Sharding Sphere 4.x分库分表解决方案
一、基本概念
http://shardingsphere.apache.org/index_zh.html【写于2021-0325】
逻辑表:水平拆分的数据库(表)的相同逻辑和数据结构表的总称。例:订单数据根据主键尾数拆分为 10 张表,分别是
t_order_0到t_order_9,他们的逻辑表名为t_order。
真实表: 在分片的数据库中真实存在的物理表。即上个示例中的
t_order_0到t_order_9。
数据节点:数据分片的最小单元。由数据源名称和数据表组成,例:
ds_0.t_order_0。
绑定表:指分片规则一致的主表和子表。例如:
t_order表和t_order_item表,均按照order_id分片,则此两张表互为绑定表关系。绑定表之间的多表关联查询不会出现笛卡尔积关联,关联查询效率将大大提升。举例说明,如果 SQL 为:
广播表:指所有的分片数据源中都存在的表,表结构和表中的数据在每个数据库中均完全一致。适用于数据量不大且需要与海量数据的表进行关联查询的场景,例如:字典表。
分片键:用于分片的数据库字段,是将数据库(表)水平拆分的关键字段。例:将订单表中的订单主键的尾数取模分片,则订单主键为分片字段。 SQL 中如果无分片字段,将执行全路由,性能较差。 除了对单分片字段的支持,Apache ShardingSphere 也支持根据多个字段进行分片。
1.1分片算法
通过分片算法将数据分片,支持通过
=、>=、<=、>、<、BETWEEN和IN分片。 分片算法需要应用方开发者自行实现,可实现的灵活度非常高。目前提供4种分片算法。 由于分片算法和业务实现紧密相关,因此并未提供内置分片算法,而是通过分片策略将各种场景提炼出来,提供更高层级的抽象,并提供接口让应用开发者自行实现分片算法。
- 标准分片算法
对应 StandardShardingAlgorithm,用于处理使用单一键作为分片键的
=、IN、BETWEEN AND、>、<、>=、<=进行分片的场景。需要配合 StandardShardingStrategy 使用。
- 复合分片算法
对应 ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm,用于处理使用多键作为分片键进行分片的场景,包含多个分片键的逻辑较复杂,需要应用开发者自行处理其中的复杂度。需要配合 ComplexShardingStrategy 使用。
- Hint分片算法
对应 HintShardingAlgorithm,用于处理使用
Hint行分片的场景。需要配合 HintShardingStrategy 使用。
内置分片算法:https://shardingsphere.apache.org/document/current/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/configuration/built-in-algorithm/sharding/
1.2分片策略
包含分片键和分片算法,由于分片算法的独立性,将其独立抽离。真正可用于分片操作的是分片键 + 分片算法,也就是分片策略。目前提供 5 种分片策略。
- 标准分片策略
对应 StandardShardingStrategy。提供对 SQ L语句中的
=,>,<,>=,<=,IN和BETWEEN AND的分片操作支持。 StandardShardingStrategy 只支持单分片键,提供 PreciseShardingAlgorithm 和 RangeShardingAlgorithm 两个分片算法。 PreciseShardingAlgorithm 是必选的,用于处理=和IN的分片。 RangeShardingAlgorithm 是可选的,用于处理BETWEEN AND,>,<,>=,<=分片,如果不配置 RangeShardingAlgorithm,SQL 中的BETWEEN AND将按照全库路由处理。
- 复合分片策略
对应 ComplexShardingStrategy。复合分片策略。提供对 SQL 语句中的
=,>,<,>=,<=,IN和BETWEEN AND的分片操作支持。 ComplexShardingStrategy 支持多分片键,由于多分片键之间的关系复杂,因此并未进行过多的封装,而是直接将分片键值组合以及分片操作符透传至分片算法,完全由应用开发者实现,提供最大的灵活度。
- Hint分片策略
对应 HintShardingStrategy。通过 Hint 指定分片值而非从 SQL 中提取分片值的方式进行分片的策略。
SQL Hint:对于分片字段非 SQL 决定,而由其他外置条件决定的场景,可使用 SQL Hint 灵活的注入分片字段。 例:内部系统,按照员工登录主键分库,而数据库中并无此字段。SQL Hint 支持通过 Java API 和 SQL 注释(待实现)两种方式使用。
- 不分片策略
对应 NoneShardingStrategy。不分片的策略。
二、分库分表
org.apache.shardingsphere
sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter
4.1.1
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-configuration-processor
true
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
3.3.2
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
runtime
true
mysql
mysql-connector-java
runtime
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
server:
port: 8888
#热部署
# spring.devtools.restart.enabled= true
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: classpath*:mapper/*Mapper.xml
global-config:
banner: false
# configuration:
# log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
spring:
main:
allow-bean-definition-overriding: true
shardingsphere:
# 数据源配置
datasource:
# 数据源名称,多数据源以逗号分隔
# names: db0,db1
names: db0
db0:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://ip:3306/ss0?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: root@tomsung
# db1:
# driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
# jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://ip:3306/ss1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
# username: root
# password: root@tomsung
# 属性配置
# props:
# sql:
# show: true
sharding:
tables:
oil_info:
# actual-data-nodes: db$->{0..1}.info$->{0..1}
actual-data-nodes: db0.oil_info_$->{2020..2021}_$->{1..4}
key-generator:
column: id
type: SNOWFLAKE
props:
worker-id: 1
table-strategy:
# inline:
# sharding-column: id
# algorithm-expression: oil_info_$->{id % 2}
standard:
sharding-column: time
precise-algorithm-class-name: com.example.demo.compent.TableInfoShardingAlgorithm
range-algorithm-class-name: com.example.demo.compent.TableInfoRange
# default-database-strategy:
# standard:
# sharding-column: id
# precise-algorithm-class-name: com.example.demo.compent.DBShardingAIgorithm
# inline:
# sharding-column: id
# algorithm-expression: db$->{id % 2}
自定义分片算法:
public class DBShardingAIgorithm implements PreciseShardingAlgorithm {
//标准处理,必须实现,IN =
@Override
public String doSharding(Collection collection, PreciseShardingValue preciseShardingValue) {
log.info("DB 开始选择:");
collection.stream().forEach(item->{
log.info("当前数据库可选值:{}",item);
});
log.info("表名:{},路由列:{}",preciseShardingValue.getLogicTableName(),preciseShardingValue.getColumnName());
//精确分片
Long value = preciseShardingValue.getValue();
log.info("准备计算的值:{}",value);
long db_index = value & (2 - 1);
for(String str:collection){
if(str.equals("db"+db_index)){
log.info("命中的库:{}",db_index);
return str;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}
package com.example.demo.compent;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import com.google.common.collect.Range;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.RangeShardingAlgorithm;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.standard.RangeShardingValue;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @ClassName TableInfoRange
* @Description TODO
* @Author ...
* @Date 2021/3/25 11:21
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TableInfoRange implements RangeShardingAlgorithm {
//处理 between > ..
@Override
public Collection doSharding(Collection collection, RangeShardingValue rangeShardingValue) {
Range range = rangeShardingValue.getValueRange();
Date between = range.lowerEndpoint();
Date end = range.upperEndpoint();
LocalDateTime betweenDate = between.toInstant().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toLocalDateTime();
LocalDateTime endDate = end.toInstant().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toLocalDateTime();
int bMonthValue = betweenDate.getMonthValue();
int bYear = betweenDate.getYear();
String bSb = new StringBuilder(TableInfoShardingAlgorithm.OIL_INFO).append(bYear).append(TableInfoShardingAlgorithm.getStr(bMonthValue)).toString();
int eMonthValue = endDate.getMonthValue();
int eYear = endDate.getYear();
String eSb = new StringBuilder(TableInfoShardingAlgorithm.OIL_INFO).append(eYear).append(TableInfoShardingAlgorithm.getStr(eMonthValue)).toString();
ArrayList list = Lists.newArrayList();
for (String each: collection){
if(each.equals(bSb)){
list.add(bSb);
}
if(each.equals(eSb)){
list.add(eSb);
}
}
log.info("匹配表:{}",list.toString());
return list;
}
}
public class TableInfoShardingAlgorithm implements PreciseShardingAlgorithm {
@Override
public String doSharding(Collection collection, PreciseShardingValue preciseShardingValue) {
log.info("table 可选值:");
collection.stream().forEach(item->{
log.info("{}",item);
});
log.info("表名:{},路由列:{}",preciseShardingValue.getLogicTableName(),preciseShardingValue.getColumnName());
//精确分片
Long value = preciseShardingValue.getValue();
log.info("下标值:{}",value);
long db_index = value & (2 - 1);
for(String str:collection){
if(str.equals("info"+db_index)){
log.info("命中的表:{}",db_index);
return str;
}
}
return null;
}
} 三、常见错误
3.1 防止预编译
insert into info (`NAME`, UPLOAD_TIME)
values (#{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{uploadTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP})
https://shardingsphere.apache.org/document/current/cn/features/sharding/use-norms/sql/#支持项
如:
SELECT MAX(tbl_name.col1) FROM tbl_name 查询列是函数表达式时,查询列前不能使用表名;若查询表存在别名,则可使用表的别名
3.2 insert时不支持 值计算
public static SecretKeySpec generateMySQLAESKey(final String key, final String encoding) {
try {
final byte[] finalKey = new byte[16];
int i = 0;
for(byte b : key.getBytes(encoding))
finalKey[i++%16] ^= b;
return new SecretKeySpec(finalKey, "AES");
} catch(UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static String encodeHex(byte[] b){
StringBuilder hs = new StringBuilder();
String stmp;
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
stmp = Integer.toHexString(b[i] & 0xFF).toUpperCase();
if (stmp.length() == 1) {
hs.append("0").append(stmp);
} else {
hs.append(stmp);
}
}
return hs.toString();
}
public static String aes_encrypt(String password, String strKey) {
try {
SecretKey key = generateMySQLAESKey(strKey,"ASCII");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key);
byte[] cleartext = password.getBytes("UTF-8");
byte[] ciphertextBytes = cipher.doFinal(cleartext);
return encodeHex(ciphertextBytes);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidKeyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BadPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}3.3插入时返回主键
因为在配置文件中,配置的主键是使用ShardingSphere的雪花ID,通过mybatis的几种获取方式显然是获取不到的,
3.3.1MyBatis获取主键ID有如下几种方式
1.可以返回一个或多个字段
mysql/oracle数据库获取主键都可以使用
select LAST_INSERT_ID()
select SEQ_ID.nextval from dual
keyProperty:selectKey标签中sql语句返回结果被设置的属性。如果需要返回多个列(eg:表中有多个字段自增),可以使用逗号分隔的属性名称;
order:获取主键(返回字段)与执行sql的顺序,取值为:AFTER/BEFORE。
1)、AFTER:先执行sql(插入数据),再获取主键设置keyProperty的值,mysql数据库中表字段自增使用;
2)、BEFORE:先获得主键(返回字段)设置keyProperty的值,再执行sql(插入数据),oracle数据库中表字段自增使用。
resultType:主键(返回字段)的类型,如果返回多个列,可以设置成map。
2.返回一个字段时使用
mysql数据库获取主键可以使用。
keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true"useGeneratedKeys:使用JDBC的getGeneratedKeys方法获取数据库自动生成的主键。
3.3.2使用ShardingSphere时,使用自定义规则生成主键
1.创建主键生成类
public class MyKeyGenerator implements ShardingKeyGenerator, IdentifierGenerator {
private static long id;
@Override
public Comparable generateKey() {
Snowflake snowflake = IdUtil.createSnowflake(1, 1);
id = snowflake.nextId();
return id;
}
@Override
public String getType() {
return "MyKeyGenerator";
}
@Override
public Properties getProperties() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
@Override
public Number nextId(Object entity) {
return id;
}
@Override
public String nextUUID(Object entity) {
return null;
}
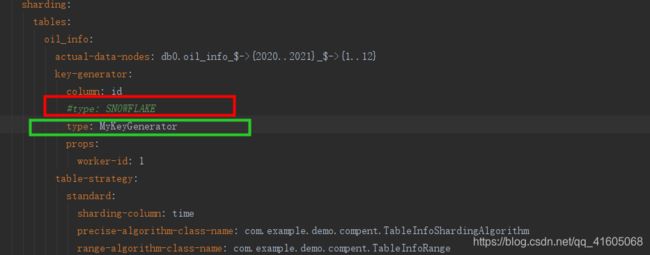
}2.修改配置文件
3.注入容器
/**
* mybatis-plus的主键生成
* @return
*/
@Bean
public IdentifierGenerator identifierGenerator(){
return new MyKeyGenerator();
}4.运行
5.配置SPI
在Apache ShardingSphere中,很多功能实现类的加载方式是通过SPI注入的方式完成的。 Service Provider Interface (SPI)是一种为了被第三方实现或扩展的API,它可以用于实现框架扩展或组件替换。
- 在resources目录下新建META-INF文件夹,再新建services文件夹,
- 新建文件的名字为org.apache.shardingsphere.spi.keygen.ShardingKeyGenerator
- 打开文件:复制自定义分布式主键的类全路径到文件中保存
3.3.3自定义MyBatis-plus的主键生成规则,并返回
@Component
public class MyKeyGenerator implements IdentifierGenerator{
private static long id;
@Override
public Number nextId(Object entity) {
Snowflake snowflake = IdUtil.createSnowflake(1, 1);
id = snowflake.nextId();
System.out.println("Mybatis-plus生成的id:"+id);
return id;
}
@Override
public String nextUUID(Object entity) {
return null;
}
} @TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.ASSIGN_ID)