/*此时 i-1 i i+1三个数的关系为 大 大 小*/
}
}
}
return true;
}
};
/*用例 3 4 1 2*/ 41.有效的括号
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
if(s.size()%2 == 1) return false;
stack st;
for(auto ch:s)
{
if(!st.empty())
{
char t = st.top();
{
if(t=='('&&ch==')' || t=='['&&ch==']' || t=='{'&&ch=='}')
{
st.pop();
continue;
}
}
}
st.push(ch);
}
return st.empty();
}
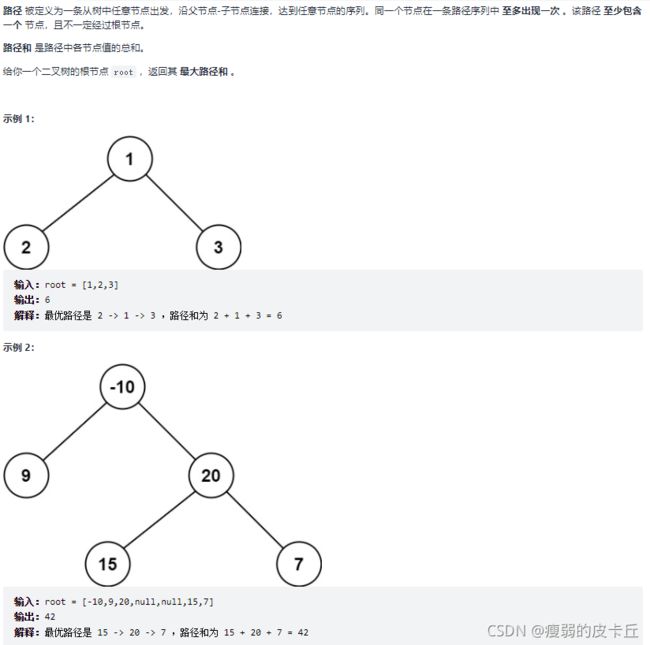
}; 42.二叉树中的最大路径和
class Solution {
public:
int ans = INT_MIN;
int maxGain(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
int left = max(maxGain(root->left),0);
int right = max(maxGain(root->right),0);
int cur = root->val+left+right;
ans = max(cur,ans);
return root->val+max(left,right);
/*
这里为什么返回的是 root->val+max(left,right),而不是max(root->val+left,root->val+right,
root->val+left+right)呢?
因为路径是没有岔路的,返回给父亲的只能是路径。如果按你说的return max(结点+左孩子,结点+右孩子,结点+左孩子+右孩子),假如某种情况,一个结点返回了(结点+左孩子+右孩子)这种情况,那么对于他的父亲结点来说,他现在的所谓的路径就是一颗树了,是有分叉的,路径是没有分叉的。
*/
}
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
maxGain(root);
return ans;
}
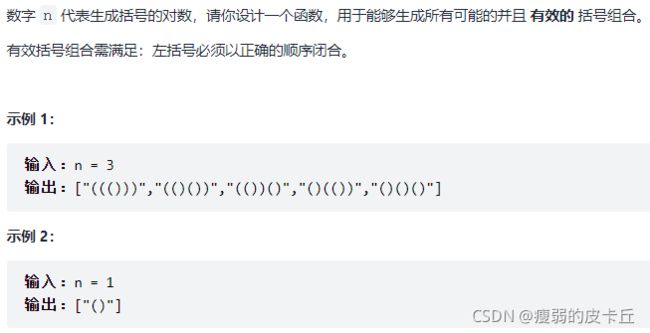
};43.括号生成
class Solution {
public:
vector ans;
vector generateParenthesis(int n) {
if(n<=0) return {};
func("",n,n);
return ans;
}
void func(string str, int left, int right){
/*
left代表剩余左括号的个数
right代表剩余右括号的个数
*/
if(left == 0 && right == 0)//当左右剩余括号个数均为0时
{
ans.push_back(str);
return;
}
if(left == right)//如果剩余左右括号数均相等时,下一个只能是左括号
{
func(str+"(",left-1,right);
}
else if(left < right)//如果剩余的左括号小于右括号,则下一个可以是左括号也可以是右括号
{
if(left > 0)
{
func(str+"(",left-1,right);
}
func(str+")",left,right-1);
}
}
}; 44.验证二叉搜索树
/*中序遍历*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return false;
stack s;
long long inorder = (long long)INT_MIN-1;//inorder保存前一个节点的值
while(!s.empty() || root != nullptr)
{
while(root != nullptr)
{
s.push(root);
root=root->left;
}
root = s.top();
s.pop();
if(root->val <= inorder)
{
return false;
}
inorder = root->val;
root = root->right;
}
return true;
}
}; /*递归*/
bool Func(TreeNode* root,long long lower,long long upper)
{
if(root == nullptr) return true;
if(root->val <= lower || root->val >= upper) return false;
return Func(root->left,lower,root->val) && Func(root->right,root->val,upper);
}
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root)
{
return Func(root,LONG_MIN,LONG_MAX);
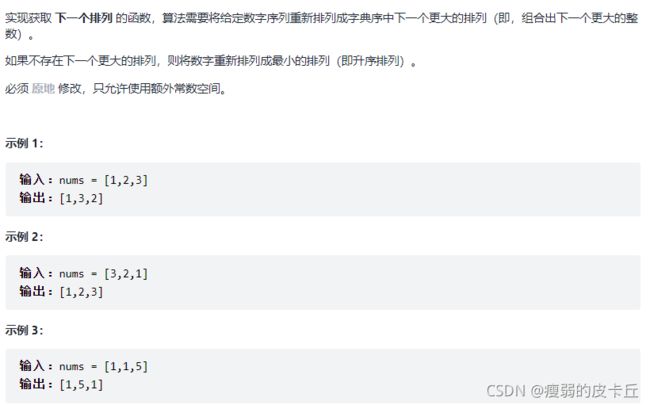
}45.下一个排列
class Solution {
public:
void nextPermutation(vector& nums) {
int i = nums.size() -2;
/*此时在找的是{4,5,2,6,3,1}中的较小数,即2*/
while(i>=0 && nums[i] >= nums[i+1])
{
--i;
}
/*此时在找的是{4,5,2,6,3,1}中的较大数,即3,且较大数尽可能的小,即第一个大于较小数2的数*/
if(i>=0){
int j = nums.size()-1;
while(j>=0 && nums[i] >= nums[j])
{
--j;
}
swap(nums[i],nums[j]);/*此时序列变为了{4,5,3,6,2,1}*/
}
reverse(nums.begin()+i+1,nums.end());/*将序列6,2,1,反转,避免了后半段的反转操作*/
}
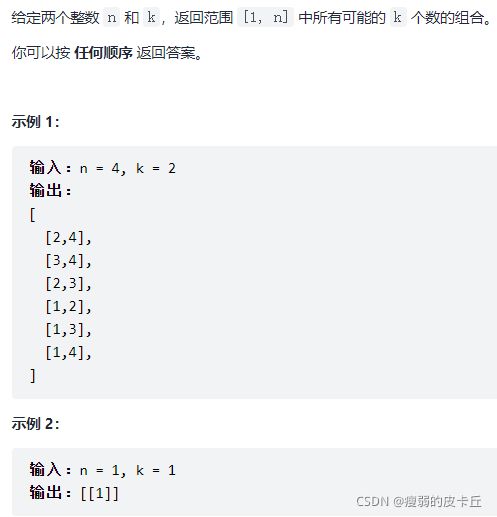
}; 46.组合
class Solution {
public:
vector temp;
vector> ans;
vector> combine(int n, int k) {
dfs(1,n,k);
return ans;
}
void dfs(int cur,int n,int k)
{
if(temp.size()+(n-cur+1) 47.求x的n次方
int func(int x,int n)
{
if(n == 0) return 1;
int t = func(x,n/2);
if(n%2 == 1)
return t*t*x;
return t*t;
}48.反转字符串2
class Solution {
public:
string reverseStr(string s, int k) {
for(int i=0;i49.替换空格
![]()
class Solution {
public:
string replaceSpace(string s) {
if(s.empty()) return s;
int count = 0;
int len = s.size();
/*首先统计空格字符的个数*/
for(auto ch:s)
{
if(ch==' ') count++;
}
s.resize(s.size()+count*2);/*为s扩容*/
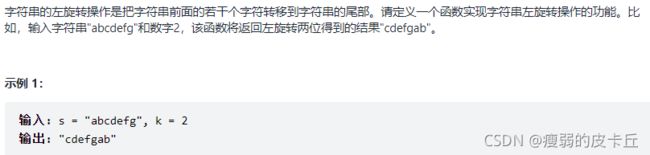
for(int i = s.size()-1,j=len-1;j50.左旋字符串
class Solution {
public:
string reverseLeftWords(string s, int n) {
if(n<=0) return s;
reverse(s.begin(),s.begin()+n);
reverse(s.begin()+n,s.end());
reverse(s.begin(),s.end());
return s;
}
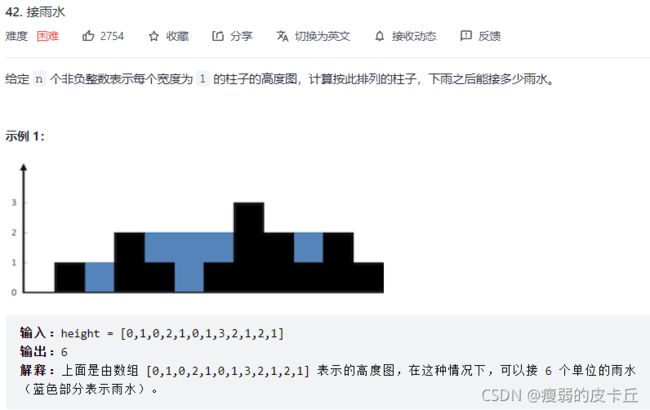
};51.接雨水
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector& height) {
if(height.empty()) return 0;
int ans = 0;
int left = 0;
int right = height.size()-1;
int leftmax = 0;
int rightmax = 0;
while(left < right)
{
leftmax = max(leftmax,height[left]);
rightmax = max(rightmax,height[right]);
if(leftmax < rightmax)
{
ans += leftmax - height[left];
++left;
}
else
{
ans += rightmax - height[right];
--right;
}
}
return ans;
}
}; 52.买卖股票的最佳时机3
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
if(n == 0) return 0;
int buy1 = -prices[0];
int sell1 = 0;
int buy2 = -prices[0];
int sell2 = 0;
for(int i=1;i 53.下一个更大的元素(单调栈)
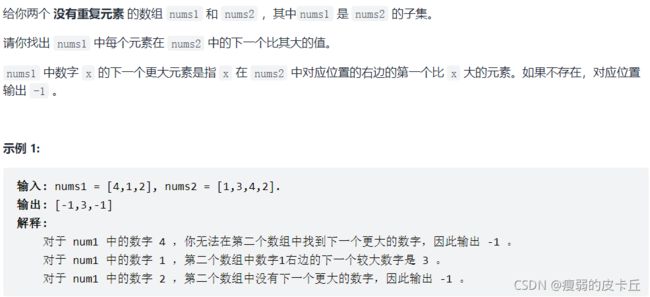
class Solution {
public:
vector nextGreaterElement(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {
if(nums1.empty() || nums2.empty()) return {};
vector ans(nums1.size());
stack s;
unordered_map m;
for(int i=0;i s.top())
{
m[s.top()] = nums2[i];
s.pop();
}
s.push(nums2[i]);
}
while(!s.empty())
{
m[s.top()] = -1;
s.pop();
}
for(int i=0;i 54.每日温度(单调栈)
class Solution {
public:
vector dailyTemperatures(vector& temperatures) {
int n = temperatures.size();
vector ans(n);
stack s;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
while (!s.empty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[s.top()]) {
int previousIndex = s.top();
ans[previousIndex] = i - previousIndex;
s.pop();
}
s.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
};
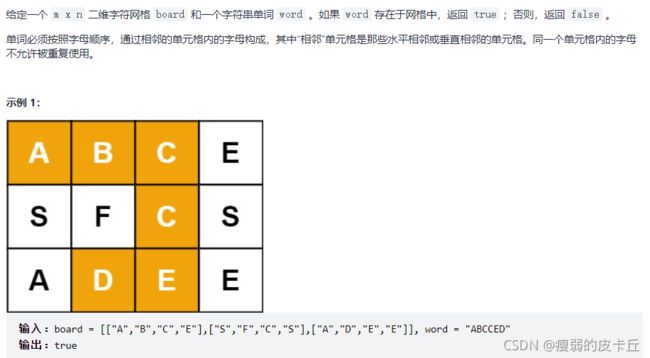
55.单词搜索 (回溯+dfs)
class Solution {
public:
bool exist(vector>& board, string word) {
int rows = board.size();
int columns = board[0].size();
for(int i=0;i>& board,string& word,int i,int j,int cur)
{
if(cur == word.length()) return true;
if(i<0 || j<0 || i>=board.size() || j>= board[0].size())
{
return false;
}
if(word[cur] != board[i][j])
{
return false;
}
board[i][j]+=32;
bool res = dfs(board,word,i,j+1,cur+1)||
dfs(board,word,i,j-1,cur+1)||
dfs(board,word,i-1,j,cur+1)||
dfs(board,word,i+1,j,cur+1);
board[i][j]-=32;
return res;
}
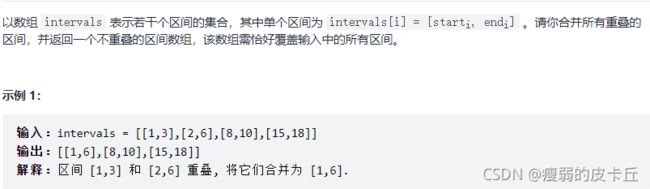
}; 56.合并区间
class Solution {
public:
vector> merge(vector>& intervals) {
if(intervals.empty()) return {};
sort(intervals.begin(),intervals.end());
vector> merge;
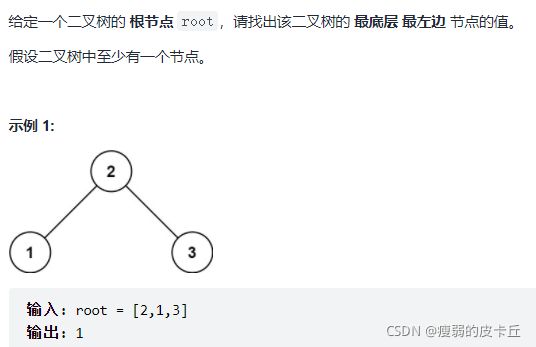
for(int i=0;i 57.找树左下角的值
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
queue q;
int ans = 0;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int n = q.size();
for(int i=0;ival;
}
if(root->left != nullptr) q.push(root->left);
if(root->right != nullptr) q.push(root->right);
}
}
return ans;
}
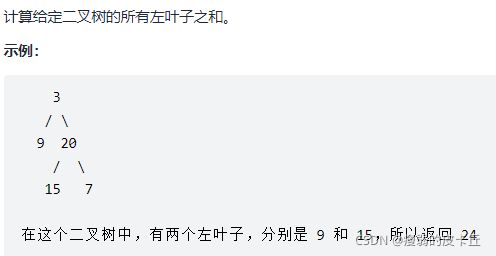
}; 58.左叶子之和
class Solution {
public:
bool isLeafNode(TreeNode* root)
{
return root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr;
}
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr || isLeafNode(root)) return 0;
queue q;
int ans = 0;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
root = q.front();
q.pop();
if(root->left != nullptr)
{
if(isLeafNode(root->left)) ans+=root->left->val;
else
{
q.push(root->left);
}
}
if(root->right!=nullptr)
{
if(!isLeafNode(root->right))
{
q.push(root->right);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
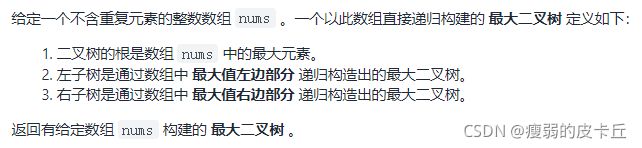
}; 59.最大二叉树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return nullptr;
return func(nums,0,nums.size());
}
TreeNode* func(vector& nums,int left,int right)
{
if(left>=right) return nullptr;//左闭右开区间 right = mid
int maxindex = left;
for(int i=left;inums[maxindex])
{
maxindex = i;
}
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[maxindex]);
root->left = func(nums,left,maxindex);
root->right = func(nums,maxindex+1,right);
return root;
}
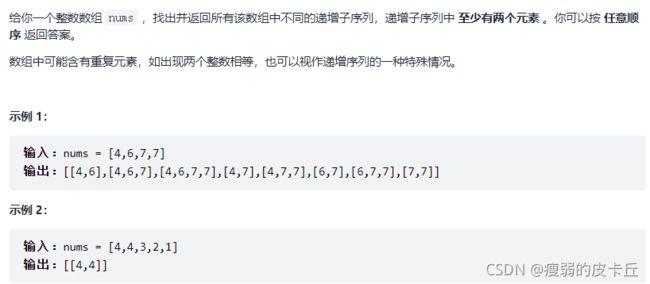
}; 60.递增子序列
class Solution {
public:
vector temp;
vector> ans;
vector> findSubsequences(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return {};
dfs(nums,0,INT_MIN);
return ans;
}
void dfs(vector& nums,int cur,int last)
{
if(cur == nums.size())
{
if(temp.size()>=2)
{
ans.push_back(temp);
}
return ;
}
if(nums[cur] >= last)
{
temp.push_back(nums[cur]);
dfs(nums,cur+1,nums[cur]);
temp.pop_back();
}
if(nums[cur]!=last)//此时nums[cur]可能大于或者小于last,即此时不考虑nums[cur]
{
dfs(nums,cur+1,last);
}
}
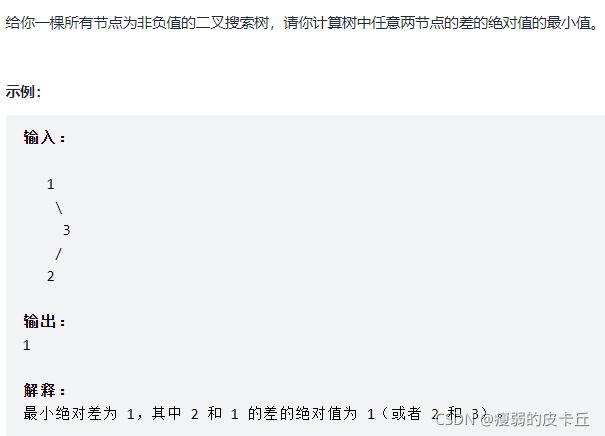
}; 61.二叉搜索树的最小绝对值差
class Solution {
public:
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
stack s;
int ans = INT_MAX;
int pre = INT_MAX;
while(!s.empty() || root != nullptr)
{
while(root != nullptr)
{
s.push(root);
root=root->left;
}
root = s.top();
s.pop();
if(pre != INT_MAX)
{
ans = min(ans,root->val-pre);
}
pre = root->val;
root = root->right;
}
return ans;
}
}; 62.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* deletenodeNode(TreeNode* cur)
{
if(cur == nullptr) return cur;
if(cur->right == nullptr) return cur->left;
TreeNode* temp = cur->right;
while(temp->left)
{
temp = temp->left;
}
temp->left = cur->left;
return cur->right;
}
TreeNode* deleteNode(TreeNode* root, int key) {
if(root == nullptr) return root;
TreeNode* cur = root;
TreeNode* pre = nullptr;
/*寻找被删除节点的前继结点*/
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val == key) break;
pre = cur;
if(cur->val>key) cur = cur->left;
else cur = cur->right;
}
/*删除的是根结点*/
if(pre == nullptr)
{
return deletenodeNode(cur);
}
/*删除的是当前结点的左孩子*/
if(pre->left != nullptr && pre->left->val == key)
{
pre->left = deletenodeNode(cur);
}
/*删除的是当前结点的右孩子*/
else if(pre->right != nullptr && pre->right->val == key)
{
pre->right = deletenodeNode(cur);
}
return root;
}
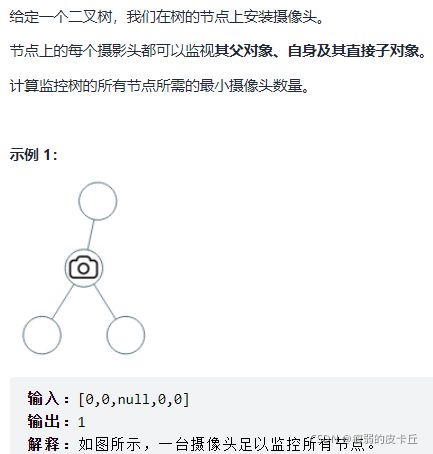
};63.监控二叉树
class Solution {
public:
int ans = 0;
int dfs(TreeNode* root)//该函数返回的是当前结点root的状态
{
if(root == nullptr) return 2;//本节点有覆盖
int left = dfs(root->left);
int right = dfs(root->right);
if(left == 2 && right == 2)//如果当前结点的左右节点都被覆盖了,则代表当前结点无覆盖
{
return 0;
}
else if(left == 0 || right == 0)//如果当前结点的左右孩子中只要有一个没有被覆盖,则代表当前结点一个应该设置摄像头
{
ans++;
return 1;
}
else{//如果当前结点的左孩子或右孩子有摄像头,则代表当前被覆盖了
return 2;
}
}
int minCameraCover(TreeNode* root) {
if(dfs(root) == 0) ans++;
return ans;
}
};64.会议室
class Solution { //C++
public:
bool canAttendMeetings(vector>& intervals) {
sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(),[&](auto a, auto b){
return a[0] < b[0];
});
for(int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); ++i)
{
if(intervals[i-1][1] > intervals[i][0])
return false;
}
return true;
}
}; 65.会议室 II(贪心+优先队列)
- 开始时间一样,先结束的在前;开始早的在前
- 优先队列存储会议结束的时间,堆顶是结束时间早的
- 下一个会议开始时间早于堆顶的房间结束时间,该会议新开一个room,push进队列
- 最后返回队列的size
class Solution {
public:
int minMeetingRooms(vector>& intervals) {
if(intervals.empty()) return 0;
sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(),[&](auto a, auto b){
if(a[0] == b[0])
return a[1] < b[1];//开始时间一样,先结束的在前
return a[0] < b[0];//开始早的在前
});
priority_queue,greater> q;//小顶堆,存放会议室结束时间,小的在上
/*priority_queue 模板有 3 个参数,其中两个有默认的参数;
第一个参数是存储对象的类型,第二个参数是存储元素的底层容器,
第三个参数是函数对象,它定义了一个用来决定元素顺序的断言。
函数对象类型 less 是一个默认的排序断言,定义在头文件 function 中,
决定了容器中最大的元素会排在队列前面。
fonction 中定义了 greater,用来作为模板的最后一个参数对元素排序,
最小元素会排在队列前面。*/
q.push(intervals[0][1]);
for(int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); ++i)
{
if(intervals[i][0] >= q.top())//最早结束的会议室可用,占用它
{
q.pop();
}
q.push(intervals[i][1]);
}
return q.size();
}
}; 66.K个一组翻转链表
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode* newhead = new ListNode(0);/*因为头结点也可能被反转,所以我们新new一个头结点*/
newhead->next = head;
ListNode* pre = newhead;
while(head != nullptr)
{
ListNode* tail = pre;//tail代表当前这个子链表的尾节点
/*查看剩余部分长度是否大于等于K*/
for(int i =0;inext;
if(tail == nullptr)
{
return newhead->next;/*剩余节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序*/
}
}
ListNode* next = tail->next;/*这个子链表的尾节点的后继结点*/
tail->next = nullptr;
/*反转这个子链表,接着再把子链表结回原链表*/
pre->next = func(head);
head->next = next;/*反转后原来的head变成了尾结点*/
pre = head;
head = head->next;
}
return newhead->next;
}
ListNode* func(ListNode* head)//反转以head为头结点的单链表
{
ListNode* s = nullptr;
while(head != nullptr)
{
ListNode* next = head->next;
head->next = s;
s = head;
head = next;
}
return s;
}
}; 67.最长回文子串(中心扩展算法)
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
int max_left = 0;
int max_right = 0;
int n = s.size();
for(int i=0;i= 0 && s[left] == s[i]) --left;
while(right < n && s[right] == s[i]) ++right;
while(left >=0 && right > dp(n,vector(n,false));
int maxlen = 0;
int right = 0;
int left = 0;
for(int i = n-1;i>=0;--i)
{
for(int j = i;jmaxlen)
{
maxlen = j-i+1;
left = i;
right = j;
}
//不考虑s[i] != s[j]是因为我们将dp全部初始化为了false
}
}
return s.substr(left,maxlen);
} 68.最长有效括号
class Solution {
public:
int longestValidParentheses(string s) {
stack st;
int ans = 0;
st.push(-1);
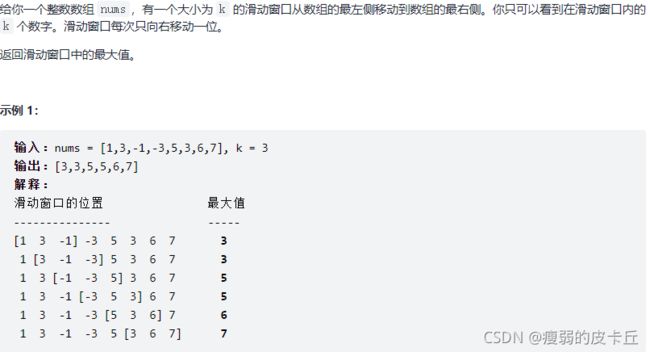
for(int i=0;i 69.滑动窗口最大值
class Solution {
public:
vector maxSlidingWindow(vector& nums, int k) {
vector ans;
deque q;
for(int i=0;i nums[q.back()]) q.pop_back();
q.push_back(i);
if(i>=k-1) ans.push_back(nums[q.front()]);
}
return ans;
}
}; 70.岛屿数量
class Solution {
public:
int numIslands(vector>& grid) {
int ans = 0;
int m = grid.size();
int n = grid[0].size();
for(int i=0;i>& grid,int i,int j)
{
if(i<0 || i>=grid.size() || j<0 || j>=grid[0].size()) return ;
if(grid[i][j] == '0') return ;
grid[i][j] = '0';
dfs(grid,i+1,j);
dfs(grid,i-1,j);
dfs(grid,i,j+1);
dfs(grid,i,j-1);
}/*大名鼎鼎的FloodFill算法*/
}; 71.岛屿的最大面积
class Solution {
public:
int maxAreaOfIsland(vector>& grid) {
int m = grid.size();
int n = grid[0].size();
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i>& grid,int i,int j)
{
if(i<0 || i>=grid.size() || j<0 || j>=grid[0].size()) return 0;
if(grid[i][j] == 0)
{
return 0;
}
grid[i][j] = 0;
return dfs(grid,i+1,j)+
dfs(grid,i-1,j)+
dfs(grid,i,j+1)+
dfs(grid,i,j-1)+1;
}
}; 72.最小覆盖子串
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map window_map, t_map;
bool check() { // 判断窗口中是否全包含 t 中所有字符
for (const auto& p : t_map) {
if (window_map[p.first] < p.second) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
string minWindow(string s, string t) {
for (const auto& c : t) { // 统计 t 中字符
++t_map[c];
}
int len = INT_MAX, left = 0, right = -1, ansLeft = -1; // ansLeft 存储可行窗口的左指针索引,len 为可行窗口的长度
int length_s = s.size();
while (right < length_s) {
if (t_map.find(s[++right]) != t_map.end()) { // 若右指针移动 1 个单位后增加的字符存在 t 中则增加到 window_map 中
++window_map[s[right]];
}
while (check() && left <= right) { // 当前窗口包含了 t 中全部字符,开始移动左指针
if (right - left + 1 < len) { // 当前窗口比上次的窗口小,记录
len = right - left + 1;
ansLeft = left;
}
if (t_map.find(s[left]) != t_map.end()) { // t 包含左指针指的字符,更新 window_map
--window_map[s[left]];
}
++left; // 左指针移动
}
}
return ansLeft == -1 ? string() : s.substr(ansLeft, len);
}
}; 73.缺失的第一个正数
class Solution {
public:
int firstMissingPositive(vector& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
for(int i=0;i0 && nums[i]<=n && nums[i] != nums[nums[i]-1])
{
int t = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[nums[i]-1];
nums[t-1] = t;
}
}
for(int i=0;i 74.排序链表(归并排序)
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast->next!=nullptr && fast->next->next!= nullptr)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
ListNode* mid = slow->next;
slow->next = nullptr;
ListNode* left = sortList(head);
ListNode* right = sortList(mid);
return mergeSort(left,right);
}
ListNode* mergeSort(ListNode* l1,ListNode* l2)
{
ListNode* ans = new ListNode();
ListNode* cur = ans;
while(l1!=nullptr && l2!=nullptr)
{
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
cur->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
cur->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
cur=cur->next;
}
cur->next = l1 == nullptr?l2:l1;
return ans->next;
}
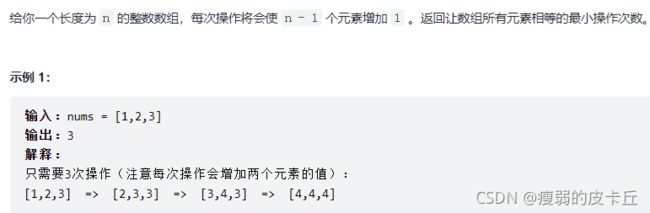
};75.最小操作次数使数组元素相等
class Solution {
public:
int minMoves(vector& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return 0;
int MIN = *min_element(nums.begin(),nums.end());
int ans = 0;
for(auto x:nums)
{
ans+=x-MIN;
}
return ans;
}
};
/*使 n-1n−1 个元素增加 11,也可以理解使 11 个元素减少 11。
于是,要计算让数组中所有元素相等的操作数,我们只需要计算将数组中所有元素都减少到数组中元素最小值所需的操作数,*/ 76.求众数2
//哈希
//变种的摩尔投票法
class Solution {
public:
vector majorityElement(vector& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
if(n == 0) return {};
vector ans;
int vote1 = 0;
int vote2 = 0;
int element1 = 0;
int element2 = 0;
for(auto &x:nums)
{
if(vote1>0 && x == element1) vote1++;
else if(vote2>0 && x == element2) vote2++;
else if(vote1 == 0)
{
element1 = x;
vote1++;
}
else if(vote2 == 0)
{
element2 = x;
vote2++;
}
else{
vote1--;
vote2--;
}
}
int count1 = 0;
int count2 = 0;
for(auto &x:nums)
{
if(vote1>0 && x == element1) count1++;
if(vote2>0 && x == element2) count2++;
}
if(vote1>0 && count1>n/3) ans.push_back(element1);
if(vote2>0 && count2>n/3) ans.push_back(element2);
return ans;
}
/*
int n = nums.size();
if(n == 0) return {};
unordered_map m;
vector ans;
for(auto x:nums)
{
m[x]++;
}
for(auto it:m)
{
if(it.second>n/3)
{
ans.push_back(it.first);
}
}
return ans;
}
*/
}; 77.判断大小端
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 0x1234;
//由于int和char的长度不同,借助int型转换成char型,只会留下低地址的部分
char c = (char)(a);
if (c == 0x12)
cout << "big endian" << endl;
else if(c == 0x34)
cout << "little endian" << endl;
}
#include
using namespace std;
//union联合体的重叠式存储,endian联合体占用内存的空间为每个成员字节长度的最大值
union endian
{
int a;
char ch;
};
int main()
{
endian value;
value.a = 0x1234;
//a和ch共用4字节的内存空间
if (value.ch == 0x12)
cout << "big endian"< 78.N皇后
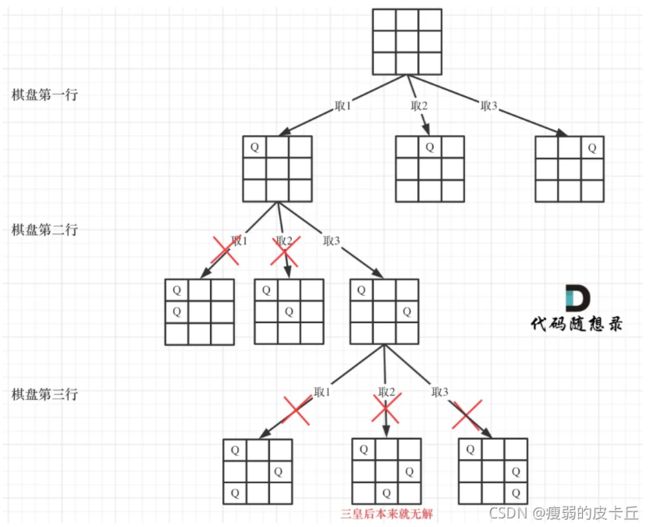
都知道n皇后问题是回溯算法解决的经典问题,但是用回溯解决多了组合、切割、子集、排列问题之后,遇到这种二位矩阵还会有点不知所措。
首先来看一下皇后们的约束条件:
-
不能同行
-
不能同列
-
不能同斜线
确定完约束条件,来看看究竟要怎么去搜索皇后们的位置,其实搜索皇后的位置,可以抽象为一棵树。
下面我用一个3 * 3 的棋牌,将搜索过程抽象为一颗树,如图:
从图中,可以看出,二维矩阵中矩阵的高就是这颗树的高度,矩阵的宽就是树形结构中每一个节点的宽度。
那么我们用皇后们的约束条件,来回溯搜索这颗树,只要搜索到了树的叶子节点,说明就找到了皇后们的合理位置了。
参数n是棋牌的大小,然后用row来记录当前遍历到棋盘的第几层了。当递归到棋盘最底层(也就是叶子节点)的时候,就可以收集结果并返回了。
递归深度就是row控制棋盘的行,每一层里for循环的col控制棋盘的列,一行一列,确定了放置皇后的位置。
每次都是要从新的一行的起始位置开始搜,所以都是从0开始。
在这份代码中,细心的同学可以发现为什么没有在同行进行检查呢?
因为在单层搜索的过程中,每一层递归,只会选for循环(也就是同一行)里的一个元素,所以不用去重了。
class Solution {
private:
vector> result;
// n 为输入的棋盘大小
// row 是当前递归到棋牌的第几行了
void backtracking(int n, int row, vector& chessboard) {
if (row == n) {
result.push_back(chessboard);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (isValid(row, col, chessboard, n)) { // 验证合法就可以放
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q'; // 放置皇后
backtracking(n, row + 1, chessboard);
chessboard[row][col] = '.'; // 回溯,撤销皇后
}
}
}
bool isValid(int row, int col, vector& chessboard, int n) {
int count = 0;
// 检查列
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) { // 这是一个剪枝
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查 45度角是否有皇后
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >=0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查 135度角是否有皇后
for(int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public:
vector> solveNQueens(int n) {
result.clear();
std::vector chessboard(n, std::string(n, '.'));
backtracking(n, 0, chessboard);
return result;
}
}; 组合总和3
class Solution {
public:
vector temp;
vector> ans;
vector> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
dfs(k,n,1);
return ans;
}
void dfs(int k,int n,int cur)
{
if(temp.size() == k)
{
if(n == 0)
{
ans.push_back(temp);
return;
}
return;
}
if(cur > 9 || cur > n) return;
temp.push_back(cur);
dfs(k,n-cur,cur+1);
temp.pop_back();
dfs(k,n,cur+1);
}
};