Spring Boot中RedisTemplate的使用
当前Spring Boot的版本为2.7.6,在使用RedisTemplate之前我们需要在pom.xml中引入下述依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
3.1.4
同时在application.yml文件中添加下述配置:
spring
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379一、opsForHash
RedisTemplate.opsForHash()是RedisTemplate类提供的用于操作Hash类型的方法,它可以用于对Redis中的Hash数据结构进行各种操作,如设置字段值、获取字段值、删除字段值等。
1.1 设置哈希字段的值
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void test(){
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put("fruit:list", "1", "苹果");
}
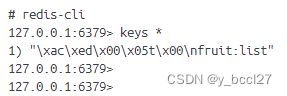
}在上述代码能正常运行的情况下,我们在终端中执行 redis-cli 命令进入到redis的控制台中,然后执行 keys * 命令查看所有的key,结果发现存储在redis中的key不是设置的string值,前面还多出了许多类似 \xac\xed\x00\x05t\x00 这种字符串,如下图所示:
这是因为Spring-Data-Redis的RedisTemplate
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
public class RedisTemplateConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
RedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
return redisTemplate;
}
} 需要说明的是这种配置只是针对所有的数据都是String类型,如果是其它类型,则根据需求修改一下序列化方式。
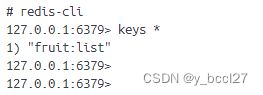
使用flushdb命令清除完所有的数据以后,再次执行上述测试案例,接着我们再次去查看所有的key,这个看到数据已经正常:
接着使用 hget fruit:list 1 命令去查询刚刚存储的数据,这时又发现对应字段的值中文显示乱码:
\xe8\x8b\xb9\xe6\x9e\x9c这个时候需要我们在进入redis控制台前,添加 --raw 参数:
redis-cli --raw1.2 设置多个哈希字段的值
设置多个哈希字段的值一种很简单的粗暴的方法是多次执行opsForHash().put()方法,另外一种更优雅的方式如下:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void test(){
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("1","苹果");
map.put("2","橘子");
map.put("3","香蕉");
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll("fruit:list",map);
}
} 1.3 获取哈希字段的值
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void test(){
String value = (String) redisTemplate.opsForHash().get("fruit:list","1");
System.out.println(value);
}
}
1.4 获取多个哈希字段的值
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void test(){
List values = redisTemplate.opsForHash().multiGet("fruit:list", Arrays.asList("1", "2","3"));
System.out.println(values);
}
} 1.5 判断哈希中是否存在指定的字段
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void test(){
Boolean hasKey = redisTemplate.opsForHash().hasKey("fruit:list", "1");
System.out.println(hasKey);
}
}1.6 获取哈希的所有字段
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import java.util.Set;
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void test(){
Set keys = redisTemplate.opsForHash().keys("fruit:list");
System.out.println(keys);
}
} 1.7 获取哈希的所有字段的值
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void test(){
List values = redisTemplate.opsForHash().values("fruit:list");
System.out.println(values);
}
} 1.8 获取哈希的所有字段和对应的值
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void test(){
Map entries = redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries("fruit:list");
System.out.println(entries);
}
} 1.9 删除指定的字段
返回值返回的是删除成功的字段的数量,如果字段不存在的话,则返回的是0。
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void test(){
Long deletedFields = redisTemplate.opsForHash().delete("fruit:list", "4");
System.out.println(deletedFields);
}
}1.10 如果哈希的字段存在则不会添加,不存在则添加
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void test(){
Boolean success = redisTemplate.opsForHash().putIfAbsent("fruit:list","4","西瓜");
System.out.println(success);
}
}1.11 将指定字段的值增加指定步长
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
@SpringBootTest
public class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void test(){
Long incrementedValue = redisTemplate.opsForHash().increment("salary:list", "1", 5);
System.out.println(incrementedValue);
}
}如果字段不存在,则将该字段的值设置为指定步长,并且返回该字段当前的值;如果字段存在,则在该字段原有值的基础上增加指定步长,返回该字段当前的最新值。 该方法只适用于字段值为int类型的数据,因此关于哈希数据结构的value值的序列化方式要有所改变:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
public class RedisTemplateConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
RedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return redisTemplate;
}
} StringRedisTemplate的好处就是在RedisTemplate基础上封装了一层,指定了所有数据的序列化方式都是采用StringRedisSerializer(即字符串),使用语法上面完全一致。
public class StringRedisTemplate extends RedisTemplate {
public StringRedisTemplate() {
this.setKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
this.setValueSerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
this.setHashKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
this.setHashValueSerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
}
}