seata分布式事务原理分析
原理
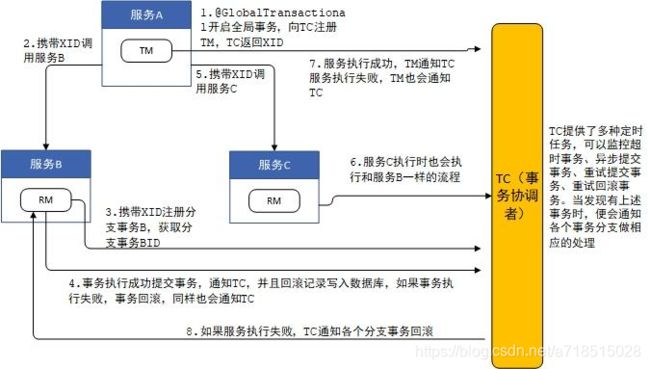
seata涉及到三个角色之间的交互,本文通过流程图将AT模式下的基本交互流程梳理一下,为我们以后的解析打下基础。
假设有三个微服务,分别是服务A、B、C,其中服务A中调用了服务B和服务C,TM、TC、RM三者之间的交互流程如下图:
- 1、服务A启动时,GlobalTransactionScanner会对有@GlobalTransaction注解的方法进行AOP增强,并生成代理,增强的代码位于GlobalTransactionalInterceptor类中,当调用@GlobalTransaction注解的方法时,增强代码首先向TC注册全局事务,表示全局事务的开始,同时TC生成XID,并返回给TM;
- 2、服务A中调用服务B时,将XID传递给服务B;
- 3、服务B得到XID后,访问TC,注册分支事务,并从TC获得分支事务ID,TC根据XID将分支事务与全局事务关联;
- 4、接下来服务B开始执行SQL语句,在执行前将表中对应的数据保存一份,执行后在保存一份,将这两份记录作为回滚记录写入到数据库中,如果执行过程中没有异常,服务B最后将事务提交,并通知TC分支事务成功,服务B也会清除本地事务数据;
- 5、服务A访问完服务B后,访问服务C;
- 6、服务C与TC之间的交互与服务B完全一致;
- 7、服务B和服务C都成功后,服务A通过TM通知TC全局事务成功,如果失败了,服务A也会通知TC全局事务失败;
- 8、TC记录了全局事务下的每个分支事务,TC收到全局事务的结果后,如果结果成功,则通知RM成功,RM收到通知后清理之前在数据库中保存的回滚记录,如果失败了,则RM要查询出之前在数据库保存的回滚记录,对之前的SQL操作进行回滚。
因为TM、RM、TC之间的交互都是通过网络完成的,很容易出现网络断开的情况,因此TC提供了四个定时线程池,定时检测系统中是否有超时事务、异步提交事务、回滚重试事务、重试提交事务,如果发现了有这四类事务,则从全局事务中获取所有的分支事务,分别调用各个分支事务完成对应的操作,依次来确保事务的一致性。
需要考虑的问题:
通过上面流程的分析可以发现,每次SQL操作(查询除外)时,都会增加额外了三次数据库操作;每次全局事务和分支事务开启时,都涉及到TM、RM与TC的交互;全局事务期间还要承担数据短时不一致的情况,这些都是我们在使用AT模式需要考虑的情况。
案例
用户购买操作:
入口BusinessServiceImpl.java,里面三个dubbo接口 storageDubboService(扣减库存) ,orderDubboService(创建订单,里面又调用了另外的接口accountDubboService-扣减账户资金)
/**
* 模拟用户购买商品下单业务逻辑流程
* @Param:
* @Return:
*/
@PostMapping("/buy")
ObjectResponse handleBusiness(@RequestBody BusinessDTO businessDTO){
LOGGER.info("请求参数:{}",businessDTO.toString());
return businessService.handleBusiness(businessDTO);
}
/**
* 处理业务逻辑 GlobalTransactional 开启全局事务,生成XID
* @Param:
* @Return:
*/
@Override
@GlobalTransactional(timeoutMills = 300000, name = "dubbo-gts-seata-example")
public ObjectResponse handleBusiness(BusinessDTO businessDTO) {
System.out.println("开始全局事务,XID = " + RootContext.getXID());
ObjectResponse<Object> objectResponse = new ObjectResponse<>();
//1、扣减库存
CommodityDTO commodityDTO = new CommodityDTO();
commodityDTO.setCommodityCode(businessDTO.getCommodityCode());
commodityDTO.setCount(businessDTO.getCount());
ObjectResponse storageResponse = storageDubboService.decreaseStorage(commodityDTO);
//2、创建订单
OrderDTO orderDTO = new OrderDTO();
orderDTO.setUserId(businessDTO.getUserId());
orderDTO.setCommodityCode(businessDTO.getCommodityCode());
orderDTO.setOrderCount(businessDTO.getCount());
orderDTO.setOrderAmount(businessDTO.getAmount());
ObjectResponse<OrderDTO> response = orderDubboService.createOrder(orderDTO);
//打开注释测试事务发生异常后,全局回滚功能
if (!flag) {
throw new RuntimeException("测试抛异常后,分布式事务回滚!");
}
if (storageResponse.getStatus() != 200 || response.getStatus() != 200) {
throw new DefaultException(RspStatusEnum.FAIL);
}
objectResponse.setStatus(RspStatusEnum.SUCCESS.getCode());
objectResponse.setMessage(RspStatusEnum.SUCCESS.getMessage());
objectResponse.setData(response.getData());
return objectResponse;
}
StorageDubboServiceImpl.java扣减库存
@Service(version = "1.0.0",protocol = "${dubbo.protocol.id}",
application = "${dubbo.application.id}",registry = "${dubbo.registry.id}",
timeout = 3000)
public class StorageDubboServiceImpl implements StorageDubboService {
@Autowired
private ITStorageService storageService;
@Override
public ObjectResponse decreaseStorage(CommodityDTO commodityDTO) {
System.out.println("全局事务id :" + RootContext.getXID());
return storageService.decreaseStorage(commodityDTO);
}
}
下单OrderDubboServiceImpl.java,createOrder里面包含两步,扣减账户余额,生成订单
@Service(version = "1.0.0",protocol = "${dubbo.protocol.id}",
application = "${dubbo.application.id}",registry = "${dubbo.registry.id}",
timeout = 3000)
public class OrderDubboServiceImpl implements OrderDubboService {
@Autowired
private ITOrderService orderService;
@Override
public ObjectResponse<OrderDTO> createOrder(OrderDTO orderDTO) {
System.out.println("全局事务id :" + RootContext.getXID());
return orderService.createOrder(orderDTO);
}
}
/**
* 创建订单
* @Param: OrderDTO 订单对象
* @Return: OrderDTO 订单对象
*/
@Override
public ObjectResponse<OrderDTO> createOrder(OrderDTO orderDTO) {
ObjectResponse<OrderDTO> response = new ObjectResponse<>();
//扣减用户账户
AccountDTO accountDTO = new AccountDTO();
accountDTO.setUserId(orderDTO.getUserId());
accountDTO.setAmount(orderDTO.getOrderAmount());
ObjectResponse objectResponse = accountDubboService.decreaseAccount(accountDTO);
//生成订单号
orderDTO.setOrderNo(UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-",""));
//生成订单
TOrder tOrder = new TOrder();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(orderDTO,tOrder);
tOrder.setCount(orderDTO.getOrderCount());
tOrder.setAmount(orderDTO.getOrderAmount().doubleValue());
try {
baseMapper.createOrder(tOrder);
} catch (Exception e) {
response.setStatus(RspStatusEnum.FAIL.getCode());
response.setMessage(RspStatusEnum.FAIL.getMessage());
return response;
}
if (objectResponse.getStatus() != 200) {
response.setStatus(RspStatusEnum.FAIL.getCode());
response.setMessage(RspStatusEnum.FAIL.getMessage());
return response;
}
response.setStatus(RspStatusEnum.SUCCESS.getCode());
response.setMessage(RspStatusEnum.SUCCESS.getMessage());
return response;
}
AT TCC Sega 区别
AT模式
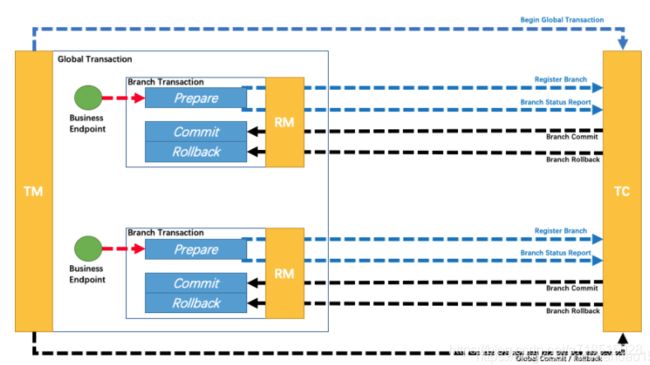
两阶段:
1.seata拦截sql,并解析,更新业务数据,记录更新前和更新后的数据快照。此时更新后的数据,是对外可见的。
2.执行成功,分布式事务提交。如果偶一个执行失败,开始回滚,由于第一阶段里面,数据已经更新到数据库,所以要对比当前数据和之前保存的数据快照是否一致,避免发生数据错误,完成校验后用before还原数据。
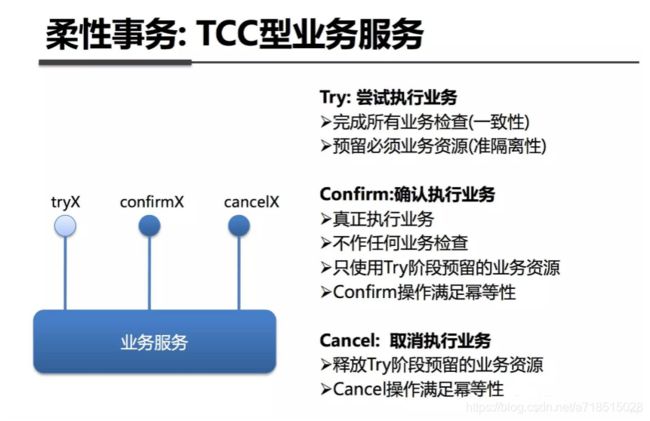
TCC模式
1.try:做业务检查和资源预留
2.confirm:确认提交
3.cancel:业务执行错误之后需要回滚的状态下执行事务的业务取消和预留。
如:下单操作有两个步骤:资金扣减、创建订单
try(数据准备):冻结资金、扣减账户余额。
confirm;数据提交。直接的提交,扣减资金,调用某个分录余额。
cancel:数据回滚
AT和TCC的区别
AT是基于支持本地ACID事务的关系型数据库
一阶段prepare 行为,在本地事务中,同时提交数据更新前、后的快照信息
二阶段commit: 成功后结束,异步清理之前的快照。
二阶段rollback: 对比之前的保存的数据更新后的快照,完成数据回滚
TCC 不依赖底层数据库的事务支持。
一阶段prepare行为:调用自定义的prepare 逻辑
二阶段commit,调用自定义的commit
三阶段rollback 调用自定义rollback
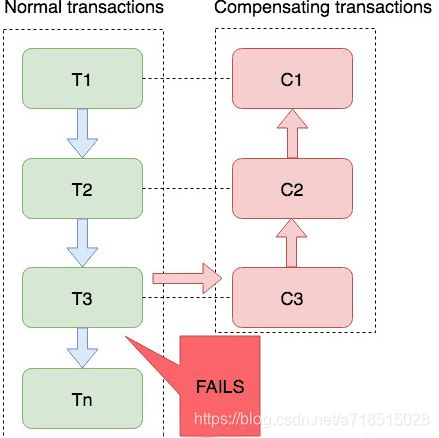
saga模式
sage是seata提供的长事务解决方案。
每个参与者单独提交自己的事务,当某一个参与者失败,则补偿回滚前面已经成功的参与者。
一阶段正向服务和二阶段补偿服务都由服务开发实现
长链路金融应用、渠道聚合等
XA模式
XA 模式是 Seata 将会开源的另一种无侵入的分布式事务解决方案
无侵入
将快照数据和行锁等通过 XA 指令委托给了数据库来完成
XA模式是分布式强一致性的解决方案,但性能低而使用较少