【教程】-在rknn-toolkit2模拟器中验证测试语义分割模型Yolov5-seg
引言
为了以后能够顺利的将模型部署在rk3568开发板中,我们首先要在rknn-toolkit2提供的模拟器环境中进行运行测试,从而保证所选模型能够在开发板上进行部署,测试环境是Ubuntu20.04。
yolov5下载地址:ultralytics/yolov5 at v7.0 (github.com)
训练和如何导出ONNX这里就不说了,yolov5已经是非常成熟的算法了,网上有其数不清的教程,所以这里就不重复说了。
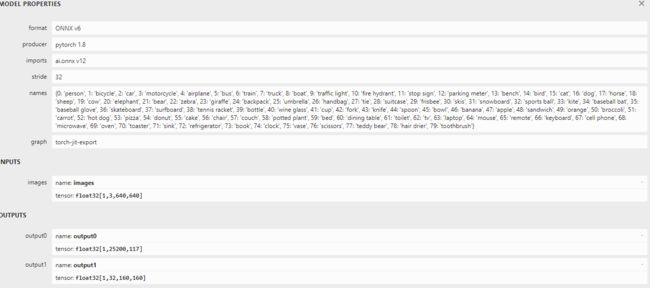
一、ONNX结构
要对yolov5-seg做部署测试,那必然要对其onnx的输出有所了解,yolov5-seg的输出如下:
上图可以看出onnx的输出有两个,分别是output0和output1。我们一个个来解释:
output0 : [1, 25200, 117] 其中,1代表批处理的数量;25200表示预测框的数量,也就是模型在输入图像中检测到的物体数量;117表示每个预测框的信息维度,具体来说117 = 4(检测框坐标) + 1(置信度)+ 80(类别数量)+ 32(mask信息)。
output1 : [1, 32, 160, 160],这个输出主要描述了模型对输入图像进行语义分割后得到的预测结果。
二、推理代码
1、老样子,转换并且加载我们的onnx模型,注意好onnx的输出名称,需要对应上。
rknn = RKNN()
# Load ONNX model
print("--> Loading model")
# ret = rknn.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL)
# rknn.config(mean_values=[82.9835, 93.9795, 82.1893], std_values=[54.02, 54.804, 54.0225], target_platform='rk3568')
rknn.config(mean_values=[0, 0, 0], std_values=[255, 255, 255], target_platform='rk3568')
ret = rknn.load_onnx(model=ONNX_MODEL, outputs=['output0', 'output1']) # 这里一定要根据onnx模型修改
ret = rknn.build(do_quantization=False, dataset='./dataset.txt')
if ret != 0:
print("Load rknn model failed!")
exit(ret)
print("done")
# init runtime environment
print("--> Init runtime environment")
ret = rknn.init_runtime(target=None)
if ret != 0:
print("Init runtime environment failed")
exit(ret)
print("done")2、图像预处理阶段:
# (1) 设置输入期望的高度和宽度、加载图像、获取图像的高度、宽度和通道数;
input_h, input_w = 640, 640
frame = cv2.imread("/home/zw/Prg/Pycharm/file/RKNN3568/onnx/yolov5-seg/bus.jpg")
fh, fw, fc = frame.shape
# (2) 调用letterbox将图像调整为模型的输入尺寸(640x640),letterbox是一个自定义函数,可能是用于缩放和填充图像的工具函数。
im, r, (dw, dh) = letterbox(frame, new_shape=(input_h, input_w), auto=False) # Resize to new shape by letterbox
# (3) 将图像从 OpenCV 默认的通道顺序BGR转化为RGB。同时,将通道维度从 HWC变为 CHW。
blob1 = im.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1]
# (4) 创建一个高效的数组来存储图像数组(浮点类型),并且添加一个维度,将单张图像转换为模型推理所需的批次维度。这样,输入张量的形状将变为(1, C, H, W)
blob2 = np.ascontiguousarray(blob1)
blob3 = np.float32(blob2)
blob = blob3[None] 3、 执行推理测试:
# rknn推理
outputs = rknn.inference(inputs=[blob],data_format='nchw')
# pred = [1,25200,38] proto = [1,32,160,160]
pred, proto = outputs[0], outputs[1]
# 将预测结果 pred 转换为 PyTorch 的张量形式。
preds = torch.tensor(pred)
# 使用非极大值抑制(NMS)函数 non_max_suppression 对预测结果 preds 进行处理,以获取过滤后的预测。
pred = non_max_suppression(preds, nm=32)[0].numpy()
# 将 pred 数组按列切分,分别提取出边界框、置信度、类别标签和物体掩码。
bboxes, confs, class_ids, masks = pred[:, :4], pred[:, 4], pred[:, 5], pred[:, 6:]
# 删除维度为1的维度 (1,32,160,160) ---> (32,160,160)
proto = np.squeeze(proto)
# 将原型张量重新调整形状为 (32,25600),将后两维展平。(32,160,160) ---> (32,25600)
proto = np.reshape(proto, (32, -1))
# 将物体掩码 masks 与原型张量 proto 进行矩阵相乘,得到目标的掩码信息。(1,32) (32,25600)
obj_masks = np.matmul(masks, proto)
# 将这些掩码信息应用 sigmoid 函数,并将其重新调整形状为 (n, 160, 160)
obj_masks = np.reshape(sigmoid(obj_masks), (-1, 160, 160))4、后处理:
# 遍历每个目标的掩码和边界框,根据边界框的尺寸从目标掩码中提取对应的区域添加masks_roi 列表中。
masks_roi = []
for obj_mask, bbox in zip(obj_masks, bboxes):
mx1 = max(0, np.int32((bbox[0] * 0.25)))
my1 = max(0, np.int32((bbox[1] * 0.25)))
mx2 = max(0, np.int32((bbox[2] * 0.25)))
my2 = max(0, np.int32((bbox[3] * 0.25)))
masks_roi.append(obj_mask[my1:my2, mx1:mx2])
# 使用 rescale_coords 函数将边界框的坐标恢复到原始图像的尺寸,然后将坐标转换为整数类型。
bboxes = rescale_coords(r[0], (dh, dw), bboxes).astype(int)
# 创建颜色掩码和黑色掩码,用于在原始图像上绘制物体掩码。
color_mask = np.zeros((fh, fw, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
black_mask = np.zeros((fh, fw), dtype=np.float32)
# 将颜色掩码 color_mask 拆分为三个通道,得到 mv,它是一个包含 R、G、B 通道的列表。
mv = cv2.split(color_mask)
for bbox, conf, class_id, mask_roi in zip(bboxes, confs, class_ids, masks_roi):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = bbox[0], bbox[1], bbox[2], bbox[3]
# Draw Mask 把映射回去的预测框在原图上绘画出来
# color = colors[int(class_id) % len(colors)]
# cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
# color = colors[int(class_id) % len(colors)]
# cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1 - 20), (x2, y1), (0, 0, 255), -1) object classs
# Draw mask of the detected objects
result_mask = cv2.resize(mask_roi, (bbox[2] - bbox[0], bbox[3] - bbox[1]))
result_mask[result_mask > 0.5] = 1.0
result_mask[result_mask <= 0.5] = 0.0
rh, rw = result_mask.shape
if (y1 + rh) >= fh:
rh = fh - y1
if (x1 + rw) >= fw:
rw = fw - x1
black_mask[y1:y1 + rh, x1:x1 + rw] = result_mask[0:rh, 0:rw]
mv[2][black_mask == 1], mv[1][black_mask == 1], mv[0][black_mask == 1] = \
[np.random.randint(0, 256), np.random.randint(0, 256), np.random.randint(0, 256)]
5、显示结果:
# 使用 cv2.merge() 函数将分离的 R、G、B 通道重新合并为一个彩色图像
color_mask = cv2.merge(mv)
# 使用 cv2.addWeighted() 函数将原始图像和带有彩色掩码的图像进行加权叠加
dst = cv2.addWeighted(frame, 0.5, color_mask, 0.5, 0)
cv2.imshow('bus', dst)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()三、测试结果如下:
附上完整的代码:
import numpy
import numpy as np
import cv2, torch, torchvision, yaml
# from openvino.runtime import Core
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
from rknn.api import RKNN
ONNX_MODEL = '/home/zw/Prg/Pycharm/file/RKNN3568/onnx/yolov5-seg/yolov5s-seg.onnx'
def xywh2xyxy(x):
y = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left x
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left y
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def box_iou(box1, box2, eps=1e-7):
(a1, a2), (b1, b2) = box1.unsqueeze(1).chunk(2, 2), box2.unsqueeze(0).chunk(2, 2)
inter = (torch.min(a2, b2) - torch.max(a1, b1)).clamp(0).prod(2)
return inter / ((a2 - a1).prod(2) + (b2 - b1).prod(2) - inter + eps)
def non_max_suppression(
prediction,
conf_thres=0.25,
iou_thres=0.45,
classes=None,
agnostic=False,
multi_label=False,
labels=(),
max_det=300,
nm=0, # number of masks
):
"""Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results to reject overlapping detections
Returns:
list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls]
"""
if isinstance(prediction, (list, tuple)): # YOLOv5 model in validation model, output = (inference_out, loss_out)
prediction = prediction[0] # select only inference output
device = prediction.device
mps = 'mps' in device.type # Apple MPS
if mps: # MPS not fully supported yet, convert tensors to CPU before NMS
prediction = prediction.cpu()
bs = prediction.shape[0] # batch size
nc = prediction.shape[2] - nm - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
# Settings
# min_wh = 2 # (pixels) minimum box width and height
max_wh = 7680 # (pixels) maximum box width and height
max_nms = 30000 # maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms()
time_limit = 0.5 + 0.05 * bs # seconds to quit after
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
merge = False # use merge-NMS
t = time.time()
mi = 5 + nc # mask start index
output = [torch.zeros((0, 6 + nm), device=prediction.device)] * bs
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
lb = labels[xi]
v = torch.zeros((len(lb), nc + nm + 5), device=x.device)
v[:, :4] = lb[:, 1:5] # box
v[:, 4] = 1.0 # conf
v[range(len(lb)), lb[:, 0].long() + 5] = 1.0 # cls
x = torch.cat((x, v), 0)
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Compute conf
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box/Mask
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4]) # center_x, center_y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
mask = x[:, mi:] # zero columns if no masks
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label:
i, j = (x[:, 5:mi] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, 5 + j, None], j[:, None].float(), mask[i]), 1)
else: # best class only
conf, j = x[:, 5:mi].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float(), mask), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
# Apply finite constraint
# if not torch.isfinite(x).all():
# x = x[torch.isfinite(x).all(1)]
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
elif n > max_nms: # excess boxes
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence
else:
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)] # sort by confidence
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
# update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
output[xi] = x[i]
if mps:
output[xi] = output[xi].to(device)
return output
def letterbox(im, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True, stride=32):
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better val mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride) # wh padding
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
def sigmoid(x):
return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def rescale_coords(ratio, pad, coords):
# Rescale coords (xyxy) from according to r and (dh, dw) from letterbox
coords[:, [1, 3]] -= pad[0] # H padding
coords[:, [0, 2]] -= pad[1] # W padding
coords[:, :4] /= ratio
return coords
if __name__ == "__main__":
rknn = RKNN()
# Load ONNX model
print("--> Loading model")
# ret = rknn.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL)
# rknn.config(mean_values=[82.9835, 93.9795, 82.1893], std_values=[54.02, 54.804, 54.0225], target_platform='rk3568')
rknn.config(mean_values=[0, 0, 0], std_values=[255, 255, 255], target_platform='rk3568')
ret = rknn.load_onnx(model=ONNX_MODEL, outputs=['output0', 'output1']) # 这里一定要根据onnx模型修改
ret = rknn.build(do_quantization=False, dataset='./dataset.txt')
if ret != 0:
print("Load rknn model failed!")
exit(ret)
print("done")
# init runtime environment
print("--> Init runtime environment")
ret = rknn.init_runtime(target=None)
if ret != 0:
print("Init runtime environment failed")
exit(ret)
print("done")
input_h, input_w = 640, 640
frame = cv2.imread("/home/zw/Prg/Pycharm/file/RKNN3568/onnx/yolov5-seg/bus.jpg")
fh, fw, fc = frame.shape
im, r, (dw, dh) = letterbox(frame, new_shape=(input_h, input_w), auto=False) # Resize to new shape by letterbox
blob1 = im.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
blob2 = np.ascontiguousarray(blob1)
# blob3 = np.float32(blob2) / 255.0 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0 ourfunction is limit it to 0 - 255, no 0-1
blob3 = np.float32(blob2) # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
blob = blob3[None] # expand for batch dim
outputs = rknn.inference(inputs=[blob],data_format='nchw')
# [1,25200,38] [1,32,160,160]
pred, proto = outputs[0], outputs[1]
# Step5: Postprocess the inference result and visulize it.
preds = torch.tensor(pred)
# [1,25200,38]>>>>>[1,38]
pred = non_max_suppression(preds, nm=32)[0].numpy() # (n,38) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls, masks]
# (n,38) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls, masks]
bboxes, confs, class_ids, masks = pred[:, :4], pred[:, 4], pred[:, 5], pred[:, 6:]
# Extract the mask of the detected object
proto = np.squeeze(proto) # 删除维度为1的维度 (1,32,160,160) >>>(32,160,160)
proto = np.reshape(proto, (32, -1)) # (32,160,160) >>>(32,25600)
obj_masks = np.matmul(masks, proto) # 两个矩阵相乘(1,32) (32,25600)
obj_masks = np.reshape(sigmoid(obj_masks), (-1, 160, 160))
masks_roi = []
for obj_mask, bbox in zip(obj_masks, bboxes):
mx1 = max(0, np.int32((bbox[0] * 0.25)))
my1 = max(0, np.int32((bbox[1] * 0.25)))
mx2 = max(0, np.int32((bbox[2] * 0.25)))
my2 = max(0, np.int32((bbox[3] * 0.25)))
masks_roi.append(obj_mask[my1:my2, mx1:mx2])
# 得到的masks_roi是带有mask的目标区域
bboxes = rescale_coords(r[0], (dh, dw), bboxes).astype(int)
color_mask = np.zeros((fh, fw, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
black_mask = np.zeros((fh, fw), dtype=np.float32)
mv = cv2.split(color_mask)
for bbox, conf, class_id, mask_roi in zip(bboxes, confs, class_ids, masks_roi):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = bbox[0], bbox[1], bbox[2], bbox[3]
# Draw Mask 把映射回去的预测框在原图上绘画出来
# color = colors[int(class_id) % len(colors)]
# cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
# color = colors[int(class_id) % len(colors)]
# cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1 - 20), (x2, y1), (0, 0, 255), -1) object classs
# Draw mask of the detected objects
result_mask = cv2.resize(mask_roi, (bbox[2] - bbox[0], bbox[3] - bbox[1]))
result_mask[result_mask > 0.5] = 1.0
result_mask[result_mask <= 0.5] = 0.0
rh, rw = result_mask.shape
if (y1 + rh) >= fh:
rh = fh - y1
if (x1 + rw) >= fw:
rw = fw - x1
black_mask[y1:y1 + rh, x1:x1 + rw] = result_mask[0:rh, 0:rw]
mv[2][black_mask == 1], mv[1][black_mask == 1], mv[0][black_mask == 1] = \
[np.random.randint(0, 256), np.random.randint(0, 256), np.random.randint(0, 256)]
color_mask = cv2.merge(mv)
dst = cv2.addWeighted(frame, 0.5, color_mask, 0.5, 0)
cv2.imshow('bus', dst)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()