实验七 动态分区分配算法
不知道是不是理解错误,感觉最近的几个实验都大同小异。
用算法思想描述就是(又是一个模拟题,甚至不需要考虑空间和时间复杂度。
设立全局变量和所需结构:
#define getpch(type) (type*)malloc(sizeof(type)) //指针建立的重命名
struct ava_memory{ //可用内存块存储.
int ID; //标记进程的号码,如果该区块未被进程占用,那么我们认为为-1.
int start; //当前区块的开始位置.
int end; //当前区块的结束位子.
int len; //当前区块的长度.
struct ava_memory *next; //我们利用指针来模拟,所以需要一个连接指针.
};
struct ava_memory *avaoc; //建立头指针.
int memory, ide; //建立全局下的变量:总内存 和 当前进程号.
bool run; //执行判断条件.
string ins; //操作选择变量.
来讲一下为我何选用结构体指针来实现,而不是结构体数组:
使用数组的话的优势区间?可以O(1)访问进程块,但是这无法弥补需要反复“移动”的缺陷。所以我更趋向于使用指针来实现,这样我们就方便修改进程块的修改。
使用指针,那么我们只能每次从头遍历,如果需要优化,可以建立哈希表存储各进程的指针。(我比较懒,就不进行实现了。
对建立的结构进行初始化:
void new_work(){ //初始化操作
cout << " please the Total system memory size: "; //提示语句
cin >> memory; //总内存的输入
run = true; //循环成立条件
ide = 1; //初始化进程号
struct ava_memory *q = getpch(struct ava_memory); //给头指针分配空间,作为最开始的内存块
avaoc = q; //将建立的空间索引给全局下的头指针
avaoc->start = 1, avaoc->end = memory, avaoc->len = memory, avaoc->ID = -1, avaoc->next = NULL; //头指针的初始化
cout << endl; //对初始化的结果观测
cout << " new~" << endl;
cout << " start:" << avaoc->start << " end:" << avaoc->end << " len:" << avaoc->len << " ID:" << avaoc->ID << " next:" << avaoc->next << endl << endl;
}
初始化的作用: 因为我的想法是开始的数据结构中就有一个ID号为 -1 (即是一个未分配进程的内存块)。它的开始位子就是1,而结束位子和总长度就是我们分配给的内存。
动态分配内存:
void add(){ //添加操作还是很好写的啦啦啦
cout << endl;
cout << " please input the size of memory: ";
int Size; cin >> Size;
if(memory < Size) {cout << " The memory is not enough!" << endl << endl; return; } //判断内存是否足够
memory -= Size; //更改剩余内存
cout << " adding~... ..." << endl;
struct ava_memory *head = avaoc; //建立用来遍历的指针
while(head && Size){
if(head->ID == -1){ //-1 表示未被进程占用
if(Size <= head->len){ //当该内存块足够分配的时候
if(Size < head->len){ //这是需要建立新的内存块的操作
int b_end = head->end; //备份
head->end = head->start + Size - 1; //-1 算上初始位
head->len = Size;
struct ava_memory *p = getpch(struct ava_memory);
p->start = head->end + 1, p->end = b_end, p->len = p->end - p->start + 1, p->ID = -1, p->next = head->next;
head->next = p;
}
Size = 0 , head->ID = ide;
}else{ //当当前内存块不足以进行分配内存时,那么该整块内存都分配给这个进程
Size -= head->len;
head->ID = ide;
}
}
head = head -> next;
}
ide ++; //标记当前进程号
cout << endl;
}
预想的动态分配内存: 对无法一个空闲内存块的进行分块存储,即对进程的分割。那么我们如何进行分配呢?如果所需的内存大于等于当前所在的空闲内存块,那么我们只需要修改进程号,当作该内存块全部分配给了当前进程。如果所需的内存大小 小于所在的内存块,那么我们需要对这个进程块进行分割(进程剩余所需内存块 和 所在空闲内存块的剩余内存)。实际操作就是,建立一个新的指针添加在这个指针后面,然后修改一些参数。

注意:上面的分配和下面的首次,最佳,最坏分配不在一个代码中实现。
首次分配算法:
void first_malloc(){
add(); //该处不是上面那个分配内存的方法,而是输入语句
cout << endl;
struct ava_memory *p = avaoc;
bool m = true;
while(p){
if(p->ID == -1 && p->len >= sum){ //寻找一个能够分配的进程块
if(p->len > sum){ //这部分还是一样的,如果刚刚好,那么只需要修改进程号即可,但是如果需要分配的内存小于当前空闲内存块,那么分块处理.
int b_end = p->end;
p->end = p->start + sum - 1; //-1 算上初始位
p->len = sum;
struct ava_memory *q = getpch(struct ava_memory);
q->ID = -1, q->start = p->start + sum, q->end = b_end, q->len = q->end - q->start + 1, q->next = p->next;
p->next = q;
}
p->ID = ide;
m = false;
break; //一旦找到就退出,因为就分配一个
}
p = p->next;
}
if(m){ //如果没找到,那么就是没有一个进程块能放下这个完整的进程
cout << "you can not do this, your memory is not enough!" << endl << endl;
return;
}
cout << " first_malloc~... ..." << endl << endl;
ide ++;
}
首次分配算法就时遇到第一个能够分配进的内存块那么我们就分配。遍历链表的同时进行修改,修改完成后直接跳出遍历。(我这里实现的是如果没找到单个内存块就表示无法执行。
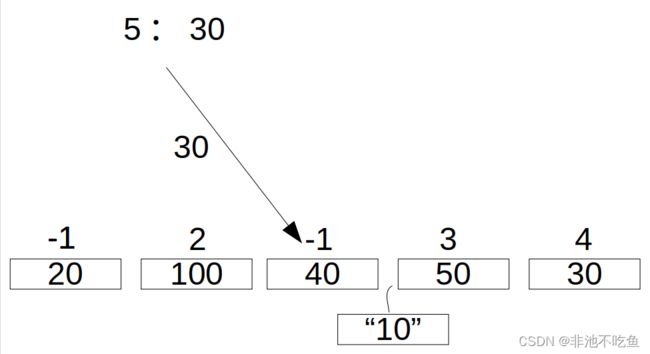
最佳分配算法:
void min_malloc(){
add();
cout << endl;
int num = memory;
struct ava_memory *head = avaoc;
struct ava_memory *p = NULL;
while(head){ //找到能够分配进去的最小的进程块
if(head->ID == -1 && head->len >= sum && head->len < num) p = head , num = head->len;
head = head->next;
}
if(p && p->len > sum){ //既然找到了最小的能够
int b_end = p->end;
p->end = p->start + sum - 1; //-1 算上初始位
p->len = sum;
struct ava_memory *q = getpch(struct ava_memory);
q->ID = -1, q->start = p->start + sum, q->end = b_end, q->len = q->end - q->start + 1, q->next = p->next;
p->next = q;
p->ID = ide;
}else{
cout << "you can not do this, your memory is not enough!" << endl << endl;
return;
}
cout << " min_malloc~... ..." << endl << endl;
ide ++;
}
最佳分配算法就是找到最小的那个可以存储进程的内存块,存储进去。我们对建立的链表进行了一次遍历查找,找到了是哪个进程块,并且保存下来了他的指针索引 (遍历只为了寻找,而不是修改)。接下来就是对指针索引,直接修改。
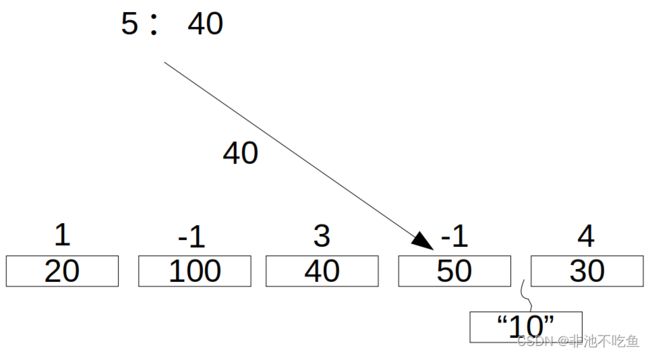
最坏分配算法:
void max_malloc(){
add();
cout << endl;
int num = 0;
struct ava_memory *head = avaoc;
struct ava_memory *p = NULL;
while(head){
if(head->ID == -1 && head->len >= sum && head->len > num) p = head , num = head->len;
head = head->next;
}
if(p && p->len > sum){
int b_end = p->end;
p->end = p->start + sum - 1; //-1 算上初始位
p->len = sum;
struct ava_memory *q = getpch(struct ava_memory);
q->ID = -1, q->start = p->start + sum, q->end = b_end, q->len = q->end - q->start + 1, q->next = p->next;
p->next = q;
p->ID = ide;
}else{
cout << "you can not do this, your memory is not enough!" << endl << endl;
return;
}
cout << " max_malloc~... ..." << endl << endl;
ide ++;
}
最坏分配算法就是找到最大的那个区块,然后足够就分配,不够就是不够,没法分配。(我们可以建立一个从大到小的有序的内存块进行索引。
其实这三个(四个)分配的原理很相似,也可呢是我的理解错误。

释放进程块:
void free(){ //删除操作的难点在于内存的合并过程,这里偷下懒
cout << endl;
cout << " the ID you want free: ";
int id; cin >> id; //输入需要删除的进程的id序号
cout << " free~... ..." << endl;
struct ava_memory *p = avaoc;
while(p){ //实现进程的释放
if(p->ID == id) p->ID = -1;
p = p->next;
}
p = avaoc;
while(p){ //实现进程块的合并
if(p->next && p->ID == -1 && p->next->ID == -1){ //合并
p->end = p->next->end;
p->len = p->len + p->next->len;
struct ava_memory* q = p->next;
p->next = p->next->next;
delete q;
}else p = p->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
我们对链表进行两次遍历,第一次将 ”ID = id“ 的进程块标记空闲 (做的实际是释放内存)。第二次链表的遍历就是对连续的 “ID == -1” 的进程块进行合并。你也可以进行一遍遍历时同时进行释放和合并操作,但是我懒,那样难写。
内存分配情况:
void all(){ //over
cout << endl;
cout << " all~" << endl;
struct ava_memory *p = avaoc;
cout << " ID: ";
while(p){
cout << setw(5) << p->ID;
p = p->next;
}cout << endl;
p = avaoc;
cout << " pc: ";
while(p){
cout << setw(5) << p->len;
p = p->next;
}cout << endl << endl;
}
就是遍历链表,全部对其输出就好了。
查询某个进程的分配情况:
void idm(){
cout << endl;
cout << " the ID pc you want get: ";
int id, m = 0; cin >> id;
cout << " idm~... ..." << endl;
struct ava_memory *p = avaoc;
cout << " start: ";
while(p){
if(p->ID == id){
cout << setw(5) << p->start;
}
p = p->next;
}cout << endl;
p = avaoc;
cout << " len: ";
while(p){
if(p->ID == id){
cout << setw(5) << p->len;
}
p = p->next;
}cout << endl;
p = avaoc;
cout << " end: ";
while(p){
if(p->ID == id){
cout << setw(5) << p->end;
}
p = p->next;
}cout << endl;
}
遍历链表,但是只对 “ID = id” 的区块进行输出。
下面是对动态分配的整体代码及结果演示:
#include我们对以下数据进行结果展示:
640
help
add
20
add
100
add
50
all
free
2
all
add
300
all
idm
4
free
4
all
free
3
all
out
please the Total system memory size:
new~
start:1 end:640 len:640 ID:-1 next:0
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
---"add": Memory allocation algorithm.
---"free": Free memory algorithm.
---"idm": the id memory algorithm.
---"use": use Memory allocation.
---"have": have Memory allocation.
---"all": all of the Memory allocation.
---"out": out allocation.
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
please input the size of memory: adding~... ...
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
please input the size of memory: adding~... ...
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
please input the size of memory: adding~... ...
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
all~
ID: 1 2 3 -1
pc: 20 100 50 470
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
the ID you want free: free~... ...
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
all~
ID: 1 -1 3 -1
pc: 20 100 50 470
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
please input the size of memory: adding~... ...
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
all~
ID: 1 4 3 4 -1
pc: 20 100 50 200 270
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
the ID pc you want get: idm~... ...
start: 21 171
len: 100 200
end: 120 370
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
the ID you want free: free~... ...
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
all~
ID: 1 -1 3 -1
pc: 20 100 50 470
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
the ID you want free: free~... ...
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
all~
ID: 1 -1
pc: 20 620
please select the action you want to perform (--help Query operation instruction):
下面是对首次,最佳,最坏分配的总体代码:
#include结果演示:
640
1
20
1
100
1
50
1
70
1
200
5
4
2
5
4
4
5
2
60
5
3
70
5
0
please the Total system memory size:
new~
start:1 end:640 len:640 ID:-1 next:0
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
How much memory do you want to use:
first_malloc~... ...
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
How much memory do you want to use:
first_malloc~... ...
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
How much memory do you want to use:
first_malloc~... ...
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
How much memory do you want to use:
first_malloc~... ...
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
How much memory do you want to use:
first_malloc~... ...
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
all~
ID: 1 2 3 4 5 -1
pc: 20 100 50 70 200 200
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
the ID you want free: free~... ...
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
all~
ID: 1 -1 3 4 5 -1
pc: 20 100 50 70 200 200
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
the ID you want free: free~... ...
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
all~
ID: 1 -1 3 -1 5 -1
pc: 20 100 50 70 200 200
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
How much memory do you want to use:
min_malloc~... ...
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
all~
ID: 1 -1 3 6 -1 5 -1
pc: 20 100 50 60 10 200 200
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
How much memory do you want to use:
max_malloc~... ...
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
all~
ID: 1 -1 3 6 -1 5 7 -1
pc: 20 100 50 60 10 200 70 130
1: 首次适应算法.
2: 最佳适应算法.
3: 最坏适应算法.
4: 释放进程.
5: 查询进程分配情况.
6: 查询某个进程的情况.
0: 退出.
你的选择是:
--over