OkHttp4.9.0源码分析
通过前面的学习,我们已经对OKHttp有了简单的认识,并对使用有了详细的了解,下面我们将以一个同步Get请求为例进行OKHttp源码分析。
一、基础同步Get请求
private val mUrl = "https://www.baidu.com"
// 1、createClient
private val mClient = OkHttpClient()
// createClientTwo
private val mClient2 = OkHttpClient.Builder().build()
// 2、createRequest
private val mRequest = Request.Builder().url(mUrl).build()
// 3、发起同步get请求
GlobalScope.launch {
mClient.newCall(mRequest).execute().use { response ->
if (response.isSuccessful) {
LogUtil.D(log = "request success code is ${response.code} body is ${response.body.toString()}")
} else {
LogUtil.D(log="request error code is ${response.code}")
}
}
}
通过代码我们发现,创建OkHttpClient的方式有两种:
- 1、直接创建 OkHttpClient()
- 2、Builder构建者方式创建 OkHttpClient.Builder().build()
二、源码分析
1、创建OKHttpClient
1.1 直接创建 val mClient = OkHttpClient()
constructor() : this(Builder())
class Builder constructor() {
// 调度器
internal var dispatcher: Dispatcher = Dispatcher()
// 连接池
internal var connectionPool: ConnectionPool = ConnectionPool()
// 应用拦截器list
internal val interceptors: MutableList = mutableListOf()
// 网络拦截器list
internal val networkInterceptors: MutableList = mutableListOf()
// eventListenerFactory
internal var eventListenerFactory: EventListener.Factory = EventListener.NONE.asFactory()
// 自动重试布尔值
internal var retryOnConnectionFailure = true
// 认证中心 默认为NONE
internal var authenticator: Authenticator = Authenticator.NONE
// 重定向布尔值
internal var followRedirects = true
// ssl重定向布尔值
internal var followSslRedirects = true
// cookie控制
internal var cookieJar: CookieJar = CookieJar.NO_COOKIES
// 缓存
internal var cache: Cache? = null
// DNS配置
internal var dns: Dns = Dns.SYSTEM
// 代理
internal var proxy: Proxy? = null
// 代理选择器
internal var proxySelector: ProxySelector? = null
// 代理认证器
internal var proxyAuthenticator: Authenticator = Authenticator.NONE
// 使用默认的Socket工厂产生Socket
internal var socketFactory: SocketFactory = SocketFactory.getDefault()
// sslSocketFactory默认为null
internal var sslSocketFactoryOrNull: SSLSocketFactory? = null
// x509认证管理器默认为null
internal var x509TrustManagerOrNull: X509TrustManager? = null
// 默认连接配置 TLS和CLEARTEXT
internal var connectionSpecs: List = DEFAULT_CONNECTION_SPECS
// 默认HTTP协议
internal var protocols: List = DEFAULT_PROTOCOLS
// HostName认证器
internal var hostnameVerifier: HostnameVerifier = OkHostnameVerifier
// 认证加密组建
internal var certificatePinner: CertificatePinner = CertificatePinner.DEFAULT
// 证书链cleaner
internal var certificateChainCleaner: CertificateChainCleaner? = null
// 默认请求超时时常
internal var callTimeout = 0
// 默认连接时常
internal var connectTimeout = 10_000
// 默认读数据超时时常
internal var readTimeout = 10_000
// 默认写数据超时时常
internal var writeTimeout = 10_000
// ping间隔,心跳时间
internal var pingInterval = 0
// websocket消息最小压缩值
internal var minWebSocketMessageToCompress = RealWebSocket.DEFAULT_MINIMUM_DEFLATE_SIZE
}
1.2 Builder方式创建 val mClient2 = OkHttpClient.Builder().build()
默认调用的方法是class Builder constructor() 与方法直接创建方式相同,通过构建者默认对外暴露了自定义配置的方法。
// 创建builder构造器
class Builder constructor()
// build创建OkHttpClient
fun build(): OkHttpClient = OkHttpClient(this)
2、创建Request
- val mRequest = Request.Builder().url(mUrl).build()
2.1 builder()
// 默认请求方式为GET
constructor() {
this.method = "GET"
this.headers = Headers.Builder()
}
2.2 url()
/**
* Sets the URL target of this request.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if [url] is not a valid HTTP or HTTPS URL. Avoid this
* exception by calling [HttpUrl.parse]; it returns null for invalid URLs.
*/
open fun url(url: String): Builder {
// 替换webSocketURL为http类型url
// Silently replace web socket URLs with HTTP URLs.
val finalUrl: String = when {
url.startsWith("ws:", ignoreCase = true) -> {
"http:${url.substring(3)}"
}
url.startsWith("wss:", ignoreCase = true) -> {
"https:${url.substring(4)}"
}
else -> url
}
return url(finalUrl.toHttpUrl())
}
2.3 build() 创建request
open fun build(): Request {
return Request(
checkNotNull(url) { "url == null" },
method,
headers.build(),
body,
tags.toImmutableMap()
)
}
通过传入的url、method、headers、body创建Request对象
3、创建Call mClient.newCall(mRequest)
3.1 Call
interface Call : Cloneable {
fun request(): Request
fun execute(): Response
fun cancel()
fun isExecuted(): Boolean
fun isCanceled(): Boolean
fun timeout(): Timeout
public override fun clone(): Call
fun interface Factory {
fun newCall(request: Request): Call
}
}
通过查看Call源码可见,Call实际上是一个接口,并定义了一些常用的方法,具体实现由其实现类提供
3.1 newCall()
/** Prepares the [request] to be executed at some point in the future. */
override fun newCall(request: Request): Call = RealCall(this, request, forWebSocket = false)
通过查看方法可见,实际创建的是一个RealCall对象
3.2 RealCall(this, request, forWebSocket = false)
默认创建的RealCall用来进行HTTP通信,不是进行websocket通信
/**
* Bridge between OkHttp's application and network layers. This class exposes high-level application
* layer primitives: connections, requests, responses, and streams.
*
* This class supports [asynchronous canceling][cancel]. This is intended to have the smallest
* blast radius possible. If an HTTP/2 stream is active, canceling will cancel that stream but not
* the other streams sharing its connection. But if the TLS handshake is still in progress then
* canceling may break the entire connection.
*/
class RealCall(
val client: OkHttpClient,
val originalRequest: Request,
val forWebSocket: Boolean
) : Call {
......
}
通过注释我们可以知道:
- RealCall是OkHttp应用和网络层连接的桥梁,并将connections、requests、responses和streams暴露出来
- 提供了小粒度异步取消方法。
- 如果取消的是活跃的HTTP/2 stream,这个stream将会被取消,但是其他共享连接池的streams不会取消。
- 如果进行HTTPS请求时,正处于握手过程中,调用该方法,会打断整个连接过程。
3.3 execute()
override fun execute(): Response {
check(executed.compareAndSet(false, true)) { "Already Executed" }
timeout.enter()
callStart()
try {
// 步骤1
client.dispatcher.executed(this)
// 步骤2
return getResponseWithInterceptorChain()
} finally {
// 标记请求完成
client.dispatcher.finished(this)
}
}
实际上execute执行的方法是通过 client.dispatcher.executed(this)实现的
4、Dispatcher(调度器)
4.1 源码查看
// Dispatcher是用于异步请求执行的策略类,每一个Dispatcher都是用Executor Service独立进行请求,如果使用本地的executor,可以支持maxRequests(默认64)数量集并发请求
class Dispatcher constructor() {
// 支持的最大请求数
@get:Synchronized var maxRequests = 64
set(maxRequests) {
require(maxRequests >= 1) { "max < 1: $maxRequests" }
synchronized(this) {
field = maxRequests
}
promoteAndExecute()
}
// 支持的单个host地址请求数
@get:Synchronized var maxRequestsPerHost = 5
set(maxRequestsPerHost) {
require(maxRequestsPerHost >= 1) { "max < 1: $maxRequestsPerHost" }
synchronized(this) {
field = maxRequestsPerHost
}
promoteAndExecute()
}
@set:Synchronized
@get:Synchronized
var idleCallback: Runnable? = null
private var executorServiceOrNull: ExecutorService? = null
// java线程池 不解释
@get:Synchronized
@get:JvmName("executorService") val executorService: ExecutorService
get() {
if (executorServiceOrNull == null) {
executorServiceOrNull = ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Int.MAX_VALUE, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
SynchronousQueue(), threadFactory("$okHttpName Dispatcher", false))
}
return executorServiceOrNull!!
}
// 可执行请求队列
private val readyAsyncCalls = ArrayDeque()
// 正在执行的异步call队列
private val runningAsyncCalls = ArrayDeque()
// 正在执行的同步请求队列
private val runningSyncCalls = ArrayDeque()
constructor(executorService: ExecutorService) : this() {
this.executorServiceOrNull = executorService
}
// 异步请求
internal fun enqueue(call: AsyncCall) {
synchronized(this) {
readyAsyncCalls.add(call)
if (!call.call.forWebSocket) {
val existingCall = findExistingCallWithHost(call.host)
if (existingCall != null) call.reuseCallsPerHostFrom(existingCall)
}
}
promoteAndExecute()
}
private fun findExistingCallWithHost(host: String): AsyncCall? {
for (existingCall in runningAsyncCalls) {
if (existingCall.host == host) return existingCall
}
for (existingCall in readyAsyncCalls) {
if (existingCall.host == host) return existingCall
}
return null
}
// 取消所有请求,包括同步请求和异步请求
@Synchronized fun cancelAll() {
for (call in readyAsyncCalls) {
call.call.cancel()
}
for (call in runningAsyncCalls) {
call.call.cancel()
}
for (call in runningSyncCalls) {
call.cancel()
}
}
// 执行请求,返回是否有异步call正在执行状态
private fun promoteAndExecute(): Boolean {
this.assertThreadDoesntHoldLock()
// 可以执行的请求队列
val executableCalls = mutableListOf()
val isRunning: Boolean
// 同步方法
synchronized(this) {
val i = readyAsyncCalls.iterator()
while (i.hasNext()) {
val asyncCall = i.next()
// 最大请求数限制策略
if (runningAsyncCalls.size >= this.maxRequests) break // Max capacity.
// 最大单host请求限制策略
if (asyncCall.callsPerHost.get() >= this.maxRequestsPerHost) continue // Host max capacity.
// 从readyAsyncCalls队列中移除
i.remove()
asyncCall.callsPerHost.incrementAndGet()
// 添加到executableCalls队列中
executableCalls.add(asyncCall)
runningAsyncCalls.add(asyncCall)
}
isRunning = runningCallsCount() > 0
}
// 执行executableCalls中请求
for (i in 0 until executableCalls.size) {
val asyncCall = executableCalls[i]
// 调用RealCall中executeOn()方法
asyncCall.executeOn(executorService)
}
return isRunning
}
// 同步请求,将RealCall添加到runningSyncCalls队列中
@Synchronized internal fun executed(call: RealCall) {
runningSyncCalls.add(call)
}
// 请求完成回调
internal fun finished(call: AsyncCall) {
// callsPerHost数量自减
call.callsPerHost.decrementAndGet()
finished(runningAsyncCalls, call)
}
internal fun finished(call: RealCall) {
finished(runningSyncCalls, call)
}
private fun finished(calls: Deque, call: T) {
val idleCallback: Runnable?
synchronized(this) {
// 从calls中移除call
if (!calls.remove(call)) throw AssertionError("Call wasn't in-flight!")
idleCallback = this.idleCallback
}
val isRunning = promoteAndExecute()
// 如果不是在running状态并且callback不为空,运行idleCallback
if (!isRunning && idleCallback != null) {
idleCallback.run()
}
}
/** Returns a snapshot of the calls currently awaiting execution. */
@Synchronized fun queuedCalls(): List {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(readyAsyncCalls.map { it.call })
}
/** Returns a snapshot of the calls currently being executed. */
@Synchronized fun runningCalls(): List {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(runningSyncCalls + runningAsyncCalls.map { it.call })
}
@Synchronized fun queuedCallsCount(): Int = readyAsyncCalls.size
@Synchronized fun runningCallsCount(): Int = runningAsyncCalls.size + runningSyncCalls.size
@JvmName("-deprecated_executorService")
@Deprecated(
message = "moved to val",
replaceWith = ReplaceWith(expression = "executorService"),
level = DeprecationLevel.ERROR)
fun executorService(): ExecutorService = executorService
}
4.2 RealCall中executeOn()方法
/**
* Attempt to enqueue this async call on [executorService]. This will attempt to clean up
* if the executor has been shut down by reporting the call as failed.
*/
fun executeOn(executorService: ExecutorService) {
client.dispatcher.assertThreadDoesntHoldLock()
var success = false
try {
// 使用线程池执行请求
executorService.execute(this)
// 成功标记
success = true
} catch (e: RejectedExecutionException) {
val ioException = InterruptedIOException("executor rejected")
ioException.initCause(e)
noMoreExchanges(ioException)
// 抛出io异常
responseCallback.onFailure(this@RealCall, ioException)
} finally {
// 如果没有请求成功,将该请求进行关闭
if (!success) {
client.dispatcher.finished(this) // This call is no longer running!
}
}
}
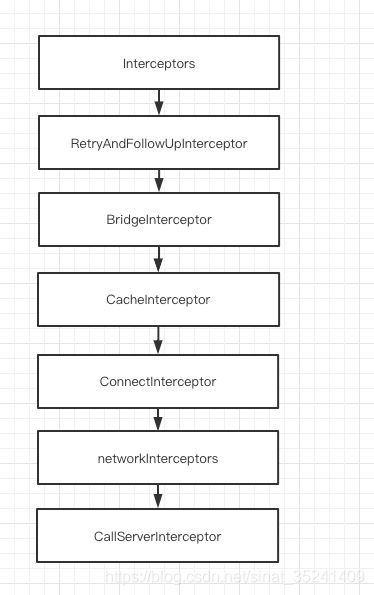
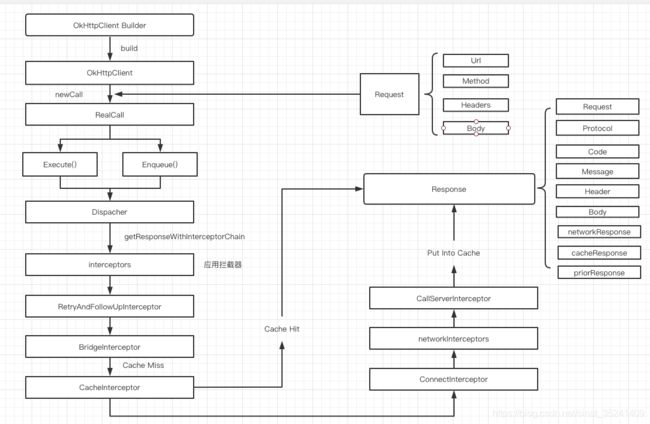
5、getResponseWithInterceptorChain() 拦截器链
@Throws(IOException::class)
internal fun getResponseWithInterceptorChain(): Response {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
val interceptors = mutableListOf()
interceptors += client.interceptors
interceptors += RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor(client)
interceptors += BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar)
interceptors += CacheInterceptor(client.cache)
interceptors += ConnectInterceptor
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors += client.networkInterceptors
}
interceptors += CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket)
// 构建RealInterceptorChain
val chain = RealInterceptorChain(
call = this,
interceptors = interceptors,
index = 0,
exchange = null,
request = originalRequest,
connectTimeoutMillis = client.connectTimeoutMillis,
readTimeoutMillis = client.readTimeoutMillis,
writeTimeoutMillis = client.writeTimeoutMillis
)
var calledNoMoreExchanges = false
// 获取response
try {
val response = chain.proceed(originalRequest)
if (isCanceled()) {
response.closeQuietly()
throw IOException("Canceled")
}
return response
} catch (e: IOException) {
calledNoMoreExchanges = true
throw noMoreExchanges(e) as Throwable
} finally {
if (!calledNoMoreExchanges) {
noMoreExchanges(null)
}
}
}
- 拦截器执行流程示意图
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-4ypL72es-1628477873951)(evernotecid://995B5497-6FAA-4C24-AE87-2F5BD5F2399B/appyinxiangcom/18006758/ENResource/p165)]
5.1 RealInterceptorChain
/**
* A concrete interceptor chain that carries the entire interceptor chain: all application
* interceptors, the OkHttp core, all network interceptors, and finally the network caller.
*
* If the chain is for an application interceptor then [exchange] must be null. Otherwise it is for
* a network interceptor and [exchange] must be non-null.
*/
class RealInterceptorChain(
internal val call: RealCall,
private val interceptors: List,
private val index: Int,
internal val exchange: Exchange?,
internal val request: Request,
internal val connectTimeoutMillis: Int,
internal val readTimeoutMillis: Int,
internal val writeTimeoutMillis: Int
) : Interceptor.Chain {
-
通过注释我们可以知道RealInterceptorChain实现了Interceptor.Chain是一个interceptors、OkHttp core、所有网络拦截器和网络调用器的集合
-
如果chain作为应用拦截器使用时,exchange必须为空;作为网络拦截器使用时,exchange必须非空
5.2 chain.proceed()
通过chain.proceed获取response
val response = chain.proceed(originalRequest)
- proceed()
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun proceed(request: Request): Response {
check(index < interceptors.size)
calls++
if (exchange != null) {
check(exchange.finder.sameHostAndPort(request.url)) {
"network interceptor ${interceptors[index - 1]} must retain the same host and port"
}
check(calls == 1) {
"network interceptor ${interceptors[index - 1]} must call proceed() exactly once"
}
}
// Call the next interceptor in the chain.
// 调用chain中的下一个拦截器
val next = copy(index = index + 1, request = request)
// 获取当前拦截器集合中拦截器
val interceptor = interceptors[index]
@Suppress("USELESS_ELVIS")
// 通过下一个拦截器获取response
val response = interceptor.intercept(next) ?: throw NullPointerException(
"interceptor $interceptor returned null")
if (exchange != null) {
check(index + 1 >= interceptors.size || next.calls == 1) {
"network interceptor $interceptor must call proceed() exactly once"
}
}
check(response.body != null) { "interceptor $interceptor returned a response with no body" }
return response
}
看到当前拦截器的Response依赖于下一个拦截器的Intercept的Response,会沿着这条拦截器链依次调用每一个拦截器,最后返回返回Response
- copy()方法
internal fun copy(
index: Int = this.index,
exchange: Exchange? = this.exchange,
request: Request = this.request,
connectTimeoutMillis: Int = this.connectTimeoutMillis,
readTimeoutMillis: Int = this.readTimeoutMillis,
writeTimeoutMillis: Int = this.writeTimeoutMillis
) = RealInterceptorChain(call, interceptors, index, exchange, request, connectTimeoutMillis,
readTimeoutMillis, writeTimeoutMillis)
通过构造传参创建RealInterceptorChain对象
- interceptor.intercept(next)
fun interface Interceptor {
@Throws(IOException::class)
fun intercept(chain: Chain): Response
...
}
通过代码我们可见,Interceptor是一个接口,具体的实现通过其实现类来提供
6、Interceptor 拦截器
6.1 RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor 重试和重定向拦截器
- intercept()
class RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor(private val client: OkHttpClient) : Interceptor {
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response {
val realChain = chain as RealInterceptorChain
var request = chain.request
val call = realChain.call
var followUpCount = 0
var priorResponse: Response? = null
var newExchangeFinder = true
var recoveredFailures = listOf()
while (true) {
// 将call请求添加到网络拦截器中
call.enterNetworkInterceptorExchange(request, newExchangeFinder)
var response: Response
var closeActiveExchange = true
try {
if (call.isCanceled()) {
throw IOException("Canceled")
}
try {
// 通过realChain处理请求
response = realChain.proceed(request)
newExchangeFinder = true
} catch (e: RouteException) {
// The attempt to connect via a route failed. The request will not have been sent.
// 路由通过失败,尝试进行恢复,如果请求不能恢复则抛出异常
if (!recover(e.lastConnectException, call, request, requestSendStarted = false)) {
throw e.firstConnectException.withSuppressed(recoveredFailures)
} else {
recoveredFailures += e.firstConnectException
}
newExchangeFinder = false
continue
} catch (e: IOException) {
// An attempt to communicate with a server failed. The request may have been sent.
// 与server通信失败,发生IO异常时,尝试进行恢复
if (!recover(e, call, request, requestSendStarted = e !is ConnectionShutdownException)) {
throw e.withSuppressed(recoveredFailures)
} else {
recoveredFailures += e
}
newExchangeFinder = false
continue
}
// Attach the prior response if it exists. Such responses never have a body.
// 如果priorResponse存在的话,附加priorResponse来创建response
if (priorResponse != null) {
response = response.newBuilder()
.priorResponse(priorResponse.newBuilder()
.body(null)
.build())
.build()
}
// exchange 用来传输独立的request和response对
val exchange = call.interceptorScopedExchange
// 重点方法 通过response和exchange获取request进行重试
val followUp = followUpRequest(response, exchange)
// followUp为空,直接返回response
if (followUp == null) {
// exchange不为空,并且exchange是双工通信方式
if (exchange != null && exchange.isDuplex) {
// 退出timeout策略
call.timeoutEarlyExit()
}
closeActiveExchange = false
return response
}
val followUpBody = followUp.body
// followUpBody不为空,并且是单工通信方式,直接返回response
if (followUpBody != null && followUpBody.isOneShot()) {
closeActiveExchange = false
return response
}
// 关闭response Body
response.body?.closeQuietly()
if (++followUpCount > MAX_FOLLOW_UPS) {
throw ProtocolException("Too many follow-up requests: $followUpCount")
}
// 缓存request
request = followUp
// 缓存response
priorResponse = response
} finally {
// 退出NetworkInterceptorExchange
call.exitNetworkInterceptorExchange(closeActiveExchange)
}
}
}
- followUpRequest(response, exchange)
@Throws(IOException::class)
private fun followUpRequest(userResponse: Response, exchange: Exchange?): Request? {
val route = exchange?.connection?.route()
val responseCode = userResponse.code
val method = userResponse.request.method
when (responseCode) {
HTTP_PROXY_AUTH -> {
val selectedProxy = route!!.proxy
if (selectedProxy.type() != Proxy.Type.HTTP) {
throw ProtocolException("Received HTTP_PROXY_AUTH (407) code while not using proxy")
}
// code 407,调用认证器重新进行认证
return client.proxyAuthenticator.authenticate(route, userResponse)
}
// 401 重新认证
HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED -> return client.authenticator.authenticate(route, userResponse)
HTTP_PERM_REDIRECT, HTTP_TEMP_REDIRECT, HTTP_MULT_CHOICE, HTTP_MOVED_PERM, HTTP_MOVED_TEMP, HTTP_SEE_OTHER -> {
// 重定向
return buildRedirectRequest(userResponse, method)
}
// 客户端超时处理
HTTP_CLIENT_TIMEOUT -> {
// 408's are rare in practice, but some servers like HAProxy use this response code. The
// spec says that we may repeat the request without modifications. Modern browsers also
// repeat the request (even non-idempotent ones.)
if (!client.retryOnConnectionFailure) {
// The application layer has directed us not to retry the request.
return null
}
val requestBody = userResponse.request.body
if (requestBody != null && requestBody.isOneShot()) {
return null
}
val priorResponse = userResponse.priorResponse
if (priorResponse != null && priorResponse.code == HTTP_CLIENT_TIMEOUT) {
// We attempted to retry and got another timeout. Give up.
return null
}
if (retryAfter(userResponse, 0) > 0) {
return null
}
return userResponse.request
}
// code 503处理
HTTP_UNAVAILABLE -> {
val priorResponse = userResponse.priorResponse
if (priorResponse != null && priorResponse.code == HTTP_UNAVAILABLE) {
// We attempted to retry and got another timeout. Give up.
return null
}
if (retryAfter(userResponse, Integer.MAX_VALUE) == 0) {
// specifically received an instruction to retry without delay
return userResponse.request
}
return null
}
// code 421处理
HTTP_MISDIRECTED_REQUEST -> {
// OkHttp can coalesce HTTP/2 connections even if the domain names are different. See
// RealConnection.isEligible(). If we attempted this and the server returned HTTP 421, then
// we can retry on a different connection.
val requestBody = userResponse.request.body
if (requestBody != null && requestBody.isOneShot()) {
return null
}
if (exchange == null || !exchange.isCoalescedConnection) {
return null
}
exchange.connection.noCoalescedConnections()
return userResponse.request
}
else -> return null
}
}
通过源码我们可以看到,该方法根据返回的不同状态码,进行了不同的重试和重定向操作
3) buildRedirectRequest
private fun buildRedirectRequest(userResponse: Response, method: String): Request? {
// Does the client allow redirects?
if (!client.followRedirects) return null
val location = userResponse.header("Location") ?: return null
// Don't follow redirects to unsupported protocols.
val url = userResponse.request.url.resolve(location) ?: return null
// If configured, don't follow redirects between SSL and non-SSL.
val sameScheme = url.scheme == userResponse.request.url.scheme
if (!sameScheme && !client.followSslRedirects) return null
// Most redirects don't include a request body.
// 根据userReponse中数据,重新构造requestBuilder
val requestBuilder = userResponse.request.newBuilder()
if (HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(method)) {
val responseCode = userResponse.code
val maintainBody = HttpMethod.redirectsWithBody(method) ||
responseCode == HTTP_PERM_REDIRECT ||
responseCode == HTTP_TEMP_REDIRECT
if (HttpMethod.redirectsToGet(method) && responseCode != HTTP_PERM_REDIRECT && responseCode != HTTP_TEMP_REDIRECT) {
requestBuilder.method("GET", null)
} else {
val requestBody = if (maintainBody) userResponse.request.body else null
requestBuilder.method(method, requestBody)
}
// 不支持body时移除相关header内容
if (!maintainBody) {
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Transfer-Encoding")
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Length")
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Type")
}
}
// When redirecting across hosts, drop all authentication headers. This
// is potentially annoying to the application layer since they have no
// way to retain them.
if (!userResponse.request.url.canReuseConnectionFor(url)) {
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Authorization")
}
// 返回构建好的request
return requestBuilder.url(url).build()
}
6.2 BridgeInterceptor 桥接拦截器
根据用户的request创建网络请求,处理网络请求,最后通过网络请求将response返回给用户
/**
* Bridges from application code to network code. First it builds a network request from a user
* request. Then it proceeds to call the network. Finally it builds a user response from the network
* response.
*/
class BridgeInterceptor(private val cookieJar: CookieJar) : Interceptor {
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response {
// 获取用户request
val userRequest = chain.request()
val requestBuilder = userRequest.newBuilder()
val body = userRequest.body
// 根据body添加相应的请求header
if (body != null) {
val contentType = body.contentType()
if (contentType != null) {
requestBuilder.header("Content-Type", contentType.toString())
}
val contentLength = body.contentLength()
if (contentLength != -1L) {
requestBuilder.header("Content-Length", contentLength.toString())
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Transfer-Encoding")
} else {
requestBuilder.header("Transfer-Encoding", "chunked")
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Length")
}
}
if (userRequest.header("Host") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("Host", userRequest.url.toHostHeader())
}
if (userRequest.header("Connection") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("Connection", "Keep-Alive")
}
// If we add an "Accept-Encoding: gzip" header field we're responsible for also decompressing
// the transfer stream.
var transparentGzip = false
if (userRequest.header("Accept-Encoding") == null && userRequest.header("Range") == null) {
transparentGzip = true
requestBuilder.header("Accept-Encoding", "gzip")
}
val cookies = cookieJar.loadForRequest(userRequest.url)
// 根据cookie配置在header中添加cookie
if (cookies.isNotEmpty()) {
requestBuilder.header("Cookie", cookieHeader(cookies))
}
if (userRequest.header("User-Agent") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("User-Agent", userAgent)
}
// 通过构建好的requestBuilder获取networkResponse
val networkResponse = chain.proceed(requestBuilder.build())
cookieJar.receiveHeaders(userRequest.url, networkResponse.headers)
val responseBuilder = networkResponse.newBuilder()
.request(userRequest)
if (transparentGzip &&
"gzip".equals(networkResponse.header("Content-Encoding"), ignoreCase = true) &&
networkResponse.promisesBody()) {
val responseBody = networkResponse.body
// 根据gzip配置对response数据进行压缩操作
if (responseBody != null) {
val gzipSource = GzipSource(responseBody.source())
val strippedHeaders = networkResponse.headers.newBuilder()
.removeAll("Content-Encoding")
.removeAll("Content-Length")
.build()
responseBuilder.headers(strippedHeaders)
val contentType = networkResponse.header("Content-Type")
responseBuilder.body(RealResponseBody(contentType, -1L, gzipSource.buffer()))
}
}
return responseBuilder.build()
}
/** Returns a 'Cookie' HTTP request header with all cookies, like `a=b; c=d`. */
private fun cookieHeader(cookies: List): String = buildString {
cookies.forEachIndexed { index, cookie ->
if (index > 0) append("; ")
append(cookie.name).append('=').append(cookie.value)
}
}
}
6.3 CacheInterceptor
用于向request提供缓存并将response数据写入缓存
- intercept 缓存拦截器
/** Serves requests from the cache and writes responses to the cache. */
class CacheInterceptor(internal val cache: Cache?) : Interceptor {
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response {
val call = chain.call()
// 通过request查询缓存中该对应的response
val cacheCandidate = cache?.get(chain.request())
val now = System.currentTimeMillis()
// 获取缓存策略
val strategy = CacheStrategy.Factory(now, chain.request(), cacheCandidate).compute()
val networkRequest = strategy.networkRequest
val cacheResponse = strategy.cacheResponse
// 根据缓存策略跟踪缓存
cache?.trackResponse(strategy)
val listener = (call as? RealCall)?.eventListener ?: EventListener.NONE
// cacheResponse为空,关闭cacheCandidate
if (cacheCandidate != null && cacheResponse == null) {
// The cache candidate wasn't applicable. Close it.
cacheCandidate.body?.closeQuietly()
}
// If we're forbidden from using the network and the cache is insufficient, fail.
// 请求为空并且缓存响应为空,返回504
if (networkRequest == null && cacheResponse == null) {
return Response.Builder()
.request(chain.request())
.protocol(Protocol.HTTP_1_1)
.code(HTTP_GATEWAY_TIMEOUT)
.message("Unsatisfiable Request (only-if-cached)")
.body(EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.sentRequestAtMillis(-1L)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build().also {
listener.satisfactionFailure(call, it)
}
}
// If we don't need the network, we're done.
// 返回cacheResponse
if (networkRequest == null) {
return cacheResponse!!.newBuilder()
// 将cacheResponse中body置为空
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.build().also {
// 回调cacheHit
listener.cacheHit(call, it)
}
}
if (cacheResponse != null) {
listener.cacheConditionalHit(call, cacheResponse)
} else if (cache != null) {
listener.cacheMiss(call)
}
var networkResponse: Response? = null
// 请求网络获取响应
try {
networkResponse = chain.proceed(networkRequest)
} finally {
// If we're crashing on I/O or otherwise, don't leak the cache body.
if (networkResponse == null && cacheCandidate != null) {
cacheCandidate.body?.closeQuietly()
}
}
// If we have a cache response too, then we're doing a conditional get.
if (cacheResponse != null) {
if (networkResponse?.code == HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED) {
// response没有变化,合并cacheResponse和networkResponse的headers,更新缓存时间
val response = cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.headers(combine(cacheResponse.headers, networkResponse.headers))
.sentRequestAtMillis(networkResponse.sentRequestAtMillis)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(networkResponse.receivedResponseAtMillis)
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build()
networkResponse.body!!.close()
// Update the cache after combining headers but before stripping the
// Content-Encoding header (as performed by initContentStream()).
cache!!.trackConditionalCacheHit()
// 更新缓存
cache.update(cacheResponse, response)
return response.also {
listener.cacheHit(call, it)
}
} else {
// networkResponse发生了变化,cacheResponse已经失效,关闭cacheResponse
cacheResponse.body?.closeQuietly()
}
}
// 使用networkResponse构建response
val response = networkResponse!!.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build()
if (cache != null) {
if (response.promisesBody() && CacheStrategy.isCacheable(response, networkRequest)) {
// Offer this request to the cache.
// 将request写入缓存之中
val cacheRequest = cache.put(response)
return cacheWritingResponse(cacheRequest, response).also {
if (cacheResponse != null) {
// This will log a conditional cache miss only.
listener.cacheMiss(call)
}
}
}
if (HttpMethod.invalidatesCache(networkRequest.method)) {
try {
cache.remove(networkRequest)
} catch (_: IOException) {
// The cache cannot be written.
}
}
}
return response
}
- cacheWritingResponse 写缓存
通过io操作将response写入到cacheResponse中
/**
* Returns a new source that writes bytes to [cacheRequest] as they are read by the source
* consumer. This is careful to discard bytes left over when the stream is closed; otherwise we
* may never exhaust the source stream and therefore not complete the cached response.
*/
@Throws(IOException::class)
private fun cacheWritingResponse(cacheRequest: CacheRequest?, response: Response): Response {
// Some apps return a null body; for compatibility we treat that like a null cache request.
if (cacheRequest == null) return response
val cacheBodyUnbuffered = cacheRequest.body()
val source = response.body!!.source()
val cacheBody = cacheBodyUnbuffered.buffer()
val cacheWritingSource = object : Source {
private var cacheRequestClosed = false
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun read(sink: Buffer, byteCount: Long): Long {
val bytesRead: Long
try {
bytesRead = source.read(sink, byteCount)
} catch (e: IOException) {
if (!cacheRequestClosed) {
cacheRequestClosed = true
cacheRequest.abort() // Failed to write a complete cache response.
}
throw e
}
if (bytesRead == -1L) {
if (!cacheRequestClosed) {
cacheRequestClosed = true
cacheBody.close() // The cache response is complete!
}
return -1
}
sink.copyTo(cacheBody.buffer, sink.size - bytesRead, bytesRead)
cacheBody.emitCompleteSegments()
return bytesRead
}
override fun timeout() = source.timeout()
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun close() {
if (!cacheRequestClosed &&
!discard(ExchangeCodec.DISCARD_STREAM_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS)) {
cacheRequestClosed = true
cacheRequest.abort()
}
source.close()
}
}
val contentType = response.header("Content-Type")
val contentLength = response.body.contentLength()
// 返回带有header的response作为cacheResponse
return response.newBuilder()
.body(RealResponseBody(contentType, contentLength, cacheWritingSource.buffer()))
.build()
}
6.4 ConnectInterceptor
ConnectInterceptor用于向目标服务器开启一个连接并指向下一个拦截器,用于返回response或者用于通过get方式刷新缓存
/**
* Opens a connection to the target server and proceeds to the next interceptor. The network might
* be used for the returned response, or to validate a cached response with a conditional GET.
*/
// 单例类
object ConnectInterceptor : Interceptor {
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response {
val realChain = chain as RealInterceptorChain
// 寻找下一个连接作为request和response的载体
val exchange = realChain.call.initExchange(chain)
// 复制到realChain中
val connectedChain = realChain.copy(exchange = exchange)
// 处理请求,返回response
return connectedChain.proceed(realChain.request)
}
}
6.5 CallServerInterceptor
最后一个拦截器,用于通过网络请求服务器
/** This is the last interceptor in the chain. It makes a network call to the server. */
class CallServerInterceptor(private val forWebSocket: Boolean) : Interceptor {
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response {
val realChain = chain as RealInterceptorChain
val exchange = realChain.exchange!!
val request = realChain.request
val requestBody = request.body
val sentRequestMillis = System.currentTimeMillis()
// 写入请求头
exchange.writeRequestHeaders(request)
var invokeStartEvent = true
var responseBuilder: Response.Builder? = null
// 根据请求方式,设置requestBody
if (HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(request.method) && requestBody != null) {
// If there's a "Expect: 100-continue" header on the request, wait for a "HTTP/1.1 100
// Continue" response before transmitting the request body. If we don't get that, return
// what we did get (such as a 4xx response) without ever transmitting the request body.
// 根据header构建responseBuilder
if ("100-continue".equals(request.header("Expect"), ignoreCase = true)) {
exchange.flushRequest()
responseBuilder = exchange.readResponseHeaders(expectContinue = true)
exchange.responseHeadersStart()
invokeStartEvent = false
}
if (responseBuilder == null) {
// 双工类型requestBody,刷新request
if (requestBody.isDuplex()) {
// Prepare a duplex body so that the application can send a request body later.
exchange.flushRequest()
val bufferedRequestBody = exchange.createRequestBody(request, true).buffer()
requestBody.writeTo(bufferedRequestBody)
} else {
// Write the request body if the "Expect: 100-continue" expectation was met.
// 非双工类型,将requestBody写入buffer中
val bufferedRequestBody = exchange.createRequestBody(request, false).buffer()
requestBody.writeTo(bufferedRequestBody)
bufferedRequestBody.close()
}
} else {
exchange.noRequestBody()
// 不支持多路输出
if (!exchange.connection.isMultiplexed) {
// If the "Expect: 100-continue" expectation wasn't met, prevent the HTTP/1 connection
// from being reused. Otherwise we're still obligated to transmit the request body to
// leave the connection in a consistent state.
exchange.noNewExchangesOnConnection()
}
}
} else {
exchange.noRequestBody()
}
// 刷新底层socket,并发出无数据需要传输信号
if (requestBody == null || !requestBody.isDuplex()) {
exchange.finishRequest()
}
// responseBuilder为空时,通过exchange读取响应头
if (responseBuilder == null) {
responseBuilder = exchange.readResponseHeaders(expectContinue = false)!!
if (invokeStartEvent) {
exchange.responseHeadersStart()
invokeStartEvent = false
}
}
// 通过responseBuilder,发起request请求,并通过exchange进行握手,获取response
var response = responseBuilder
.request(request)
.handshake(exchange.connection.handshake())
.sentRequestAtMillis(sentRequestMillis)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build()
var code = response.code
// code为100,重新通过exchange读取响应头来获取responseBuilder
if (code == 100) {
// Server sent a 100-continue even though we did not request one. Try again to read the actual
// response status.
responseBuilder = exchange.readResponseHeaders(expectContinue = false)!!
// 读取响应头
if (invokeStartEvent) {
exchange.responseHeadersStart()
}
// 通过responseBuilder重新获取response
response = responseBuilder
.request(request)
.handshake(exchange.connection.handshake())
.sentRequestAtMillis(sentRequestMillis)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build()
code = response.code
}
exchange.responseHeadersEnd(response)
response = if (forWebSocket && code == 101) {
// Connection is upgrading, but we need to ensure interceptors see a non-null response body.
// 构建websocket响应
response.newBuilder()
.body(EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.build()
} else {
// 构建response
response.newBuilder()
.body(exchange.openResponseBody(response))
.build()
}
if ("close".equals(response.request.header("Connection"), ignoreCase = true) ||
"close".equals(response.header("Connection"), ignoreCase = true)) {
exchange.noNewExchangesOnConnection()
}
if ((code == 204 || code == 205) && response.body?.contentLength() ?: -1L > 0L) {
throw ProtocolException(
"HTTP $code had non-zero Content-Length: ${response.body?.contentLength()}")
}
return response
}
}
- 1、先通过exchange写入请求头
- 2、根据请求方式设置请求体
- 3、调用finishRequest刷新底部socket,并发射完成信号
- 4、读取responseHeaders并通过responseBuilder构建response
- 5、通过exchange.openResponseBody(response)将带请求体的response返回
7、整体流程图
[> 通过前面的学习,我们已经对OKHttp有了简单的认识,并对使用有了详细的了解,下面我们将以一个同步Get请求为例进行OKHttp源码分析。
一、基础同步Get请求
private val mUrl = "https://www.baidu.com"
// 1、createClient
private val mClient = OkHttpClient()
// createClientTwo
private val mClient2 = OkHttpClient.Builder().build()
// 2、createRequest
private val mRequest = Request.Builder().url(mUrl).build()
// 3、发起同步get请求
GlobalScope.launch {
mClient.newCall(mRequest).execute().use { response ->
if (response.isSuccessful) {
LogUtil.D(log = "request success code is ${response.code} body is ${response.body.toString()}")
} else {
LogUtil.D(log="request error code is ${response.code}")
}
}
}
通过代码我们发现,创建OkHttpClient的方式有两种:
- 1、直接创建 OkHttpClient()
- 2、Builder构建者方式创建 OkHttpClient.Builder().build()
二、源码分析
1、创建OKHttpClient
1.1 直接创建 val mClient = OkHttpClient()
constructor() : this(Builder())
class Builder constructor() {
// 调度器
internal var dispatcher: Dispatcher = Dispatcher()
// 连接池
internal var connectionPool: ConnectionPool = ConnectionPool()
// 应用拦截器list
internal val interceptors: MutableList = mutableListOf()
// 网络拦截器list
internal val networkInterceptors: MutableList = mutableListOf()
// eventListenerFactory
internal var eventListenerFactory: EventListener.Factory = EventListener.NONE.asFactory()
// 自动重试布尔值
internal var retryOnConnectionFailure = true
// 认证中心 默认为NONE
internal var authenticator: Authenticator = Authenticator.NONE
// 重定向布尔值
internal var followRedirects = true
// ssl重定向布尔值
internal var followSslRedirects = true
// cookie控制
internal var cookieJar: CookieJar = CookieJar.NO_COOKIES
// 缓存
internal var cache: Cache? = null
// DNS配置
internal var dns: Dns = Dns.SYSTEM
// 代理
internal var proxy: Proxy? = null
// 代理选择器
internal var proxySelector: ProxySelector? = null
// 代理认证器
internal var proxyAuthenticator: Authenticator = Authenticator.NONE
// 使用默认的Socket工厂产生Socket
internal var socketFactory: SocketFactory = SocketFactory.getDefault()
// sslSocketFactory默认为null
internal var sslSocketFactoryOrNull: SSLSocketFactory? = null
// x509认证管理器默认为null
internal var x509TrustManagerOrNull: X509TrustManager? = null
// 默认连接配置 TLS和CLEARTEXT
internal var connectionSpecs: List = DEFAULT_CONNECTION_SPECS
// 默认HTTP协议
internal var protocols: List = DEFAULT_PROTOCOLS
// HostName认证器
internal var hostnameVerifier: HostnameVerifier = OkHostnameVerifier
// 认证加密组建
internal var certificatePinner: CertificatePinner = CertificatePinner.DEFAULT
// 证书链cleaner
internal var certificateChainCleaner: CertificateChainCleaner? = null
// 默认请求超时时常
internal var callTimeout = 0
// 默认连接时常
internal var connectTimeout = 10_000
// 默认读数据超时时常
internal var readTimeout = 10_000
// 默认写数据超时时常
internal var writeTimeout = 10_000
// ping间隔,心跳时间
internal var pingInterval = 0
// websocket消息最小压缩值
internal var minWebSocketMessageToCompress = RealWebSocket.DEFAULT_MINIMUM_DEFLATE_SIZE
}
1.2 Builder方式创建 val mClient2 = OkHttpClient.Builder().build()
默认调用的方法是class Builder constructor() 与方法直接创建方式相同,通过构建者默认对外暴露了自定义配置的方法。
// 创建builder构造器
class Builder constructor()
// build创建OkHttpClient
fun build(): OkHttpClient = OkHttpClient(this)
2、创建Request
- val mRequest = Request.Builder().url(mUrl).build()
2.1 builder()
// 默认请求方式为GET
constructor() {
this.method = "GET"
this.headers = Headers.Builder()
}
2.2 url()
/**
* Sets the URL target of this request.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if [url] is not a valid HTTP or HTTPS URL. Avoid this
* exception by calling [HttpUrl.parse]; it returns null for invalid URLs.
*/
open fun url(url: String): Builder {
// 替换webSocketURL为http类型url
// Silently replace web socket URLs with HTTP URLs.
val finalUrl: String = when {
url.startsWith("ws:", ignoreCase = true) -> {
"http:${url.substring(3)}"
}
url.startsWith("wss:", ignoreCase = true) -> {
"https:${url.substring(4)}"
}
else -> url
}
return url(finalUrl.toHttpUrl())
}
2.3 build() 创建request
open fun build(): Request {
return Request(
checkNotNull(url) { "url == null" },
method,
headers.build(),
body,
tags.toImmutableMap()
)
}
通过传入的url、method、headers、body创建Request对象
3、创建Call mClient.newCall(mRequest)
3.1 Call
interface Call : Cloneable {
fun request(): Request
fun execute(): Response
fun cancel()
fun isExecuted(): Boolean
fun isCanceled(): Boolean
fun timeout(): Timeout
public override fun clone(): Call
fun interface Factory {
fun newCall(request: Request): Call
}
}
通过查看Call源码可见,Call实际上是一个接口,并定义了一些常用的方法,具体实现由其实现类提供
3.1 newCall()
/** Prepares the [request] to be executed at some point in the future. */
override fun newCall(request: Request): Call = RealCall(this, request, forWebSocket = false)
通过查看方法可见,实际创建的是一个RealCall对象
3.2 RealCall(this, request, forWebSocket = false)
默认创建的RealCall用来进行HTTP通信,不是进行websocket通信
/**
* Bridge between OkHttp's application and network layers. This class exposes high-level application
* layer primitives: connections, requests, responses, and streams.
*
* This class supports [asynchronous canceling][cancel]. This is intended to have the smallest
* blast radius possible. If an HTTP/2 stream is active, canceling will cancel that stream but not
* the other streams sharing its connection. But if the TLS handshake is still in progress then
* canceling may break the entire connection.
*/
class RealCall(
val client: OkHttpClient,
val originalRequest: Request,
val forWebSocket: Boolean
) : Call {
......
}
通过注释我们可以知道:
- RealCall是OkHttp应用和网络层连接的桥梁,并将connections、requests、responses和streams暴露出来
- 提供了小粒度异步取消方法。
- 如果取消的是活跃的HTTP/2 stream,这个stream将会被取消,但是其他共享连接池的streams不会取消。
- 如果进行HTTPS请求时,正处于握手过程中,调用该方法,会打断整个连接过程。
3.3 execute()
override fun execute(): Response {
check(executed.compareAndSet(false, true)) { "Already Executed" }
timeout.enter()
callStart()
try {
// 步骤1
client.dispatcher.executed(this)
// 步骤2
return getResponseWithInterceptorChain()
} finally {
// 标记请求完成
client.dispatcher.finished(this)
}
}
实际上execute执行的方法是通过 client.dispatcher.executed(this)实现的
4、Dispatcher(调度器)
4.1 源码查看
// Dispatcher是用于异步请求执行的策略类,每一个Dispatcher都是用Executor Service独立进行请求,如果使用本地的executor,可以支持maxRequests(默认64)数量集并发请求
class Dispatcher constructor() {
// 支持的最大请求数
@get:Synchronized var maxRequests = 64
set(maxRequests) {
require(maxRequests >= 1) { "max < 1: $maxRequests" }
synchronized(this) {
field = maxRequests
}
promoteAndExecute()
}
// 支持的单个host地址请求数
@get:Synchronized var maxRequestsPerHost = 5
set(maxRequestsPerHost) {
require(maxRequestsPerHost >= 1) { "max < 1: $maxRequestsPerHost" }
synchronized(this) {
field = maxRequestsPerHost
}
promoteAndExecute()
}
@set:Synchronized
@get:Synchronized
var idleCallback: Runnable? = null
private var executorServiceOrNull: ExecutorService? = null
// java线程池 不解释
@get:Synchronized
@get:JvmName("executorService") val executorService: ExecutorService
get() {
if (executorServiceOrNull == null) {
executorServiceOrNull = ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Int.MAX_VALUE, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
SynchronousQueue(), threadFactory("$okHttpName Dispatcher", false))
}
return executorServiceOrNull!!
}
// 可执行请求队列
private val readyAsyncCalls = ArrayDeque()
// 正在执行的异步call队列
private val runningAsyncCalls = ArrayDeque()
// 正在执行的同步请求队列
private val runningSyncCalls = ArrayDeque()
constructor(executorService: ExecutorService) : this() {
this.executorServiceOrNull = executorService
}
// 异步请求
internal fun enqueue(call: AsyncCall) {
synchronized(this) {
readyAsyncCalls.add(call)
if (!call.call.forWebSocket) {
val existingCall = findExistingCallWithHost(call.host)
if (existingCall != null) call.reuseCallsPerHostFrom(existingCall)
}
}
promoteAndExecute()
}
private fun findExistingCallWithHost(host: String): AsyncCall? {
for (existingCall in runningAsyncCalls) {
if (existingCall.host == host) return existingCall
}
for (existingCall in readyAsyncCalls) {
if (existingCall.host == host) return existingCall
}
return null
}
// 取消所有请求,包括同步请求和异步请求
@Synchronized fun cancelAll() {
for (call in readyAsyncCalls) {
call.call.cancel()
}
for (call in runningAsyncCalls) {
call.call.cancel()
}
for (call in runningSyncCalls) {
call.cancel()
}
}
// 执行请求,返回是否有异步call正在执行状态
private fun promoteAndExecute(): Boolean {
this.assertThreadDoesntHoldLock()
// 可以执行的请求队列
val executableCalls = mutableListOf()
val isRunning: Boolean
// 同步方法
synchronized(this) {
val i = readyAsyncCalls.iterator()
while (i.hasNext()) {
val asyncCall = i.next()
// 最大请求数限制策略
if (runningAsyncCalls.size >= this.maxRequests) break // Max capacity.
// 最大单host请求限制策略
if (asyncCall.callsPerHost.get() >= this.maxRequestsPerHost) continue // Host max capacity.
// 从readyAsyncCalls队列中移除
i.remove()
asyncCall.callsPerHost.incrementAndGet()
// 添加到executableCalls队列中
executableCalls.add(asyncCall)
runningAsyncCalls.add(asyncCall)
}
isRunning = runningCallsCount() > 0
}
// 执行executableCalls中请求
for (i in 0 until executableCalls.size) {
val asyncCall = executableCalls[i]
// 调用RealCall中executeOn()方法
asyncCall.executeOn(executorService)
}
return isRunning
}
// 同步请求,将RealCall添加到runningSyncCalls队列中
@Synchronized internal fun executed(call: RealCall) {
runningSyncCalls.add(call)
}
// 请求完成回调
internal fun finished(call: AsyncCall) {
// callsPerHost数量自减
call.callsPerHost.decrementAndGet()
finished(runningAsyncCalls, call)
}
internal fun finished(call: RealCall) {
finished(runningSyncCalls, call)
}
private fun finished(calls: Deque, call: T) {
val idleCallback: Runnable?
synchronized(this) {
// 从calls中移除call
if (!calls.remove(call)) throw AssertionError("Call wasn't in-flight!")
idleCallback = this.idleCallback
}
val isRunning = promoteAndExecute()
// 如果不是在running状态并且callback不为空,运行idleCallback
if (!isRunning && idleCallback != null) {
idleCallback.run()
}
}
/** Returns a snapshot of the calls currently awaiting execution. */
@Synchronized fun queuedCalls(): List {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(readyAsyncCalls.map { it.call })
}
/** Returns a snapshot of the calls currently being executed. */
@Synchronized fun runningCalls(): List {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(runningSyncCalls + runningAsyncCalls.map { it.call })
}
@Synchronized fun queuedCallsCount(): Int = readyAsyncCalls.size
@Synchronized fun runningCallsCount(): Int = runningAsyncCalls.size + runningSyncCalls.size
@JvmName("-deprecated_executorService")
@Deprecated(
message = "moved to val",
replaceWith = ReplaceWith(expression = "executorService"),
level = DeprecationLevel.ERROR)
fun executorService(): ExecutorService = executorService
}
4.2 RealCall中executeOn()方法
/**
* Attempt to enqueue this async call on [executorService]. This will attempt to clean up
* if the executor has been shut down by reporting the call as failed.
*/
fun executeOn(executorService: ExecutorService) {
client.dispatcher.assertThreadDoesntHoldLock()
var success = false
try {
// 使用线程池执行请求
executorService.execute(this)
// 成功标记
success = true
} catch (e: RejectedExecutionException) {
val ioException = InterruptedIOException("executor rejected")
ioException.initCause(e)
noMoreExchanges(ioException)
// 抛出io异常
responseCallback.onFailure(this@RealCall, ioException)
} finally {
// 如果没有请求成功,将该请求进行关闭
if (!success) {
client.dispatcher.finished(this) // This call is no longer running!
}
}
}
5、getResponseWithInterceptorChain() 拦截器链
@Throws(IOException::class)
internal fun getResponseWithInterceptorChain(): Response {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
val interceptors = mutableListOf()
interceptors += client.interceptors
interceptors += RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor(client)
interceptors += BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar)
interceptors += CacheInterceptor(client.cache)
interceptors += ConnectInterceptor
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors += client.networkInterceptors
}
interceptors += CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket)
// 构建RealInterceptorChain
val chain = RealInterceptorChain(
call = this,
interceptors = interceptors,
index = 0,
exchange = null,
request = originalRequest,
connectTimeoutMillis = client.connectTimeoutMillis,
readTimeoutMillis = client.readTimeoutMillis,
writeTimeoutMillis = client.writeTimeoutMillis
)
var calledNoMoreExchanges = false
// 获取response
try {
val response = chain.proceed(originalRequest)
if (isCanceled()) {
response.closeQuietly()
throw IOException("Canceled")
}
return response
} catch (e: IOException) {
calledNoMoreExchanges = true
throw noMoreExchanges(e) as Throwable
} finally {
if (!calledNoMoreExchanges) {
noMoreExchanges(null)
}
}
}
5.1 RealInterceptorChain
/**
* A concrete interceptor chain that carries the entire interceptor chain: all application
* interceptors, the OkHttp core, all network interceptors, and finally the network caller.
*
* If the chain is for an application interceptor then [exchange] must be null. Otherwise it is for
* a network interceptor and [exchange] must be non-null.
*/
class RealInterceptorChain(
internal val call: RealCall,
private val interceptors: List,
private val index: Int,
internal val exchange: Exchange?,
internal val request: Request,
internal val connectTimeoutMillis: Int,
internal val readTimeoutMillis: Int,
internal val writeTimeoutMillis: Int
) : Interceptor.Chain {
-
通过注释我们可以知道RealInterceptorChain实现了Interceptor.Chain是一个interceptors、OkHttp core、所有网络拦截器和网络调用器的集合
-
如果chain作为应用拦截器使用时,exchange必须为空;作为网络拦截器使用时,exchange必须非空
5.2 chain.proceed()
通过chain.proceed获取response
val response = chain.proceed(originalRequest)
- proceed()
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun proceed(request: Request): Response {
check(index < interceptors.size)
calls++
if (exchange != null) {
check(exchange.finder.sameHostAndPort(request.url)) {
"network interceptor ${interceptors[index - 1]} must retain the same host and port"
}
check(calls == 1) {
"network interceptor ${interceptors[index - 1]} must call proceed() exactly once"
}
}
// Call the next interceptor in the chain.
// 调用chain中的下一个拦截器
val next = copy(index = index + 1, request = request)
// 获取当前拦截器集合中拦截器
val interceptor = interceptors[index]
@Suppress("USELESS_ELVIS")
// 通过下一个拦截器获取response
val response = interceptor.intercept(next) ?: throw NullPointerException(
"interceptor $interceptor returned null")
if (exchange != null) {
check(index + 1 >= interceptors.size || next.calls == 1) {
"network interceptor $interceptor must call proceed() exactly once"
}
}
check(response.body != null) { "interceptor $interceptor returned a response with no body" }
return response
}
看到当前拦截器的Response依赖于下一个拦截器的Intercept的Response,会沿着这条拦截器链依次调用每一个拦截器,最后返回返回Response
- copy()方法
internal fun copy(
index: Int = this.index,
exchange: Exchange? = this.exchange,
request: Request = this.request,
connectTimeoutMillis: Int = this.connectTimeoutMillis,
readTimeoutMillis: Int = this.readTimeoutMillis,
writeTimeoutMillis: Int = this.writeTimeoutMillis
) = RealInterceptorChain(call, interceptors, index, exchange, request, connectTimeoutMillis,
readTimeoutMillis, writeTimeoutMillis)
通过构造传参创建RealInterceptorChain对象
- interceptor.intercept(next)
fun interface Interceptor {
@Throws(IOException::class)
fun intercept(chain: Chain): Response
...
}
通过代码我们可见,Interceptor是一个接口,具体的实现通过其实现类来提供
6、Interceptor 拦截器
6.1 RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor 重试和重定向拦截器
- intercept()
class RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor(private val client: OkHttpClient) : Interceptor {
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response {
val realChain = chain as RealInterceptorChain
var request = chain.request
val call = realChain.call
var followUpCount = 0
var priorResponse: Response? = null
var newExchangeFinder = true
var recoveredFailures = listOf()
while (true) {
// 将call请求添加到网络拦截器中
call.enterNetworkInterceptorExchange(request, newExchangeFinder)
var response: Response
var closeActiveExchange = true
try {
if (call.isCanceled()) {
throw IOException("Canceled")
}
try {
// 通过realChain处理请求
response = realChain.proceed(request)
newExchangeFinder = true
} catch (e: RouteException) {
// The attempt to connect via a route failed. The request will not have been sent.
// 路由通过失败,尝试进行恢复,如果请求不能恢复则抛出异常
if (!recover(e.lastConnectException, call, request, requestSendStarted = false)) {
throw e.firstConnectException.withSuppressed(recoveredFailures)
} else {
recoveredFailures += e.firstConnectException
}
newExchangeFinder = false
continue
} catch (e: IOException) {
// An attempt to communicate with a server failed. The request may have been sent.
// 与server通信失败,发生IO异常时,尝试进行恢复
if (!recover(e, call, request, requestSendStarted = e !is ConnectionShutdownException)) {
throw e.withSuppressed(recoveredFailures)
} else {
recoveredFailures += e
}
newExchangeFinder = false
continue
}
// Attach the prior response if it exists. Such responses never have a body.
// 如果priorResponse存在的话,附加priorResponse来创建response
if (priorResponse != null) {
response = response.newBuilder()
.priorResponse(priorResponse.newBuilder()
.body(null)
.build())
.build()
}
// exchange 用来传输独立的request和response对
val exchange = call.interceptorScopedExchange
// 重点方法 通过response和exchange获取request进行重试
val followUp = followUpRequest(response, exchange)
// followUp为空,直接返回response
if (followUp == null) {
// exchange不为空,并且exchange是双工通信方式
if (exchange != null && exchange.isDuplex) {
// 退出timeout策略
call.timeoutEarlyExit()
}
closeActiveExchange = false
return response
}
val followUpBody = followUp.body
// followUpBody不为空,并且是单工通信方式,直接返回response
if (followUpBody != null && followUpBody.isOneShot()) {
closeActiveExchange = false
return response
}
// 关闭response Body
response.body?.closeQuietly()
if (++followUpCount > MAX_FOLLOW_UPS) {
throw ProtocolException("Too many follow-up requests: $followUpCount")
}
// 缓存request
request = followUp
// 缓存response
priorResponse = response
} finally {
// 退出NetworkInterceptorExchange
call.exitNetworkInterceptorExchange(closeActiveExchange)
}
}
}
- followUpRequest(response, exchange)
@Throws(IOException::class)
private fun followUpRequest(userResponse: Response, exchange: Exchange?): Request? {
val route = exchange?.connection?.route()
val responseCode = userResponse.code
val method = userResponse.request.method
when (responseCode) {
HTTP_PROXY_AUTH -> {
val selectedProxy = route!!.proxy
if (selectedProxy.type() != Proxy.Type.HTTP) {
throw ProtocolException("Received HTTP_PROXY_AUTH (407) code while not using proxy")
}
// code 407,调用认证器重新进行认证
return client.proxyAuthenticator.authenticate(route, userResponse)
}
// 401 重新认证
HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED -> return client.authenticator.authenticate(route, userResponse)
HTTP_PERM_REDIRECT, HTTP_TEMP_REDIRECT, HTTP_MULT_CHOICE, HTTP_MOVED_PERM, HTTP_MOVED_TEMP, HTTP_SEE_OTHER -> {
// 重定向
return buildRedirectRequest(userResponse, method)
}
// 客户端超时处理
HTTP_CLIENT_TIMEOUT -> {
// 408's are rare in practice, but some servers like HAProxy use this response code. The
// spec says that we may repeat the request without modifications. Modern browsers also
// repeat the request (even non-idempotent ones.)
if (!client.retryOnConnectionFailure) {
// The application layer has directed us not to retry the request.
return null
}
val requestBody = userResponse.request.body
if (requestBody != null && requestBody.isOneShot()) {
return null
}
val priorResponse = userResponse.priorResponse
if (priorResponse != null && priorResponse.code == HTTP_CLIENT_TIMEOUT) {
// We attempted to retry and got another timeout. Give up.
return null
}
if (retryAfter(userResponse, 0) > 0) {
return null
}
return userResponse.request
}
// code 503处理
HTTP_UNAVAILABLE -> {
val priorResponse = userResponse.priorResponse
if (priorResponse != null && priorResponse.code == HTTP_UNAVAILABLE) {
// We attempted to retry and got another timeout. Give up.
return null
}
if (retryAfter(userResponse, Integer.MAX_VALUE) == 0) {
// specifically received an instruction to retry without delay
return userResponse.request
}
return null
}
// code 421处理
HTTP_MISDIRECTED_REQUEST -> {
// OkHttp can coalesce HTTP/2 connections even if the domain names are different. See
// RealConnection.isEligible(). If we attempted this and the server returned HTTP 421, then
// we can retry on a different connection.
val requestBody = userResponse.request.body
if (requestBody != null && requestBody.isOneShot()) {
return null
}
if (exchange == null || !exchange.isCoalescedConnection) {
return null
}
exchange.connection.noCoalescedConnections()
return userResponse.request
}
else -> return null
}
}
通过源码我们可以看到,该方法根据返回的不同状态码,进行了不同的重试和重定向操作
3) buildRedirectRequest
private fun buildRedirectRequest(userResponse: Response, method: String): Request? {
// Does the client allow redirects?
if (!client.followRedirects) return null
val location = userResponse.header("Location") ?: return null
// Don't follow redirects to unsupported protocols.
val url = userResponse.request.url.resolve(location) ?: return null
// If configured, don't follow redirects between SSL and non-SSL.
val sameScheme = url.scheme == userResponse.request.url.scheme
if (!sameScheme && !client.followSslRedirects) return null
// Most redirects don't include a request body.
// 根据userReponse中数据,重新构造requestBuilder
val requestBuilder = userResponse.request.newBuilder()
if (HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(method)) {
val responseCode = userResponse.code
val maintainBody = HttpMethod.redirectsWithBody(method) ||
responseCode == HTTP_PERM_REDIRECT ||
responseCode == HTTP_TEMP_REDIRECT
if (HttpMethod.redirectsToGet(method) && responseCode != HTTP_PERM_REDIRECT && responseCode != HTTP_TEMP_REDIRECT) {
requestBuilder.method("GET", null)
} else {
val requestBody = if (maintainBody) userResponse.request.body else null
requestBuilder.method(method, requestBody)
}
// 不支持body时移除相关header内容
if (!maintainBody) {
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Transfer-Encoding")
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Length")
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Type")
}
}
// When redirecting across hosts, drop all authentication headers. This
// is potentially annoying to the application layer since they have no
// way to retain them.
if (!userResponse.request.url.canReuseConnectionFor(url)) {
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Authorization")
}
// 返回构建好的request
return requestBuilder.url(url).build()
}
6.2 BridgeInterceptor 桥接拦截器
根据用户的request创建网络请求,处理网络请求,最后通过网络请求将response返回给用户
/**
* Bridges from application code to network code. First it builds a network request from a user
* request. Then it proceeds to call the network. Finally it builds a user response from the network
* response.
*/
class BridgeInterceptor(private val cookieJar: CookieJar) : Interceptor {
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response {
// 获取用户request
val userRequest = chain.request()
val requestBuilder = userRequest.newBuilder()
val body = userRequest.body
// 根据body添加相应的请求header
if (body != null) {
val contentType = body.contentType()
if (contentType != null) {
requestBuilder.header("Content-Type", contentType.toString())
}
val contentLength = body.contentLength()
if (contentLength != -1L) {
requestBuilder.header("Content-Length", contentLength.toString())
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Transfer-Encoding")
} else {
requestBuilder.header("Transfer-Encoding", "chunked")
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Length")
}
}
if (userRequest.header("Host") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("Host", userRequest.url.toHostHeader())
}
if (userRequest.header("Connection") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("Connection", "Keep-Alive")
}
// If we add an "Accept-Encoding: gzip" header field we're responsible for also decompressing
// the transfer stream.
var transparentGzip = false
if (userRequest.header("Accept-Encoding") == null && userRequest.header("Range") == null) {
transparentGzip = true
requestBuilder.header("Accept-Encoding", "gzip")
}
val cookies = cookieJar.loadForRequest(userRequest.url)
// 根据cookie配置在header中添加cookie
if (cookies.isNotEmpty()) {
requestBuilder.header("Cookie", cookieHeader(cookies))
}
if (userRequest.header("User-Agent") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("User-Agent", userAgent)
}
// 通过构建好的requestBuilder获取networkResponse
val networkResponse = chain.proceed(requestBuilder.build())
cookieJar.receiveHeaders(userRequest.url, networkResponse.headers)
val responseBuilder = networkResponse.newBuilder()
.request(userRequest)
if (transparentGzip &&
"gzip".equals(networkResponse.header("Content-Encoding"), ignoreCase = true) &&
networkResponse.promisesBody()) {
val responseBody = networkResponse.body
// 根据gzip配置对response数据进行压缩操作
if (responseBody != null) {
val gzipSource = GzipSource(responseBody.source())
val strippedHeaders = networkResponse.headers.newBuilder()
.removeAll("Content-Encoding")
.removeAll("Content-Length")
.build()
responseBuilder.headers(strippedHeaders)
val contentType = networkResponse.header("Content-Type")
responseBuilder.body(RealResponseBody(contentType, -1L, gzipSource.buffer()))
}
}
return responseBuilder.build()
}
/** Returns a 'Cookie' HTTP request header with all cookies, like `a=b; c=d`. */
private fun cookieHeader(cookies: List): String = buildString {
cookies.forEachIndexed { index, cookie ->
if (index > 0) append("; ")
append(cookie.name).append('=').append(cookie.value)
}
}
}
6.3 CacheInterceptor
用于向request提供缓存并将response数据写入缓存
- intercept 缓存拦截器
/** Serves requests from the cache and writes responses to the cache. */
class CacheInterceptor(internal val cache: Cache?) : Interceptor {
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response {
val call = chain.call()
// 通过request查询缓存中该对应的response
val cacheCandidate = cache?.get(chain.request())
val now = System.currentTimeMillis()
// 获取缓存策略
val strategy = CacheStrategy.Factory(now, chain.request(), cacheCandidate).compute()
val networkRequest = strategy.networkRequest
val cacheResponse = strategy.cacheResponse
// 根据缓存策略跟踪缓存
cache?.trackResponse(strategy)
val listener = (call as? RealCall)?.eventListener ?: EventListener.NONE
// cacheResponse为空,关闭cacheCandidate
if (cacheCandidate != null && cacheResponse == null) {
// The cache candidate wasn't applicable. Close it.
cacheCandidate.body?.closeQuietly()
}
// If we're forbidden from using the network and the cache is insufficient, fail.
// 请求为空并且缓存响应为空,返回504
if (networkRequest == null && cacheResponse == null) {
return Response.Builder()
.request(chain.request())
.protocol(Protocol.HTTP_1_1)
.code(HTTP_GATEWAY_TIMEOUT)
.message("Unsatisfiable Request (only-if-cached)")
.body(EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.sentRequestAtMillis(-1L)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build().also {
listener.satisfactionFailure(call, it)
}
}
// If we don't need the network, we're done.
// 返回cacheResponse
if (networkRequest == null) {
return cacheResponse!!.newBuilder()
// 将cacheResponse中body置为空
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.build().also {
// 回调cacheHit
listener.cacheHit(call, it)
}
}
if (cacheResponse != null) {
listener.cacheConditionalHit(call, cacheResponse)
} else if (cache != null) {
listener.cacheMiss(call)
}
var networkResponse: Response? = null
// 请求网络获取响应
try {
networkResponse = chain.proceed(networkRequest)
} finally {
// If we're crashing on I/O or otherwise, don't leak the cache body.
if (networkResponse == null && cacheCandidate != null) {
cacheCandidate.body?.closeQuietly()
}
}
// If we have a cache response too, then we're doing a conditional get.
if (cacheResponse != null) {
if (networkResponse?.code == HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED) {
// response没有变化,合并cacheResponse和networkResponse的headers,更新缓存时间
val response = cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.headers(combine(cacheResponse.headers, networkResponse.headers))
.sentRequestAtMillis(networkResponse.sentRequestAtMillis)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(networkResponse.receivedResponseAtMillis)
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build()
networkResponse.body!!.close()
// Update the cache after combining headers but before stripping the
// Content-Encoding header (as performed by initContentStream()).
cache!!.trackConditionalCacheHit()
// 更新缓存
cache.update(cacheResponse, response)
return response.also {
listener.cacheHit(call, it)
}
} else {
// networkResponse发生了变化,cacheResponse已经失效,关闭cacheResponse
cacheResponse.body?.closeQuietly()
}
}
// 使用networkResponse构建response
val response = networkResponse!!.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build()
if (cache != null) {
if (response.promisesBody() && CacheStrategy.isCacheable(response, networkRequest)) {
// Offer this request to the cache.
// 将request写入缓存之中
val cacheRequest = cache.put(response)
return cacheWritingResponse(cacheRequest, response).also {
if (cacheResponse != null) {
// This will log a conditional cache miss only.
listener.cacheMiss(call)
}
}
}
if (HttpMethod.invalidatesCache(networkRequest.method)) {
try {
cache.remove(networkRequest)
} catch (_: IOException) {
// The cache cannot be written.
}
}
}
return response
}
- cacheWritingResponse 写缓存
通过io操作将response写入到cacheResponse中
/**
* Returns a new source that writes bytes to [cacheRequest] as they are read by the source
* consumer. This is careful to discard bytes left over when the stream is closed; otherwise we
* may never exhaust the source stream and therefore not complete the cached response.
*/
@Throws(IOException::class)
private fun cacheWritingResponse(cacheRequest: CacheRequest?, response: Response): Response {
// Some apps return a null body; for compatibility we treat that like a null cache request.
if (cacheRequest == null) return response
val cacheBodyUnbuffered = cacheRequest.body()
val source = response.body!!.source()
val cacheBody = cacheBodyUnbuffered.buffer()
val cacheWritingSource = object : Source {
private var cacheRequestClosed = false
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun read(sink: Buffer, byteCount: Long): Long {
val bytesRead: Long
try {
bytesRead = source.read(sink, byteCount)
} catch (e: IOException) {
if (!cacheRequestClosed) {
cacheRequestClosed = true
cacheRequest.abort() // Failed to write a complete cache response.
}
throw e
}
if (bytesRead == -1L) {
if (!cacheRequestClosed) {
cacheRequestClosed = true
cacheBody.close() // The cache response is complete!
}
return -1
}
sink.copyTo(cacheBody.buffer, sink.size - bytesRead, bytesRead)
cacheBody.emitCompleteSegments()
return bytesRead
}
override fun timeout() = source.timeout()
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun close() {
if (!cacheRequestClosed &&
!discard(ExchangeCodec.DISCARD_STREAM_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS)) {
cacheRequestClosed = true
cacheRequest.abort()
}
source.close()
}
}
val contentType = response.header("Content-Type")
val contentLength = response.body.contentLength()
// 返回带有header的response作为cacheResponse
return response.newBuilder()
.body(RealResponseBody(contentType, contentLength, cacheWritingSource.buffer()))
.build()
}
6.4 ConnectInterceptor
ConnectInterceptor用于向目标服务器开启一个连接并指向下一个拦截器,用于返回response或者用于通过get方式刷新缓存
/**
* Opens a connection to the target server and proceeds to the next interceptor. The network might
* be used for the returned response, or to validate a cached response with a conditional GET.
*/
// 单例类
object ConnectInterceptor : Interceptor {
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response {
val realChain = chain as RealInterceptorChain
// 寻找下一个连接作为request和response的载体
val exchange = realChain.call.initExchange(chain)
// 复制到realChain中
val connectedChain = realChain.copy(exchange = exchange)
// 处理请求,返回response
return connectedChain.proceed(realChain.request)
}
}
6.5 CallServerInterceptor
最后一个拦截器,用于通过网络请求服务器
/** This is the last interceptor in the chain. It makes a network call to the server. */
class CallServerInterceptor(private val forWebSocket: Boolean) : Interceptor {
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response {
val realChain = chain as RealInterceptorChain
val exchange = realChain.exchange!!
val request = realChain.request
val requestBody = request.body
val sentRequestMillis = System.currentTimeMillis()
// 写入请求头
exchange.writeRequestHeaders(request)
var invokeStartEvent = true
var responseBuilder: Response.Builder? = null
// 根据请求方式,设置requestBody
if (HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(request.method) && requestBody != null) {
// If there's a "Expect: 100-continue" header on the request, wait for a "HTTP/1.1 100
// Continue" response before transmitting the request body. If we don't get that, return
// what we did get (such as a 4xx response) without ever transmitting the request body.
// 根据header构建responseBuilder
if ("100-continue".equals(request.header("Expect"), ignoreCase = true)) {
exchange.flushRequest()
responseBuilder = exchange.readResponseHeaders(expectContinue = true)
exchange.responseHeadersStart()
invokeStartEvent = false
}
if (responseBuilder == null) {
// 双工类型requestBody,刷新request
if (requestBody.isDuplex()) {
// Prepare a duplex body so that the application can send a request body later.
exchange.flushRequest()
val bufferedRequestBody = exchange.createRequestBody(request, true).buffer()
requestBody.writeTo(bufferedRequestBody)
} else {
// Write the request body if the "Expect: 100-continue" expectation was met.
// 非双工类型,将requestBody写入buffer中
val bufferedRequestBody = exchange.createRequestBody(request, false).buffer()
requestBody.writeTo(bufferedRequestBody)
bufferedRequestBody.close()
}
} else {
exchange.noRequestBody()
// 不支持多路输出
if (!exchange.connection.isMultiplexed) {
// If the "Expect: 100-continue" expectation wasn't met, prevent the HTTP/1 connection
// from being reused. Otherwise we're still obligated to transmit the request body to
// leave the connection in a consistent state.
exchange.noNewExchangesOnConnection()
}
}
} else {
exchange.noRequestBody()
}
// 刷新底层socket,并发出无数据需要传输信号
if (requestBody == null || !requestBody.isDuplex()) {
exchange.finishRequest()
}
// responseBuilder为空时,通过exchange读取响应头
if (responseBuilder == null) {
responseBuilder = exchange.readResponseHeaders(expectContinue = false)!!
if (invokeStartEvent) {
exchange.responseHeadersStart()
invokeStartEvent = false
}
}
// 通过responseBuilder,发起request请求,并通过exchange进行握手,获取response
var response = responseBuilder
.request(request)
.handshake(exchange.connection.handshake())
.sentRequestAtMillis(sentRequestMillis)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build()
var code = response.code
// code为100,重新通过exchange读取响应头来获取responseBuilder
if (code == 100) {
// Server sent a 100-continue even though we did not request one. Try again to read the actual
// response status.
responseBuilder = exchange.readResponseHeaders(expectContinue = false)!!
// 读取响应头
if (invokeStartEvent) {
exchange.responseHeadersStart()
}
// 通过responseBuilder重新获取response
response = responseBuilder
.request(request)
.handshake(exchange.connection.handshake())
.sentRequestAtMillis(sentRequestMillis)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build()
code = response.code
}
exchange.responseHeadersEnd(response)
response = if (forWebSocket && code == 101) {
// Connection is upgrading, but we need to ensure interceptors see a non-null response body.
// 构建websocket响应
response.newBuilder()
.body(EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.build()
} else {
// 构建response
response.newBuilder()
.body(exchange.openResponseBody(response))
.build()
}
if ("close".equals(response.request.header("Connection"), ignoreCase = true) ||
"close".equals(response.header("Connection"), ignoreCase = true)) {
exchange.noNewExchangesOnConnection()
}
if ((code == 204 || code == 205) && response.body?.contentLength() ?: -1L > 0L) {
throw ProtocolException(
"HTTP $code had non-zero Content-Length: ${response.body?.contentLength()}")
}
return response
}
}
- 1、先通过exchange写入请求头
- 2、根据请求方式设置请求体
- 3、调用finishRequest刷新底部socket,并发射完成信号
- 4、读取responseHeaders并通过responseBuilder构建response
- 5、通过exchange.openResponseBody(response)将带请求体的response返回
7、整体流程图
- 参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/mwq384807683/article/details/71173442
https://blog.csdn.net/heng615975867/article/details/105289872