【驱动篇】韦东山嵌入式Linux笔记——基于IMX6ULL
设备驱动开发
1. Char 驱动框架
Step 1: 编写fops,确定驱动所需的函数
static struct file_operations hello_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = hello_drv_open,
.read = hello_drv_read,
.write = hello_drv_write,
.release = hello_drv_close,
};
Step 2: 编写fops里的函数及init和exit函数
fops函数:open/close/read/write
static ssize_t hello_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = copy_to_user(buf, kernel_buf, MIN(1024, size));
return MIN(1024, size);
}
static ssize_t hello_drv_write (struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = copy_from_user(kernel_buf, buf, MIN(1024, size));
return MIN(1024, size);
}
static int hello_drv_open (struct inode *node, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
static int hello_drv_close (struct inode *node, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
init函数
//调用register_xxx获得major
major = register_chrdev(0, "hello", &hello_drv); /* /dev/hello */
//调用class_create创造对应的class
hello_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello_class");
//调用device_create在/dev下创建相应设备节点
device_create(hello_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "hello"); /* /dev/hello */
完整代码
static int __init hello_init(void)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
major = register_chrdev(0, "hello", &hello_drv); /* /dev/hello */
hello_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello_class");
err = PTR_ERR(hello_class);
if (IS_ERR(hello_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "hello");
return -1;
}
device_create(hello_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "hello"); /* /dev/hello */
return 0;
}
exit函数(和init全逆向)
static void __exit hello_exit(void)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
device_destroy(hello_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(hello_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "hello");
}
注意:init和exit需要修饰才可以在module_init/exit中注册
Step 3: module_init 中注册init / module_exit中注册exit
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
major(主设备号)相当于fops数组的索引,当入口函数调用register_chardev()时,传入0系统会分配一个major号(其本质就是在fops数组里找到个空位存储新的fops),以便于索引fops数组。
2. LED 驱动
基本流程
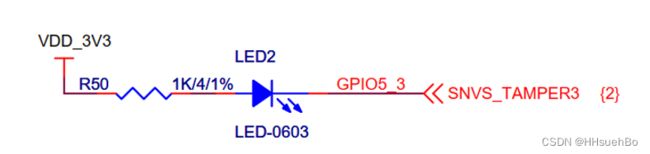
Step 1:确定引脚,配置引脚模式
引脚:GPIO5_3
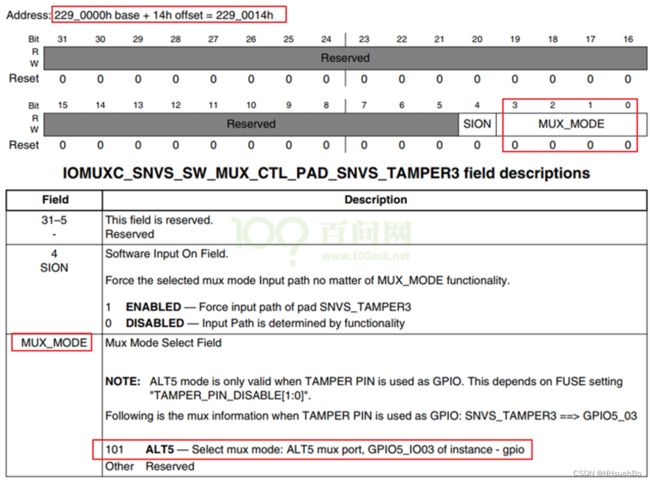
寄存器:IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3
地址:0x02290000 + 0x14
赋值:寄存器后三位设为101则为GPIO模式
Step 2:配置引脚数据方向
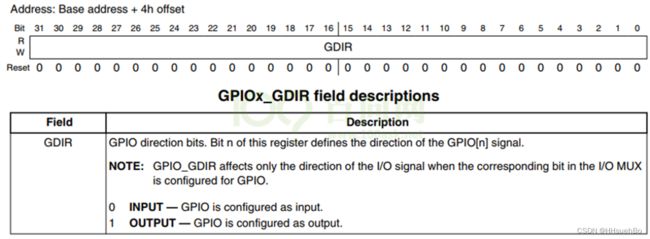
寄存器:GPIO5_GDIR
地址:0x020AC004
赋值:第3位置1为OUTPUT模式
Step 3:R/W数据
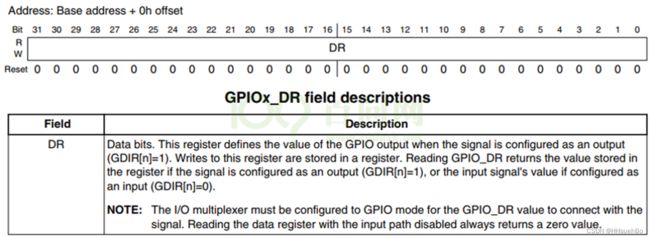
寄存器:GPIO5_DR
地址:0x020AC000
赋值:对第3位置1/0即可
代码-基础版
Step 1:定义寄存器
/* registers */
// IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 地址:0x02290000 + 0x14
static volatile unsigned int *IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3;
// GPIO5_GDIR 地址:0x020AC004
static volatile unsigned int *GPIO5_GDIR;
//GPIO5_DR 地址:0x020AC000
static volatile unsigned int *GPIO5_DR;
Tips: 注意用volatile修饰,表示该变量不允许被编译器优化
Step 2:init / exit函数
功能:init 完成ioremap以及device create工作,exit完成逆操作
Tips: ioremap的 4 表示映射1页
/* 入口函数 */
static int __init led_init(void)
{
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
major = register_chrdev(0, "100ask_led", &led_fops);
/* ioremap */
// IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 地址:0x02290000 + 0x14
IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 = ioremap(0x02290000 + 0x14, 4);
// GPIO5_GDIR 地址:0x020AC004
GPIO5_GDIR = ioremap(0x020AC004, 4);
//GPIO5_DR 地址:0x020AC000
GPIO5_DR = ioremap(0x020AC000, 4);
led_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "myled");
device_create(led_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "myled"); /* /dev/myled */
return 0;
}
static void __exit led_exit(void)
{
iounmap(IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3);
iounmap(GPIO5_GDIR);
iounmap(GPIO5_DR);
device_destroy(led_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(led_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_led");
}
Step 3: open/write函数
open功能:完成输出配置
static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
/* enable gpio5
* configure gpio5_io3 as gpio
* configure gpio5_io3 as output
*/
*IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 &= ~0xf;//清空后四位
*IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 |= 0x5;//后四位置101
*GPIO5_GDIR |= (1<<3);//第三位置1,表示数据方向为OUTPUT
return 0;
}
write功能:完成写数据
Tips:
1) 从上层获取数据 copy_from_user ,传数据给上层 copy_to_user
2) 快速清零:&= ~(1<static ssize_t led_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
char val;
int ret;
/* copy_from_user : get data from app */
ret = copy_from_user(&val, buf, 1);
/* to set gpio register: out 1/0 */
if (val)
{
/* set gpio to let led on */
*GPIO5_DR &= ~(1<<3);
}
else
{
/* set gpio to let led off */
*GPIO5_DR |= (1<<3);
}
return 1;
}
代码-板子分离
核心思想:针对不同的硬件编写不同的.c,对于操作LED,抽象出一个led_opr结构体,内部包含硬件相关的操作。之后在具体板子的.c文件中进行实现。
led_opr.h:结构体抽象
#ifndef _LED_OPR_H
#define _LED_OPR_H
struct led_operations {
int (*init) (int which); /* 初始化LED, which-哪个LED */
int (*ctl) (int which, char status); /* 控制LED, which-哪个LED, status:1-亮,0-灭 */
};
struct led_operations *get_board_led_opr(void);
#endif
board_demo.c:具体硬件实现
#include 之后在leddrv.c的write和open函数中进行调用:
struct led_operations *p_led_opr;
static int __init led_init(void)
{
...
p_led_opr = get_board_led_opr();
...
}
static int led_drv_open (struct inode *node, struct file *file)
{
int minor = iminor(node);
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
/* 根据次设备号初始化LED */
p_led_opr->init(minor);
return 0;
}
/* write(fd, &val, 1); */
static ssize_t led_drv_write (struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
int err;
char status;
struct inode *inode = file_inode(file);
int minor = iminor(inode);
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = copy_from_user(&status, buf, 1);
/* 根据次设备号和status控制LED */
p_led_opr->ctl(minor, status);
return 1;
}
如此一来,当有板子ABCD时,只需要关注borad.c文件内部的实现即可。对于led_drv则不需要动,在编译的时候用哪个板子编哪个board文件即可。